目录
一.反射的作用和关键
二. 反射获取对象
1.反射获取类对象
2.反射获取构造器对象
3.反射获取成员变量对象
4. 反射获取方法对象
5.用反射绕过编译阶段为集合添加数据
反射做通用框架
一.反射的作用和关键
作用: 反射是在运行时获取类的字节码文件对象: 然后可以解析类中的全部成分
关键: 反射的核心思想和关键就是:得到编译以后的class文件对象
二. 反射获取对象
1.反射获取类对象
(1)使用 Class类中的静态方法
(2)使用 类名.class
(3)使用 对象.getClass( )
代码示范:
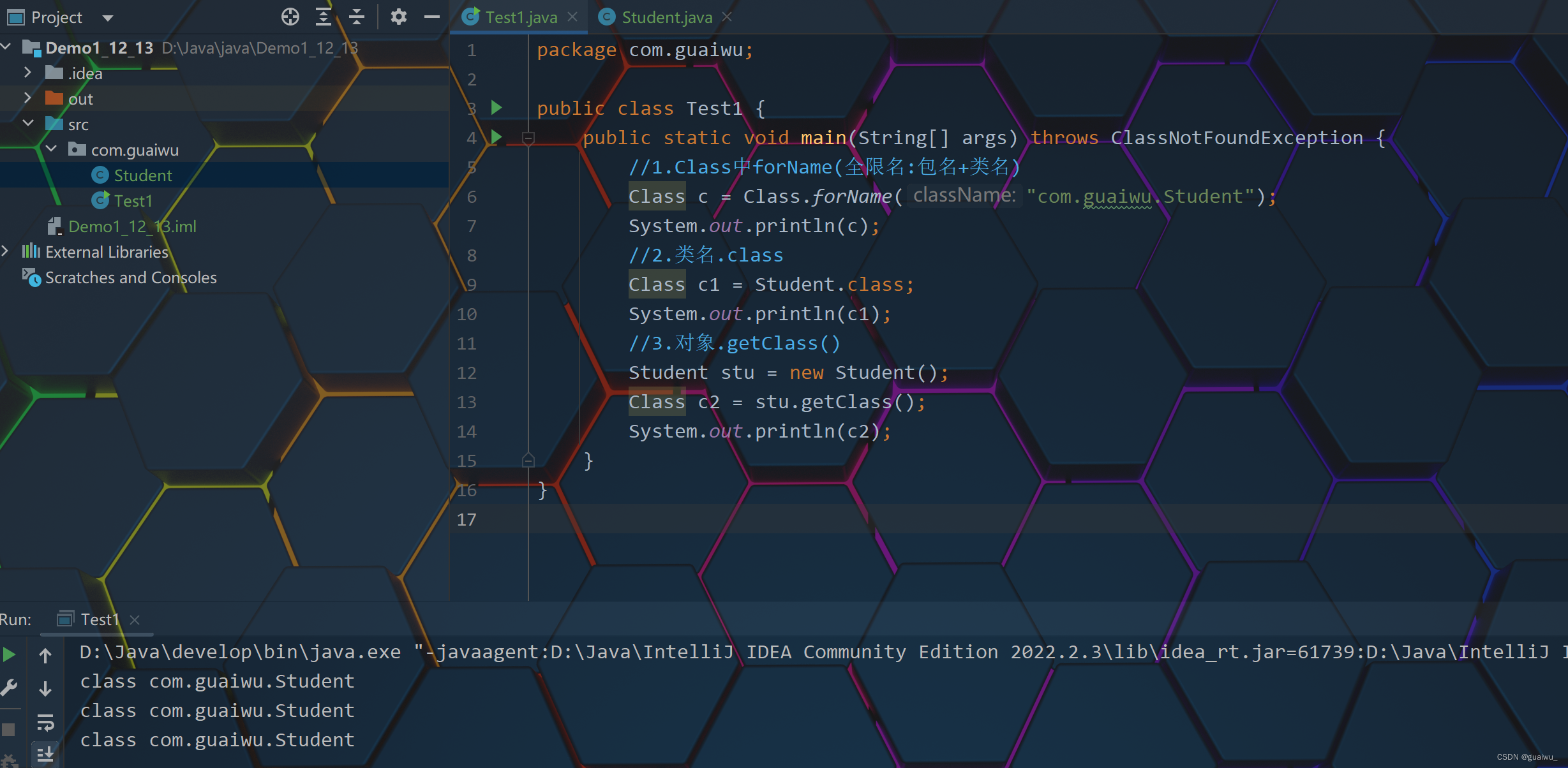
package com.guaiwu; public class Test1 { public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException { //1.Class中forName(全限名:包名+类名) Class c = Class.forName("com.guaiwu.Student"); System.out.println(c); //2.类名.class Class c1 = Student.class; System.out.println(c1); //3.对象.getClass() Student stu = new Student(); Class c2 = stu.getClass(); System.out.println(c2); } }结果展示:
2.反射获取构造器对象
使用反射技术获取构造器对象并使用
反射的第一步是先得到类对象,然后从类对象中获取类的成分对象反射得到的构造器可以做什么?
依然可以创建对象
public newlnstance(Object... initargs)如果是非public的构造器,需要打开权限(暴力反射),然后再创建对象
setAccessible(boolean)
反射可以破坏封装性,私有的也可以执行了
Class类中用于获取构造器的方法
方法
Constructor<?>[ ] getConstructors() 返回所有构造器对象的数组 (只能拿public的)
Constructor<?>[ ] getDeclaredConstructors()返回所有构造器对象的数组,存在就能拿到
Constructor<T> getConstructor(Class<?>...parameterTypes) 返回单个构造器对象 (只能拿public的)
Constructor<T> getDeclaredConstructor(Class<?>... parameterTypes) 返回单个构造器对象,存在就能拿到
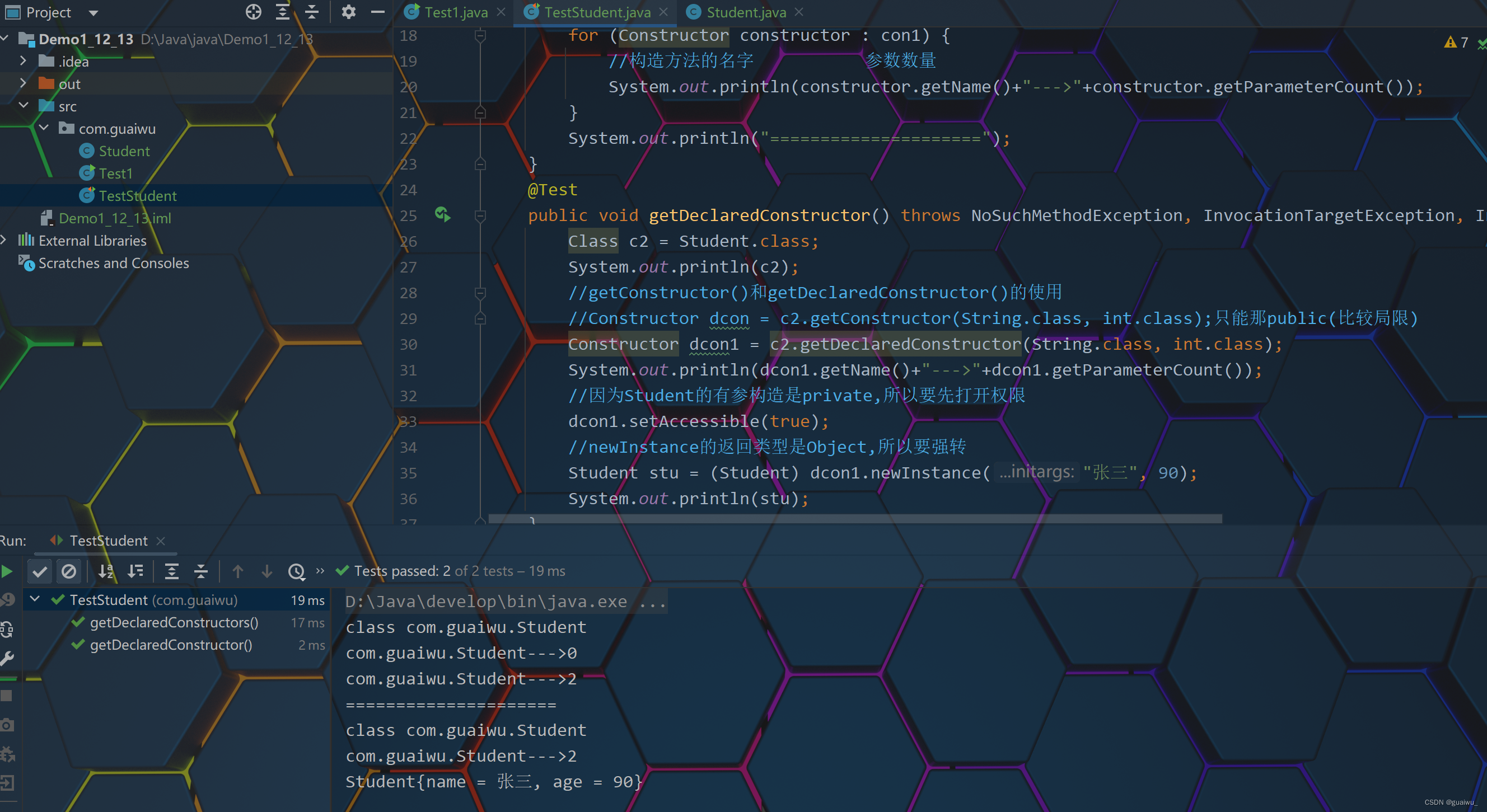
代码示范: 第一段是测试类, 第二段是Student类package com.guaiwu; import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test; import java.lang.reflect.Constructor; import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException; import java.sql.SQLOutput; public class TestStudent { @Test public void getDeclaredConstructors(){ Class c1 = Student.class; System.out.println(c1); //getConstructor()和getDeclaredConstructor()的使用 // Constructor con = c1.getConstructor();只能那public(比较局限) Constructor[] con1 = c1.getDeclaredConstructors(); for (Constructor constructor : con1) { //构造方法的名字 参数数量 System.out.println(constructor.getName()+"--->"+constructor.getParameterCount()); } System.out.println("====================="); } @Test public void getDeclaredConstructor() throws NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException { Class c2 = Student.class; System.out.println(c2); //getConstructor()和getDeclaredConstructor()的使用 //Constructor dcon = c2.getConstructor(String.class, int.class);只能那public(比较局限) Constructor dcon1 = c2.getDeclaredConstructor(String.class, int.class); System.out.println(dcon1.getName()+"--->"+dcon1.getParameterCount()); //因为Student的有参构造是private,所以要先打开权限 dcon1.setAccessible(true); //newInstance的返回类型是Object,所以要强转 Student stu = (Student) dcon1.newInstance("张三", 90); System.out.println(stu); } }package com.guaiwu; public class Student { private String name; private int age; private Student() { } private Student(String name, int age) { this.name = name; this.age = age; } /** * 获取 * @return name */ public String getName() { return name; } /** * 设置 * @param name */ public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } /** * 获取 * @return age */ public int getAge() { return age; } /** * 设置 * @param age */ public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } public String toString() { return "Student{name = " + name + ", age = " + age + "}"; } }结果展示:
3.反射获取成员变量对象
使用反射技术获取成员变量对象并使用
反射的第一步是先得到类对象,然后从类对象中获取类的成分对象
Class类中用于获取成员变量的方法
方法 说明
Field[ ] getFields() 返回所有成员变量对象的数组 (只能拿public的)
Fieldl getDeclaredFields() 返回所有成员变量对象的数组,存在就能拿到
Field getField(String name) 返回单个成员变量对象 (只能拿public的)
Field getDeclaredField(String name) 返回单个成员变量对象,存在就能拿到
Field类中用于取值、赋值的方法
void set(Object obj, Object value): 赋值
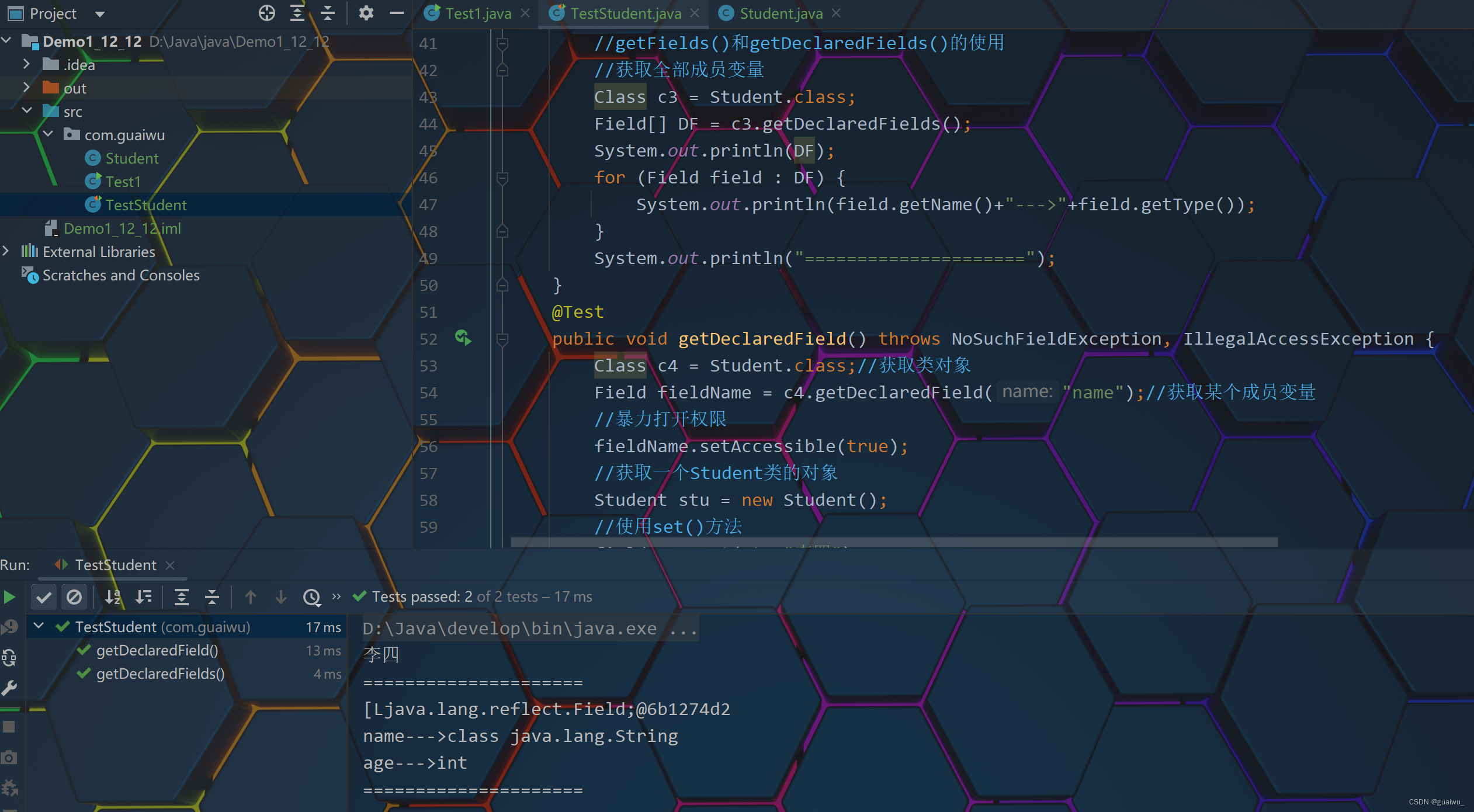
Object get(Object obj) 获取值代码示范: 第一段是测试类, 第二段是Student类
package com.guaiwu; import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test; import java.lang.reflect.Constructor; import java.lang.reflect.Field; import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException; public class TestStudent { /*@Test public void getDeclaredConstructors(){ Class c1 = Student.class; System.out.println(c1); //getConstructor()和getDeclaredConstructor()的使用 // Constructor con = c1.getConstructor();只能那public(比较局限) Constructor[] con1 = c1.getDeclaredConstructors(); for (Constructor constructor : con1) { //构造方法的名字 参数数量 System.out.println(constructor.getName()+"--->"+constructor.getParameterCount()); } System.out.println("====================="); } @Test public void getDeclaredConstructor() throws NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException { Class c2 = Student.class; System.out.println(c2); //getConstructor()和getDeclaredConstructor()的使用 //Constructor dcon = c2.getConstructor(String.class, int.class);只能那public(比较局限) Constructor dcon1 = c2.getDeclaredConstructor(String.class, int.class); System.out.println(dcon1.getName()+"--->"+dcon1.getParameterCount()); //因为Student的有参构造是private,所以要先打开权限 dcon1.setAccessible(true); //newInstance的返回类型是Object,所以要强转 Student stu = (Student) dcon1.newInstance("张三", 90); System.out.println(stu); System.out.println("====================="); }*/ @Test public void getDeclaredFields(){ //getFields()和getDeclaredFields()的使用 //获取全部成员变量 Class c3 = Student.class; Field[] DF = c3.getDeclaredFields(); System.out.println(DF); for (Field field : DF) { System.out.println(field.getName()+"--->"+field.getType()); } System.out.println("====================="); } @Test public void getDeclaredField() throws NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException { Class c4 = Student.class;//获取类对象 Field fieldName = c4.getDeclaredField("name");//获取某个成员变量 //暴力打开权限 fieldName.setAccessible(true); //获取一个Student类的对象 Student stu = new Student(); //使用set()方法 fieldName.set(stu,"李四"); String str = (String) fieldName.get(stu); System.out.println(str); System.out.println("====================="); } }package com.guaiwu; public class Student { private String name; private int age; public Student() { } private Student(String name, int age) { this.name = name; this.age = age; } /** * 获取 * @return name */ public String getName() { return name; } /** * 设置 * @param name */ public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } /** * 获取 * @return age */ public int getAge() { return age; } /** * 设置 * @param age */ public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } public String toString() { return "Student{name = " + name + ", age = " + age + "}"; } }结果展示:
4. 反射获取方法对象
使用反射技术获取方法对象并使用
反射的第一步是先得到类对象,然后从类对象中获取类的成分对象
Class类中用于获取成员方法的方法
方法
Method[] getMethods() 返回所有成员方法对象的数组 (只能拿public的)
Method[] getDeclaredMethods() 返回所有成员方法对象的数组,存在就能拿到
Method getMethod(String name,Class<?>...parameterTypes) 返回单个成员方法对象 (只能拿public的)
Method getDeclaredMethod(String name, Class<?>... parameterTypes) 返回单个成员方法对象,存在就能拿到Method类中用于触发执行的方法
运行方法Obiect invoke(Object obj,Object... args)
参数一:用obj对象调用该方法
参数二:调用方法的传递的参数(如果没有就不写)
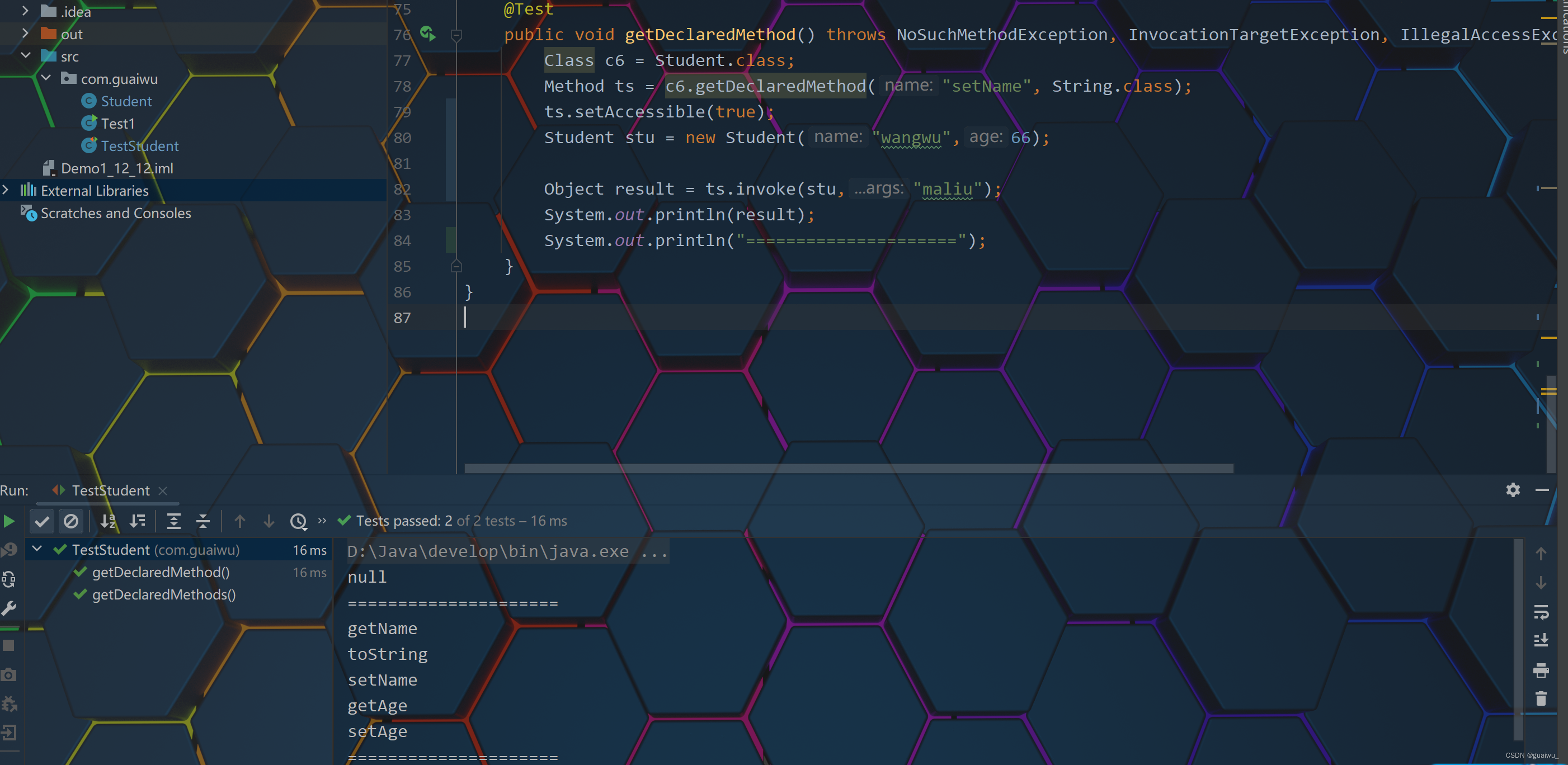
返回值:方法的返回值(如果没有就不写)代码示范:
package com.guaiwu; public class Student { private String name; private int age; public Student() { } public Student(String name, int age) { this.name = name; this.age = age; } /** * 获取 * @return name */ public String getName() { return name; } /** * 设置 * @param name */ public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } /** * 获取 * @return age */ public int getAge() { return age; } /** * 设置 * @param age */ public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } public String toString() { return "Student{name = " + name + ", age = " + age + "}"; } }package com.guaiwu; import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test; import java.lang.reflect.Constructor; import java.lang.reflect.Field; import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException; import java.lang.reflect.Method; public class TestStudent { @Test public void getDeclaredMethods(){ Class c5 = Student.class; Method[] mt1 = c5.getDeclaredMethods(); for (Method method : mt1) { System.out.println(method.getName()); } System.out.println("====================="); } @Test public void getDeclaredMethod() throws NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException { Class c6 = Student.class; Method ts = c6.getDeclaredMethod("setName", String.class); ts.setAccessible(true); Student stu = new Student("wangwu",66); Object result = ts.invoke(stu,"maliu"); System.out.println(result); System.out.println("====================="); } }结果示范:
5.用反射绕过编译阶段为集合添加数据
原理: 编译成Class文件进入运行阶段的时候, 泛型会自动擦除
反射是作用在运行时的技术, 此时已经不存在泛型了
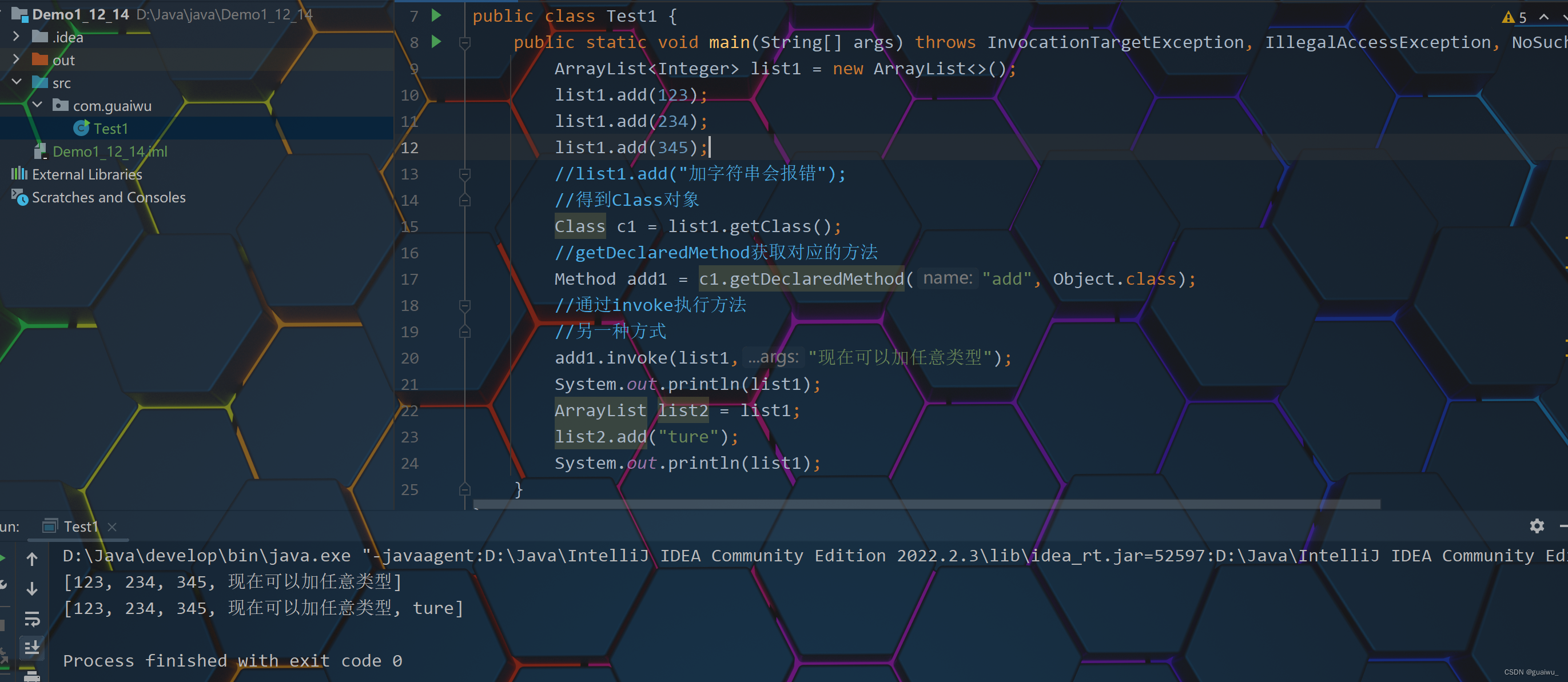
代码示范:
package com.guaiwu; import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException; import java.lang.reflect.Method; import java.util.ArrayList; public class Test1 { public static void main(String[] args) throws InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException, NoSuchMethodException { ArrayList<Integer> list1 = new ArrayList<>(); list1.add(123); list1.add(234); list1.add(345); //list1.add("加字符串会报错"); //得到Class对象 Class c1 = list1.getClass(); //getDeclaredMethod获取对应的方法 Method add1 = c1.getDeclaredMethod("add", Object.class); //通过invoke执行方法 //另一种方式 add1.invoke(list1,"现在可以加任意类型"); System.out.println(list1); ArrayList list2 = list1; list2.add("ture"); System.out.println(list1); } }结果展示:
反射做通用框架
练习: 给你任意一个对象,在不清楚对象字段的情况可以,可以把对象的字段名称和对应值存储到文件中去
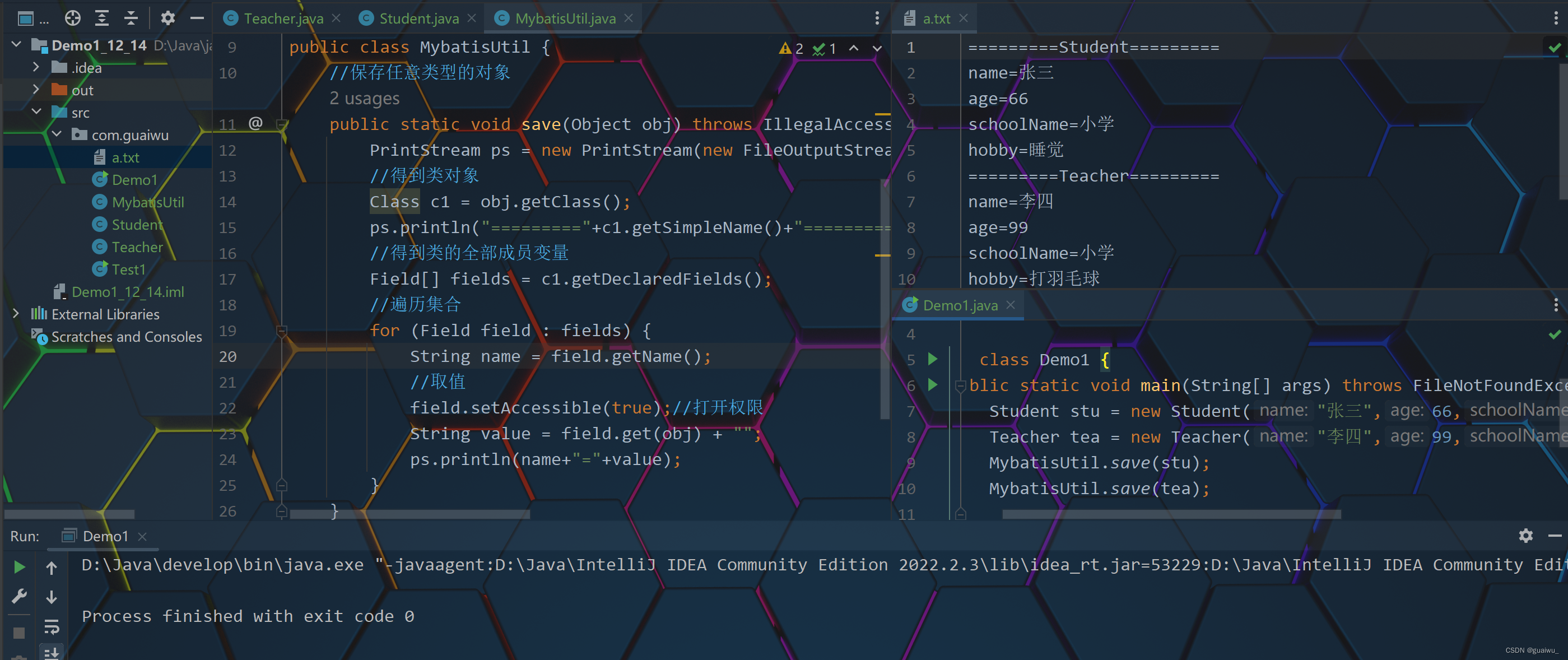
代码示范: 第一,第二段是类的代码, 第三段是通用框架的代码(重点), 第四段是测试代码
package com.guaiwu; public class Teacher { private String name; private int age; private String schoolName; private String hobby; public Teacher() { } public Teacher(String name, int age, String schoolName, String hobby) { this.name = name; this.age = age; this.schoolName = schoolName; this.hobby = hobby; } /** * 获取 * @return name */ public String getName() { return name; } /** * 设置 * @param name */ public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } /** * 获取 * @return age */ public int getAge() { return age; } /** * 设置 * @param age */ public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } /** * 获取 * @return schoolName */ public String getSchoolName() { return schoolName; } /** * 设置 * @param schoolName */ public void setSchoolName(String schoolName) { this.schoolName = schoolName; } /** * 获取 * @return hobby */ public String getHobby() { return hobby; } /** * 设置 * @param hobby */ public void setHobby(String hobby) { this.hobby = hobby; } public String toString() { return "Teacher{name = " + name + ", age = " + age + ", schoolName = " + schoolName + ", hobby = " + hobby + "}"; } }package com.guaiwu; public class Student { private String name; private int age; private String schoolName; private String hobby; public Student() { } public Student(String name, int age, String schoolName, String hobby) { this.name = name; this.age = age; this.schoolName = schoolName; this.hobby = hobby; } /** * 获取 * @return name */ public String getName() { return name; } /** * 设置 * @param name */ public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } /** * 获取 * @return age */ public int getAge() { return age; } /** * 设置 * @param age */ public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } /** * 获取 * @return schoolName */ public String getSchoolName() { return schoolName; } /** * 设置 * @param schoolName */ public void setSchoolName(String schoolName) { this.schoolName = schoolName; } /** * 获取 * @return hobby */ public String getHobby() { return hobby; } /** * 设置 * @param hobby */ public void setHobby(String hobby) { this.hobby = hobby; } public String toString() { return "Student{name = " + name + ", age = " + age + ", schoolName = " + schoolName + ", hobby = " + hobby + "}"; } }package com.guaiwu; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.FilterOutputStream; import java.io.PrintStream; import java.lang.reflect.Field; public class MybatisUtil { //保存任意类型的对象 public static void save(Object obj) throws IllegalAccessException, FileNotFoundException { PrintStream ps = new PrintStream(new FileOutputStream("D:\\Java\\java\\Demo1_12_14\\src\\com\\guaiwu\\a.txt",true)); //得到类对象 Class c1 = obj.getClass(); ps.println("========="+c1.getSimpleName()+"========="); //得到类的全部成员变量 Field[] fields = c1.getDeclaredFields(); //遍历集合 for (Field field : fields) { String name = field.getName(); //取值 field.setAccessible(true);//打开权限 String value = field.get(obj) + ""; ps.println(name+"="+value); } } }package com.guaiwu; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; public class Demo1 { public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException, IllegalAccessException { Student stu = new Student("张三",66,"小学","睡觉"); Teacher tea = new Teacher("李四",99,"小学","打羽毛球"); MybatisUtil.save(stu); MybatisUtil.save(tea); } }结果展示:


![[附源码]Python计算机毕业设计仿咸鱼二手物品交易系统Django(程序+LW)](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/c86adeddb61f439abf2636b3b556efcf.png)