文章目录
- 1. JZ66 构建乘积数组
- 暴力解法
- 双向遍历
- 2. JZ19 正则表达式匹配
- 3. JZ20 表示数值的字符串
- 有限状态机
- 遍历
- 4. JZ75 字符流中第一个不重复的字符
- 5. JZ23 链表中环的入口结点
- 快慢指针
- 哈希表
- 6. JZ76 删除链表中重复的结点
- 快慢指针
- 三指针
- 如果只保留一个重复结点
- 7. JZ8 二叉树的下一个结点
- 数组保存结点
- 直接查找 分类讨论
- 8. JZ28 对称的二叉树
- 9. JZ77 按之字形顺序打印二叉树
- 栈实现
- 队列实现
- 10. JZ78 把二叉树打印成多行
1. JZ66 构建乘积数组

暴力解法
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> multiply(vector<int>& A) {
// write code here
vector<int> result(A.size(), 0);
int flag, res, index = 0;
while(index < result.size())
{
flag = A[index];
res = 1;
//cout << "flag = " << flag << endl;
for(int i=0; i<A.size(); i++)
{
if(A[i] == flag && i==index) continue;
res *= A[i];
}
result[index] = res;
index++;
}
return result;
}
};
双向遍历
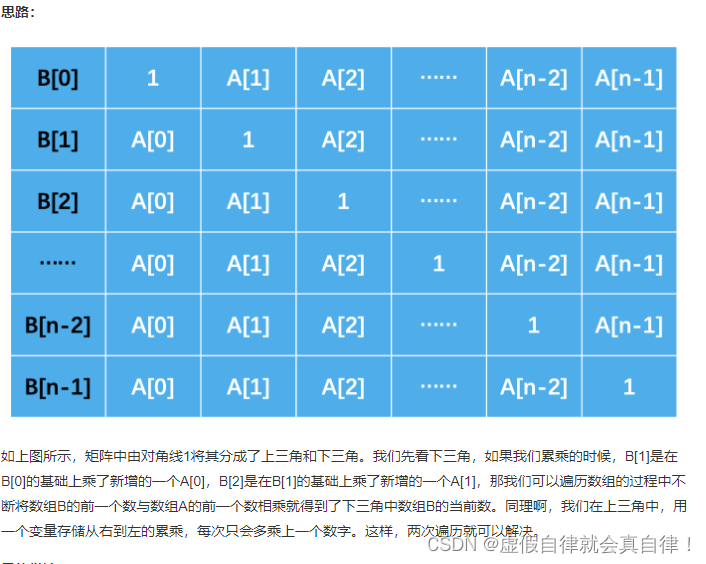
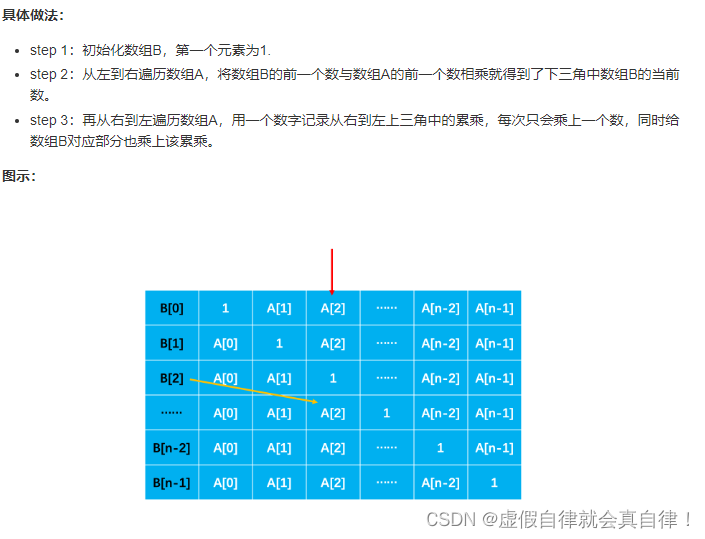
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> multiply(vector<int>& A) {
//双向遍历
int len = A.size();
vector<int> result(len, 1);
int cur = 1;
//先乘左边,从左到右
for(int i=1; i<A.size(); i++)
{
//每多一位由数组B左边的元素多乘一个前面A的元素
result[i] = result[i-1] * A[i - 1];//cur *= A[i];result[i] = cur;
}
//再乘右边,从右到左
for(int i=len-1; i>=0; i--)
{
result[i] *= cur;//左右两边都乘起来
cur *= A[i];//cur为右边的累乘
}
return result;
}
};
2. JZ19 正则表达式匹配
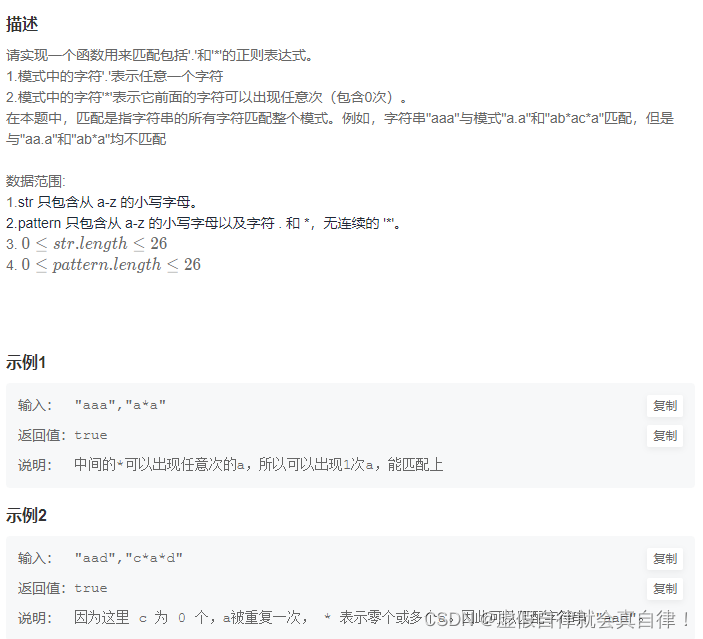

好难啊,我真的服了,搬运K神题解
- 解题思路:


初始化
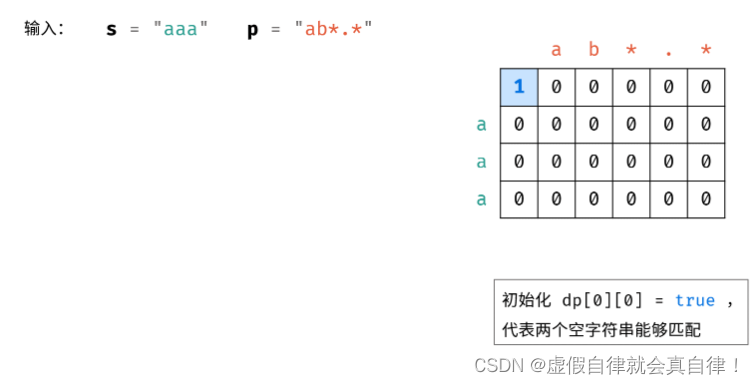
初始化首行
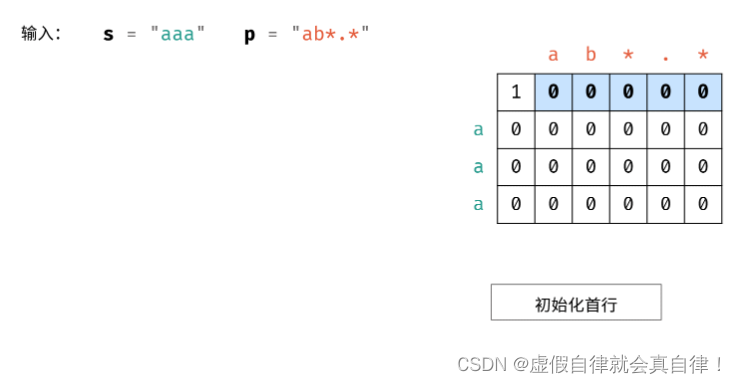
dp数组更新
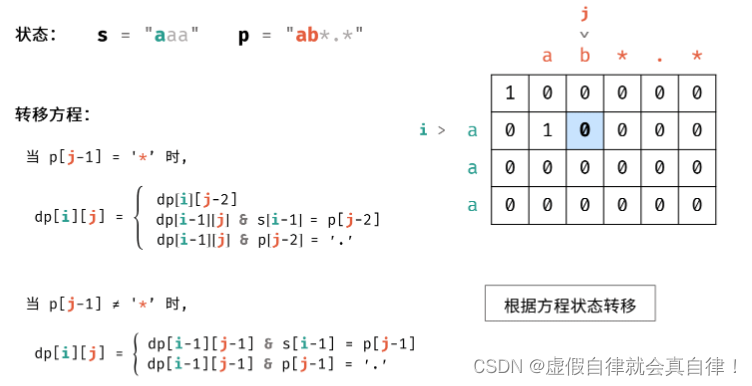
class Solution {
public:
bool isMatch(string s, string p) {
//1.dp定义 s前i个字符和p前j个字符都匹配 不包括i、j
int m = s.size()+1, n = p.size()+1;
vector<vector<bool>> dp(m, vector<bool>(n, false));
//2.初始化
dp[0][0] = true;//两个字符串都为空
for(int j=2; j<n; j+=2)//s空 p不空
dp[0][j] = dp[0][j-2] && p[j-1]=='*';//如果j-1是* 看j-2的匹配状态
//3.更新dp
/*
for(int i=1; i<m; i++)
{
for(int j=1; j<n; j++)
{
dp[i][j] = p[j-1] == '*' ?
dp[i][j-2] || dp[i-1][j] && (s[i-1] == p[j-2] || p[j-2] == '.') :
dp[i-1][j-1] && (p[j-1]=='.' || s[i-1]==p[j-1]);
}
}*/
for(int i=1; i<m; i++)
{
for(int j=1; j<n; j++)
{
if(p[j-1] == '*')
{
if(dp[i][j-2]) dp[i][j] = true;// *可以为0,所以aa和aab*中 *前前一个字符匹配,就可以匹配
// 此时看不加s串最后一个字母,能不能匹配到这个位置,如果能的话,
// 再看 * 前面的字母和s串新加的这个字母一样不,如果一样,就能匹配,如果不一样,因为此时s串多了一个字母,
// 就无法跟现在的 p 进行匹配了;例如:从 aa 可以匹配 aab* ,但是 aaa 匹配到 aab* 的时候,dp[i - 1][j]为true,
// 但是s[i - 1] 与 p[j - 2]不一样,就无法匹配;
else if(dp[i-1][j] && s[i-1]==p[j-2]) dp[i][j] = true;// 但是,如果 * 的前一个字符是万能的 . ,即可匹配;
else if(dp[i-1][j] && p[j-2]=='.') dp[i][j] = true;
}
else
{
// 不是 * 的情况下,新加的两个字符相同,则可以继续匹配
if(dp[i-1][j-1] && s[i-1]==p[j-1]) dp[i][j] = true;
// 新加的字符不同,但是 p 中新加的是万能的 . ,就能随便匹配;
else if(dp[i-1][j-1] && p[j-1]=='.') dp[i][j] = true;
}
}
}
return dp[m-1][n-1];
}
};
3. JZ20 表示数值的字符串

无语了,又很难的样子,搬运力扣K神的题解了。
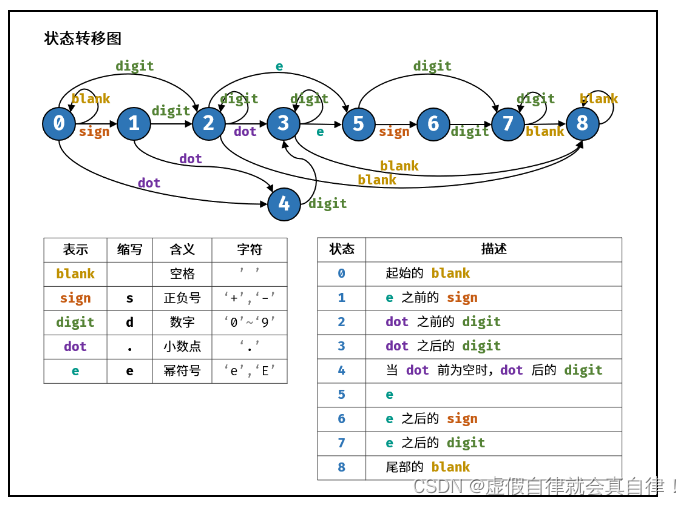
有限状态机
-
解题思路:
本题使用有限状态自动机。根据字符类型和合法数值的特点,先定义状态,再画出状态转移图,最后编写代码即可。 -
字符类型:
空格:「 」、数字:「 0—90—90—9 」、正负号:「 +−±+− 」、小数点:「 … 」、幂符号:「 eEeEeE 」。 -
状态定义:
按照字符串从左到右的顺序,定义以下 9 种状态。- 0 开始的空格
- 1 幂符号前的正负号
- 2 小数点前的数字
- 3 小数点、小数点后的数字
- 4 当小数点前为空格时,小数点、小数点后的数字
- 5 幂符号
- 6 幂符号后的正负号
- 7 幂符号后的数字
- 8 结尾的空格
-
结束状态,合法的结束状态有 2, 3, 7, 8 。

class Solution {
public:
bool isNumber(string s) {
//2.有限状态机
unordered_map<State, unordered_map<CharType, State>> transfer
{
{ STATE_INTITIAL, //初始状态
{
{CHAR_SPACE, STATE_INTITIAL},
{CHAR_NUMBER, STATE_INTEGER},
{CHAR_POINT, STATE_DOT_WITHOUT_INT},
{CHAR_SIGN, STATE_INT_SIGN}
}
},
{ STATE_INT_SIGN,
{
{CHAR_NUMBER, STATE_INTEGER},
{CHAR_POINT, STATE_DOT_WITHOUT_INT}
}
},
{ STATE_INTEGER,
{
{CHAR_NUMBER, STATE_INTEGER},
{CHAR_EXP, STATE_EXP},
{CHAR_POINT, STATE_DOT},
{CHAR_SPACE, STATE_END}
}
},
{ STATE_DOT,
{
{CHAR_NUMBER, STATE_FRACTION},
{CHAR_EXP, STATE_EXP},
{CHAR_SPACE, STATE_END}
}
},
{
STATE_DOT_WITHOUT_INT, {
{CHAR_NUMBER, STATE_FRACTION}
}
},
{
STATE_FRACTION,
{
{CHAR_NUMBER, STATE_FRACTION},
{CHAR_EXP, STATE_EXP},
{CHAR_SPACE, STATE_END}
}
},
{
STATE_EXP,
{
{CHAR_NUMBER, STATE_EXP_NUMBER},
{CHAR_SIGN, STATE_EXP_SIGN}
}
},
{
STATE_EXP_SIGN, {
{CHAR_NUMBER, STATE_EXP_NUMBER}
}
},
{
STATE_EXP_NUMBER, {
{CHAR_NUMBER, STATE_EXP_NUMBER},
{CHAR_SPACE, STATE_END}
}
},
{
STATE_END, {
{CHAR_SPACE, STATE_END}
}
}
};
int len = s.size();
State st = STATE_INTITIAL;
for(int i=0; i<len; i++)
{
CharType typ = toCharType(s[i]);
if(transfer[st].find(typ) == transfer[st].end()) return false;
else st = transfer[st][typ];
}
return st == STATE_INTEGER || st==STATE_DOT || st==STATE_FRACTION || st==STATE_EXP_NUMBER || st==STATE_END;
}
enum State
{
STATE_INTITIAL,
STATE_INT_SIGN,
STATE_INTEGER,
STATE_DOT,
STATE_DOT_WITHOUT_INT,
STATE_FRACTION,
STATE_EXP,
STATE_EXP_SIGN,
STATE_EXP_NUMBER,
STATE_END
};
enum CharType {
CHAR_NUMBER,
CHAR_EXP,
CHAR_POINT,
CHAR_SIGN,
CHAR_SPACE,
CHAR_ILLEGAL
};
CharType toCharType(char ch) {
if (ch >= '0' && ch <= '9') {
return CHAR_NUMBER;
} else if (ch == 'e' || ch == 'E') {
return CHAR_EXP;
} else if (ch == '.') {
return CHAR_POINT;
} else if (ch == '+' || ch == '-') {
return CHAR_SIGN;
} else if (ch == ' ') {
return CHAR_SPACE;
} else {
return CHAR_ILLEGAL;
}
}
};
遍历
小天才才的题解

class Solution {
public:
bool isNumber(string s) {
//1. 遍历 找到所有合法情况
int i = 0, j = s.size() - 1;
//找到字符串中第一个不为空的位置
for(; i<s.size(); i++)
{
if(s[i] != ' ') break;
}
//从末尾找到字符串最后一个不为空的位置
for(; j>=0; j--)
{
if(s[j] != ' ') break;
}
//判断是否为数值,以及是否有小数点和e/E
bool numFlag = false;
bool dotFlag = false;
bool eFlag = false;
for(int k=i; k<=j; k++)
{
//判断是否为数字
//if(isdigit(s[k])) numFlag=true;
if(s[k] >= '0' && s[k] <= '9') numFlag = true;
//判断是否为小数点,并且之前是否出现过小数点和e/E
else if(s[k]=='.' && !dotFlag && !eFlag) dotFlag = true;//是小数点 且之前没有出现过小数点和e/E
//判断是否为e/E,并且之前是否出现过e/E和数字
else if((s[k]=='e' || s[k]=='E') && !eFlag && numFlag)//是e/E 之前没有出现过e/E 且e/E 前后是数字
{
eFlag = true;
//因为e/E的前后必须都是数字,所以如果找到了e/E就把num_flag设为false,
//遇到下一个数字再设为true,避免出现12e的情况
numFlag = false;
}
//判断是否为+-,并且符号是否在数值的首位,或者前一位是e/E
else if((s[k]=='+' || s[k]=='-') && (k==i || s[k-1]=='e' || s[k-1]=='E')) continue;//在数值的首位或者前一位是e/E
else return false;//其他均为非法情况,输出false
}
return numFlag;//肯定有数字
}
};
4. JZ75 字符流中第一个不重复的字符

class Solution
{
public:
//Insert one char from stringstream
void Insert(char ch) {
v.push_back(ch);
result[ch]++;//统计次数
}
//return the first appearence once char in current stringstream
char FirstAppearingOnce() {
for(int i=0; i<v.size(); i++)
{
if(result[v[i]] == 1) return v[i];
}
return '#';
}
vector<char> v;
unordered_map<char, int> result;
};
5. JZ23 链表中环的入口结点
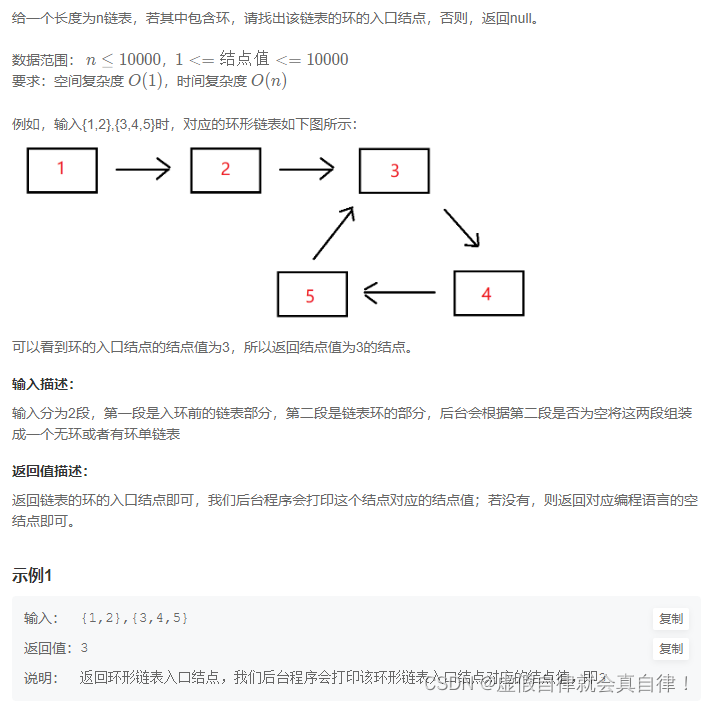
快慢指针
/*
struct ListNode {
int val;
struct ListNode *next;
ListNode(int x) :
val(x), next(NULL) {
}
};
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* EntryNodeOfLoop(ListNode* pHead) {
if(pHead == nullptr || pHead->next == nullptr) return nullptr;
ListNode* fast = pHead, *slow = pHead;
//写法1
while(fast && fast->next)
{
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
if(fast == slow)//第一次相遇
{
slow = pHead;
while(slow != fast)
{
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next;
}
return fast;
}
}
return nullptr;
}
};
- 写法2
/*
struct ListNode {
int val;
struct ListNode *next;
ListNode(int x) :
val(x), next(NULL) {
}
};
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* EntryNodeOfLoop(ListNode* pHead) {
if(pHead == nullptr || pHead->next == nullptr) return nullptr;
ListNode* fast = pHead, *slow = pHead;
//写法2
while(fast!=nullptr && fast->next!=nullptr)
{
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
if(slow == fast) break;//不应该直接返回 要做判断 return fast->next;
//cout << slow->val << fast->val<<endl;
}
// 若是快指针指向null,则不存在环
if(fast==nullptr || fast->next==nullptr) return nullptr;
//此时fast在环入口 让slow从头出发 同时走
slow = pHead;//再次相遇就是环入口
while (fast != slow)
{
fast = fast->next;
slow = slow->next;
}
return fast;
}
};
哈希表
/*
struct ListNode {
int val;
struct ListNode *next;
ListNode(int x) :
val(x), next(NULL) {
}
};
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* EntryNodeOfLoop(ListNode* pHead) {
if(pHead == nullptr || pHead->next == nullptr) return nullptr;
//哈希表
unordered_set<ListNode*> hashset;
while (pHead)
{
if(hashset.count(pHead)) return pHead;
hashset.insert(pHead);
pHead = pHead->next;
}
return nullptr;
}
};
6. JZ76 删除链表中重复的结点
快慢指针
/*
struct ListNode {
int val;
struct ListNode *next;
ListNode(int x) :
val(x), next(NULL) {
}
};
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* deleteDuplication(ListNode* pHead) {
if (!pHead) return NULL;
ListNode* slow = new ListNode(-1), *fast = new ListNode(-1), *dummy = new ListNode(-1);
dummy->next = pHead;
// 初始化两个指针
slow = dummy;
fast = dummy->next;
while(fast)
{
while(fast->next && fast->val == fast->next->val)// 遇到重复
fast = fast->next;
cout << "fast " << fast->val <<endl;
cout << "slow " << slow->val <<endl;
if(slow->next != fast)// 此时slow连接的还是fast的重复结点 需要删除结点
{
slow->next = fast->next;
fast = fast->next;
}
else// 没有重复
{
fast = fast->next;
slow = slow->next;
}
}
return dummy->next;
}
};
三指针
/*
struct ListNode {
int val;
struct ListNode *next;
ListNode(int x) :
val(x), next(NULL) {
}
};
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* deleteDuplication(ListNode* pHead) {
if (!pHead) return NULL;
//三指针
ListNode* pre = new ListNode(-1), *cur = new ListNode(-1), *dummyhead = new ListNode(-1);
dummyhead->next = pHead;
cur = pHead;//遍历链表 判断是否有重复
pre = dummyhead;//虚拟链表尾
while(cur)
{
if(cur->next!=nullptr && cur->val == cur->next->val)
{
while(cur->next!=nullptr && cur->val == cur->next->val)
cur = cur->next;
//此时没有重复了
pre->next = cur->next;
cur = cur->next;
}
else
{
cur = cur->next;
pre = pre->next;
}
}
return dummyhead->next;
}
};
如果只保留一个重复结点
在一个排序的链表中,存在重复的结点,请删除该链表中重复的结点,重复的结点保留,返回链表头指针。 例如,链表1->2->3->3->4->4->5 处理后为 1->2->3->4->5
ListNode* deleteDuplication(ListNode* pHead)
{
if (pHead == nullptr) return nullptr;
ListNode* node = (ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
node = pHead;
while (node != nullptr) {
if (node->next!=nullptr && node->val == node->next->val) {//这里千万要判断node->next也不为空才可以
while (node->next != nullptr && node->val == node->next->val) {
node->next = node->next->next;
}
}
node = node->next;
}
return pHead;
}
- 写法2
ListNode* deleteDuplication(ListNode* pHead)
{
if (pHead == nullptr || pHead->next == nullptr) return pHead;
ListNode dummpyHead(0);
dummpyHead.next = pHead;
ListNode* pre = &dummpyHead;
ListNode* cur = dummpyHead.next;
while (cur != nullptr) {
if (cur->next != nullptr && cur->val == cur->next->val) {
while (cur->next != nullptr && cur->val == cur->next->val)
{
cur = cur->next;
}
pre->next = cur;//删除重复结点
pre = pre->next;
cur = cur->next;
}
else {
pre = pre->next;
cur = cur->next;
}
}
return dummpyHead->next;
}
7. JZ8 二叉树的下一个结点
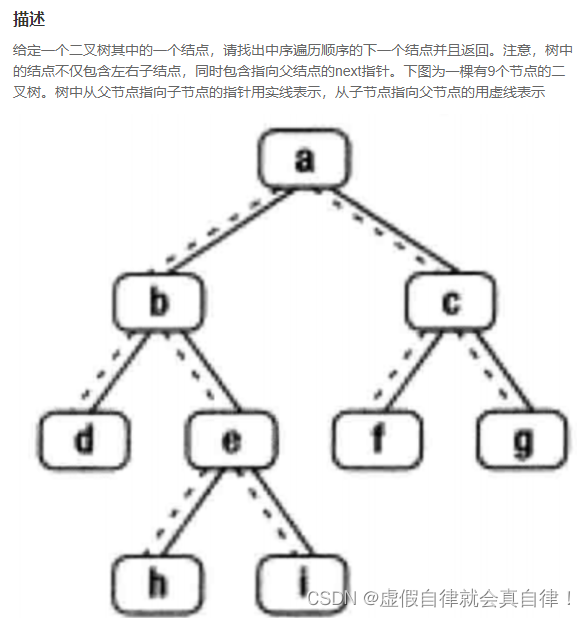
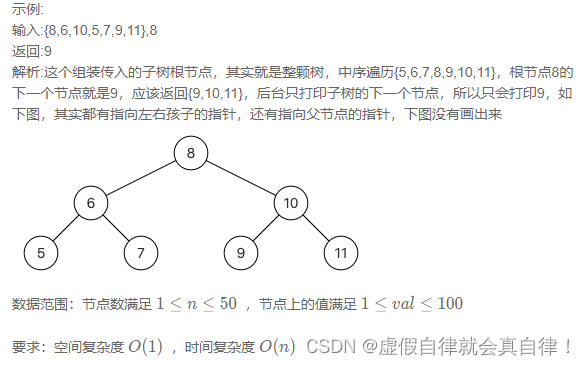
数组保存结点
中序遍历,保存节点在数组中,再匹配目标节点
/*
struct TreeLinkNode {
int val;
struct TreeLinkNode *left;
struct TreeLinkNode *right;
struct TreeLinkNode *next;
TreeLinkNode(int x) :val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL), next(NULL) {
}
};
*/
class Solution {
public:
TreeLinkNode* GetNext(TreeLinkNode* pNode) {
if(pNode == nullptr) return nullptr;
vector<TreeLinkNode*> v;
//1.获取根节点
TreeLinkNode* root = pNode;
while(root->next != nullptr) root = root->next;
//2.保存节点
inOrder(root, v);
//3.匹配目标节点
for(int i=0; i<v.size(); i++)
{
if(pNode == v[i]) return v[i+1];
}
return nullptr;
}
void inOrder(TreeLinkNode* root, vector<TreeLinkNode*>& v)
{
if(root == nullptr) return;
if(root->left) inOrder(root->left, v);
v.push_back(root);
if(root->right) inOrder(root->right, v);
}
};
直接查找 分类讨论
默认当前节点作为根节点,那么中序遍历的下一个节点应该是其右子节点,如果
有右子树
有左子树,中序遍历的下一个节点

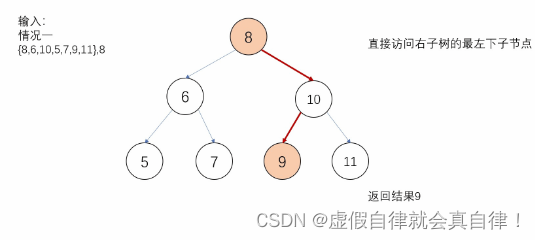
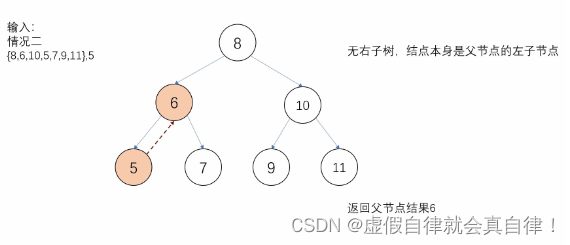
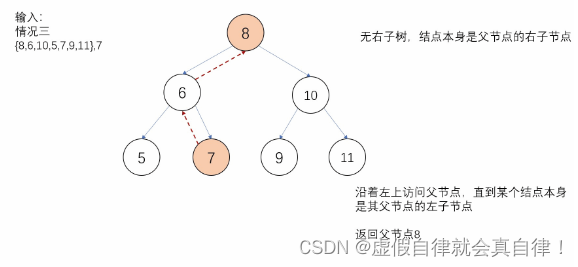
- 写法1
/*
struct TreeLinkNode {
int val;
struct TreeLinkNode *left;
struct TreeLinkNode *right;
struct TreeLinkNode *next;
TreeLinkNode(int x) :val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL), next(NULL) {
}
};
*/
class Solution {
public:
TreeLinkNode* GetNext(TreeLinkNode* pNode) {
if(pNode == nullptr) return nullptr;
//分类
// 如果有右子树
TreeLinkNode* cur = nullptr;
if(pNode->right != nullptr)
{
pNode = pNode->right;
// 一直找到右子树的最左下的结点为返回值
while(pNode->left != nullptr) pNode = pNode->left;
return pNode;
}
//如果有父节点 先看有没左子节点 有就返回;没有,说明当前节点是右叶子节点 只有右子节点 一直往上找父节点
while(pNode->next != nullptr)
{
cur = pNode->next;//当前结点的父节点
if(cur->left == pNode) return cur;//无右子树 直到当前结点是其父节点的左子结点 返回
pNode = pNode->next;
}
return nullptr;
}
};
- 写法2
/*
struct TreeLinkNode {
int val;
struct TreeLinkNode *left;
struct TreeLinkNode *right;
struct TreeLinkNode *next;
TreeLinkNode(int x) :val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL), next(NULL) {
}
};
*/
#include <unistd.h>
class Solution {
public:
TreeLinkNode* GetNext(TreeLinkNode* pNode) {
if(pNode == nullptr) return nullptr;
//分类 写法2
TreeLinkNode* node = nullptr;
if(pNode->right != nullptr)//如果当前节点有右子树,则右子树最左边的那个节点就是
{
node = pNode->right;
while(node->left != nullptr) node = node->left;
return node;
}
node = pNode;
while(node->next != nullptr && node == node->next->right)//当前节点有右子树
{
node = node->next;//找到当前节点是其父亲节点的左孩子的那个节点,然后返回其父亲节点 相当于一直往上找父节点
}
return node->next;//如果当前节点没有右子树 有左子树 返回当前节点的父节点
}
};
- 写法3
/*
struct TreeLinkNode {
int val;
struct TreeLinkNode *left;
struct TreeLinkNode *right;
struct TreeLinkNode *next;
TreeLinkNode(int x) :val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL), next(NULL) {
}
};
*/
#include <unistd.h>
class Solution {
public:
TreeLinkNode* GetNext(TreeLinkNode* pNode) {
if(pNode == nullptr) return nullptr;
//分类 写法3
TreeLinkNode* cur = nullptr;
if(pNode->right)// 如果有右子树 一直找到右子树的最左下的结点为返回值
{
cur = pNode->right;
while(cur->left != nullptr) cur = cur->left;
return cur;
}
// 如果无右子树 且当前结点是其父节点的左子结点
if(pNode->next != nullptr && pNode == pNode->next->left)
return pNode->next;// 返回当前结点的父节点
// 如果无右子树 且当前结点是其父节点的右子节点
if(pNode->next != nullptr)
{
cur = pNode->next;
// 沿着左上一直爬树,爬到当前结点是其父节点的左自己结点为止
while(cur->next != nullptr && cur == cur->next->right) cur = cur->next;
return cur->next;// 返回当前结点的父节点
}
return nullptr;
}
};
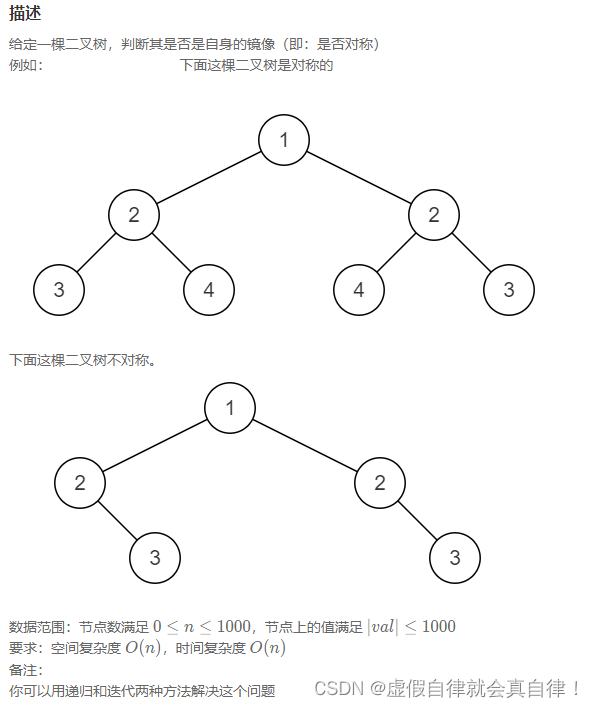
8. JZ28 对称的二叉树
/**
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* struct TreeNode *left;
* struct TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
bool isSymmetrical(TreeNode* pRoot) {
if(pRoot == nullptr) return true;
return dfs(pRoot->left, pRoot->right);
}
bool dfs(TreeNode* node1, TreeNode* node2)
{
if(node1 == nullptr && node2 == nullptr) return true;
if(node1 == nullptr || node2 == nullptr) return false;
if(node1->val != node2->val) return false;
return dfs(node1->left, node2->right) && dfs(node1->right, node2->left);
}
};
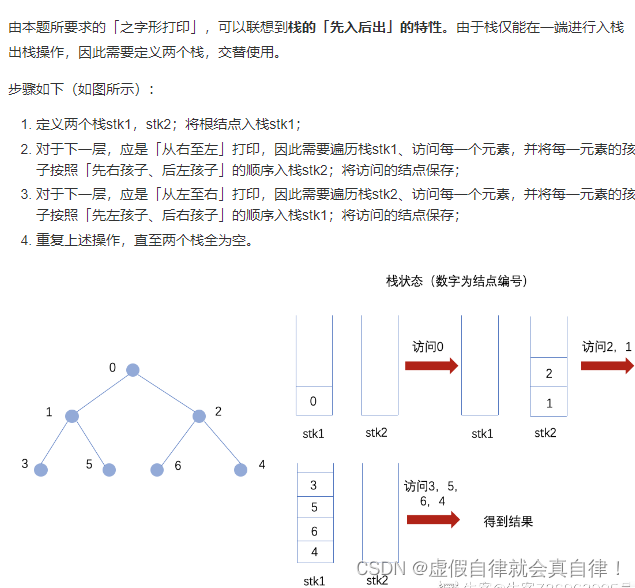
9. JZ77 按之字形顺序打印二叉树

栈实现
/**
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* struct TreeNode *left;
* struct TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int> > Print(TreeNode* pRoot) {
vector<vector<int>> result;
if(pRoot == nullptr) return result;
stack<TreeNode*> st1;//保存从右向左节点
stack<TreeNode*> st2;//保存从左向右节点
st1.push(pRoot);
while(!st1.empty() || !st2.empty())
{
vector<int> temp;
TreeNode* cur;
if(!st1.empty())
{
while(!st1.empty())
{
cur = st1.top();//访问st1节点后 从左向右存入st2
temp.push_back(cur->val);//当前层的节点
if(cur->left) st2.push(cur->left);
if(cur->right) st2.push(cur->right);
st1.pop();
}
result.push_back(temp);
}
temp.clear();
if(!st2.empty())
{
while (!st2.empty())
{
cur = st2.top();
temp.push_back(cur->val);
if(cur->right) st1.push(cur->right);
if(cur->left) st1.push(cur->left);
st2.pop();
}
result.push_back(temp);
}
}
return result;
}
};
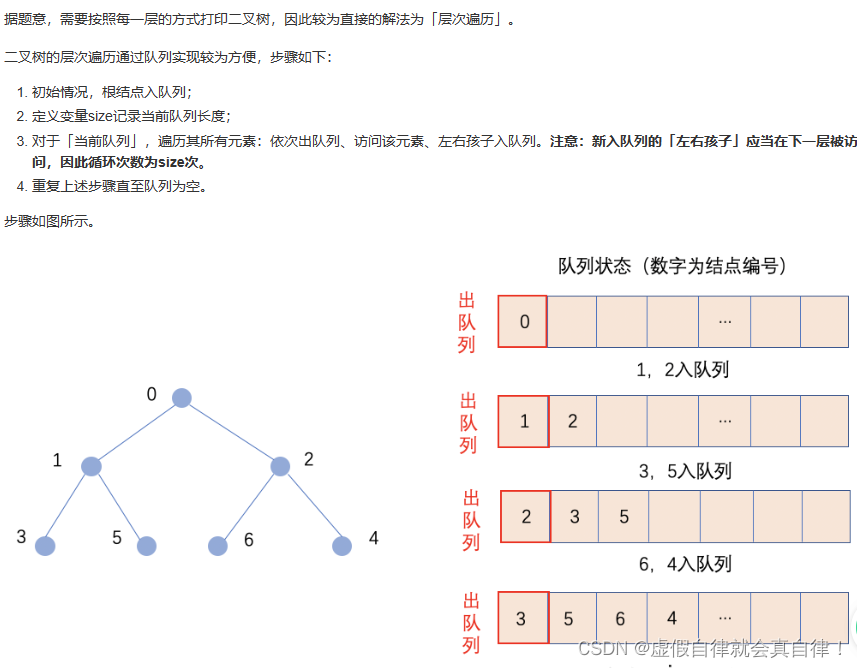
队列实现
/**
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* struct TreeNode *left;
* struct TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* };
*/
#include <vector>
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int> > Print(TreeNode* pRoot) {
vector<vector<int>> result;
if(pRoot == nullptr) return result;
//队列实现
queue<TreeNode*> que;
que.push(pRoot);
int level = 0, size = 0;
//TreeNode* cur = nullptr;
while(!que.empty())
{
vector<int> temp;//存储每一行结果
size = que.size();// 当前队列长度 否则后面会更新
for(int i=0; i<size; i++)
{
TreeNode* cur = que.front();
que.pop();
if(cur == nullptr) continue; // 空元素跳过
que.push(cur->left); // 左孩子入队列
que.push(cur->right); // 右孩子入队列
//第一层从左向右 level从0开始 level为偶数 左到右;下一层从右向左 level为奇数 右到左
if(level % 2 == 0) temp.push_back(cur->val);// 从左至右打印
else temp.insert(temp.begin(), cur->val);// 从右至左打印
}
level++;
if(!temp.empty()) result.push_back(temp);
}
return result;
}
};
10. JZ78 把二叉树打印成多行
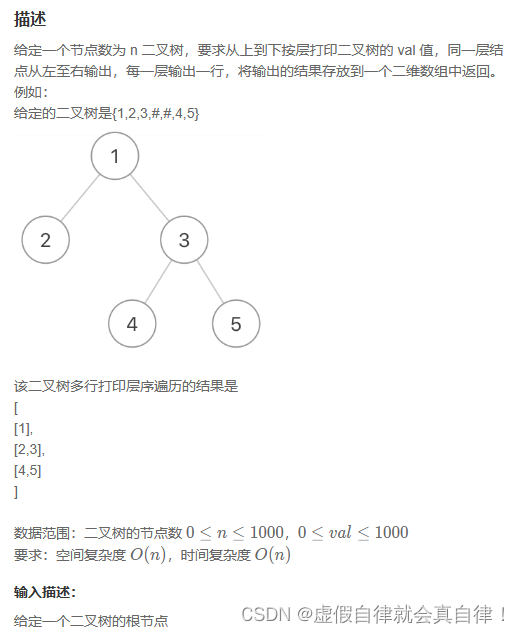
队列+迭代,和上面那道题有点像,简单一点
/**
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* struct TreeNode *left;
* struct TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int> > Print(TreeNode* pRoot) {
vector<vector<int>> result;
if(pRoot == nullptr) return result;
//队列
queue<TreeNode*> que;
que.push(pRoot);
vector<int> v;
TreeNode* cur;
int size = 0;
while(!que.empty())
{
v.clear();
size = que.size();
for(int i=0; i<size; i++)
{
cur = que.front();
que.pop();
v.push_back(cur->val);
if(cur->left) que.push(cur->left);
if(cur->right) que.push(cur->right);
}
result.push_back(v);
}
return result;
}
};