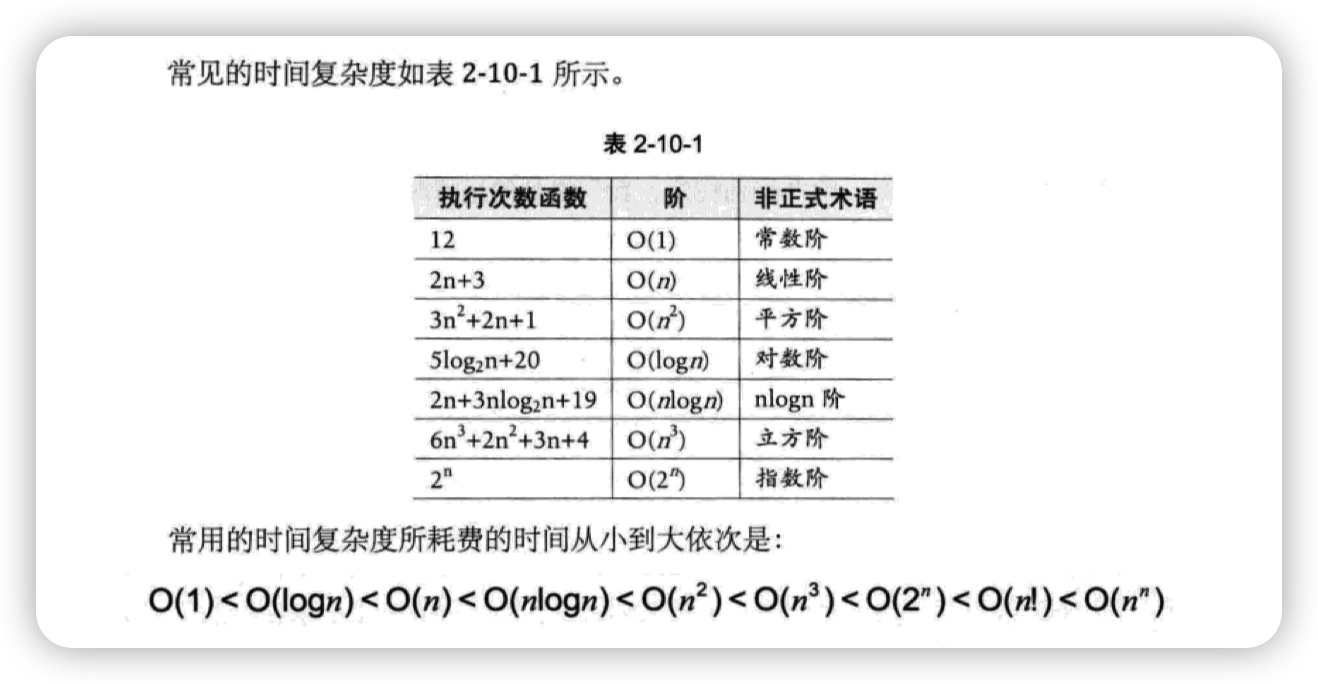
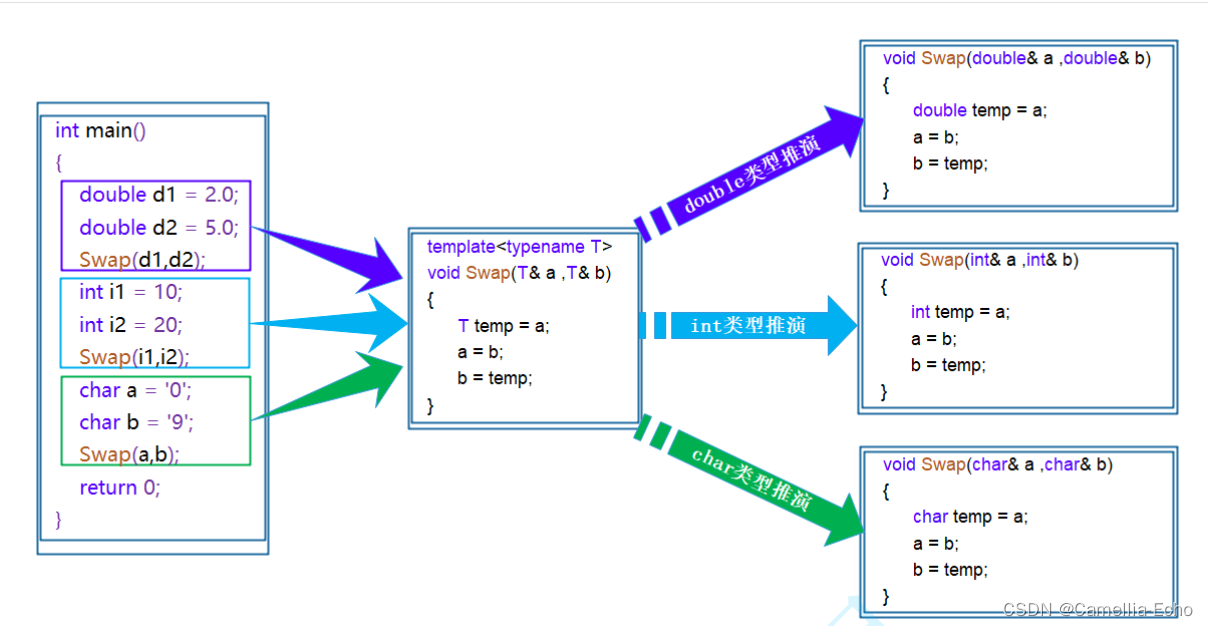
给定一个链表的 头节点
head,请判断其是否为回文链表。如果一个链表是回文,那么链表节点序列从前往后看和从后往前看是相同的。
回文链表类似于回文串,正读倒读的顺序是一样的,那么我们怎么去判断一个链表是否是回文链表呢?
今天我们用多种方法、多种角度去思考问题,带你领略算法的奥秘
- 字符串化比较

public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {
if(head==null){
return false;
}
//一般通过StringBuilder进行字符操作
StringBuilder s1=new StringBuilder();
StringBuilder s2=new StringBuilder();
//通过while循环将链表中的节点添加到字符串中
while(head!=null){
s1.append(head.val);
s2.append(head.val);
head=head.next;
}
//将s2进行翻转
s2.reverse();
return s1.toString().equals(s2.toString());}
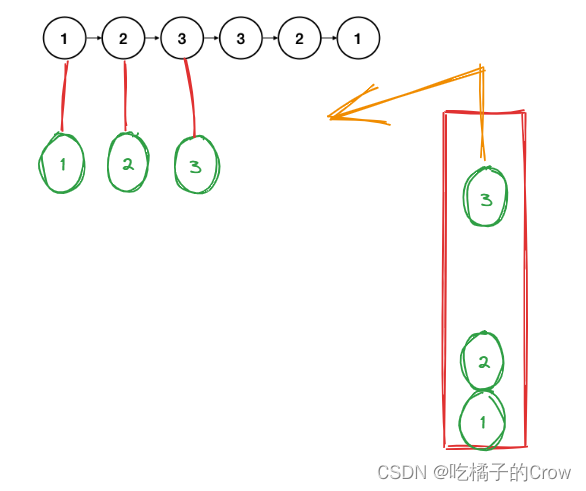
- 栈
通过维护一个栈去保存链表中的节点,栈是先进后出的数据结构,这样也可以做到使得链表进行翻转,然后与原链表进行对比,得出正确的结果

public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {
ListNode cur1=head;
ListNode cur2=head;
Stack<ListNode> stack=new Stack<>();
while(cur1!=null){
stack.add(cur1);
cur1=cur1.next;
}
while(cur2!=null&&!stack.isEmpty()){
ListNode curNode=stack.pop();
if(curNode.val!=cur2.val){
return false;
}
cur2=cur2.next;
}
return true;
}
- 中点翻转对比
链表为偶数时: 链表为奇数时:
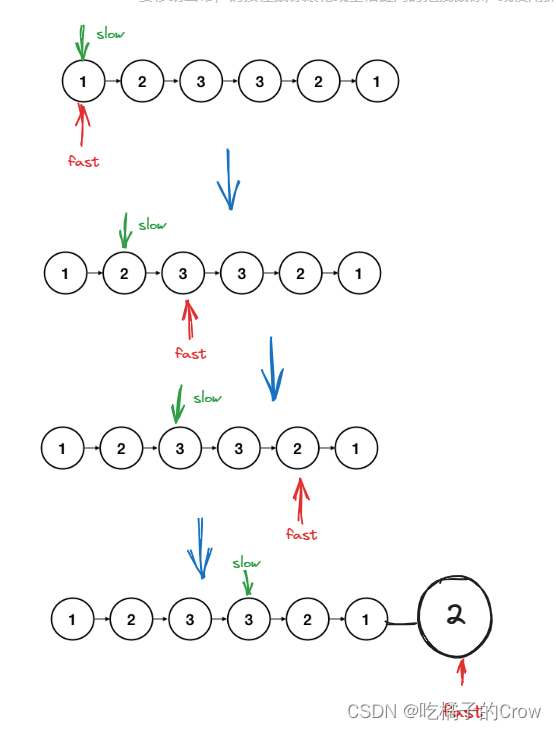

- 通过快慢指针找到链表的中心点
public ListNode findMid(ListNode head){ ListNode fast=head; ListNode slow=head; //快慢指针,快走两步,慢走一步,最后slow的位置就是链表的中心点 while(fast.next!=null&&fast.next.next!=null){ fast=fast.next.next; slow=slow.next; } return slow; } - 将中心点后面的链表进行翻转

public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head){ if(head==null){ return head; } //前驱 ListNode pre=null; //当前节点 ListNode cur=head; //后继 ListNode next=null; while(cur!=null){ next=cur.next; cur.next=pre; pre=cur; cur=next; } //返回前驱 return pre; } - 判断前半段链表和后半段链表是否相等
public boolean isSame(ListNode l1,ListNode l2){ ListNode p1=l1; ListNode p2=l2; //这里只能判断p2,因为p1d的话,它上半段遍历完,它会接着遍历下半段 while(p2!=null){ if(p1.val!=p2.val){ return false; } p1=p1.next; p2=p2.next; } return true; }
源码:
public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {
if(head==null){
return true;
}
ListNode mid=findMid(head);
ListNode l1=head;
ListNode l2=mid.next;
l2=reverseList(l2);
return isSame(l1,l2);
}
public ListNode findMid(ListNode head){
ListNode fast=head;
ListNode slow=head;
while(fast.next!=null&&fast.next.next!=null){
fast=fast.next.next;
slow=slow.next;
}
return slow;
}
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head){
if(head==null){
return head;
}
ListNode pre=null;
ListNode cur=head;
ListNode next=null;
while(cur!=null){
next=cur.next;
cur.next=pre;
pre=cur;
cur=next;
}
return pre;
}
public boolean isSame(ListNode l1,ListNode l2){
ListNode p1=l1;
ListNode p2=l2;
while(p2!=null){
if(p1.val!=p2.val){
return false;
}
p1=p1.next;
p2=p2.next;
}
return true;
}
- 双端队列
通过维护一个双端队列去进行操作,所谓的双端队列就是可以从队尾进,也可以从队头进

while(head!=null){
queue.addLast(head);
head=head.next;
}将链表中的元素都塞入双端队列中,结束后,同时从队头队尾取节点,判断是否相等(相当于反向双指针)

ListNode h=queue.removeFirst();
ListNode t=queue.removeLast();
if(h.val!=t.val){
return false;
}链表的节点为偶数时:
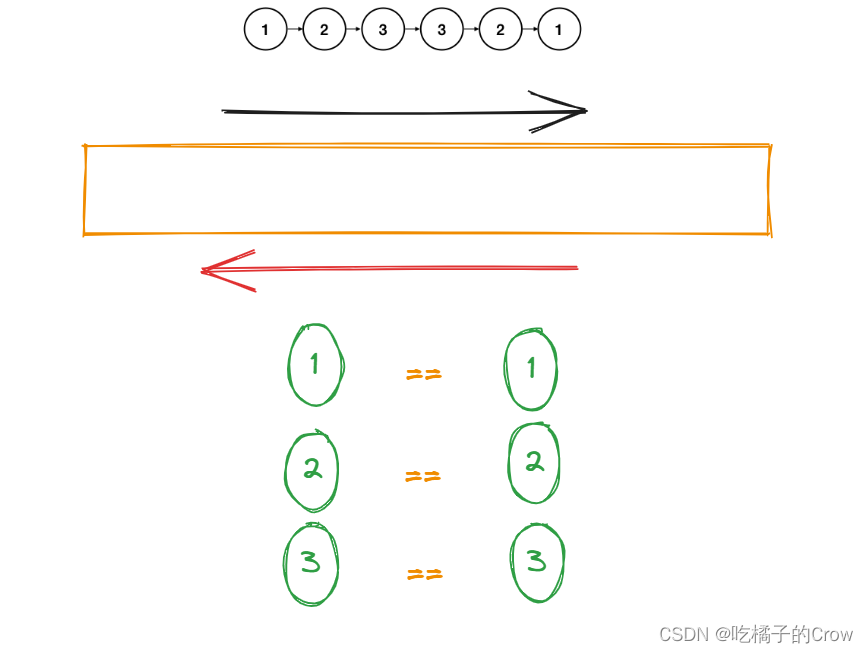
链表的节点为偶数时:

所以循环的结束条件则为:
while(queue.size()>1){
...
}
- 递归(链表递归相互奔向)
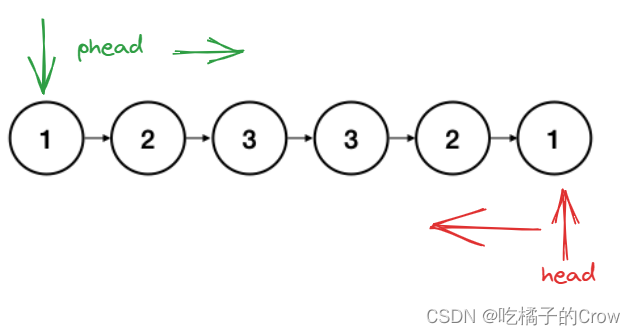
递归到最后一个结点直接返回,与当前节点比较,如果相等,当前节点往后移动一位,递归再返回,这种就可以做到从两边进行比较
private void dfs(ListNode head, ListNode phead, boolean res) {
if (head == null || !res) {
return;
}
dfs(head.next, phead, res);
if (head.val != phead.val) {
res = false;
}
phead = phead.next;
}
public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {
boolean res = true;
ListNode phead = head;
dfs(head, phead, res);
return res;
}你们觉得这个代码有问题么?

测试的结果都是true,说明我们这个过程并没有改变我们res的默认值,因为我们的java是值传递,并不是引用传递,所以并不会改变我们的值,所以我们需要将res、遍历的节点分别封装成一个对象进行传递
private void dfs(ListNode head, ListNode[] phead, boolean[] res) {
if (head == null || !res[0]) {
return;
}
dfs(head.next, phead, res);
if (head.val != phead[0].val) {
res[0] = false;
}
phead[0] = phead[0].next;
}
public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {
boolean[] res = {true};
ListNode[] phead = {head};
dfs(head, phead, res);
return res[0];
}
这几种方式已经全部介绍结束,希望大家做题的时候,不要死记住一种解法去解决问题,多思考别的方式,拓宽自己的思路,不局限于一种解法