一、介绍
Node,就是节点,在整体结构中,就是黄色那一块,红色也算
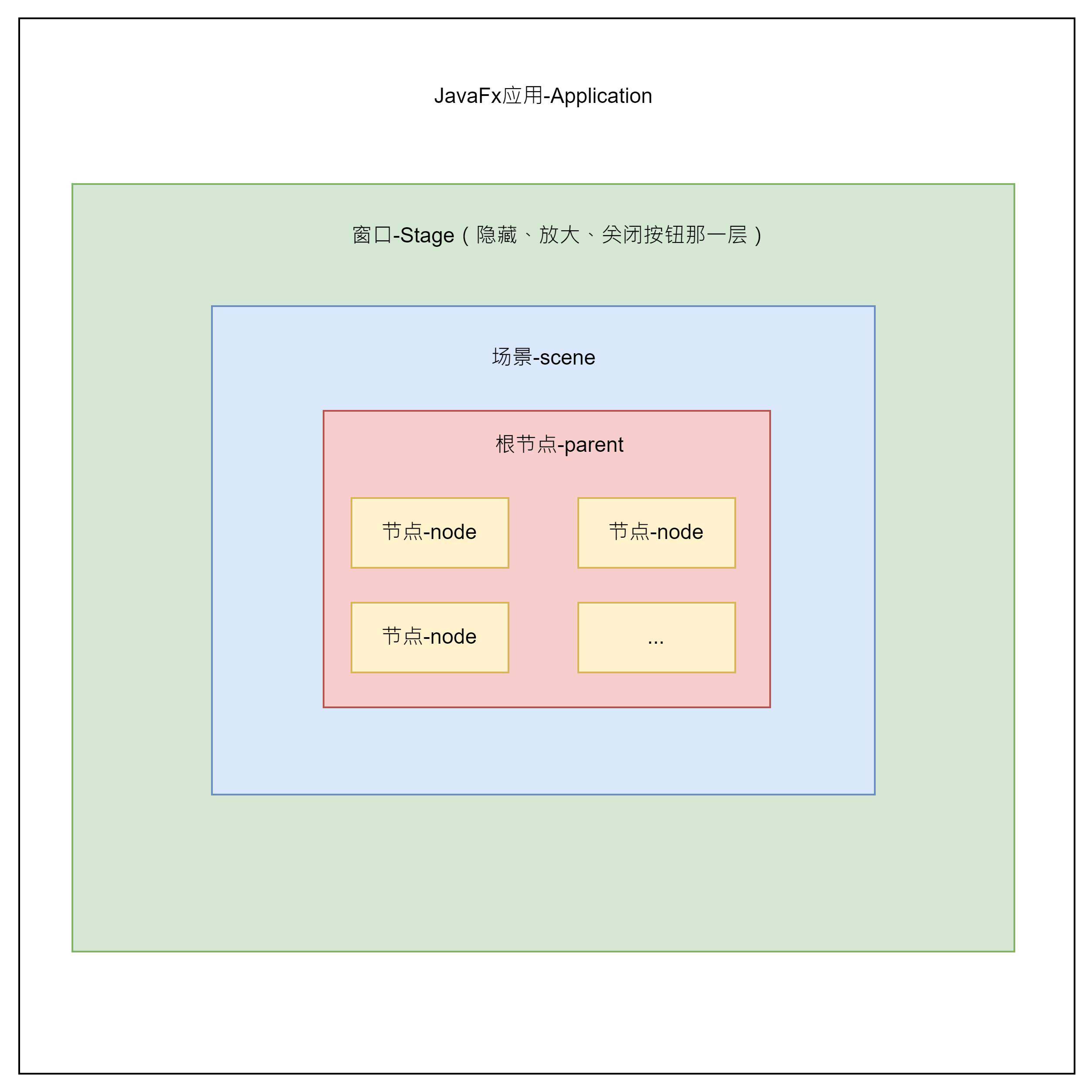
个人理解,在实际中,Node可以说是我们的UI页面上的每一个节点了,比如按钮、标签之类的控件,而这些控件,大多都是有一些通用属性的,以下简单介绍一下。
二、继承关系
所有的UI控件,都继承了Node类,在Node类中,定义了控件的通用属性的设置
@IDProperty("id")
public abstract class Node implements EventTarget, Styleable {
.....
}对此类感兴趣的小伙伴可以自行了解
三、常用通用属性
以下以Button控件为进行介绍:
public class App extends Application{
@Override
public void start(Stage primaryStage) throws Exception {
BUtton button = new Button("我是一个按钮");
AnchorPane anchorPane = new AnchorPane();
anchorPane.getChildren().add(button);
Scene scene = new Scene(anchorPane, 400, 400);
primaryStage.setScene(scene);
primaryStage.show();
}
public static void main(String[] args )
{
launch(args);
}
}1、layoutX,设置控件在Scene场景中的x轴位置
button.setLayoutX(20);2、layoutY ,设置控件在Scene场景中的y轴位置
button.setLayoutY(20);3、preWidth,设置控件宽度
button.setPrefWidth(200);4、preHeight,设置控件高度
button.setPrefHeight(200);5、alignment,设置内容显示位置
button.setAlignment(Pos.BOTTOM_RIGHT);6、visible,设置控件是否可视
button.setVisible(false);7、opacity,设置控件透明度
button.setOpacity(0.5);8、rotate,设置控件倾斜度
button.setRotate(90);9、translateX、translateY、translateZ,控件在各个轴移动多少
button.setTranslateX(20);
button.setTranslateY(45);
button.setTranslateZ(180);10、更多前往文档查找并且使用
四、属性Properties
上诉通用属性中,基本上都有对应的Properties子类类型,
比如,在Button控件中:
layoutX属性对应有layoutXProperty方法,返回的是DoubleProperty对象,
layoutY属性对应有layoutYProperty方法,返回的是DoubleProperty对象,
disable属性对应有disableProperty方法,返回的是BooleanProperty对象,
依次类推,具体看不同属性的返回值是哪一个Properties子类类型;
我们可以对这些属性的Property类型返回进行绑定bind或者监听addListener,细节请看下面属性绑定和属性监听章节
五、属性绑定
JavaFx中我们的属性可以与其它属性进行绑定,当其他属性的值发生改变之后,我们被绑定的属性值也将发生改变,参考如下案例:
1)属性没有进行绑定前:
public class HelloApplication extends Application {
@Override
public void start(Stage stage) throws IOException {
Button button = new Button("我是一个按钮");
BorderPane pane = new BorderPane(button);
Scene scene = new Scene(pane, 320, 240);
button.setPrefWidth(160);
button.setPrefHeight(20);
stage.setTitle("Hello!");
stage.setScene(scene);
stage.show();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
launch();
}
}运行效果:
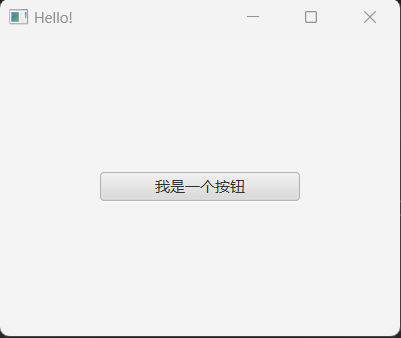
我们做如下操作,当我们拖动窗口大小,使窗口变长,发现按钮大小固定不变,并没有随着窗口变大而调整大小:
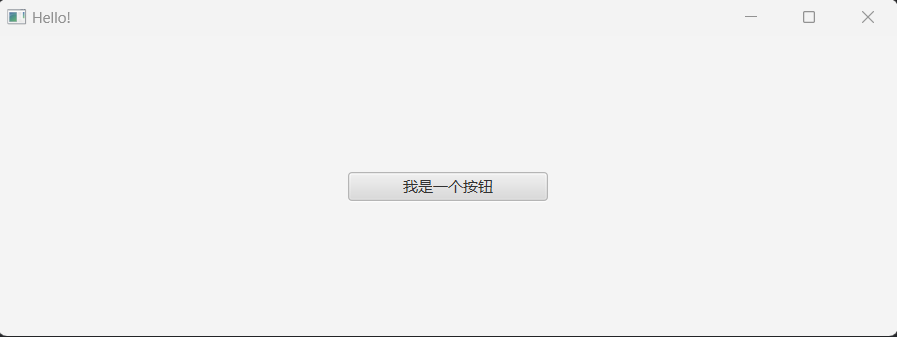
2) 进行属性绑定,以下我们将按钮的宽度属性与窗口的宽度属性进行绑定,当窗口宽度属性发生变化的时候,我们的按钮宽度属性也随之改变。
添加如下代码:
button.prefWidthProperty().bind(pane.widthProperty().divide(2));观察效果,当我们拖到窗口宽度使之变宽之后,可以看到,按钮的宽度也随着窗口的宽度发生变化:
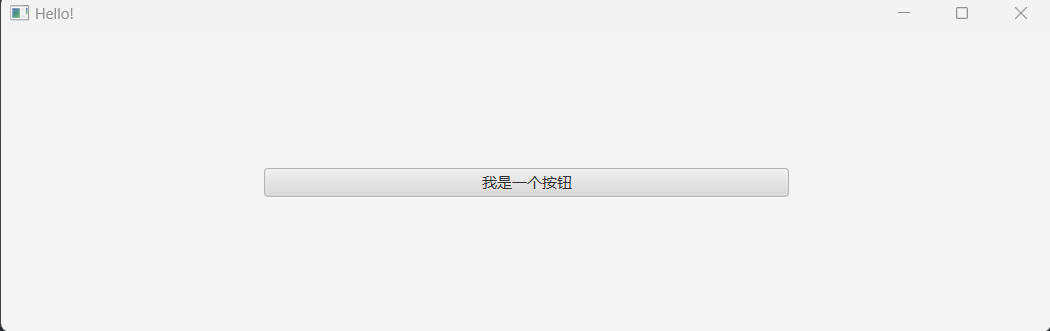
以上就是关于我们的属性绑定了,更多玩法还需要小伙伴自行进行拓展哦
六、属性监听
顾名思义,如果我们控件的属性进行了改变,我们可以对这些属性进行监听
public class App extends Application{
@Override
public void start(Stage primaryStage) throws Exception {
Button button = new Button("我是一个按钮");
button.disableProperty().addListener(new ChangeListener<Boolean>() {
@Override
public void changed(ObservableValue<? extends Boolean> observable, Boolean oldValue, Boolean newValue) {
System.out.println("我是第一个按钮,我被禁用了");
}
});
AnchorPane anchorPane = new AnchorPane();
anchorPane.getChildren().add(button);
Button button2 = new Button("禁用");
button2.setLayoutY(50);
button2.setOnAction(event -> {
button.setDisable(true);
});
anchorPane.getChildren().add(button2);
Scene scene = new Scene(anchorPane, 400, 400);
primaryStage.setScene(scene);
primaryStage.show();
}
public static void main(String[] args )
{
launch(args);
}
}以上就是关于我们的属性监听了,更多玩法还需要小伙伴自行进行拓展哦
七、事件驱动
事件驱动,也就是比如我们有一个按钮,我们点击按钮、鼠标点击、鼠标释放、鼠标移入、鼠标移出、键盘事件等的事件响应
在JavaFx中,事件驱动主要相关的函数是以setOnxxx命名的,接下来简单体验一下事件驱动吧
1、setOnAction,控件基础的功能事件
button.setOnAction(actionEvent -> {
System.out.println("点击");
});2、setOnKeyPressed,键盘按下事件,需要对场景Scene设置
scene.setOnKeyPressed(keyEvent -> {
System.out.println("键盘按下");
});3、setOnKeyReleased,键盘松开事件,需要对场景Scene设置
scene.setOnKeyReleased(keyEvent -> {
System.out.println("键盘松开");
});4、setOnMouseEntered,鼠标移入事件
button.setOnMouseEntered(mouseEvent -> {
System.out.println("鼠标移入");
});5、setOnMouseEntered,鼠标移出事件
button.setOnMouseMoved(mouseEvent -> {
System.out.println("鼠标移出");
});6、还有更多其他事件,详情请参考文档
八、其他章节
待补充