cf暑假训练 1700-1800 day1
- 1852B Imbalanced Arrays
- 1850H. The Third Letter
- 1833G Ksyusha and Chinchilla
- 1833F Ira and Flamenco(补完线段树来看)
- 1809D Binary String Sorting
- 1780D Bit Guessing Game(这题真的好难,我只能说我看懂答案了,但是我真的推不出来)
1852B Imbalanced Arrays
- bi + bj肯定不能为0,比如bi的绝对值为n的话bi只能在n和-n这一对数字中间选择一个
- 双指针(这也是为什么升序排序的原因),类似要么在l的答案里面不带r,要么在r的答案里面带上l,但是两者不能同时满足,因为我刚开始打1800的题目我无法很清楚的表达我的意思,还请见谅
1850H. The Third Letter
思路: 就是搜索,但是用val[]验证结果是我没想到的
trick :
- 学习
vector<pair<int, int>>a、vector<pair<int, int>>a[3]、vector<vector<pair<int, int>>> a、vector<array<int, 3>>a这些容器的区别,具体一些api类似clear,emplace,push_back这种可以去查文档
不知道为什么一直wa,明明和题解写的差不多
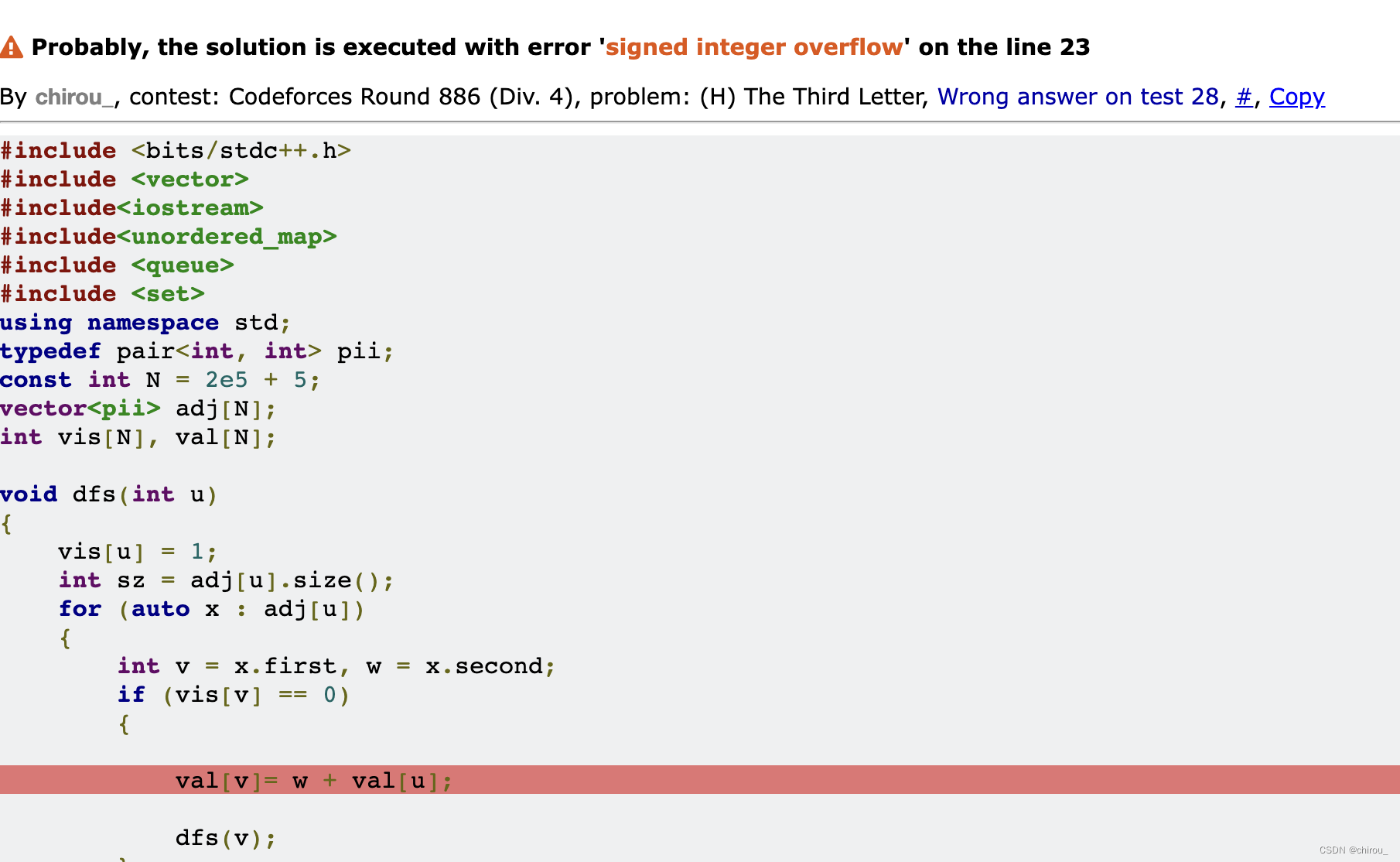
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <vector>
#include<iostream>
#include<unordered_map>
#include <queue>
#include <set>
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
const int N = 2e5 + 5;
vector<pii> adj[N];
int vis[N], val[N];
void dfs(int u)
{
vis[u] = 1;
int sz = adj[u].size();
for (auto x : adj[u])
{
int v = x.first, w = x.second;
if (vis[v] == 0)
{
val[v]= w + val[u];
dfs(v);
}
}
}
void solve()
{
int n, m;
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++ i)
{
adj[i].clear();
vis[i] = 0, val[i] = 0;
}
vector<array<int, 3>> c;
for (int i = 1; i <= m; ++ i)
{
int a, b, d;
cin >> a >> b >> d;
adj[a].push_back({b, d});
adj[b].push_back({a, -d});
c.push_back({a, b, d});
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++ i)
{
if (vis[i] == 0) dfs(i);
}
for (int i =1; i <= m; ++ i)
{
int a = c[i - 1][0], b = c[i - 1][1], d = c[i - 1][2];
if (val[a] + d != val[b] )
{
cout << "NO" << endl;
return ;
}
}
cout << "YES" << endl;
}
int32_t main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
int T;
cin >> T;
while (T --) solve();
return 0;
}
1833G Ksyusha and Chinchilla
题意在这
trick:
- 学会了在方法里面创建一个方法对象
- 对dfs有了更深的理解,原来可以传入idx表示当前通过哪个边到达当前点的,正好可以在满足条件的时候直接收集结果;
- 通过ok全局变量表示子树是否满足条件,siz[1]判断根节点是否满足条件,因为在dfs的时候 sz>3才会让ok = false,但是根节点的话sz != 0也是不满足题意的
- 用联通块 == 3 将题意化简,降低思维的难度
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
void solve()
{
int n;
cin >> n;
vector<vector<pii>> edges(n + 1);
for (int i = 1; i < n; ++ i)
{
int u, v; cin >> u >> v;
edges[u].push_back({v, i}), edges[v].push_back({u, i});
}
bool ok = true;
vector<int> sz(n + 1);
vector<int> ans;
//idx指的是由哪条边找到当前点的
function<void(int, int, int)> dfs = [&](int u, int fa, int idx)
{
sz[u] = 1;
for (auto [v, idx] : edges[u])
{
if (v == fa) continue;
else
{
dfs(v, u, idx);
sz[u] += sz[v];
}
}
if (sz[u] > 3)
{
ok = false;
return ;
}
else if (sz[u] == 3)
{
sz[u] = 0;
if (idx != 0) ans.push_back(idx);//u = 1的时候一条边都不需要剪
}
};
dfs(1, 0, 0);
ok &= !sz[1];//根节点所在的联通块为0才说明当前树全被剪完了
if (ok)
{
cout << ans.size() << endl;
for (auto idx : ans) cout << idx << " ";
cout << endl;
}
else cout << -1 << endl;
}
int32_t main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
int T;
cin >> T;
while (T --) solve();
return 0;
}
1833F Ira and Flamenco(补完线段树来看)
这题好像要用线段树,主席树啥的,题解在洛古有,很清楚。。我要去补提高课了。
1809D Binary String Sorting
题意:
两个操作把当前的字符串变成一个非递减的字符串
- 删除一个元素,代价是1e12 + 1
- 交换两个连续的元素,代价是1e12
其实就是一道贪心的题目

#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
const long long pw10 = 1e12;
void solve()
{
string s;
cin >> s;
long long ans = 1e18;
int cnt0 = 0, cnt1 = count(s.begin(), s.end(), '1');
//cnt0表示当前位置之前有多少0,cnt1表示当前位置之后有多少1
int n = s.size();
if (n == 1) ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; ++ i)
{
if (s[i] == '0') cnt0 ++;
else cnt1 --;
int k = cnt0 + cnt1 + (s[i] == '1') + (s[i + 1] == '0');
long long cur = 0;
cur = (n - k) * (pw10 + 1);
if (s[i] > s[i + 1]) cur += pw10;
ans = min(cur, ans);
}
cout << ans << endl;
}
int32_t main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
int T;
cin >> T;
while (T --) solve();
return 0;
}
1780D Bit Guessing Game(这题真的好难,我只能说我看懂答案了,但是我真的推不出来)
trick:
- 如何获得迭代过程中的n’的最后一个1的位置,仅仅靠题目给我n’的二进制表示中的1的个数
- 如何让n的二进制最后一个1到最后一位0之间全部变成1,设二进制n的最后一位0的位置为i,n’ - 2i即可
我大概总结了一下:
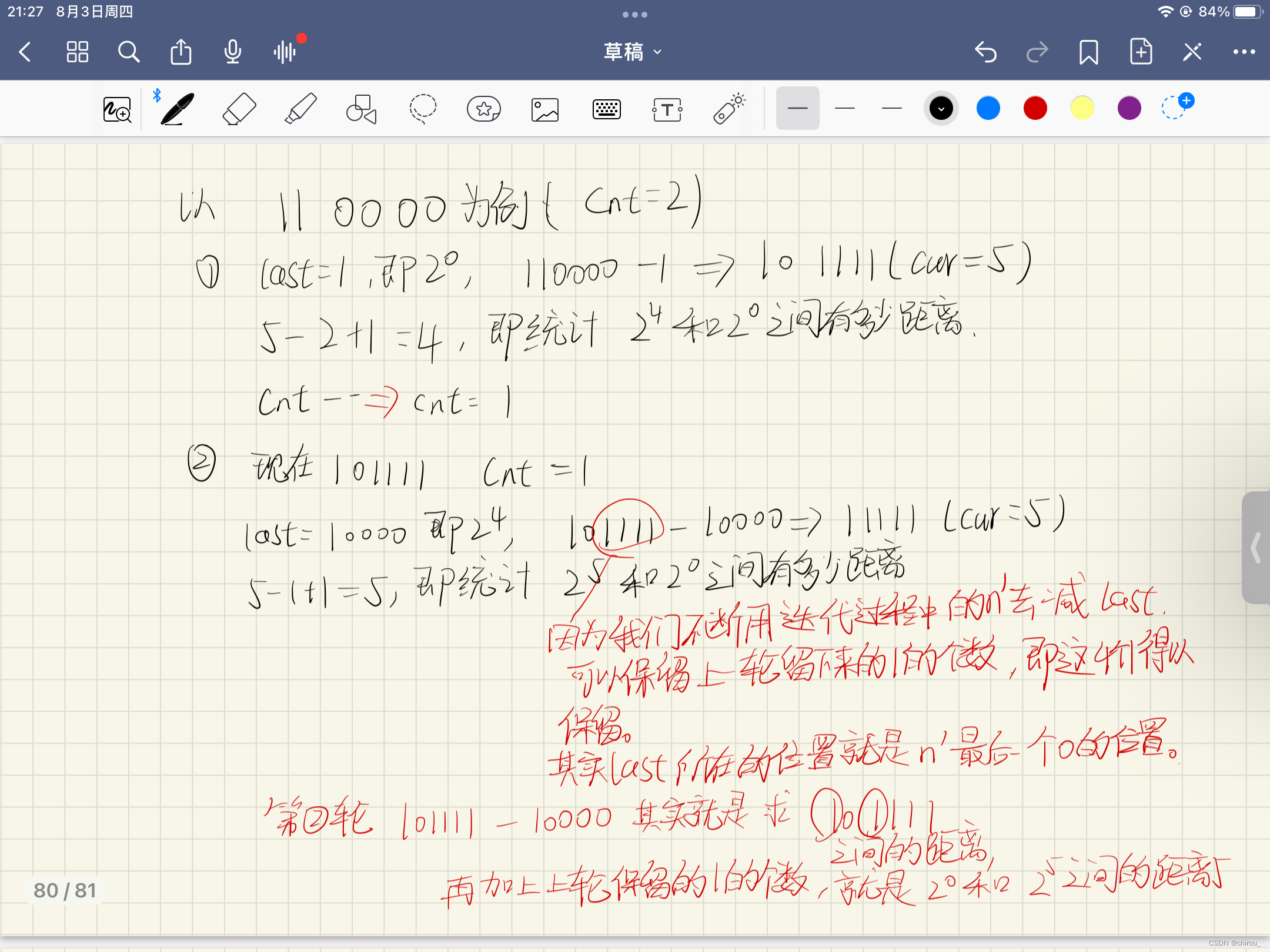
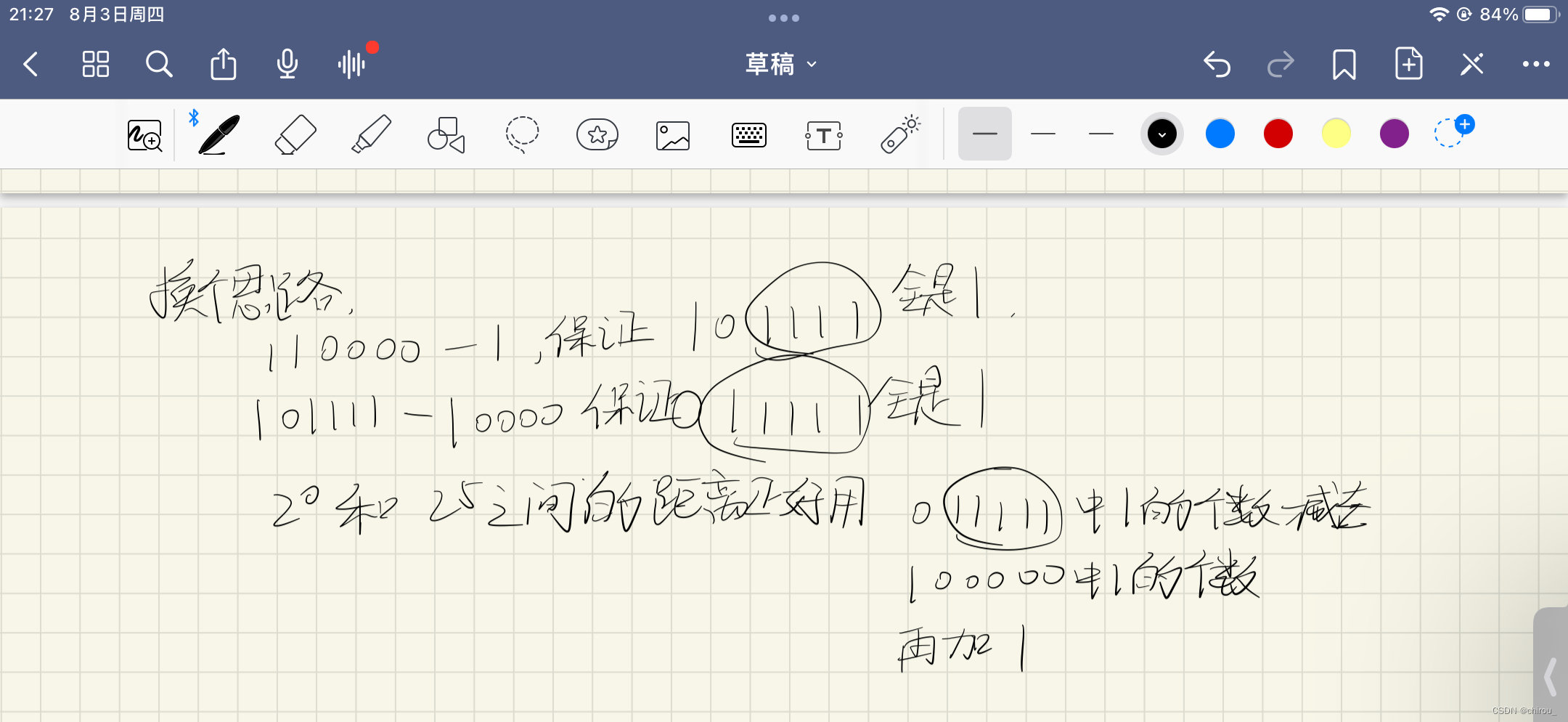
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
int ask(int x)
{
cout << "- " << x << endl;
cout.flush();
int t_cnt; cin >> t_cnt;
return t_cnt;
}
void solve()
{
int cnt; cin >> cnt;
int last = 1;
int ans = 0;
while (cnt)
{
int t_cnt = ask(last);//减last的目的其实就是让n'最后一个1和第0位之间全部变成1,这样我们就知道最后1位1所在的位置了
last = (1 << (t_cnt - cnt + 1));//t - cnt + 1获得当前n'的最后一个1和第0位的距离
ans |= last;// |=就是+=
cnt -- ;
}
cout << "! " << ans << endl;
}
int32_t main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
int T;
cin >> T;
while (T --) solve();
return 0;
}