文章目录
- 说明
- 1. 网络结构与参数
- 1.1 单层
- 1.2 多层管理
- 2. CNN网络构建
- 2.1 构建CNN网络建构
- 2.2 初始化卷积神经网络FullCnn对象
- 2.3 获取数据集
- 2.4 训练数据
- 2.4.1 前向传播函数forward
- 2.4.1.1 CONVOLUTION卷积层
- 2.4.1.2 SAMPLING 池化层
- 2.4.1.3 OUTPUT 输出层
- 2.4.2 反向传播函数backPropagatio
- 2.4.2.1 输出层
- 2.4.2.2 反卷积运算
- 2.4.2.3 反池化层运算
- 2.4.2.4 训练结果
说明
闵老师的文章链接: 日撸 Java 三百行(总述)_minfanphd的博客-CSDN博客
自己也把手敲的代码放在了github上维护:https://github.com/fulisha-ok/sampledata
1. 网络结构与参数
1.1 单层
这个类主要用于表示CNN中的一个层,提供了初始化卷积核、偏置、误差等操作的方法,以及获取特征图、卷积核等属性的方法。它的作用是在卷积神经网络中管理和操作每个层的相关信息
package machinelearing.cnn;
/**
* @author: fulisha
* @date: 2023/7/29 16:07
* @description:
*/
public class CnnLayer {
/**
* The type of the layer.
*/
LayerTypeEnum type;
/**
* The number of out map.-输出特征图数量
*/
int outMapNum;
/**
* The map size. - 特征图尺寸
*/
Size mapSize;
/**
* The kernel size.-卷积核尺寸
*/
Size kernelSize;
/**
* The scale size.-缩放尺寸
*/
Size scaleSize;
/**
* The index of the class (label) attribute. -分类数量(当层类型为OUTPUT时使用)
*/
int classNum = -1;
/**
* Kernel. Dimensions: [front map][out map][width][height].-卷积核
*/
private double[][][][] kernel;
/**
* Bias. The length is outMapNum. - 偏置,长度为输出特征图的数量
*/
private double[] bias;
/**
* Out maps. Dimensions:
* [batchSize][outMapNum][mapSize.width][mapSize.height]. - 输出特征图,维度:[batch大小][输出特征图数量][特征图宽度][特征图高度]
*/
private double[][][][] outMaps;
/**
* Errors. - 误差
*/
private double[][][][] errors;
/**
* For batch processing. - 用于批处理
*/
private static int recordInBatch = 0;
/**
* The first constructor.
*
* @param paraNum
* When the type is CONVOLUTION, it is the out map number. when
* the type is OUTPUT, it is the class number.
* @param paraSize
* When the type is INPUT, it is the map size; when the type is
* CONVOLUTION, it is the kernel size; when the type is SAMPLING,
* it is the scale size.
*/
public CnnLayer(LayerTypeEnum paraType, int paraNum, Size paraSize) {
type = paraType;
switch (type) {
case INPUT:
outMapNum = 1;
mapSize = paraSize; // No deep copy.
break;
case CONVOLUTION:
outMapNum = paraNum;
kernelSize = paraSize;
break;
case SAMPLING:
scaleSize = paraSize;
break;
case OUTPUT:
classNum = paraNum;
mapSize = new Size(1, 1);
outMapNum = classNum;
break;
default:
System.out.println("Internal error occurred in AbstractLayer.java constructor.");
}
}
/**
* Initialize the kernel.
* @param paraFrontMapNum When the type is CONVOLUTION, it is the out map number. when
*/
public void initKernel(int paraFrontMapNum) {
kernel = new double[paraFrontMapNum][outMapNum][][];
for (int i = 0; i < paraFrontMapNum; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < outMapNum; j++) {
kernel[i][j] = MathUtils.randomMatrix(kernelSize.width, kernelSize.height, true);
}
}
}
/**
* Initialize the output kernel. The code is revised to invoke
* initKernel(int).
*/
public void initOutputKernel(int paraFrontMapNum, Size paraSize) {
kernelSize = paraSize;
initKernel(paraFrontMapNum);
}
/**
* Initialize the bias. No parameter. "int frontMapNum" is claimed however
* not used.
*/
public void initBias() {
bias = MathUtils.randomArray(outMapNum);
}
/**
* Initialize the errors.
* @param paraBatchSize The batch size.
*/
public void initErrors(int paraBatchSize) {
errors = new double[paraBatchSize][outMapNum][mapSize.width][mapSize.height];
}
/**
* Initialize out maps.
* @param paraBatchSize The batch size.
*/
public void initOutMaps(int paraBatchSize) {
outMaps = new double[paraBatchSize][outMapNum][mapSize.width][mapSize.height];
}
/**
* Prepare for a new batch.
*/
public static void prepareForNewBatch() {
recordInBatch = 0;
}
public static void prepareForNewRecord() {
recordInBatch++;
}
public void setMapValue(int paraMapNo, int paraX, int paraY, double paraValue) {
outMaps[recordInBatch][paraMapNo][paraX][paraY] = paraValue;
}
public void setMapValue(int paraMapNo, double[][] paraOutMatrix) {
outMaps[recordInBatch][paraMapNo] = paraOutMatrix;
}
public Size getMapSize() {
return mapSize;
}
public void setMapSize(Size paraMapSize) {
mapSize = paraMapSize;
}
public LayerTypeEnum getType() {
return type;
}
public int getOutMapNum() {
return outMapNum;
}
public void setOutMapNum(int paraOutMapNum) {
outMapNum = paraOutMapNum;
}
public Size getKernelSize() {
return kernelSize;
}
public Size getScaleSize() {
return scaleSize;
}
public double[][] getMap(int paraIndex) {
return outMaps[recordInBatch][paraIndex];
}
public double[][] getKernel(int paraFrontMap, int paraOutMap) {
return kernel[paraFrontMap][paraOutMap];
}
/**
* Setter. Set one error.
*/
public void setError(int paraMapNo, int paraMapX, int paraMapY, double paraValue) {
errors[recordInBatch][paraMapNo][paraMapX][paraMapY] = paraValue;
}
/**
* Setter. Set one error matrix.
*/
public void setError(int paraMapNo, double[][] paraMatrix) {
errors[recordInBatch][paraMapNo] = paraMatrix;
}
/**
* Getter. Get one error matrix.
*/
public double[][] getError(int paraMapNo) {
return errors[recordInBatch][paraMapNo];
}
/**
* Getter. Get the whole error tensor.
*/
public double[][][][] getErrors() {
return errors;
}
/**
* Setter. Set one kernel.
*/
public void setKernel(int paraLastMapNo, int paraMapNo, double[][] paraKernel) {
kernel[paraLastMapNo][paraMapNo] = paraKernel;
}
/**
* Getter.
*/
public double getBias(int paraMapNo) {
return bias[paraMapNo];
}
/**
* Setter.
*/
public void setBias(int paraMapNo, double paraValue) {
bias[paraMapNo] = paraValue;
}
/**
* Getter.
*/
public double[][][][] getMaps() {
return outMaps;
}
/**
* Getter.
*/
public double[][] getError(int paraRecordId, int paraMapNo) {
return errors[paraRecordId][paraMapNo];
}
/**
* Getter.
*/
public double[][] getMap(int paraRecordId, int paraMapNo) {
return outMaps[paraRecordId][paraMapNo];
}
/**
* Getter.
*/
public int getClassNum() {
return classNum;
}
/**
* Getter. Get the whole kernel tensor.
*/
public double[][][][] getKernel() {
return kernel;
}
}
1.2 多层管理
用于构建卷积神经网络的层结构。
这个类用于管理卷积神经网络的层结构。它允许用户添加不同的层到网络中,获取指定索引的层、输出层,以及获取网络中层的数量。通过LayerBuilder类,用户可以逐层构建卷积神经网络的结构。
package machinelearing.cnn;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @author: fulisha
* @date: 2023/7/29 16:10
* @description:
*/
public class LayerBuilder {
/**
* Layers.
*/
private List<CnnLayer> layers;
/**
* The first constructor.
*/
public LayerBuilder() {
layers = new ArrayList<CnnLayer>();
}// Of the first constructor
/**
* The second constructor.
*/
public LayerBuilder(CnnLayer paraLayer) {
this();
layers.add(paraLayer);
}
/**
* Add a layer.
* @param paraLayer The new layer.
*/
public void addLayer(CnnLayer paraLayer) {
layers.add(paraLayer);
}
/**
* Get the specified layer.
* @param paraIndex The index of the layer.
*/
public CnnLayer getLayer(int paraIndex) throws RuntimeException{
if (paraIndex >= layers.size()) {
throw new RuntimeException("CnnLayer " + paraIndex + " is out of range: "
+ layers.size() + ".");
}
return layers.get(paraIndex);
}
/**
* Get the output layer.
*/
public CnnLayer getOutputLayer() {
return layers.get(layers.size() - 1);
}
/**
* Get the number of layers.
*/
public int getNumLayers() {
return layers.size();
}
}
2. CNN网络构建
package machinelearing.cnn;
import java.util.Arrays;
import machinelearing.cnn.Dataset.Instance;
import machinelearing.cnn.MathUtils.Operator;
/**
* @author: fulisha
* @date: 2023/8/8 13:48
* @description:
*/
public class FullCnn {
/**
* The value changes.
*/
private static double ALPHA = 0.85;
/**
* A constant.
*/
public static double LAMBDA = 0;
/**
* Manage layers.
*/
private static LayerBuilder layerBuilder;
/**
* Train using a number of instances simultaneously.
*/
private int batchSize;
/**
* Divide the batch size with the given value.
*/
private Operator divideBatchSize;
/**
* Multiply alpha with the given value.
*/
private Operator multiplyAlpha;
/**
* Multiply lambda and alpha with the given value.
*/
private Operator multiplyLambda;
/**
* The first constructor.
*/
public FullCnn(LayerBuilder paraLayerBuilder, int paraBatchSize) {
layerBuilder = paraLayerBuilder;
batchSize = paraBatchSize;
setup();
initOperators();
}
/**
* Initialize operators using temporary classes.
*/
private void initOperators() {
divideBatchSize = new Operator() {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 7424011281732651055L;
@Override
public double process(double value) {
return value / batchSize;
}
};
multiplyAlpha = new Operator() {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 5761368499808006552L;
@Override
public double process(double value) {
return value * ALPHA;
}
};
multiplyLambda = new Operator() {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 4499087728362870577L;
@Override
public double process(double value) {
return value * (1 - LAMBDA * ALPHA);
}
};
}
/**
* Setup according to the layer builder.
*/
public void setup() {
CnnLayer tempInputLayer = layerBuilder.getLayer(0);
tempInputLayer.initOutMaps(batchSize);
for (int i = 1; i < layerBuilder.getNumLayers(); i++) {
CnnLayer tempLayer = layerBuilder.getLayer(i);
CnnLayer tempFrontLayer = layerBuilder.getLayer(i - 1);
int tempFrontMapNum = tempFrontLayer.getOutMapNum();
switch (tempLayer.getType()) {
case INPUT:
// Should not be input. Maybe an error should be thrown out.
break;
case CONVOLUTION:
tempLayer.setMapSize(
tempFrontLayer.getMapSize().subtract(tempLayer.getKernelSize(), 1));
tempLayer.initKernel(tempFrontMapNum);
tempLayer.initBias();
tempLayer.initErrors(batchSize);
tempLayer.initOutMaps(batchSize);
break;
case SAMPLING:
tempLayer.setOutMapNum(tempFrontMapNum);
tempLayer.setMapSize(tempFrontLayer.getMapSize().divide(tempLayer.getScaleSize()));
tempLayer.initErrors(batchSize);
tempLayer.initOutMaps(batchSize);
break;
case OUTPUT:
tempLayer.initOutputKernel(tempFrontMapNum, tempFrontLayer.getMapSize());
tempLayer.initBias();
tempLayer.initErrors(batchSize);
tempLayer.initOutMaps(batchSize);
break;
}
}
}
/**
* Forward computing.
*/
private void forward(Instance instance) {
setInputLayerOutput(instance);
for (int l = 1; l < layerBuilder.getNumLayers(); l++) {
CnnLayer tempCurrentLayer = layerBuilder.getLayer(l);
CnnLayer tempLastLayer = layerBuilder.getLayer(l - 1);
switch (tempCurrentLayer.getType()) {
case CONVOLUTION:
setConvolutionOutput(tempCurrentLayer, tempLastLayer);
break;
case SAMPLING:
setSampOutput(tempCurrentLayer, tempLastLayer);
break;
case OUTPUT:
setConvolutionOutput(tempCurrentLayer, tempLastLayer);
break;
default:
break;
}
}
}
/**
* Set the in layer output. Given a record, copy its values to the input
* map.
*/
private void setInputLayerOutput(Instance paraRecord) {
CnnLayer tempInputLayer = layerBuilder.getLayer(0);
Size tempMapSize = tempInputLayer.getMapSize();
double[] tempAttributes = paraRecord.getAttributes();
if (tempAttributes.length != tempMapSize.width * tempMapSize.height) {
throw new RuntimeException("input record does not match the map size.");
}
for (int i = 0; i < tempMapSize.width; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < tempMapSize.height; j++) {
tempInputLayer.setMapValue(0, i, j, tempAttributes[tempMapSize.height * i + j]);
}
}
}
/**
* Compute the convolution output according to the output of the last layer.
* @param paraLastLayer the last layer.
* @param paraLayer the current layer.
*/
private void setConvolutionOutput(final CnnLayer paraLayer, final CnnLayer paraLastLayer) {
// int mapNum = paraLayer.getOutMapNum();
final int lastMapNum = paraLastLayer.getOutMapNum();
// Attention: paraLayer.getOutMapNum() may not be right.
for (int j = 0; j < paraLayer.getOutMapNum(); j++) {
double[][] tempSumMatrix = null;
for (int i = 0; i < lastMapNum; i++) {
double[][] lastMap = paraLastLayer.getMap(i);
double[][] kernel = paraLayer.getKernel(i, j);
if (tempSumMatrix == null) {
// On the first map.
tempSumMatrix = MathUtils.convnValid(lastMap, kernel);
} else {
// Sum up convolution maps
tempSumMatrix = MathUtils.matrixOp(MathUtils.convnValid(lastMap, kernel),
tempSumMatrix, null, null, MathUtils.plus);
}
}
// Activation.
final double bias = paraLayer.getBias(j);
tempSumMatrix = MathUtils.matrixOp(tempSumMatrix, new Operator() {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 2469461972825890810L;
@Override
public double process(double value) {
return MathUtils.sigmod(value + bias);
}
});
paraLayer.setMapValue(j, tempSumMatrix);
}
}
/**
* Compute the convolution output according to the output of the last layer.
* @param paraLastLayer the last layer.
* @param paraLayer the current layer.
*/
private void setSampOutput(final CnnLayer paraLayer, final CnnLayer paraLastLayer) {
// int tempLastMapNum = paraLastLayer.getOutMapNum();
// Attention: paraLayer.outMapNum may not be right.
for (int i = 0; i < paraLayer.outMapNum; i++) {
double[][] lastMap = paraLastLayer.getMap(i);
Size scaleSize = paraLayer.getScaleSize();
double[][] sampMatrix = MathUtils.scaleMatrix(lastMap, scaleSize);
paraLayer.setMapValue(i, sampMatrix);
}
}
/**
* Train the cnn.
*/
public void train(Dataset paraDataset, int paraRounds) {
for (int t = 0; t < paraRounds; t++) {
System.out.println("Iteration: " + t);
int tempNumEpochs = paraDataset.size() / batchSize;
if (paraDataset.size() % batchSize != 0) {
tempNumEpochs++;
}
// logger.info("第{}次迭代,epochsNum: {}", t, epochsNum);
double tempNumCorrect = 0;
int tempCount = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < tempNumEpochs; i++) {
int[] tempRandomPerm = MathUtils.randomPerm(paraDataset.size(), batchSize);
CnnLayer.prepareForNewBatch();
for (int index : tempRandomPerm) {
boolean isRight = train(paraDataset.getInstance(index));
if (isRight) {
tempNumCorrect++;
}
tempCount++;
CnnLayer.prepareForNewRecord();
}
updateParameters();
if (i % 50 == 0) {
System.out.print("..");
if (i + 50 > tempNumEpochs) {
System.out.println();
}
}
}
double p = 1.0 * tempNumCorrect / tempCount;
if (t % 10 == 1 && p > 0.96) {
ALPHA = 0.001 + ALPHA * 0.9;
// logger.info("设置 alpha = {}", ALPHA);
}
System.out.println("Training precision: " + p);
// logger.info("计算精度: {}/{}={}.", right, count, p);
}
}
/**
* Train the cnn with only one record.
* @param paraRecord The given record.
*/
private boolean train(Instance paraRecord) {
forward(paraRecord);
boolean result = backPropagation(paraRecord);
return result;
}
/**
* Back-propagation.
* @param paraRecord The given record.
*/
private boolean backPropagation(Instance paraRecord) {
boolean result = setOutputLayerErrors(paraRecord);
setHiddenLayerErrors();
return result;
}
/**
* Update parameters.
*/
private void updateParameters() {
for (int l = 1; l < layerBuilder.getNumLayers(); l++) {
CnnLayer layer = layerBuilder.getLayer(l);
CnnLayer lastLayer = layerBuilder.getLayer(l - 1);
switch (layer.getType()) {
case CONVOLUTION:
case OUTPUT:
updateKernels(layer, lastLayer);
updateBias(layer, lastLayer);
break;
default:
break;
}
}
}
/**
***********************
* Update bias.
***********************
*/
private void updateBias(final CnnLayer paraLayer, CnnLayer paraLastLayer) {
final double[][][][] errors = paraLayer.getErrors();
// int mapNum = paraLayer.getOutMapNum();
// Attention: getOutMapNum() may not be correct.
for (int j = 0; j < paraLayer.getOutMapNum(); j++) {
double[][] error = MathUtils.sum(errors, j);
double deltaBias = MathUtils.sum(error) / batchSize;
double bias = paraLayer.getBias(j) + ALPHA * deltaBias;
paraLayer.setBias(j, bias);
}
}
/**
* Update kernels.
*/
private void updateKernels(final CnnLayer paraLayer, final CnnLayer paraLastLayer) {
// int mapNum = paraLayer.getOutMapNum();
int tempLastMapNum = paraLastLayer.getOutMapNum();
// Attention: getOutMapNum() may not be right
for (int j = 0; j < paraLayer.getOutMapNum(); j++) {
for (int i = 0; i < tempLastMapNum; i++) {
double[][] tempDeltaKernel = null;
for (int r = 0; r < batchSize; r++) {
double[][] error = paraLayer.getError(r, j);
if (tempDeltaKernel == null) {
tempDeltaKernel = MathUtils.convnValid(paraLastLayer.getMap(r, i), error);
} else {
tempDeltaKernel = MathUtils.matrixOp(
MathUtils.convnValid(paraLastLayer.getMap(r, i), error),
tempDeltaKernel, null, null, MathUtils.plus);
}
}
tempDeltaKernel = MathUtils.matrixOp(tempDeltaKernel, divideBatchSize);
if (!rangeCheck(tempDeltaKernel, -10, 10)) {
System.exit(0);
}
double[][] kernel = paraLayer.getKernel(i, j);
tempDeltaKernel = MathUtils.matrixOp(kernel, tempDeltaKernel, multiplyLambda,
multiplyAlpha, MathUtils.plus);
paraLayer.setKernel(i, j, tempDeltaKernel);
}
}
}
/**
* Set errors of all hidden layers.
*/
private void setHiddenLayerErrors() {
// System.out.println("setHiddenLayerErrors");
for (int l = layerBuilder.getNumLayers() - 2; l > 0; l--) {
CnnLayer layer = layerBuilder.getLayer(l);
CnnLayer nextLayer = layerBuilder.getLayer(l + 1);
// System.out.println("layertype = " + layer.getType());
switch (layer.getType()) {
case SAMPLING:
setSamplingErrors(layer, nextLayer);
break;
case CONVOLUTION:
setConvolutionErrors(layer, nextLayer);
break;
default:
break;
}
}
}
/**
* Set errors of a sampling layer.
*/
private void setSamplingErrors(final CnnLayer paraLayer, final CnnLayer paraNextLayer) {
// int mapNum = layer.getOutMapNum();
int tempNextMapNum = paraNextLayer.getOutMapNum();
// Attention: getOutMapNum() may not be correct
for (int i = 0; i < paraLayer.getOutMapNum(); i++) {
double[][] sum = null;
for (int j = 0; j < tempNextMapNum; j++) {
double[][] nextError = paraNextLayer.getError(j);
double[][] kernel = paraNextLayer.getKernel(i, j);
if (sum == null) {
sum = MathUtils.convnFull(nextError, MathUtils.rot180(kernel));
} else {
sum = MathUtils.matrixOp(
MathUtils.convnFull(nextError, MathUtils.rot180(kernel)), sum, null,
null, MathUtils.plus);
}
}
paraLayer.setError(i, sum);
if (!rangeCheck(sum, -2, 2)) {
System.out.println(
"setSampErrors, error out of range.\r\n" + Arrays.deepToString(sum));
}
}
}
/**
* Set errors of a sampling layer.
*/
private void setConvolutionErrors(final CnnLayer paraLayer, final CnnLayer paraNextLayer) {
// System.out.println("setConvErrors");
for (int m = 0; m < paraLayer.getOutMapNum(); m++) {
Size tempScale = paraNextLayer.getScaleSize();
double[][] tempNextLayerErrors = paraNextLayer.getError(m);
double[][] tempMap = paraLayer.getMap(m);
double[][] tempOutMatrix = MathUtils.matrixOp(tempMap, MathUtils.cloneMatrix(tempMap),
null, MathUtils.one_value, MathUtils.multiply);
tempOutMatrix = MathUtils.matrixOp(tempOutMatrix,
MathUtils.kronecker(tempNextLayerErrors, tempScale), null, null,
MathUtils.multiply);
paraLayer.setError(m, tempOutMatrix);
// System.out.println("range check nextError");
if (!rangeCheck(tempNextLayerErrors, -10, 10)) {
System.out.println("setConvErrors, nextError out of range:\r\n"
+ Arrays.deepToString(tempNextLayerErrors));
System.out.println("the new errors are:\r\n" + Arrays.deepToString(tempOutMatrix));
System.exit(0);
}
if (!rangeCheck(tempOutMatrix, -10, 10)) {
System.out.println("setConvErrors, error out of range.");
System.exit(0);
}
}
}
/**
* Set errors of a sampling layer.
*/
private boolean setOutputLayerErrors(Instance paraRecord) {
CnnLayer tempOutputLayer = layerBuilder.getOutputLayer();
int tempMapNum = tempOutputLayer.getOutMapNum();
double[] tempTarget = new double[tempMapNum];
double[] tempOutMaps = new double[tempMapNum];
for (int m = 0; m < tempMapNum; m++) {
double[][] outmap = tempOutputLayer.getMap(m);
tempOutMaps[m] = outmap[0][0];
}
int tempLabel = paraRecord.getLabel().intValue();
tempTarget[tempLabel] = 1;
// Log.i(record.getLable() + "outmaps:" +
// Util.fomart(outmaps)
// + Arrays.toString(target));
for (int m = 0; m < tempMapNum; m++) {
tempOutputLayer.setError(m, 0, 0,
tempOutMaps[m] * (1 - tempOutMaps[m]) * (tempTarget[m] - tempOutMaps[m]));
}
return tempLabel == MathUtils.getMaxIndex(tempOutMaps);
}
/**
* Setup the network.
*/
public void setup(int paraBatchSize) {
CnnLayer tempInputLayer = layerBuilder.getLayer(0);
tempInputLayer.initOutMaps(paraBatchSize);
for (int i = 1; i < layerBuilder.getNumLayers(); i++) {
CnnLayer tempLayer = layerBuilder.getLayer(i);
CnnLayer tempLastLayer = layerBuilder.getLayer(i - 1);
int tempLastMapNum = tempLastLayer.getOutMapNum();
switch (tempLayer.getType()) {
case INPUT:
break;
case CONVOLUTION:
tempLayer.setMapSize(
tempLastLayer.getMapSize().subtract(tempLayer.getKernelSize(), 1));
tempLayer.initKernel(tempLastMapNum);
tempLayer.initBias();
tempLayer.initErrors(paraBatchSize);
tempLayer.initOutMaps(paraBatchSize);
break;
case SAMPLING:
tempLayer.setOutMapNum(tempLastMapNum);
tempLayer.setMapSize(tempLastLayer.getMapSize().divide(tempLayer.getScaleSize()));
tempLayer.initErrors(paraBatchSize);
tempLayer.initOutMaps(paraBatchSize);
break;
case OUTPUT:
tempLayer.initOutputKernel(tempLastMapNum, tempLastLayer.getMapSize());
tempLayer.initBias();
tempLayer.initErrors(paraBatchSize);
tempLayer.initOutMaps(paraBatchSize);
break;
}
}
}
/**
* Predict for the dataset.
*/
public int[] predict(Dataset paraDataset) {
System.out.println("Predicting ... ");
CnnLayer.prepareForNewBatch();
int[] resultPredictions = new int[paraDataset.size()];
double tempCorrect = 0.0;
Instance tempRecord;
for (int i = 0; i < paraDataset.size(); i++) {
tempRecord = paraDataset.getInstance(i);
forward(tempRecord);
CnnLayer outputLayer = layerBuilder.getOutputLayer();
int tempMapNum = outputLayer.getOutMapNum();
double[] tempOut = new double[tempMapNum];
for (int m = 0; m < tempMapNum; m++) {
double[][] outmap = outputLayer.getMap(m);
tempOut[m] = outmap[0][0];
}
resultPredictions[i] = MathUtils.getMaxIndex(tempOut);
if (resultPredictions[i] == tempRecord.getLabel().intValue()) {
tempCorrect++;
}
}
System.out.println("Accuracy: " + tempCorrect / paraDataset.size());
return resultPredictions;
}
/**
* Range check, only for debugging.
* @param paraMatrix
* @param paraLowerBound
* @param paraUpperBound
*/
public boolean rangeCheck(double[][] paraMatrix, double paraLowerBound, double paraUpperBound) {
for (int i = 0; i < paraMatrix.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < paraMatrix[0].length; j++) {
if ((paraMatrix[i][j] < paraLowerBound) || (paraMatrix[i][j] > paraUpperBound)) {
System.out.println("" + paraMatrix[i][j] + " out of range (" + paraLowerBound
+ ", " + paraUpperBound + ")\r\n");
return false;
}
}
}
return true;
}
/**
* The main entrance.
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
LayerBuilder builder = new LayerBuilder();
// Input layer, the maps are 28*28
builder.addLayer(new CnnLayer(LayerTypeEnum.INPUT, -1, new Size(28, 28)));
// Convolution output has size 24*24, 24=28+1-5
builder.addLayer(new CnnLayer(LayerTypeEnum.CONVOLUTION, 6, new Size(5, 5)));
// Sampling output has size 12*12,12=24/2
builder.addLayer(new CnnLayer(LayerTypeEnum.SAMPLING, -1, new Size(2, 2)));
// Convolution output has size 8*8, 8=12+1-5
builder.addLayer(new CnnLayer(LayerTypeEnum.CONVOLUTION, 12, new Size(5, 5)));
// Sampling output has size4×4,4=8/2
builder.addLayer(new CnnLayer(LayerTypeEnum.SAMPLING, -1, new Size(2, 2)));
// output layer, digits 0 - 9.
builder.addLayer(new CnnLayer(LayerTypeEnum.OUTPUT, 10, null));
// Construct the full CNN.
FullCnn tempCnn = new FullCnn(builder, 10);
Dataset tempTrainingSet = new Dataset("D:/sampledata/sampledata/src/data/train.format", ",", 784);
// Train the model.
tempCnn.train(tempTrainingSet, 10);
// tempCnn.predict(tempTrainingSet);
}
}
代码实现了一个完整的卷积神经网络(CNN)模型,包括前向传播、反向传播、参数更新和训练等。我将从函数入口开始去理解整个代码的一个运行过程。
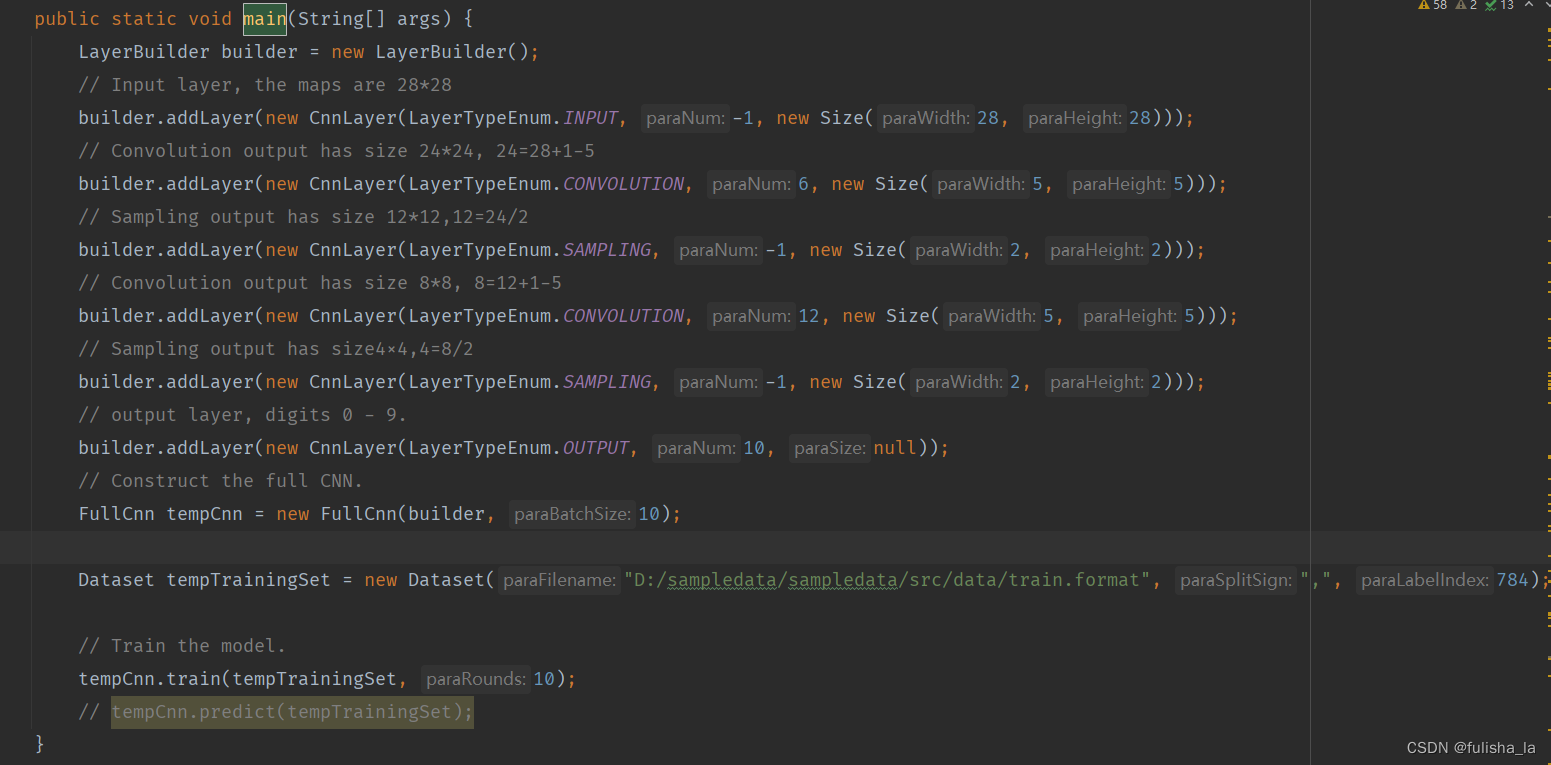
2.1 构建CNN网络建构
初始化了一个对象:LayerBuilder builder = new LayerBuilder();
- INPUT: 添加了一个输入层,图像大小为28*28
- CONVOLUTION: 添加了一个卷积层,包含6个卷积核,每个卷积核的大小为5x5 (经过卷积层后输出6个特征图,每个特征图大小为24*24)
- SAMPLING: 添加了一个池化层(将前一层的特征图进行向下采样)(经过池化层后,输出6个特征图,没个特征图的大小为12*12)
- CONVOLUTION: 再添加一个卷积层,包含12个卷积核,每个卷积核的大小为5x5 (经过卷积层后输出12个特征图,特征图的大小为8*8)
- SAMPLING: 再添加一个池化层 (经过池化层后,输出12个特征图,没个特征图的大小为4*4)
- OUTPUT: 添加一个输出层(经过输出层,输出10个类别对应的特征值大小)
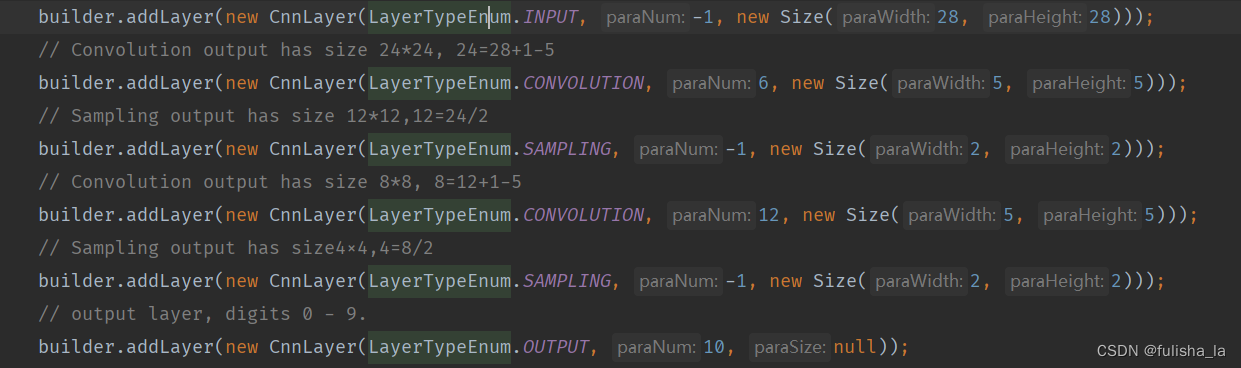
2.2 初始化卷积神经网络FullCnn对象

/**
* The first constructor.
*/
public FullCnn(LayerBuilder paraLayerBuilder, int paraBatchSize) {
layerBuilder = paraLayerBuilder;
batchSize = paraBatchSize;
setup();
initOperators();
}
/**
* Initialize operators using temporary classes.
*/
private void initOperators() {
divideBatchSize = new Operator() {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 7424011281732651055L;
@Override
public double process(double value) {
return value / batchSize;
}
};
multiplyAlpha = new Operator() {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 5761368499808006552L;
@Override
public double process(double value) {
return value * ALPHA;
}
};
multiplyLambda = new Operator() {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 4499087728362870577L;
@Override
public double process(double value) {
return value * (1 - LAMBDA * ALPHA);
}
};
}
/**
* Setup according to the layer builder.
*/
public void setup() {
CnnLayer tempInputLayer = layerBuilder.getLayer(0);
tempInputLayer.initOutMaps(batchSize);
for (int i = 1; i < layerBuilder.getNumLayers(); i++) {
CnnLayer tempLayer = layerBuilder.getLayer(i);
CnnLayer tempFrontLayer = layerBuilder.getLayer(i - 1);
int tempFrontMapNum = tempFrontLayer.getOutMapNum();
switch (tempLayer.getType()) {
case INPUT:
// Should not be input. Maybe an error should be thrown out.
break;
case CONVOLUTION:
tempLayer.setMapSize(
tempFrontLayer.getMapSize().subtract(tempLayer.getKernelSize(), 1));
tempLayer.initKernel(tempFrontMapNum);
tempLayer.initBias();
tempLayer.initErrors(batchSize);
tempLayer.initOutMaps(batchSize);
break;
case SAMPLING:
tempLayer.setOutMapNum(tempFrontMapNum);
tempLayer.setMapSize(tempFrontLayer.getMapSize().divide(tempLayer.getScaleSize()));
tempLayer.initErrors(batchSize);
tempLayer.initOutMaps(batchSize);
break;
case OUTPUT:
tempLayer.initOutputKernel(tempFrontMapNum, tempFrontLayer.getMapSize());
tempLayer.initBias();
tempLayer.initErrors(batchSize);
tempLayer.initOutMaps(batchSize);
break;
}
}
}
- setup方法
- 对于CNN第一层(输入层): 初始化输入层的输出特征图数量
- 对于除输入层以为其他层:
- 卷积层:设置卷积后特征图的大小(上一层的尺寸减卷积核尺寸大小再加1) 我们从这里代码知道,第一层图像是2828,经过第一层卷积后,卷积核为55, 得到的特征图为24*24;初始化偏置、误差和输出映射
- 池化层:设置向下采样的特征图大小(上一层的尺寸除以尺寸大小) 我们从这里代码知道,上一层图像是2424,经过池化层后,尺寸为(22), 得到的特征图为12*12;初始化误差
- 输出层:初始化输出层的输出核、偏置、误差和输出映射
- initOperators()方法
初始化三个操作器对象。(都实现了 Operator 的接口)
- divideBatchSize 操作器
它将传入的浮点数值除以 batchSize,返回结果 - multiplyAlpha
它将传入的浮点数值乘以常数 ALPHA,返回结果 - multiplyLambda
它将传入的浮点数值乘以 (1 - LAMBDA * ALPHA),返回结果
2.3 获取数据集
读取文件,获取相应的数据集tempTrainingSet;train.format数据集包含的内容:
- 一共12001行数据(12001个instance)
- 每一行有784个元素(可以理解为28*28的矩阵像素点)
- 一共10个标签值(0~9)

2.4 训练数据
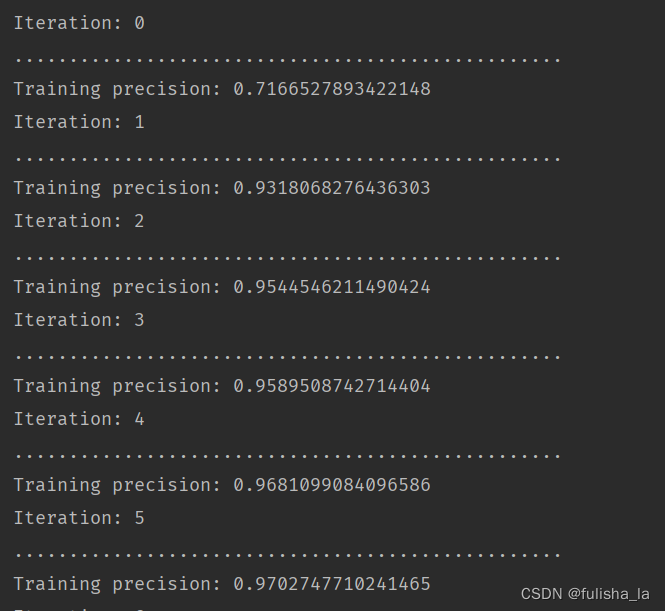
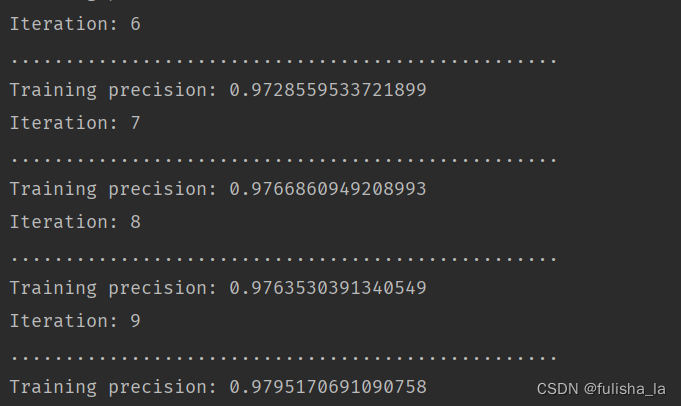
整体的一个训练方法代码如下。以本文给出的train.format数据集为例子。
在进行训练时,数据是一个4维张量:[i批次][i批次中的第j个数据实例][实例宽度weight][实例长度height]
/**
* Train the cnn.
*/
public void train(Dataset paraDataset, int paraRounds) {
for (int t = 0; t < paraRounds; t++) {
System.out.println("Iteration: " + t);
int tempNumEpochs = paraDataset.size() / batchSize;
//无法将所有样本划分为完整的批次,因此需要再额外增加一个批次来容纳余下的样本
if (paraDataset.size() % batchSize != 0) {
tempNumEpochs++;
}
// logger.info("第{}次迭代,epochsNum: {}", t, epochsNum);
//正确分类数量的变量
double tempNumCorrect = 0;
//统计总样本数量的变量
int tempCount = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < tempNumEpochs; i++) {
//当前批次中样本的随机排列索引
int[] tempRandomPerm = MathUtils.randomPerm(paraDataset.size(), batchSize);
//准备网络层以处理新的批次
CnnLayer.prepareForNewBatch();
for (int index : tempRandomPerm) {
boolean isRight = train(paraDataset.getInstance(index));
if (isRight) {
tempNumCorrect++;
}
tempCount++;
CnnLayer.prepareForNewRecord();
}
updateParameters();
if (i % 50 == 0) {
System.out.print("..");
if (i + 50 > tempNumEpochs) {
System.out.println();
}
}
}
double p = 1.0 * tempNumCorrect / tempCount;
if (t % 10 == 1 && p > 0.96) {
ALPHA = 0.001 + ALPHA * 0.9;
// logger.info("设置 alpha = {}", ALPHA);
}
System.out.println("Training precision: " + p);
// logger.info("计算精度: {}/{}={}.", right, count, p);
}
}
在进行每一轮时,先将样本进行划分批次。再每一批次过程中随机获取样本集,针对每一个样本的一个训练过程如下:
- 最外层循环paraRounds 是训练的次数
- 第二层循环批次数tempNumEpochs (将所有数据集划分为tempNumEpochs 批次)例如数据集一共1200个,每批次大小为10,则可以划分120个批次
- 第三层循环某一批次中所有的数据实例tempRandomPerm。(这段代码中数据实例是随机获取的) 一次循环就是一行数据。而其中CnnLayer.prepareForNewRecord()方法就是累加。
而下面的前向传播函数和反向传播函数都是针对的某一行个数据实例进行训练。
2.4.1 前向传播函数forward
在前向传播过程中,获取当前层和上一层,判断当前层输入那一类(卷积层,池化层,输出层)并执行相应的操作。针对不同的网络层,处理有所区别
private void forward(Instance instance) {
setInputLayerOutput(instance);
for (int l = 1; l < layerBuilder.getNumLayers(); l++) {
CnnLayer tempCurrentLayer = layerBuilder.getLayer(l);
CnnLayer tempLastLayer = layerBuilder.getLayer(l - 1);
switch (tempCurrentLayer.getType()) {
case CONVOLUTION:
setConvolutionOutput(tempCurrentLayer, tempLastLayer);
break;
case SAMPLING:
setSampOutput(tempCurrentLayer, tempLastLayer);
break;
case OUTPUT:
setConvolutionOutput(tempCurrentLayer, tempLastLayer);
break;
default:
break;
}
}
}
- setInputLayerOutput(instance)方法
输入数据实例映射到卷积神经网络的输入层特征图中(直白点就是将读入的数据一一赋值给输入层)
2.4.1.1 CONVOLUTION卷积层
输入是当前层paraLayer和上一层paraLastLayer。卷积计算:
private void setConvolutionOutput(final CnnLayer paraLayer, final CnnLayer paraLastLayer) {
// int mapNum = paraLayer.getOutMapNum(); 输出特征图数量
final int lastMapNum = paraLastLayer.getOutMapNum();
// Attention: paraLayer.getOutMapNum() may not be right.
//对于当前卷积层的每个输出特征图
for (int j = 0; j < paraLayer.getOutMapNum(); j++) {
//存储卷积操作的累积结果
double[][] tempSumMatrix = null;
//对于上一层的每个特征图
for (int i = 0; i < lastMapNum; i++) {
//获取上一层特征图中的第 i 个特征图
double[][] lastMap = paraLastLayer.getMap(i);
//获取卷积层中连接到第 i 个上一层特征图的第 j 个卷积核
double[][] kernel = paraLayer.getKernel(i, j);
//第一个特征图的卷积操作
if (tempSumMatrix == null) {
// On the first map.
tempSumMatrix = MathUtils.convnValid(lastMap, kernel);
} else {
// Sum up convolution maps
tempSumMatrix = MathUtils.matrixOp(MathUtils.convnValid(lastMap, kernel),
tempSumMatrix, null, null, MathUtils.plus);
}
}
// Activation.获取当前特征图对应的偏置值
final double bias = paraLayer.getBias(j);
//执行激活函数操作.激活函数使用 sigmoid 函数来进行非线性映射,将矩阵中的每个元素加上偏置值并应用 sigmoid 函数
tempSumMatrix = MathUtils.matrixOp(tempSumMatrix, new Operator() {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 2469461972825890810L;
@Override
public double process(double value) {
return MathUtils.sigmod(value + bias);
}
});
//将经过卷积和激活函数处理后的特征图矩阵设置到当前卷积层的第 j 个输出特征图中
paraLayer.setMapValue(j, tempSumMatrix);
}
}
首先我们要知道这是某一行的一个数据实例,进行的卷积运算,其大致过程:
- 外层循环j 输出特征图的数量(这是与卷积核有关的);
- 内层循环i 是上一层参与卷积运算的矩阵,获取卷积层中连接到第 i 个上一层特征图的第 j 个卷积核,进行卷积运算(MathUtils.convnValid操作)。如下图中A1特征图对应的卷积核就是B1,A2特征图对应的卷积核就是B2,A3特征图对应的卷积核就是B3,这三个分别进行卷积运算后再想加(MathUtils.matrixOp操作),再加上偏置数得C矩阵。
- 激活函数操作. 对输出的特征图进行激活函数操作(MathUtils.sigmod操作)
- 设置当前层第 j 个输出特征图。进入下次循环。
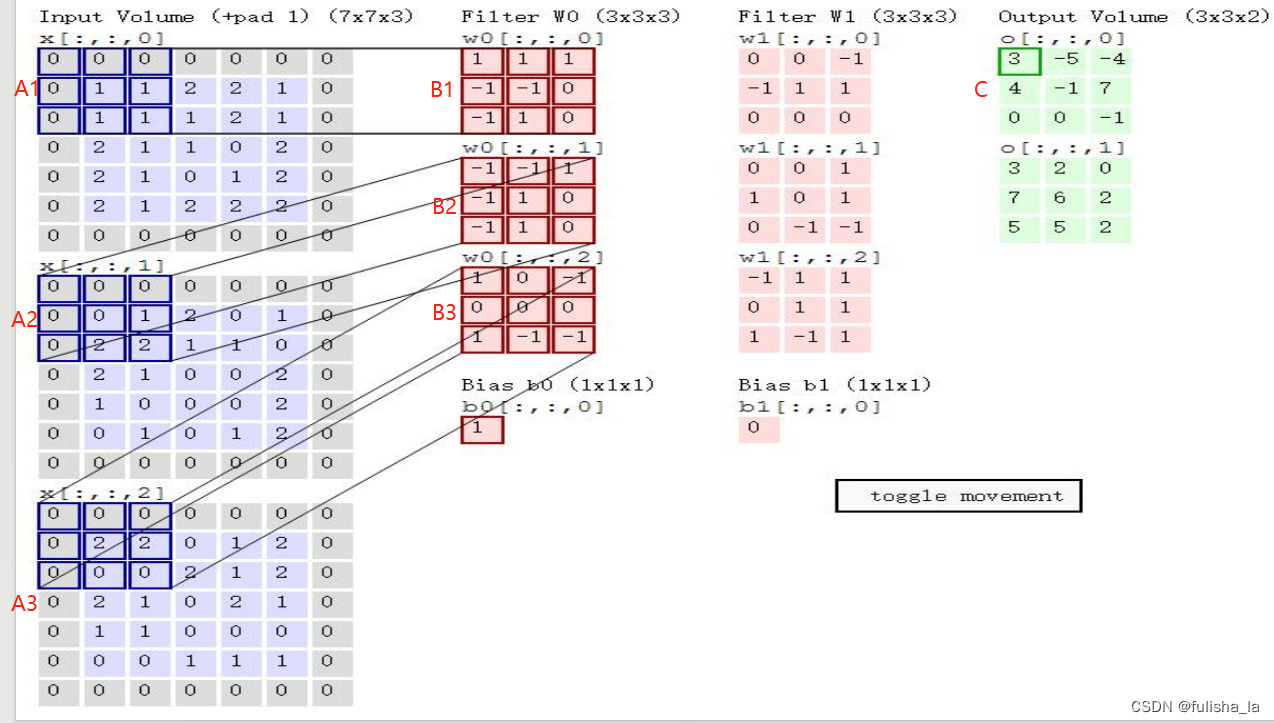
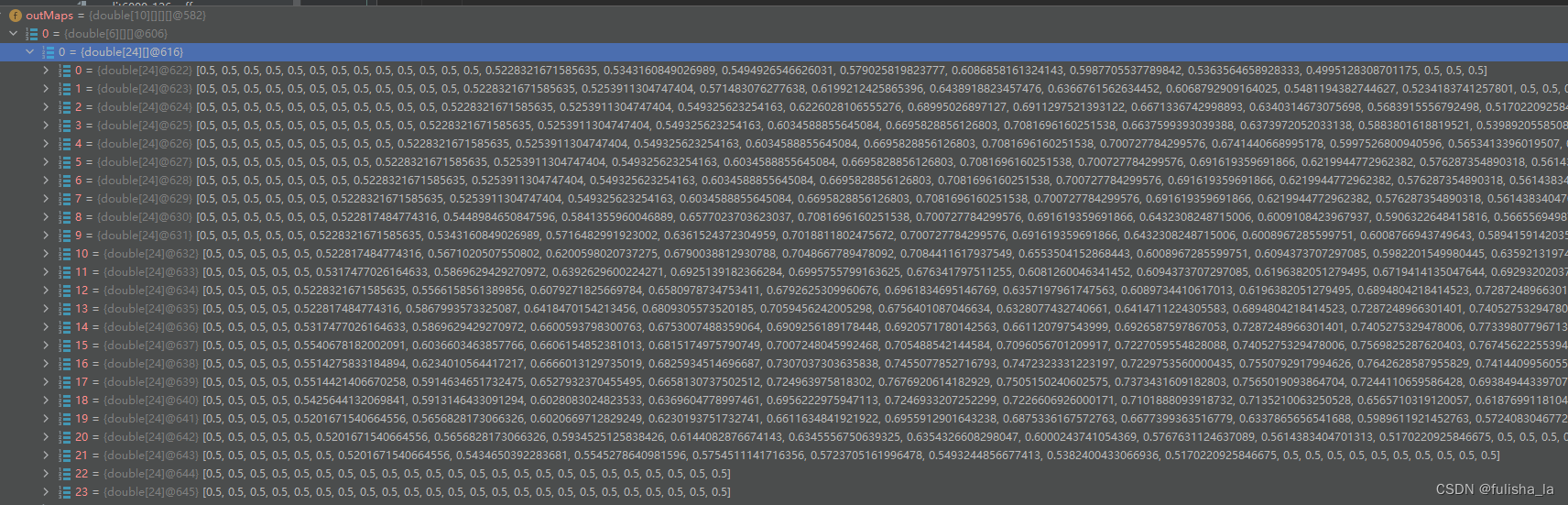
如下是一个实例:
卷积运算后输出的数据 2828的矩阵,卷积核6个,卷积核大小55,最后的特征图大小为24*24:

如下是6个特征图中的一个:
2.4.1.2 SAMPLING 池化层
private void setSampOutput(final CnnLayer paraLayer, final CnnLayer paraLastLayer) {
// int tempLastMapNum = paraLastLayer.getOutMapNum();
// Attention: paraLayer.outMapNum may not be right.
for (int i = 0; i < paraLayer.outMapNum; i++) {
获取上一层的特征图
double[][] lastMap = paraLastLayer.getMap(i);
// 获取当前池化层的缩放大小
Size scaleSize = paraLayer.getScaleSize();
//对前一层的特征图进行缩放操作
double[][] sampMatrix = MathUtils.scaleMatrix(lastMap, scaleSize);
// 将缩放后的特征图设置为当前池化层的输出
paraLayer.setMapValue(i, sampMatrix);
}
}
大致过程
- 获取上一层特征图
- 获取当前池化层的缩放大小
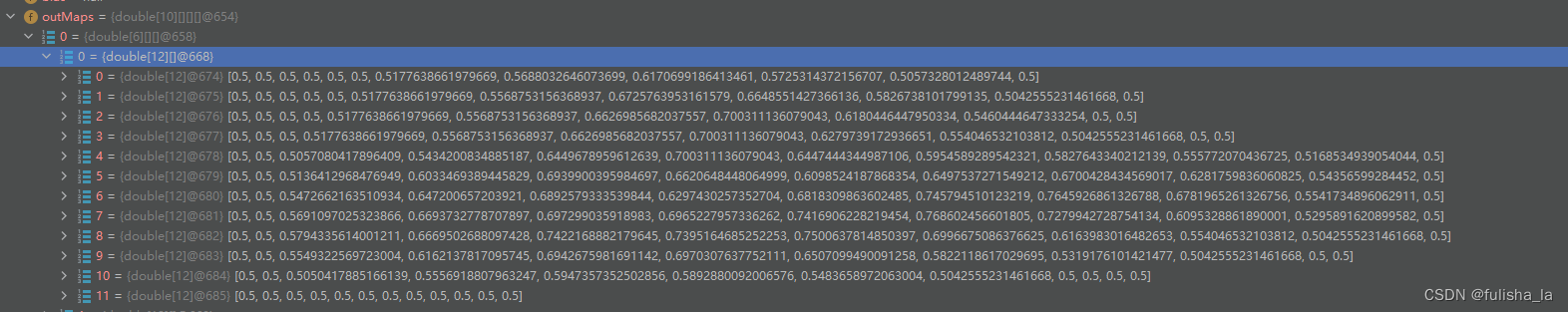
- 对上一层特征图进行缩放。例如我上一层特征图大小为2424,池化层缩放大小为22,则经过池化层后特征图大小则为1212.(MathUtils.scaleMatrix操作:将原始矩阵缩小到一个更小的尺寸,通过将相邻元素的值进行平均来得到新的缩放后的矩阵)例如:
m a t r i x = [ 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 ] matrix = \left[\begin {array}{c} 1 & 2 & 3 & 4 \\ 5 & 6 & 7 & 8 \\ 9 & 10 & 11 & 12 \\ 13 & 14 & 15 & 16 \\ \end{array}\right] matrix= 15913261014371115481216
输出:
o u t M a t r i x = [ 3.5 5.5 11.5 13.5 ] outMatrix = \left[\begin {array}{c} 3.5 & 5.5 \\ 11.5 & 13.5\\ \end{array}\right] outMatrix=[3.511.55.513.5]
如下是一个实例:
是上一个2424的特征图 经过池化变为12*12的特征图(6个特征图中的一个)
2.4.1.3 OUTPUT 输出层
调用和卷积层同样的方法,但是他的输出不是特征图,而且他输出个数和卷积核也没有关系。例如一个实例最终的输出数据:

2.4.2 反向传播函数backPropagatio
反向传播过程中其实会涉及许多公式推导,我自己将推导过程放在了另一篇文章,文章链接
2.4.2.1 输出层
/**
* Set errors of a sampling layer.
*/
private boolean setOutputLayerErrors(Instance paraRecord) {
//获取输出层
CnnLayer tempOutputLayer = layerBuilder.getOutputLayer();
//获取输出层的特征图数量
int tempMapNum = tempOutputLayer.getOutMapNum();
//创建临时数组来存储目标值和输出值
double[] tempTarget = new double[tempMapNum];
double[] tempOutMaps = new double[tempMapNum];
// 从输出层的特征图中获取输出值
for (int m = 0; m < tempMapNum; m++) {
double[][] outmap = tempOutputLayer.getMap(m);
tempOutMaps[m] = outmap[0][0];
}
// 获取输入记录的标签(真实值)
int tempLabel = paraRecord.getLabel().intValue();
// 将目标值数组中对应标签位置的值设为1,其他位置设为0
tempTarget[tempLabel] = 1;
// Log.i(record.getLable() + "outmaps:" +
// Util.fomart(outmaps)
// + Arrays.toString(target));
// 计算输出层的误差并更新误差
for (int m = 0; m < tempMapNum; m++) {
// 使用sigmoid函数的导数计算误差
tempOutputLayer.setError(m, 0, 0,
tempOutMaps[m] * (1 - tempOutMaps[m]) * (tempTarget[m] - tempOutMaps[m]));
}
// 检查预测是否正确
return tempLabel == MathUtils.getMaxIndex(tempOutMaps);
}
输出层误差项的公式为:
δ
l
=
∂
J
∂
z
l
=
(
y
^
−
y
)
⋅
σ
′
(
z
l
)
\delta^{l} =\frac{\partial J}{\partial z^l}=(\hat{y} - y)\cdot \sigma ' (z^{l})
δl=∂zl∂J=(y^−y)⋅σ′(zl)
而在代码中,我们采用的激活函数为sigmod,所以误差项公式可以写为如下(
y
^
\hat{y}
y^为预测值,
y
y
y为真实值):
∂
J
∂
z
l
=
(
y
^
−
y
)
⋅
σ
′
(
z
l
)
=
(
y
^
−
y
)
⋅
σ
(
z
l
)
⋅
(
1
−
σ
(
z
l
)
)
\frac{\partial J}{\partial z^l}=(\hat{y} - y)\cdot\sigma ' (z^{l})=(\hat{y} - y)\cdot\sigma (z^{l})\cdot (1-\sigma (z^{l}))
∂zl∂J=(y^−y)⋅σ′(zl)=(y^−y)⋅σ(zl)⋅(1−σ(zl))
即代码中的: tempOutputLayer.setError(m, 0, 0, tempOutMaps[m] * (1 - tempOutMaps[m]) * (tempTarget[m] -tempOutMaps[m]));
2.4.2.2 反卷积运算
已知输出层(或卷积层)的误差项,反推池化层的误差项
private void setSamplingErrors(final CnnLayer paraLayer, final CnnLayer paraNextLayer) {
// int mapNum = layer.getOutMapNum();
// 获取下一层的特征图数量
int tempNextMapNum = paraNextLayer.getOutMapNum();
// Attention: getOutMapNum() may not be correct
// 循环遍历当前池化层的特征图
for (int i = 0; i < paraLayer.getOutMapNum(); i++) {
// 初始化一个临时变量 sum 用于存储误使用卷积操作(通常是 MathUtils.convnFull 函数)将下一层特征图 j 的误差与卷积核进行卷积。这相当于计算了上一层的误差如何影响池化层的输出差的总和 (这相当于在所有影响的区域上进行累积)
double[][] sum = null;
// 获取下一层的 j 号特征图的误差和卷积核
for (int j = 0; j < tempNextMapNum; j++) {
//下一层的误差矩阵
double[][] nextError = paraNextLayer.getError(j);
//下一层的卷积核
double[][] kernel = paraNextLayer.getKernel(i, j);
// 计算当前特征图的误差,特征图 j 的误差与卷积核进行卷积。(计算了上一层的误差如何影响池化层的输出)
if (sum == null) {
sum = MathUtils.convnFull(nextError, MathUtils.rot180(kernel));
} else {
// 如果 sum 不为 null,将当前计算的误差与之前的误差累积起来
sum = MathUtils.matrixOp(
MathUtils.convnFull(nextError, MathUtils.rot180(kernel)), sum, null,
null, MathUtils.plus);
}
}
// 将计算得到的误差设置为当前采样层的第 i 个特征图的误差
paraLayer.setError(i, sum);
// 检查误差是否超出了给定的范围,如果超出范围,输出警告信息
if (!rangeCheck(sum, -2, 2)) {
System.out.println(
"setSampErrors, error out of range.\r\n" + Arrays.deepToString(sum));
}
}
}
主要是通过反卷积运算,公式如下:
δ
l
−
1
=
δ
l
⋅
∂
z
l
∂
a
l
−
1
⋅
σ
′
(
z
l
−
1
)
=
δ
l
c
o
n
v
(
r
o
t
189
(
w
l
)
)
⋅
σ
′
(
z
l
−
1
)
\delta^{l-1} =\delta^{l}\cdot \frac{\partial z^{l}}{\partial a^{l-1}}\cdot \sigma ' (z^{l-1})= \delta^{l} conv ( rot189(w^l))\cdot \sigma ' (z^{l-1})
δl−1=δl⋅∂al−1∂zl⋅σ′(zl−1)=δlconv(rot189(wl))⋅σ′(zl−1)
其中
δ
l
\delta^{l}
δl为卷积层的误差项,
w
l
w^l
wl为卷积层的卷积核,因为池化层没有用什么激活函数,也可以理解起激活函数就是
δ
(
x
)
=
x
\delta(x)=x
δ(x)=x,则求偏导就是1。正如代码中的运算:MathUtils.convnFull(nextError, MathUtils.rot180(kernel))
2.4.2.3 反池化层运算
private void setConvolutionErrors(final CnnLayer paraLayer, final CnnLayer paraNextLayer) {
// System.out.println("setConvErrors");
for (int m = 0; m < paraLayer.getOutMapNum(); m++) {
//获取下一层(通常是池化层)的缩放尺寸
Size tempScale = paraNextLayer.getScaleSize();
// 获取与当前特征图相关的下一层误差矩阵
double[][] tempNextLayerErrors = paraNextLayer.getError(m);
// 获取当前卷积层的特征图
double[][] tempMap = paraLayer.getMap(m);
// 对当前特征图执行操作,生成一个新的矩阵(这一步用于准备进一步的误差传播)
double[][] tempOutMatrix = MathUtils.matrixOp(tempMap, MathUtils.cloneMatrix(tempMap),
null, MathUtils.one_value, MathUtils.multiply);
//在准备好的矩阵和下一层误差之间执行克罗内克积(Kronecker product) 这一步是误差向后传播的一部分
tempOutMatrix = MathUtils.matrixOp(tempOutMatrix,
MathUtils.kronecker(tempNextLayerErrors, tempScale), null, null,
MathUtils.multiply);
// 将计算得到的误差矩阵设置为当前卷积层中第 m 个特征图的误差
paraLayer.setError(m, tempOutMatrix);
// System.out.println("range check nextError");
if (!rangeCheck(tempNextLayerErrors, -10, 10)) {
System.out.println("setConvErrors, nextError out of range:\r\n"
+ Arrays.deepToString(tempNextLayerErrors));
System.out.println("the new errors are:\r\n" + Arrays.deepToString(tempOutMatrix));
System.exit(0);
}
if (!rangeCheck(tempOutMatrix, -10, 10)) {
System.out.println("setConvErrors, error out of range.");
System.exit(0);
}
}
}
已知池化层计算的误差项,去推池化层的误差项,在代码中主要是进行kronecker积来实现。
2.4.2.4 训练结果