补遗: CS61a
通过“圣经”《SICP》 了解到这门课。SCIP读着有点困难,想通过课程的引导。但是这个课程要比书基础很多,就当对计科学习的回顾和补遗了。本笔记也会在我读完 SICP 后更新。
课程地址:CS 61A Fall 2022
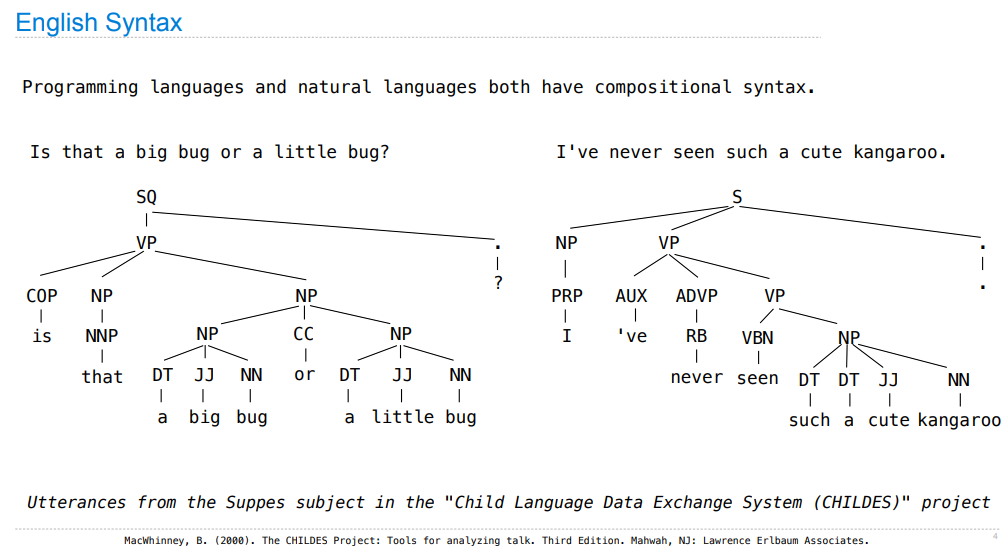
参照原书目录,本课程主要讲了一下内容:大概
-
构造过程抽象(主要以 python 为例)
- 程序设计的基本元素
- 过程及其产生的计算
- 用高阶函数做抽象
-
构造数据抽象
- (可变数据)
- 层次性数据和闭包性质
- (递归对象)
-
模块化、对象和状态
- (着重讲了 python 的栈帧)
- (面向对象编程)
-
元语言抽象
- (python 实现 Scheme 解释器)
- (程序即数据)
-
(数据处理)
- (声明式编程 SQL)
以下是听课时的一些非常粗略的笔记:从第一讲到第39讲完。
笔记
Lecture 1
课程注意事项 与 为什么选择 python
Lecture 2
python 的 frame 与 作用域 什么的…
Lecture 3
进入交互模式
python -i xxx.py
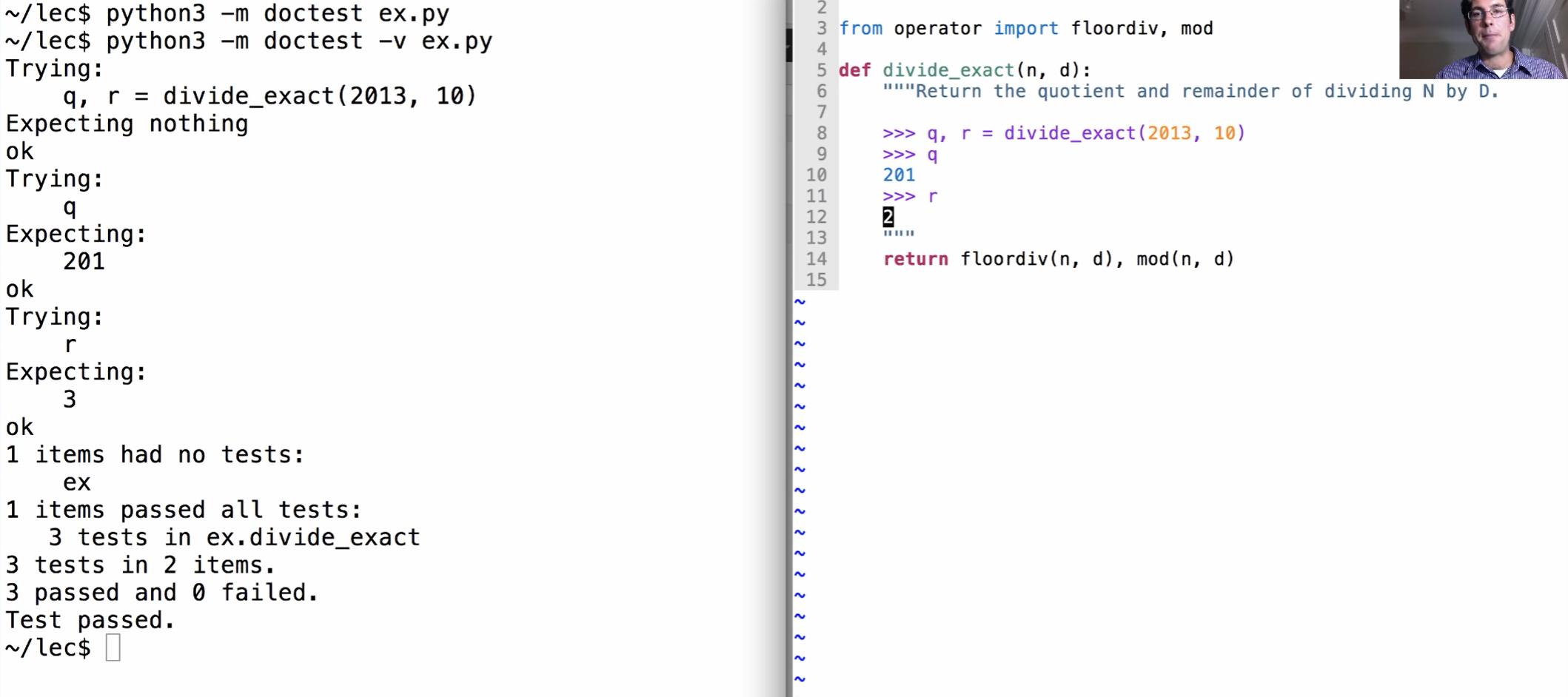
doctest:
参见:1.5 Control (composingprograms.com) 1.5.6
python -m doctest -v ex.py
# Conditional expressions
def absolute_value(x):
"""Return the absolute value of X.
>>> absolute_value(-3)
3
>>> absolute_value(0)
0
>>> absolute_value(3)
3
"""
if x < 0:
return -x
elif x == 0:
return 0
else:
return x
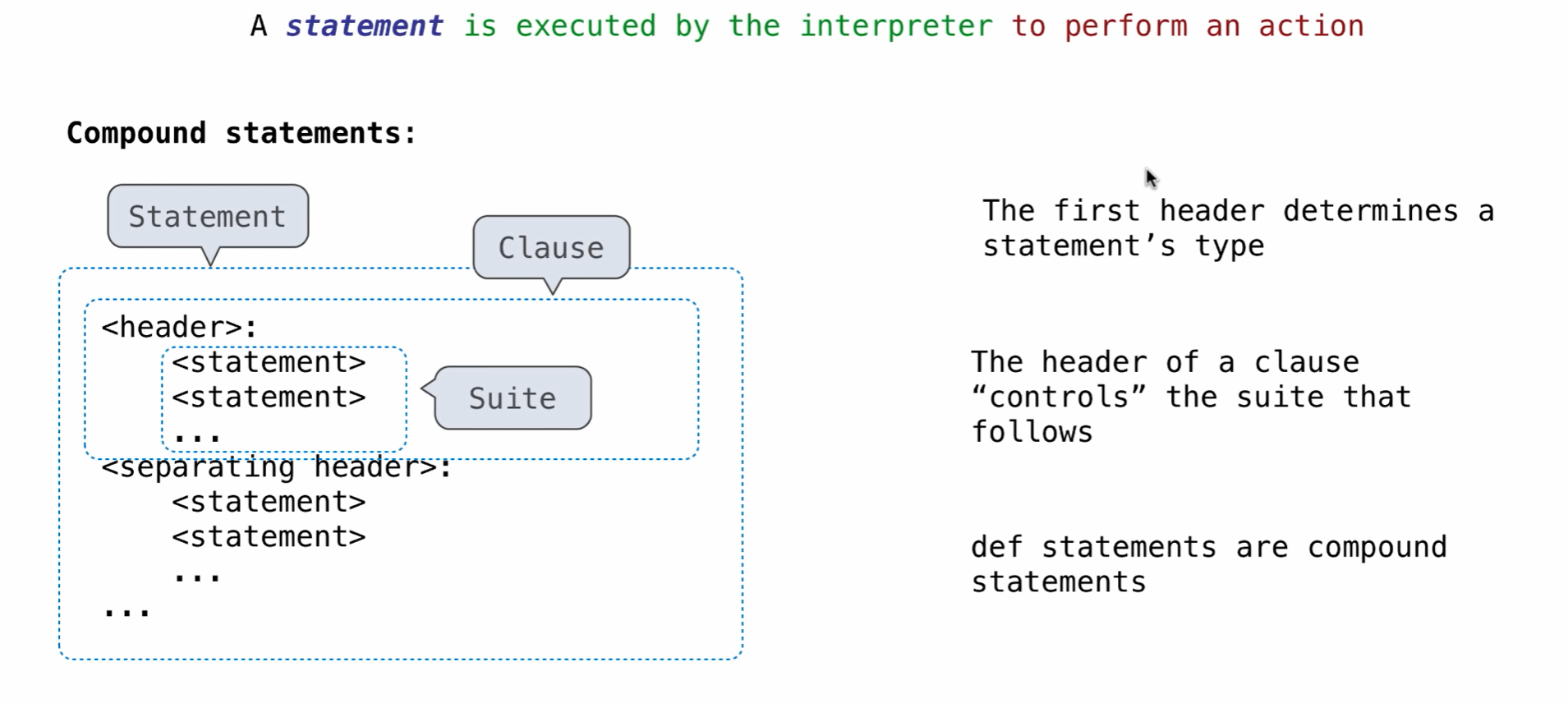
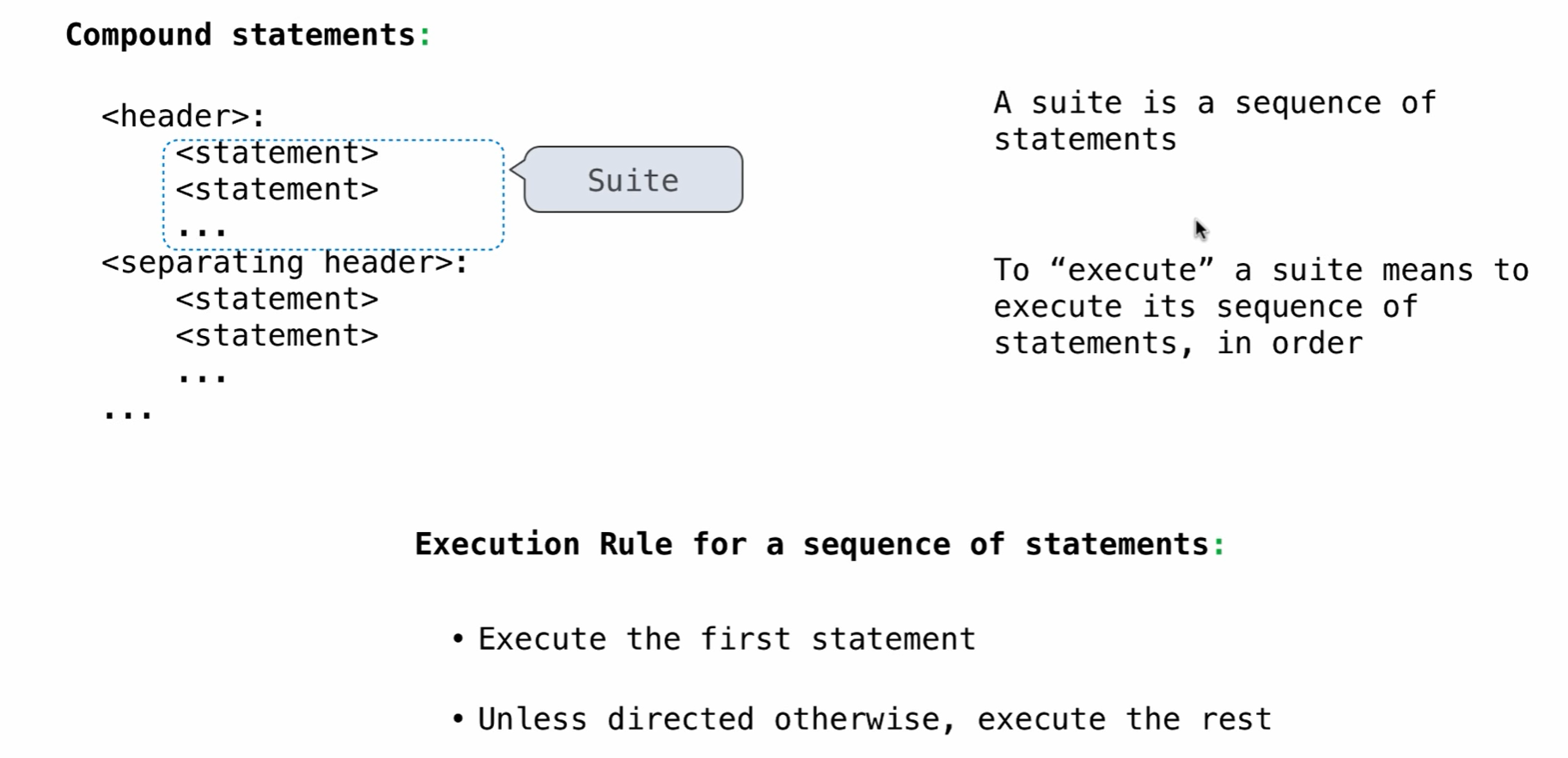
statements:

Lecture 4
04-Higher-Order_Functions.key (cs61a.org)
高阶函数引入
Lecture 5
05-Environments.key (cs61a.org)
高阶函数的环境与帧
lambda 表达式

Function Currying (柯里化_百度百科 (baidu.com))
Curry: Transform a multi-argument function into a single-argument, higher-order function
Lecture 6
Function Example: Sound
很有趣的使用高阶函数的一个例子(作马里奥主题曲)
Lecture 7
为何 程序控制流必须存在,而非只有函数?反例:
def if_(c, t, f):
if c:
return t
else:
return f
from math import sqrt
def real_sqrt(x):
"""Return the real part of the square root of x.
>>> real_sqrt(4)
2.0
>>> real_sqrt(-4)
0.0
"""
if x > 0:
return sqrt(x)
else:
return 0.0
# if_(x > 0, sqrt(x), 0.0)
能不能有解决方法?
使用短路或许是一个方法
此节其余内容是一些编程思想方法等
还有大讨论 2 与其讲解
Lecture 8
复习 与 函数装饰器
Midterm 1
Lecture 9
Recursion
自指、递归
Lecture 10
Tree Recursion
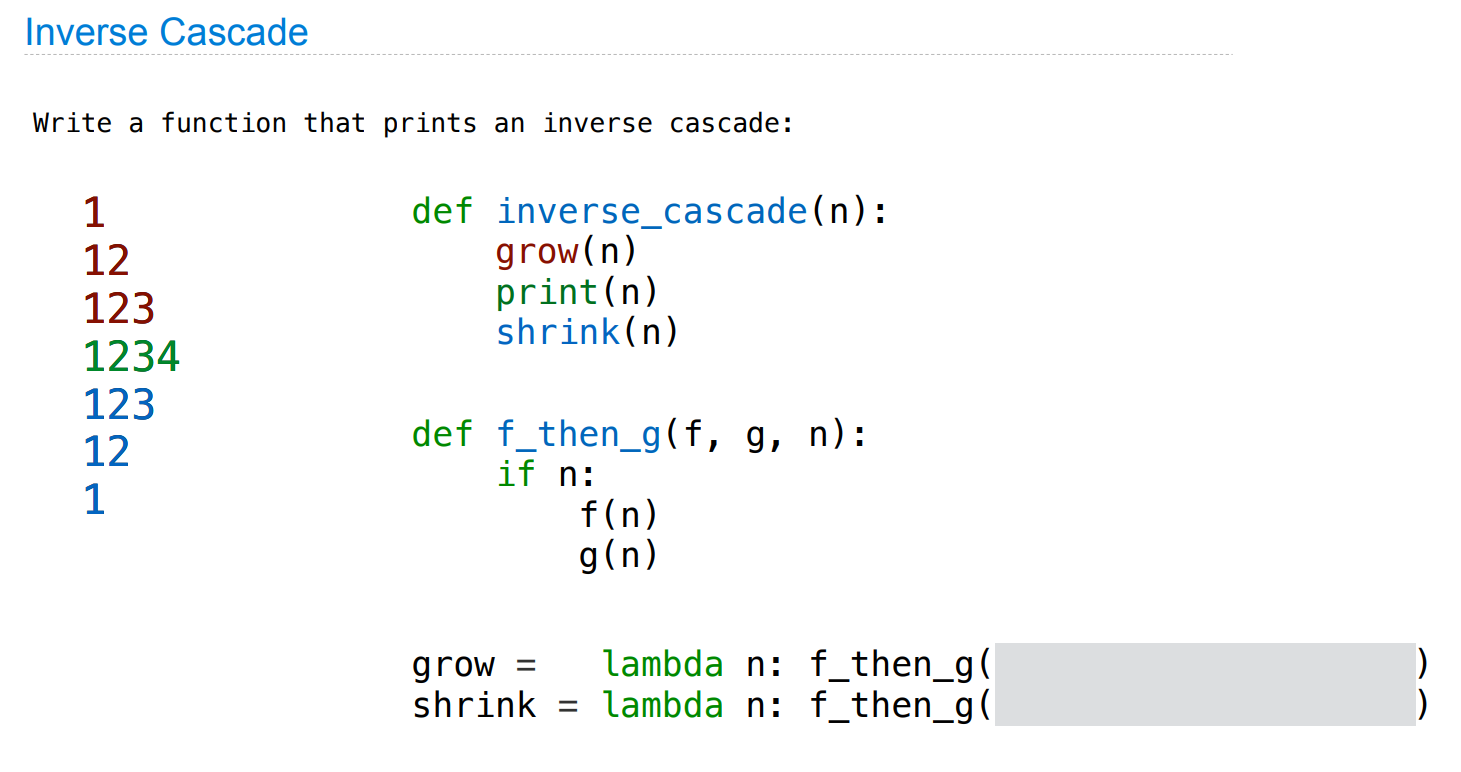
def i_c(n):
grow(n)
print(n)
shrink(n)
def f_then_g(f, g, n):
if n:
f(n)
g(n)
grow = lambda n : f_then_g(grow, print, n//10)
shrink = lambda n : f_then_g(print , shrink, n //10)
i_c(1234)
Lecture 11
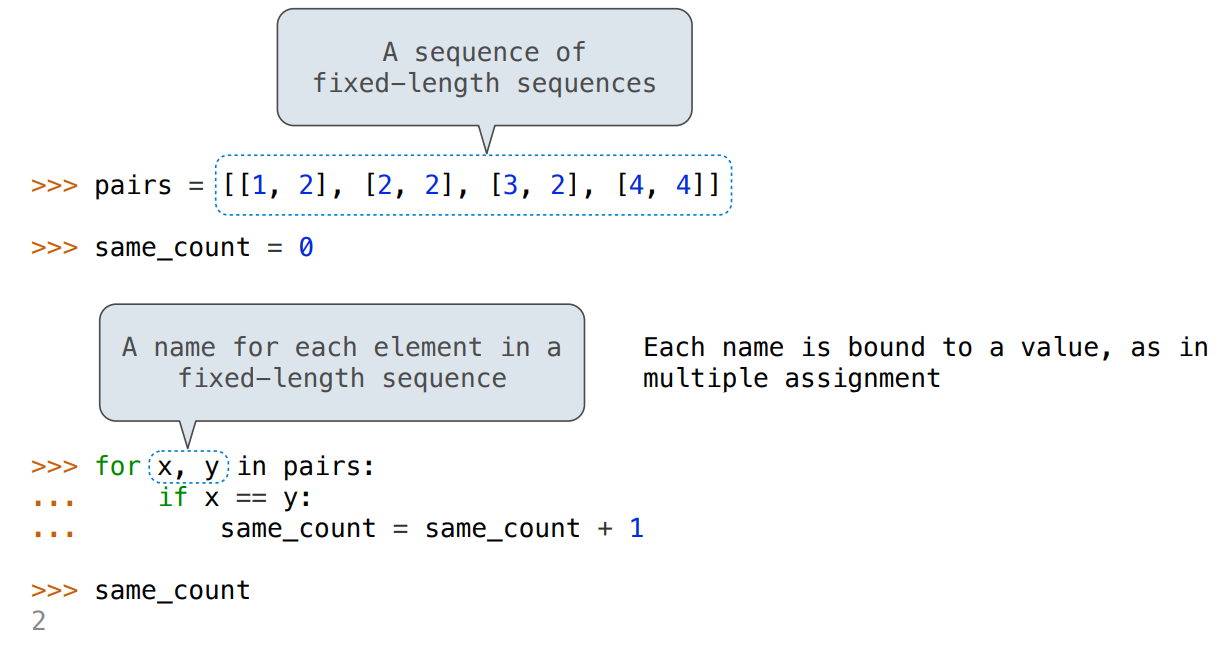
Sequences
Lists 、 for 、 列表推导
Lecture 12
Containers
Box-and-Pointer Notation
Slicing

# Aggregation
>>> sum({3:9, 5:25})
8
>>> sum([[2, 3], [4]], [])
[2, 3, 4]
>>> max(range(10), key=lambda x: 7 - (x-2)*(x-4))
3
>>> all([x < 5 for x in range(5)])
perfect_square = lambda x: x == round(x ** 0.5) ** 2
any([perfect_square(x) for x in range(50, 60)]) # Try ,65)
深度辨析 Python 的 eval() 与 exec() - 腾讯云开发者社区-腾讯云 (tencent.com)
Lecture 13
Data Abstraction

数据抽象
用函数实现数据结构:
# Functional implementation
def rational(n, d):
"""A representation of the rational number N/D."""
g = gcd(n, d)
n, d = n//g, d//g
def select(name):
if name == 'n':
return n
elif name == 'd':
return d
return select
def numer(x):
"""Return the numerator of rational number X in lowest terms and having
the sign of X."""
return x('n')
def denom(x):
"""Return the denominator of rational number X in lowest terms and positive."""
return x('d')
Lecture 14
Trees
数据结构 树 的实现
Lecture 15
Mutability
对象 object
python 的可变对象(Mutation)和不可变(immutable)对象
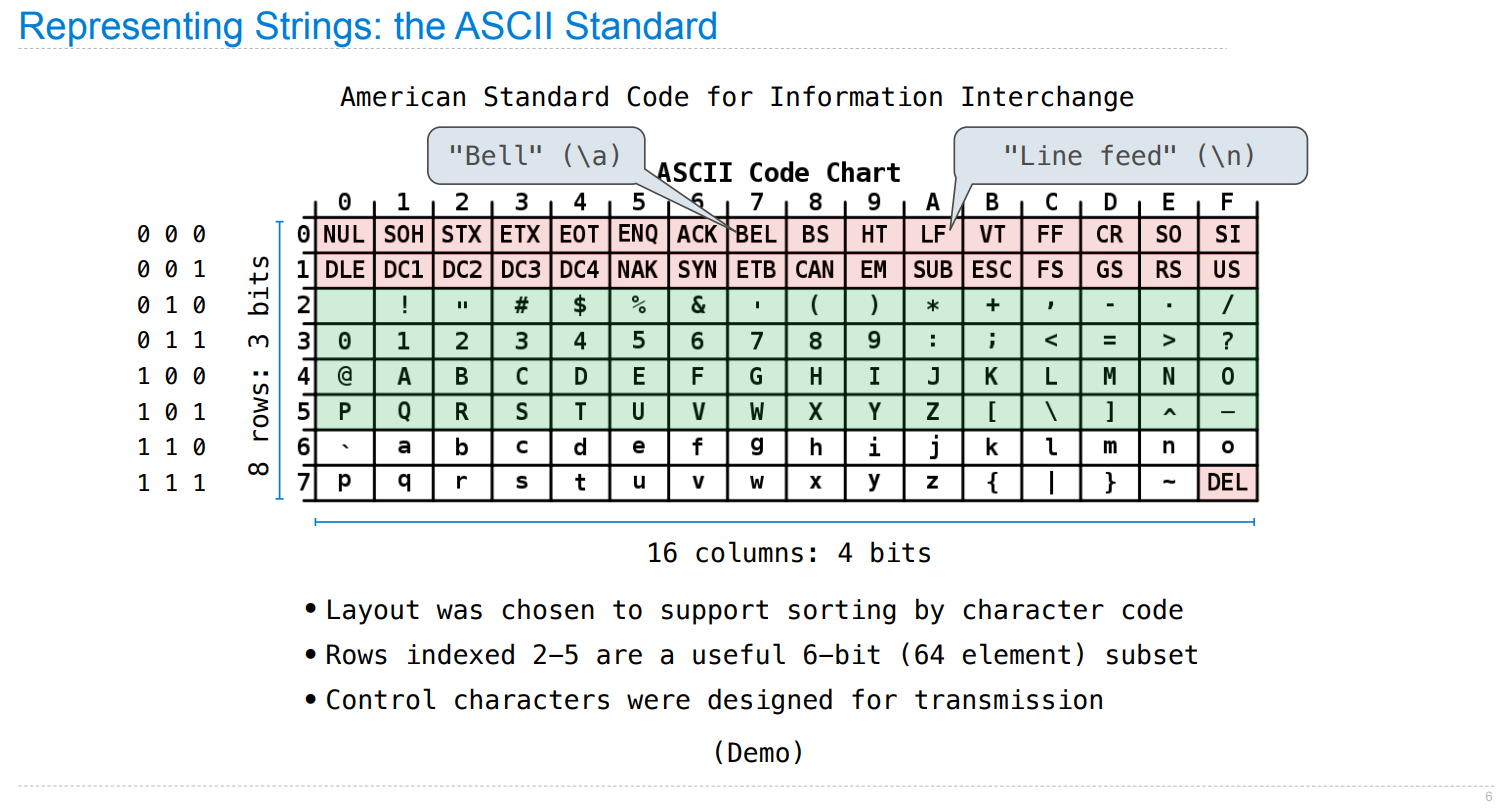
String
ASCII 的设计
from unicodedata import lookup, name
name('A')
lookup('SNOWMAN')
lookup('SOCCER BALL')
lookup('BABY')
s = lookup('SNOWMAN')
关于 tuple 的发音有争议
def tuple_demos():
(3, 4, 5, 6)
3, 4, 5, 6
()
tuple()
tuple([1, 2, 3])
# tuple(2)
(2,)
(3, 4) + (5, 6)
(3, 4, 5) * 2
5 in (3, 4, 5)
# {[1]: 2}
{1: [2]}
{(1, 2): 3}
# {([1], 2): 3}
{tuple([1, 2]): 3}

Identity
<exp0> is <exp1>
evaluates to True if both <exp0> and <exp1> evaluate to the same object
Equality
<exp0> == <exp1>
evaluates to True if both <exp0> and <exp1> evaluate to equal values
Identical objects are always equal values
Mutable Default Arguments are Dangerous
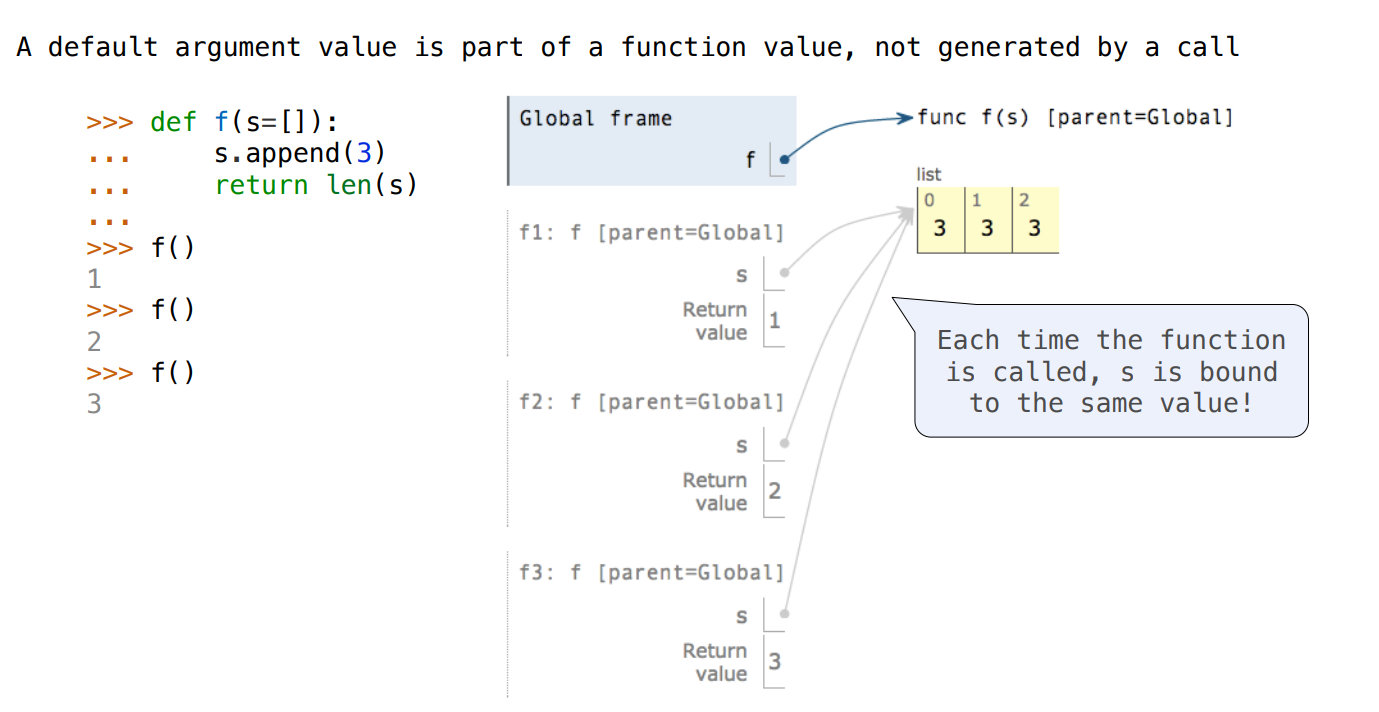
可以达到 C 语言中函数类似静态变量的作用
def make_withdraw_list(balance):
b = [balance]
def withdraw(amount):
if amount > b[0]:
return 'Insufficient funds'
b[0] = b[0] - amount
return b[0]
return withdraw
Lecture 16
Syntax
Useful string methods for processing the contents of a file:
.strip() returns a string without whitespace (spaces, tabs, etc.) on the ends
>>> ' hello '.strip()
'hello'
.split() returns a list of strings that were separated by whitespace
>>> 'hi there'.split()
['hi', 'there']
.replace(a, b) returns a string with all instances of string a replaced by string b
>>> '2+2'.replace('+', ' + ')
'2 + 2'
用类似 lisp 的语法举例子
Lecture 17
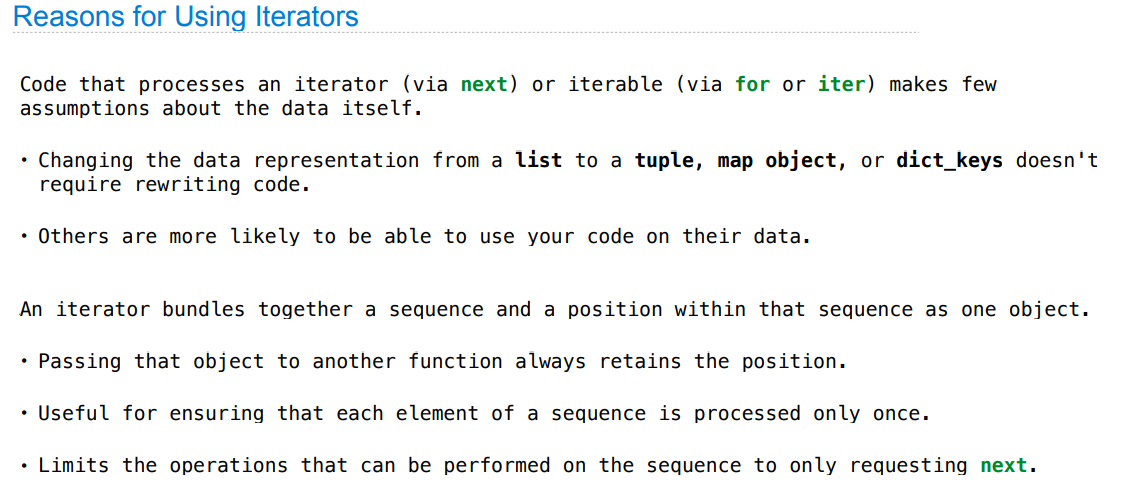
Iterators


字典能在迭代中改变值,而不能改变结构
迭代器是“一次性”的!
for 循环与迭代器的关系(跟 range 对象的不同)

lazily:懒惰执行

Lecture 18
Generators
Generators and Generator Functions

yield from
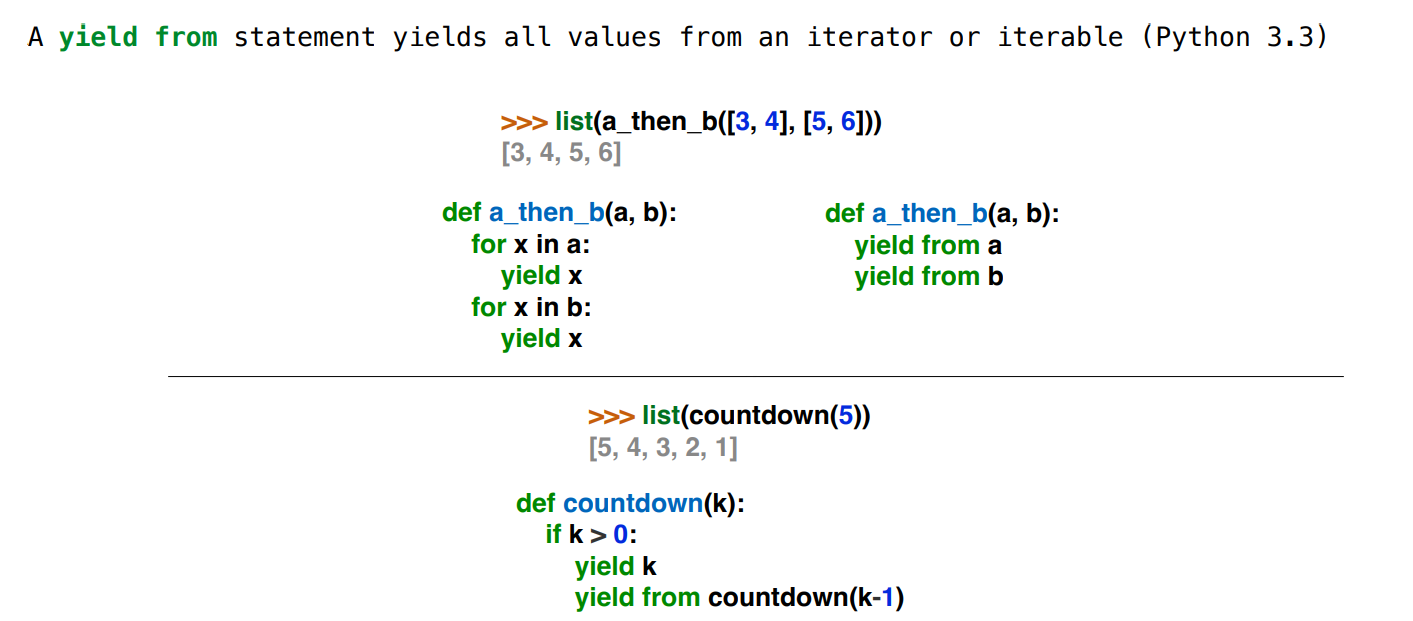
def yield_partitions(n, m):
"""List partitions.
>>> for p in yield_partitions(6, 4): print(p)
2 + 4
1 + 1 + 4
3 + 3
1 + 2 + 3
1 + 1 + 1 + 3
2 + 2 + 2
1 + 1 + 2 + 2
1 + 1 + 1 + 1 + 2
1 + 1 + 1 + 1 + 1 + 1
"""
if n > 0 and m > 0:
if n == m:
yield str(m)
for p in yield_partitions(n-m, m):
yield p + ' + ' + str(m)
yield from yield_partitions(n, m-1)
Lecture 19
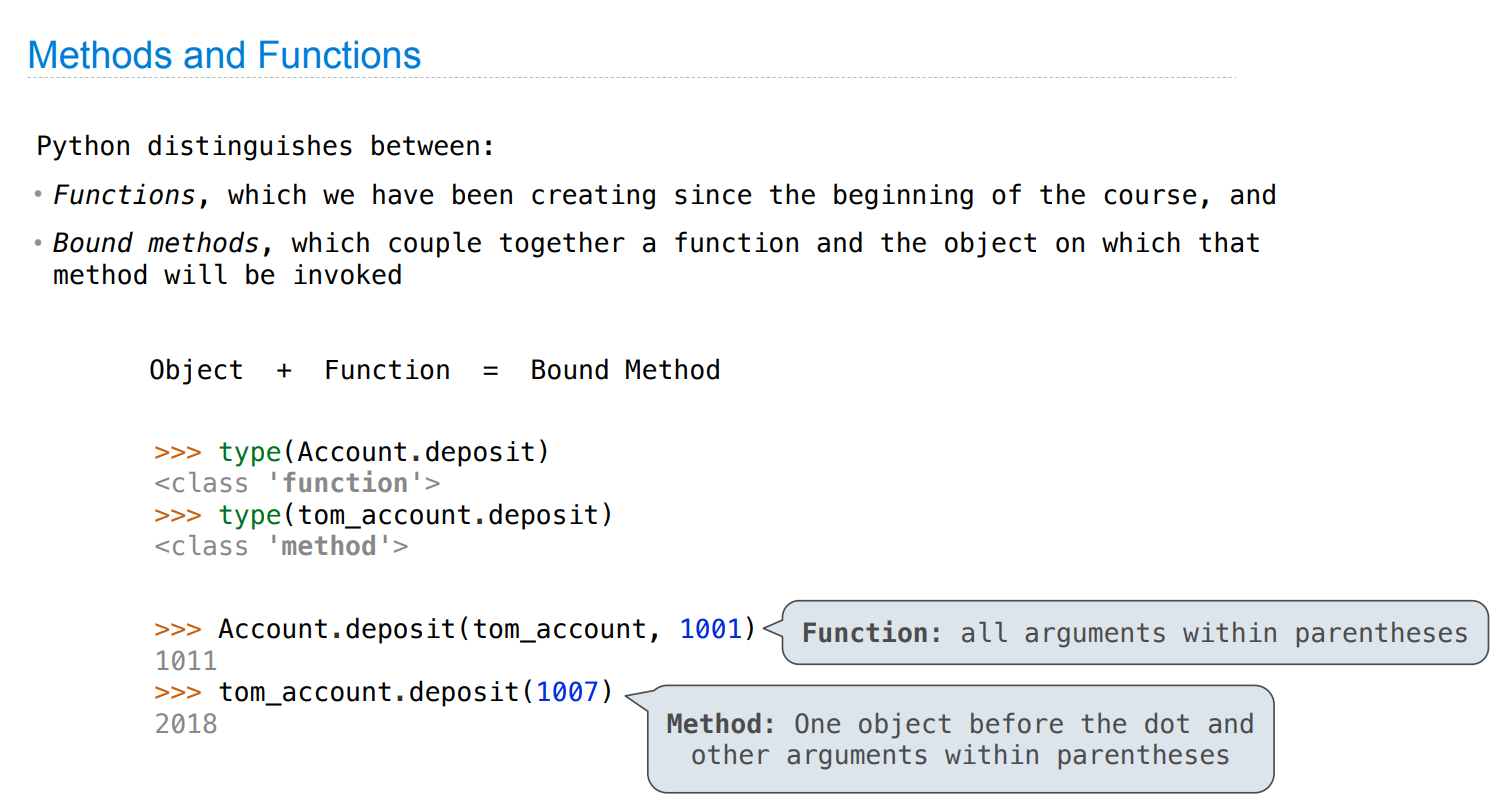
Objects
面向对象编程
Binding an object to a new name using assignment does not create a new object:
>>> c = a
>>> c is a
True
Lecture 20
Inheritance
类、实例、属性、方法、多继承
Lecture 21
Representation
string 实现
String Representations
An object value should behave like the kind of data it is meant to represent
For instance, by producing a string representation of itself
Strings are important: they represent language and programs
In Python, all objects produce two string representations:
• The str is legible to humans
• The repr is legible to the Python interpreter
The str and repr strings are often the same, but not always
The repr String for an Object
The str String for an Object
from fractions import Fraction
half = Fraction(1, 2)
half
print(half)
str(half)
repr(half)
s = 'hello world'
str(s)
repr(s)
"'hello world'"
repr(repr(repr(s)))
eval(eval(eval(repr(repr(repr(s))))))
# Errors: eval('hello world')
String Interpolation
注意实现细节:
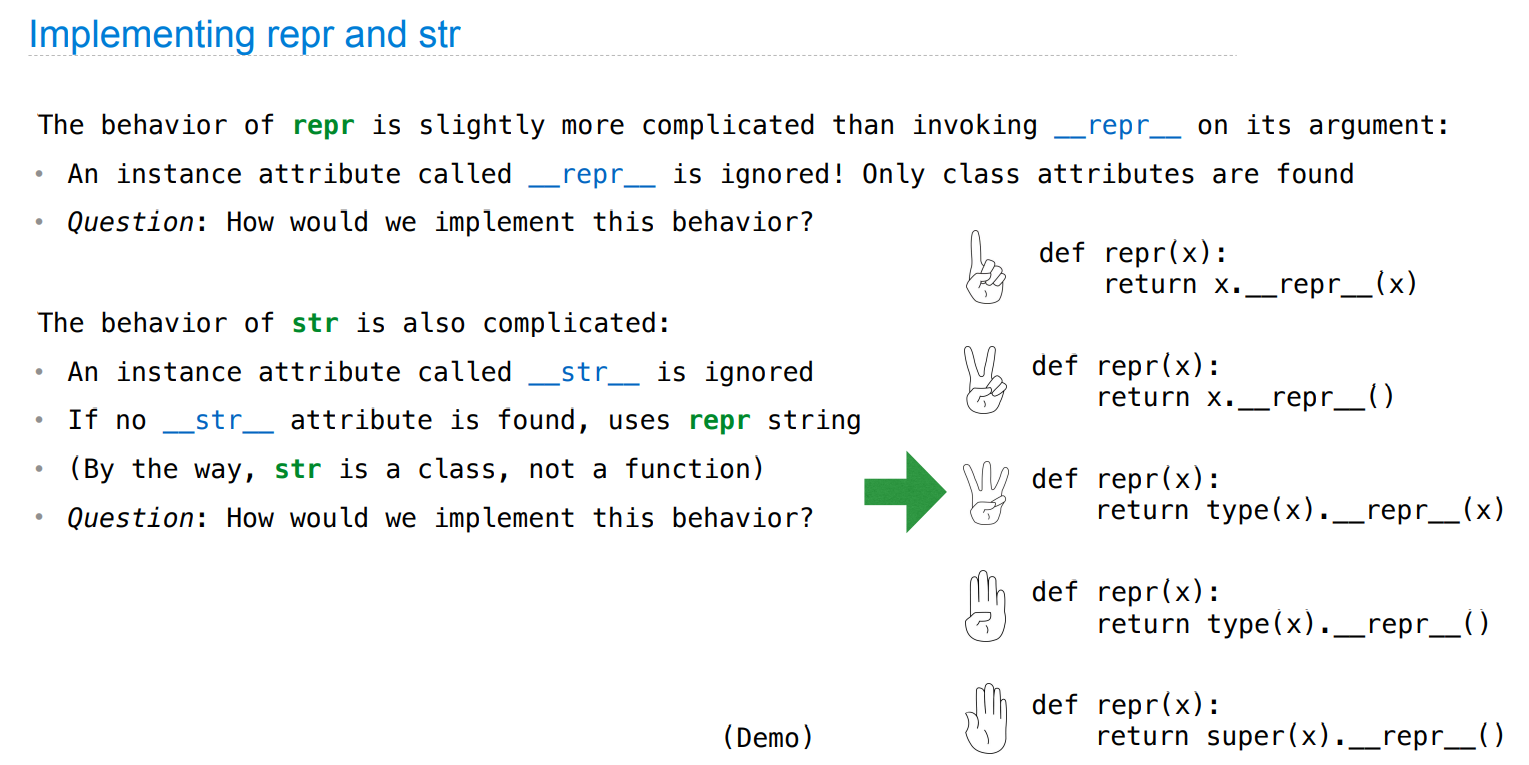
class Bear:
"""A Bear.
>>> oski = Bear()
>>> oski
Bear()
>>> print(oski)
a bear
>>> print(str(oski))
a bear
>>> print(repr(oski))
Bear()
>>> print(oski.__repr__())
oski
>>> print(oski.__str__())
oski the bear
>>> print(str_(oski))
a bear
>>> print(repr_(oski))
Bear()
"""
def __init__(self):
self.__repr__ = lambda: 'oski' # instance attribute
self.__str__ = lambda: 'oski the bear'
def __repr__(self): # class attribute
return 'Bear()'
def __str__(self):
return 'a bear'
具体实现:
def repr_(x):
s = type(x).__repr__(x)
if not isinstance(s, str):
raise TypeError
return s
def str_(x):
s = type(x).__str__(x)
if not isinstance(s, str):
raise TypeError
return s
接口的思想
3. Data model — Python 3.11.0 documentation
3. 数据模型 — Python 3.11.0 文档
__init__
__repr__
__add__
__bool__
__float__
Method invoked automatically when an object is constructed
Method invoked to display an object as a Python expression
Method invoked to add one object to another
Method invoked to convert an object to True or False
Method invoked to convert an object to a float (real number)
Lecture 22
Composition
实现链表、树的数据结构
Lecture 23
Efficiency
从斐波那契函数的树状递归引入
Memoization 来提高效率
(官方更好的实现: @functools.lru_cache(maxsize=128, typed=False))
快速幂
增长的数量级
时间空间复杂度
Lecture 24
Decomposition
模块化设计
Lecture 25
Data Examples
数据操作的举例
List 的内置操作。对帧的影响。区分哪些操作会新建列表,哪些操作不会。
类的操作对帧的影响
Iterables & Iterators:使用内置函数与实现。一些"一行代码实现"的技巧
Lecture 26
Web Apps (Optional)
未开放
Lecture 27
Scheme
3.2 函数式编程 (composingprograms.com)
终于开始进入正题~~~
“可以一天内学完的语言”?!
A combination that is not a call expression is a special form:
• if expression: (if )
• and and or: (and … ), (or … )
• Binding symbols: (define )
• New procedures: (define ( ) )
SICP 中的例子:


python 中也可以用 lambda 实现?
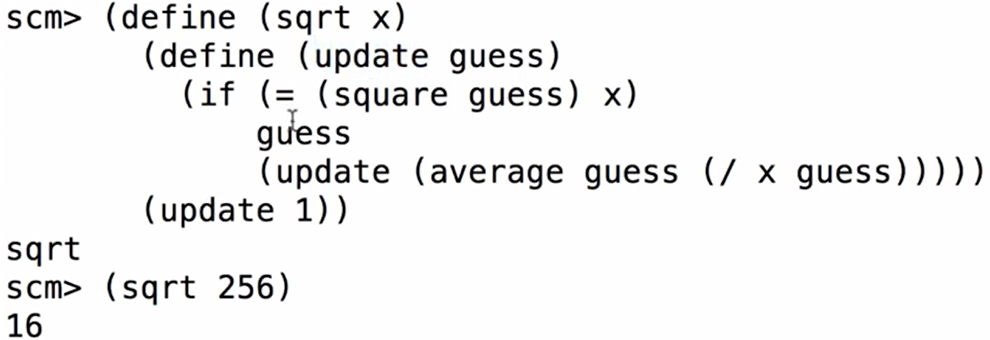
变量作用域,其他各种语言都可以有实现;python?(使用函数,不优雅)
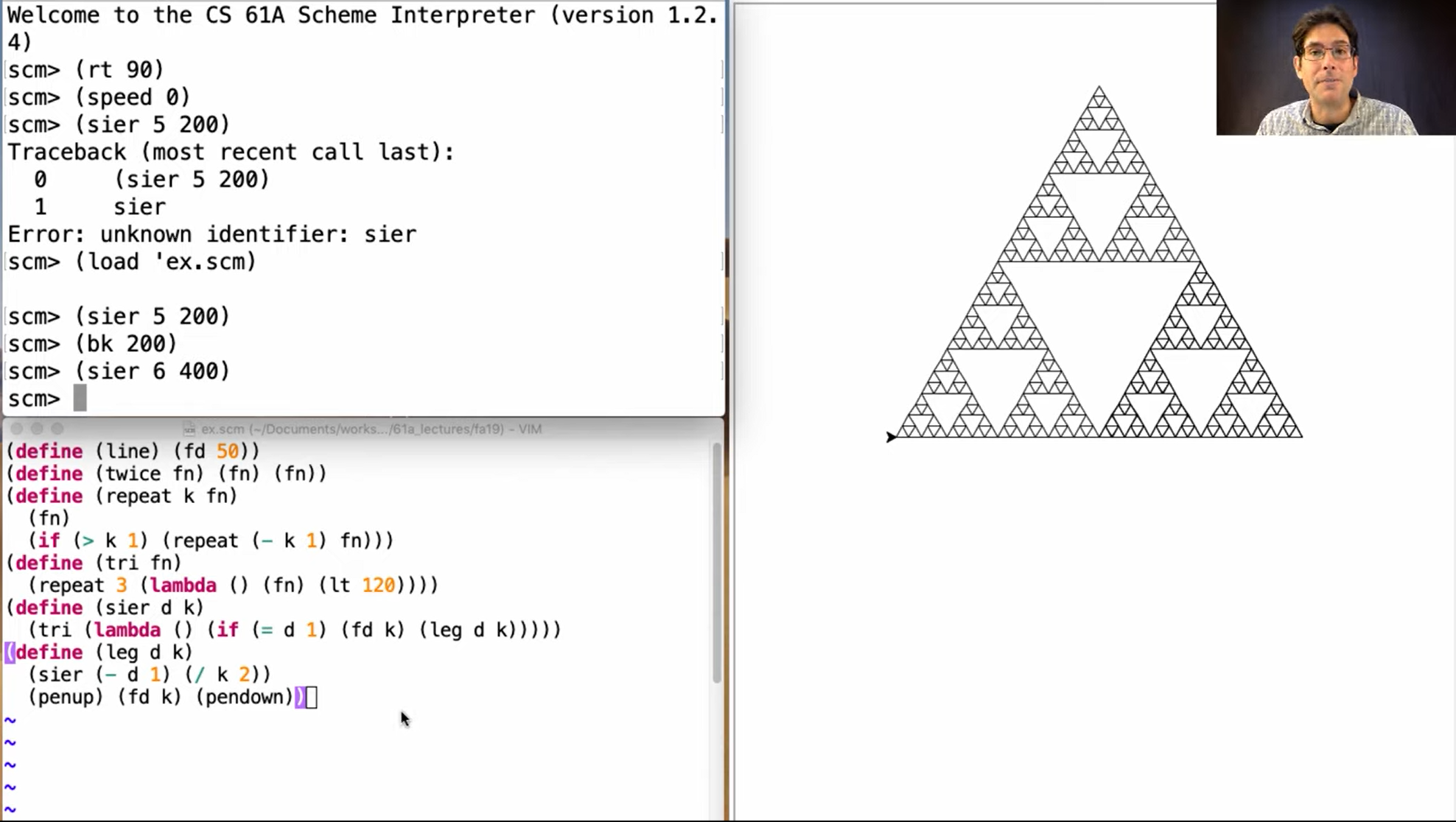
> (define (repeat k fn)
(if (> k 0)
(begin (fn) (repeat (- k 1) fn))
nil))
> (define (tri fn)
(repeat 3 (lambda () (fn) (lt 120))))
> (define (sier d k)
(tri (lambda ()
(if (= k 1) (fd d) (leg d k)))))
> (define (leg d k)
(sier (/ d 2) (- k 1))
(penup)
(fd d)
(pendown))
Lecture 28
Scheme Lists
Scheme 中唯一的数据结构

Symbolic Programming
Example: Even Subsets
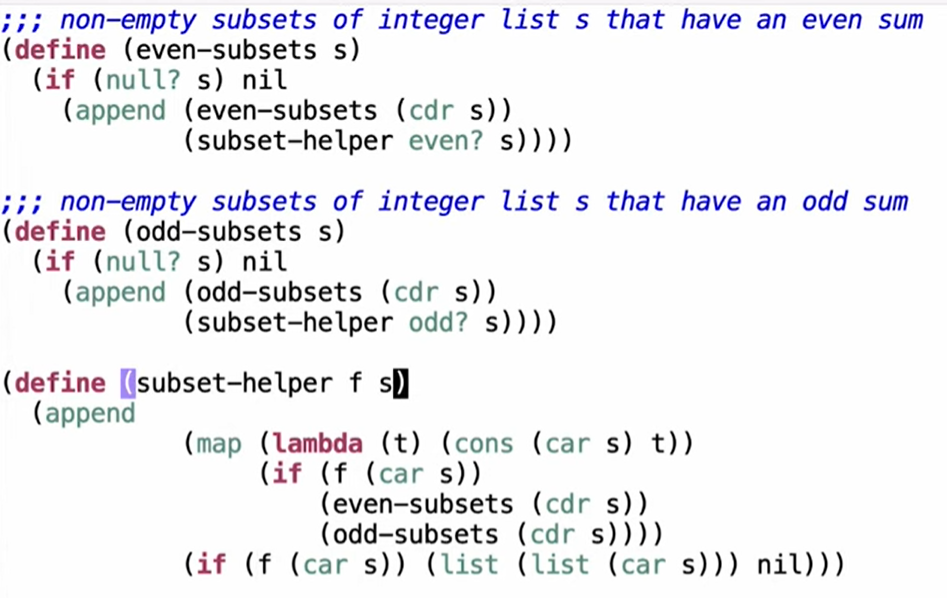
更简单发方法:使用 filter

附:#TODO#
(* 通过推广序对的定义,数值'列表'类型可以这样描述: “一个列表要么是空的,要么就是由一个数和另一个列表组成的序对。” *)
Inductive natlist : Type :=
| nil
| cons (n : nat) (l : natlist).
(* 例如,这是一个三元素列表: *)
Definition mylist := cons 1 (cons 2 (cons 3 nil)).
Lecture 29
Calculator
使用 python 做一个解释器
python 异常处理
Python exceptions are raised with a raise statement
raise <expression>
<expression> must evaluate to a subclass of BaseException or an instance of one
Exceptions are constructed like any other object. E.g., TypeError('Bad argument!')
TypeError -- A function was passed the wrong number/type of argument
NameError -- A name wasn't found
KeyError -- A key wasn't found in a dictionary
RecursionError -- Too many recursive calls
Python exceptions are raised with a raise statement
raise
must evaluate to a subclass of BaseException or an instance of one
Exceptions are constructed like any other object. E.g., TypeError(‘Bad argument!’)
TypeError – A function was passed the wrong number/type of argument
NameError – A name wasn’t found
KeyError – A key wasn’t found in a dictionary
RecursionError – Too many recursive calls
常用于不信任的输入中
Parsing
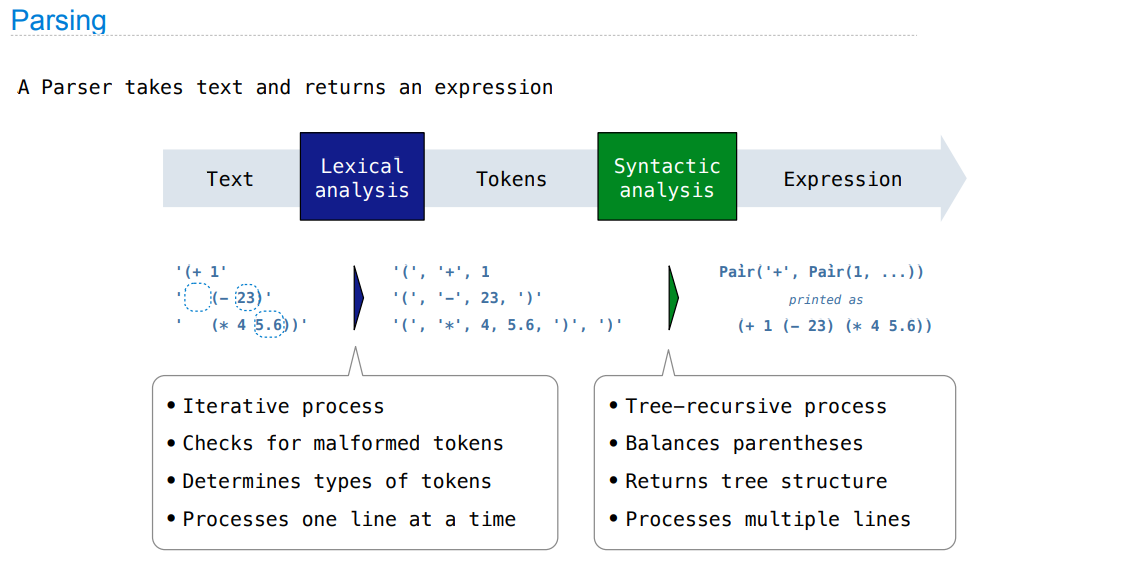
Read-Eval-Print Loop REPL
The user interface for many programming languages is an interactive interpreter
- Print a prompt
- Read text input from the user
- Parse the text input into an expression
- Evaluate the expression
- If any errors occur, report those errors, otherwise
- Print the value of the expression and repeat
Lecture 30
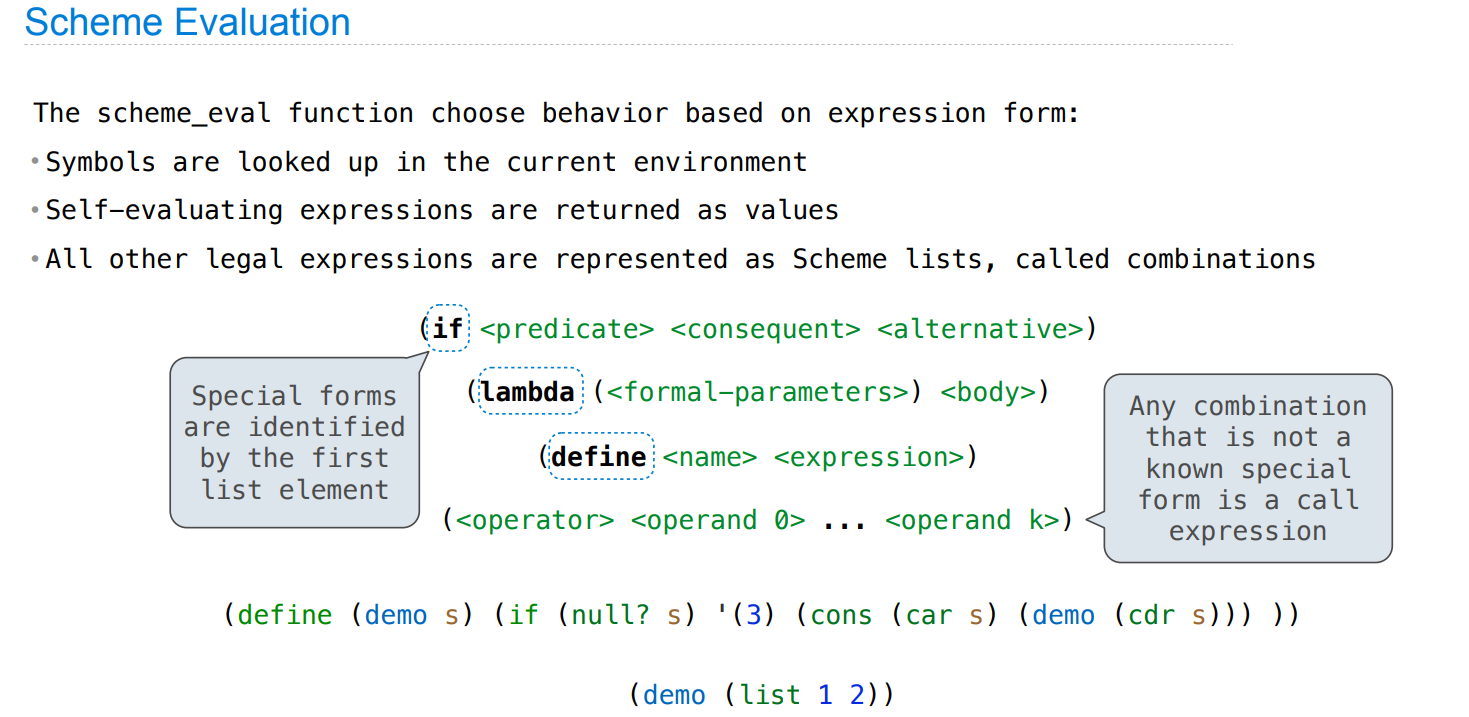
Interpreters
讲了 scheme 解释器的各部分构造,但没有讲具体实现细节
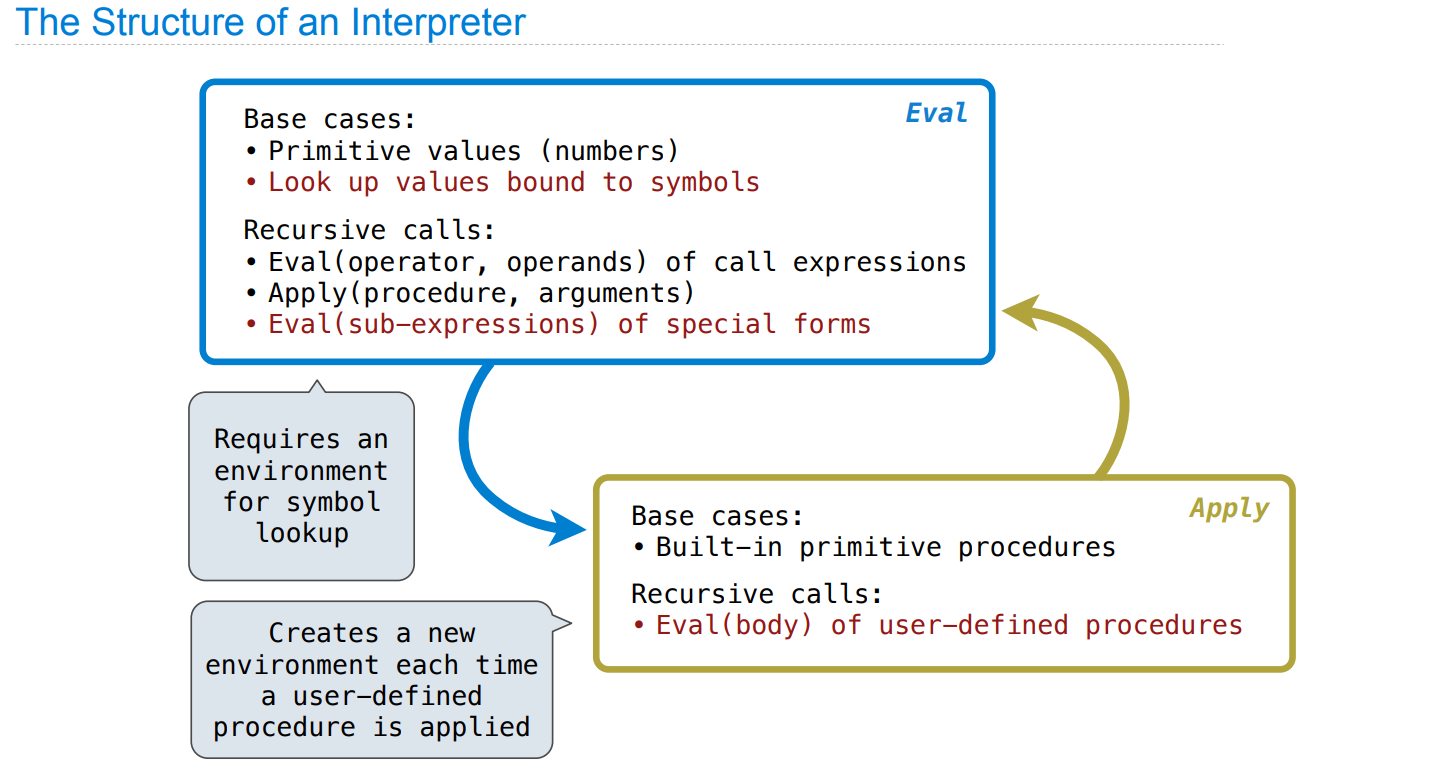
Special Forms
Logical Special Forms

这里提到了分支结构导致语句不执行的情况(跟纯函数不同,参见原书)
Quotation

Lambda Expressions
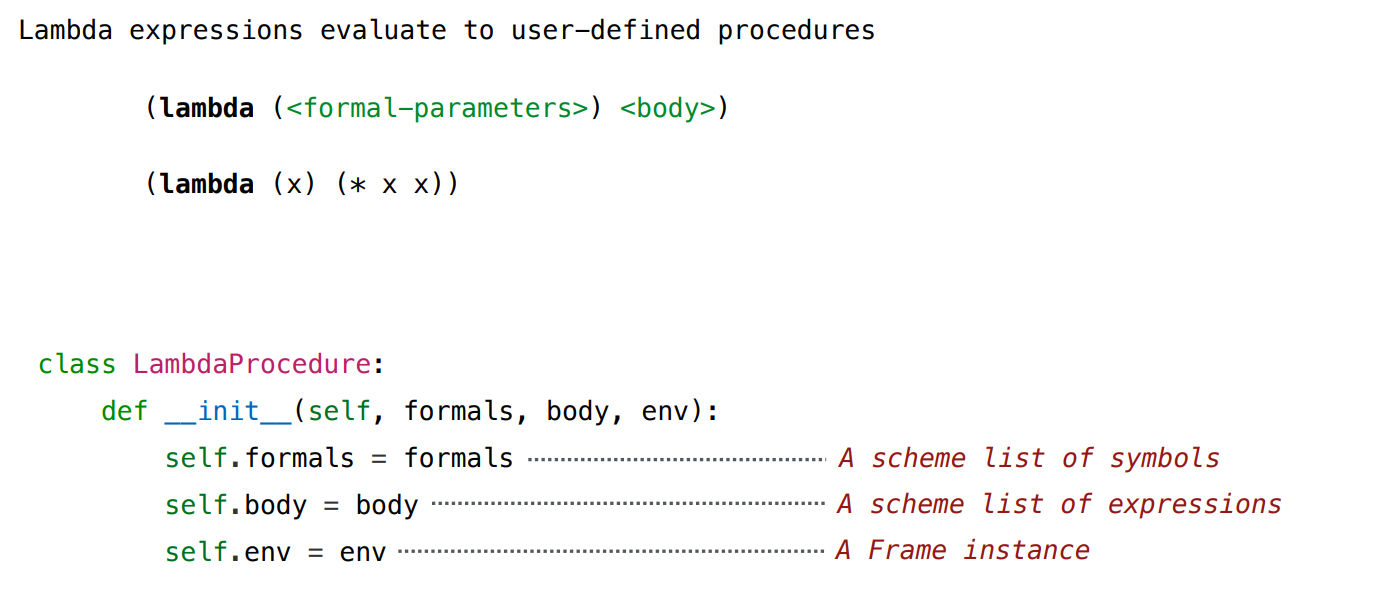
A frame represents an environment by having a parent frame
Frames are Python instances with methods lookup and define
In Project 4, Frames do not hold return values
Define Expressions
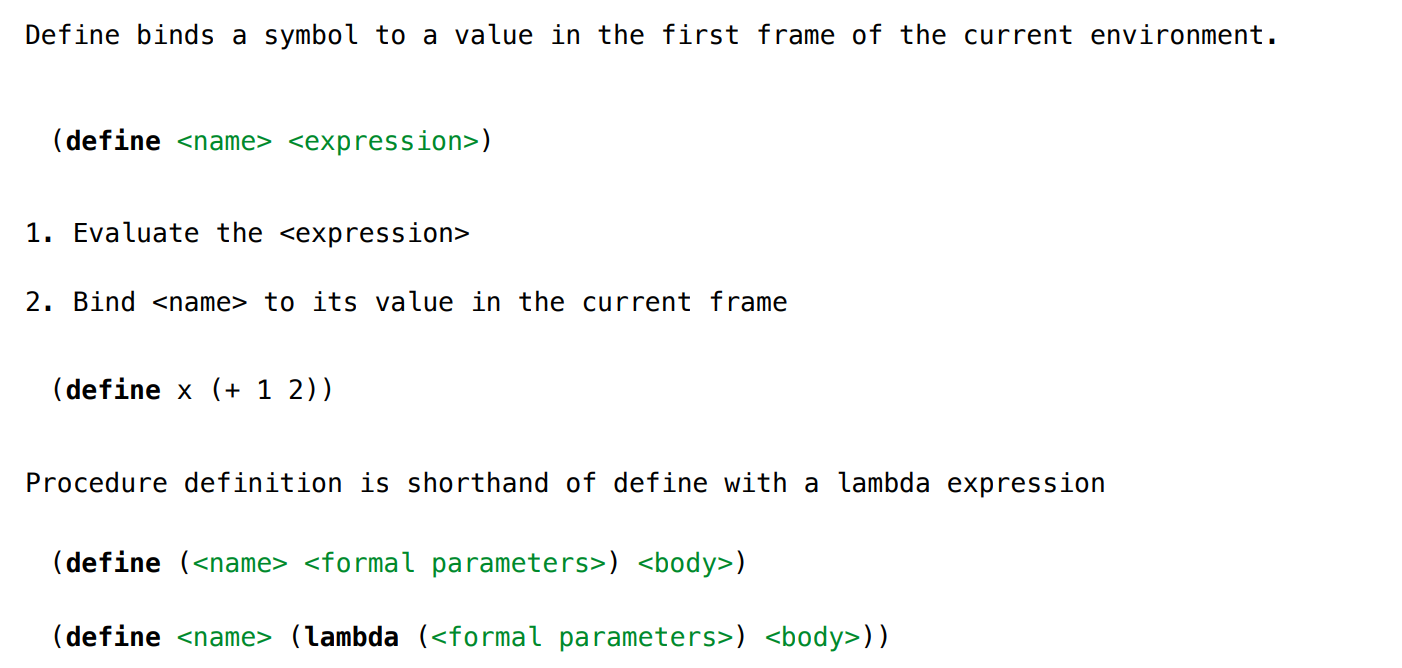
Procedure definition is shorthand of define with a lambda expression
Applying User-Defined Procedures
To apply a user-defined procedure, create a new frame in which formal parameters are bound to argument values, whose parent is the env attribute of the procedure
Evaluate the body of the procedure in the environment that starts with this new frame
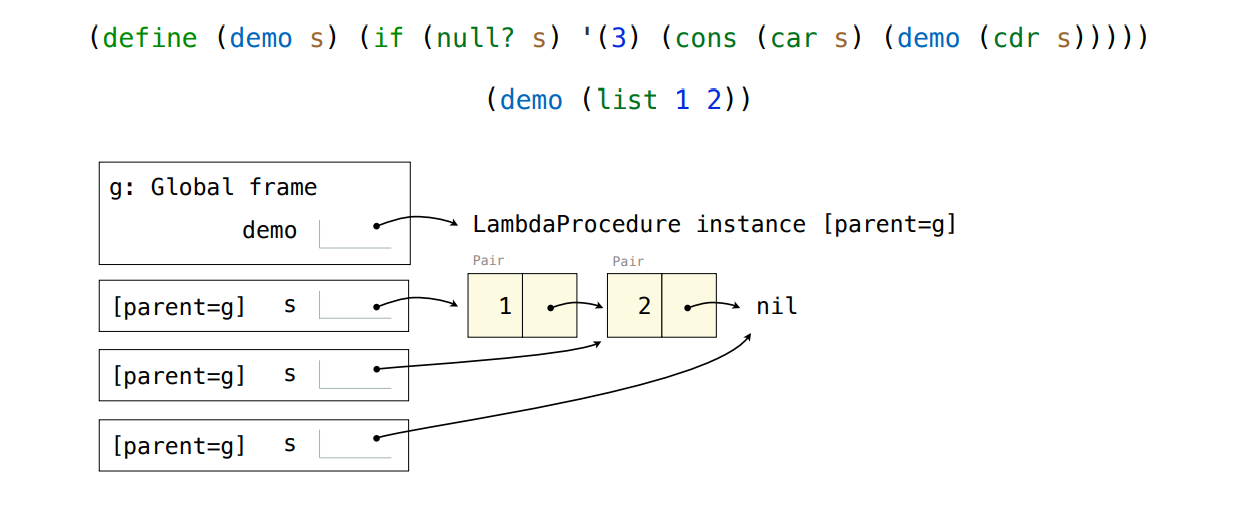
Lecture 31
Tail Calls 尾调用
Dynamic Scope
动态作用域?
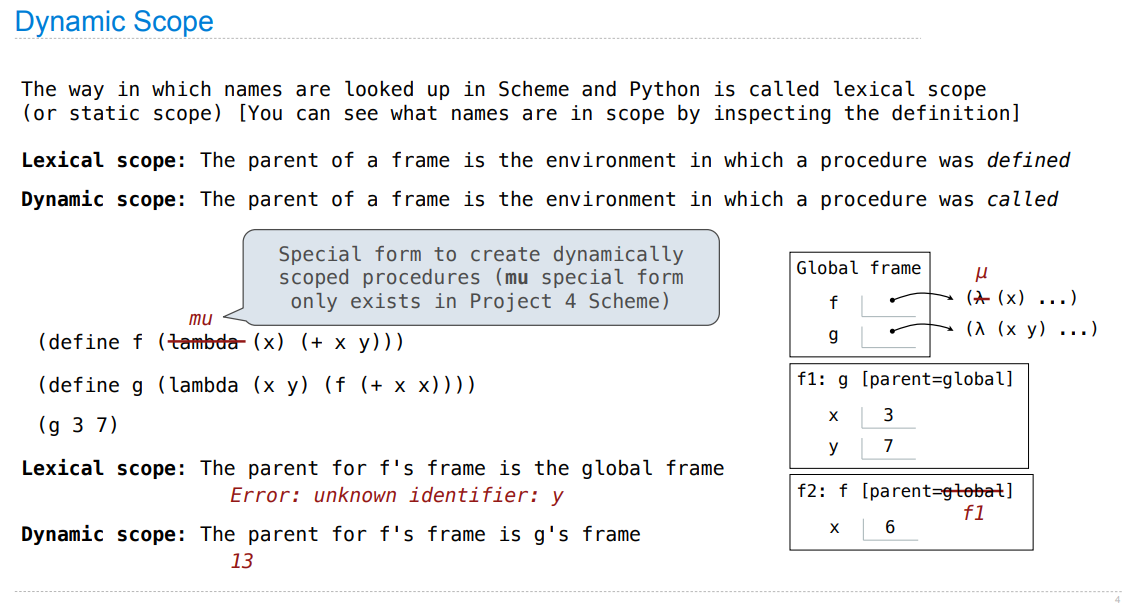
python 函数中的未定义变量是默认为全局变量(定义时无论该全局变量是否存在都不会报错,也不会在 g 函数中寻找,即不会在父 frame 中寻找,直接去 global frame 寻找,而scheme 则会)。python 好像局部作用域的概念没有其他语言强?
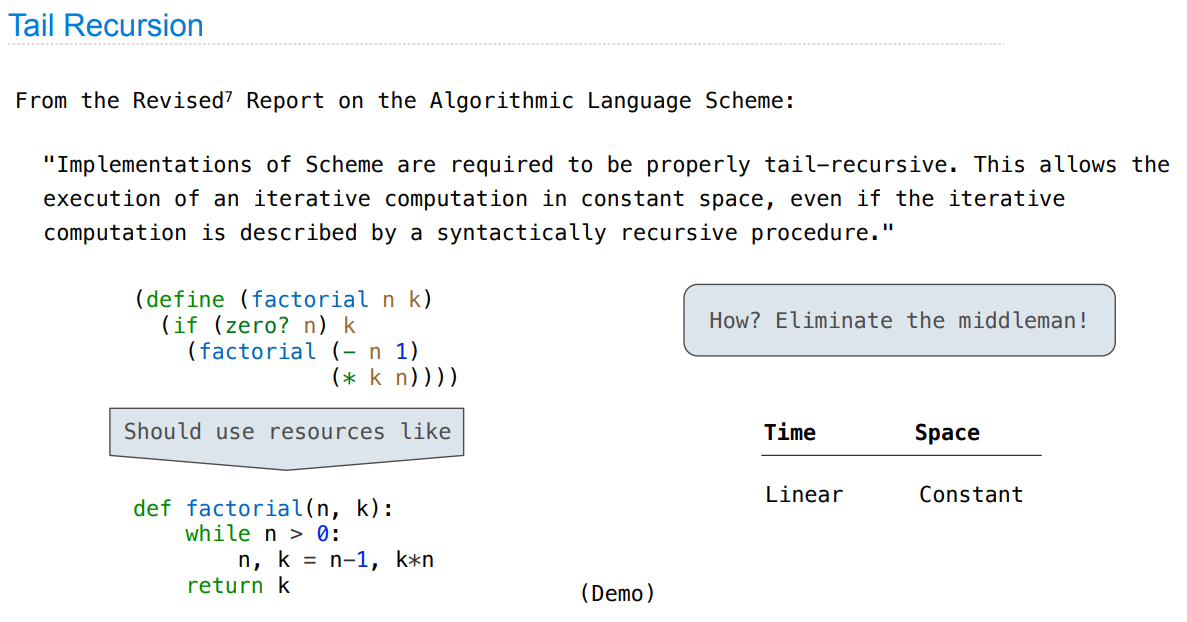
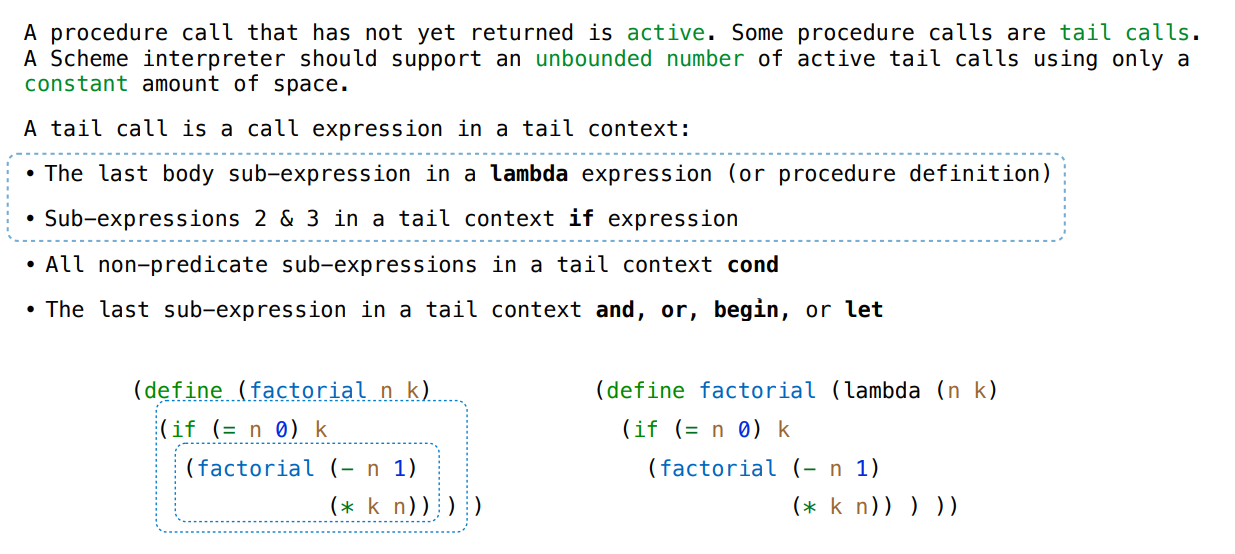
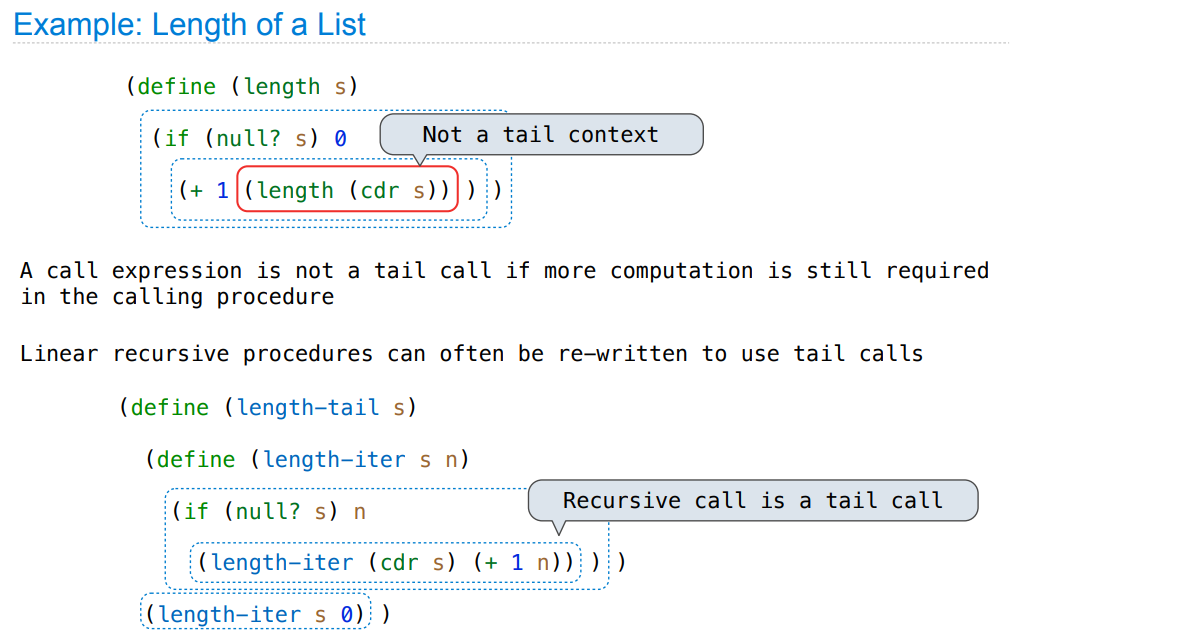
Tail Recursion
233
Functional Programming
-
All functions are pure functions
-
No re-assignment and no mutable data types
-
Name-value bindings are permanent
-
Advantages of functional programming:
- The value of an expression is independent of the order in which sub-expressions are evaluated
- Sub-expressions can safely be evaluated in parallel or only on demand (lazily)
- Referential transparency: The value of an expression does not change when we substitute one of its subexpression with the value of that subexpression
But… no for/while statements! Can we make basic iteration efficient? Yes!
关于 python 的尾递归优化的一些参考:
Python开启尾递归优化! - 简书 (jianshu.com)
尾调用 - 维基百科,自由的百科全书 (wikipedia.org)
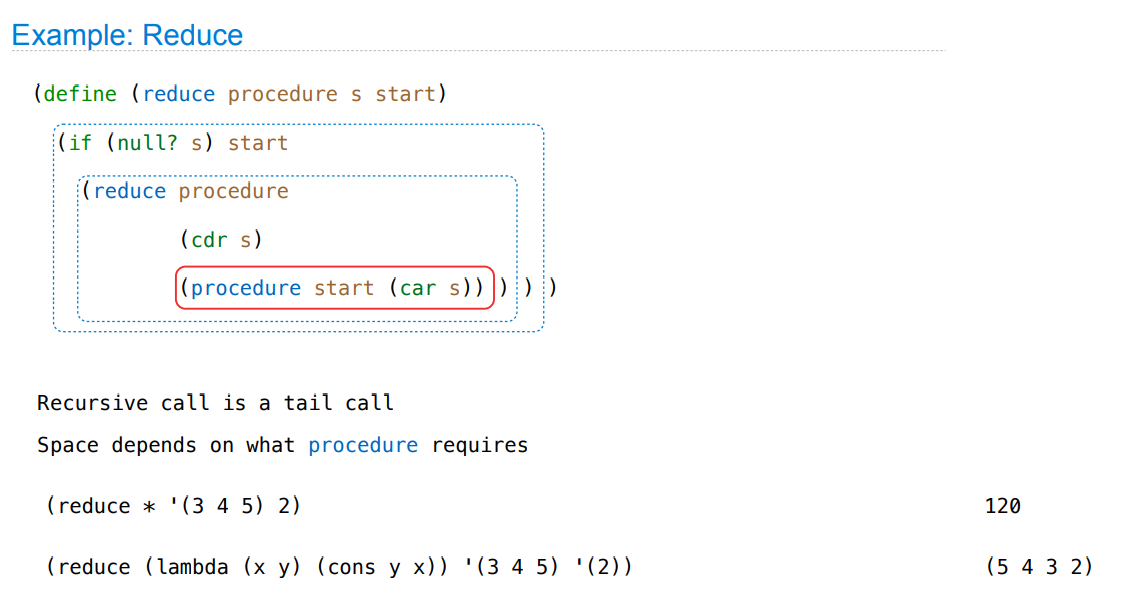
Map and Reduce
建立尾调用
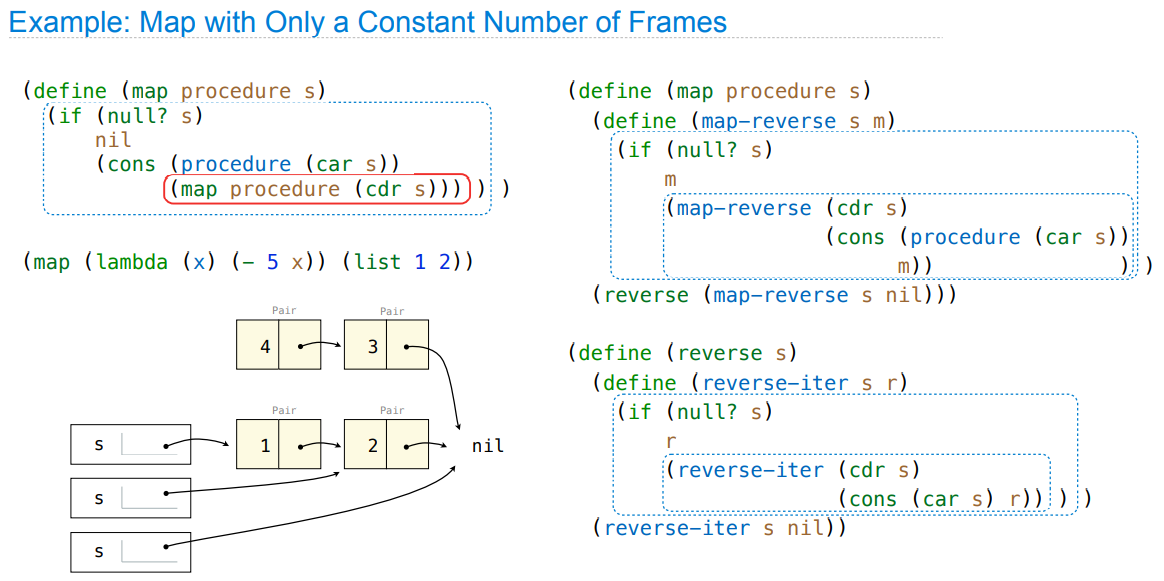
General Computing Machines
Interpreters are General Computing Machine
An interpreter can be parameterized to simulate any machine
Our Scheme interpreter is a universal machine
A bridge between the data objects that are manipulated by our programming language and the programming language itself
Internally, it is just a set of evaluation rules
解释器是通用计算机
解释器可以被参数化,以模拟任何机器
我们的Scheme解释器是一个通用机器
是我们的编程语言所操作的数据对象与编程语言本身之间的桥梁
内在地,它只是一套评估规则
Lecture 32
Programs as Data 程序作为数据
有些内容只在 recording 中有, 而在 YouTube 上的视频没有。但是 recording 外部人员听不了 QAQ

Quasiquotation

一种方便强大的抽象方式,其他语言能不能实现?#TODO#
Example: While statement

Lecture 33
Macros
宏
配合引号表达式达成更完善的抽象手段
Macros Perform Code Transformations
A macro is an operation performed on the source code of a program before evaluation
Macros exist in many languages, but are easiest to define correctly in a language like Lisp
Scheme has a define-macro special form that defines a source code transformation
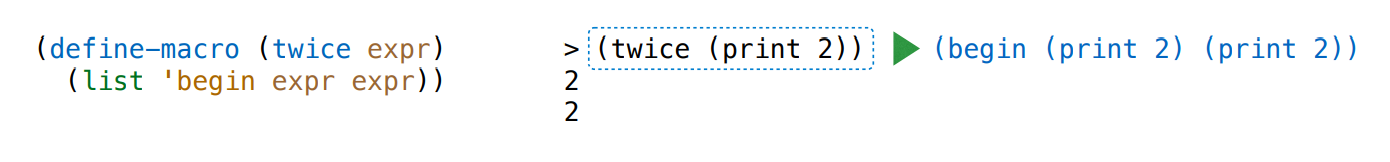
Evaluation procedure of a macro call expression:
- Evaluate the operator sub-expression, which evaluates to a macro
- Call the macro procedure on the operand expressions without evaluating them first
- Evaluate the expression returned from the macro procedure
有点像正则序求值的概念
正则序求值:“完全展开而后归约”的求值模型
应用序求值:“先对参数求值而后应用”的求值模型
一个应用例子:实现类似断言assert的功能并输出错误
; Macros
(define x -2)
(define (check val) (if val 'Passed 'Failed))
(check (> x 0))
(define-macro (check expr) (list 'if expr ''Passed ''Failed))
(check (> x 0))
(define-macro (check expr) (list 'if expr ''Passed (list 'quote (list 'Failed: expr))))
(check (> x 0))


For Macro
用宏实现 Scheme 里面没有的 For 语句
lambda、list 和他们的语法糖们
Define a macro that evaluates an expression for each value in a sequence

; For
(define (map fn vals)
(if (null? vals)
()
(cons (fn (car vals))
(map fn (cdr vals)))))
(map (lambda (x) (* x x)) '(2 3 4 5))
(define-macro (for sym vals expr)
(list 'map (list 'lambda (list sym) expr) vals))
(define-macro (for sym vals exprs)
`(map (lambda (,sym) ,@exprs) ,vals))
(for x '(2 3 4 5) (* x x))
Tracing Recursive Calls
另一个例子:实现 @trace
def trace(fn):
def traced(n):
print(f'{fn.__name__}({n})')
return fn(n)
return traced
@trace
def fact(n):
if n == 0:
return 1
else:
return n * fact(n - 1)
>>> fact(5)
fact(5)
fact(4)
fact(3)
fact(2)
fact(1)
fact(0)
120
(define fact (lambda (n)
(if (zero? n) 1 (* n (fact (- n 1))))))
(define original fact)
(define fact (lambda (n)
(print (list 'fact n))
(original n)))
scm> (fact 5)
(fact 5)
(fact 4)
(fact 3)
(fact 2)
(fact 1)
(fact 0)
120
;; 使用宏后
;; E.g., (trace (fact 5))
(define-macro (trace expr)
(define operator (car expr))
`(begin
(define original ,operator)
(define ,operator (lambda (n)
(print (list (quote ,operator) n))
(original n)))
(define result ,expr)
(define ,operator original)
result))
(fact 5)
(trace (fact 5))
(fact 5)
仍待优化:现在输入函数参数还只能固定为1
但相比 Python 实现的优势在于可以自由选择是否被 trace。(装饰器装饰后就永久被装饰了)
cool~
Lecture 34
SQL
这里有些很好玩的:同学们都 tql
Optional Contest: Scheme Art | CS 61A Fall 2022
还有往年内容~
一些有趣的摘录如下:
Quine
The marvelous quine:
a program that prints itself.
A strange loop, indeed!Tokens: 1901
code: ttps://code.cs61a.org/fa21/proj/scheme_gallery/entries/f8134ff2/contest.scm
【翻译】Quine - 自我复制的程序(上) - 知乎 (zhihu.com)
exec(s:='print("exec(s:=%r)"%s)')fiat lux
Light rays aimlessly
bouncing everywhere just like
61A kidsTokens: 966
View Code View Primitives
A Random Tree and Blossom
Plum blossoms from the bitter cold.
梅花香自苦寒来。
Does pseudorandom == random?Tokens: 271
View Code
A Line I’m Submitting So I Can Satisfy The Urge To Complete Every Assignment (摆烂人 ;-)
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-CJA2N0LL-1670951751267)(http://framist-bucket-openread.oss-cn-shanghai.aliyuncs.com/img/net-img-artwork-20221206011130-xgyc2n4.png)]
I must submit now
It’s an urge I can’t avoid
Now please forgive meTokens: 16
View Code
Databases
为什么会突然提到数据库?
Database management systems (DBMS)
declarative languages
In declarative languages(声明式语言) such as SQL & Prolog:
- A “program” is a description of the desired result
- The interpreter figures out how to generate the result
In imperative languages(命令式语言) such as Python & Scheme:
- A “program” is a description of computational processes
- The interpreter carries out execution/evaluation rules
Prolog - 维基百科,自由的百科全书 (wikipedia.org)
这样看来 Prolog 确实像SQL,是同一类语言,只不过查询的是成真赋值。
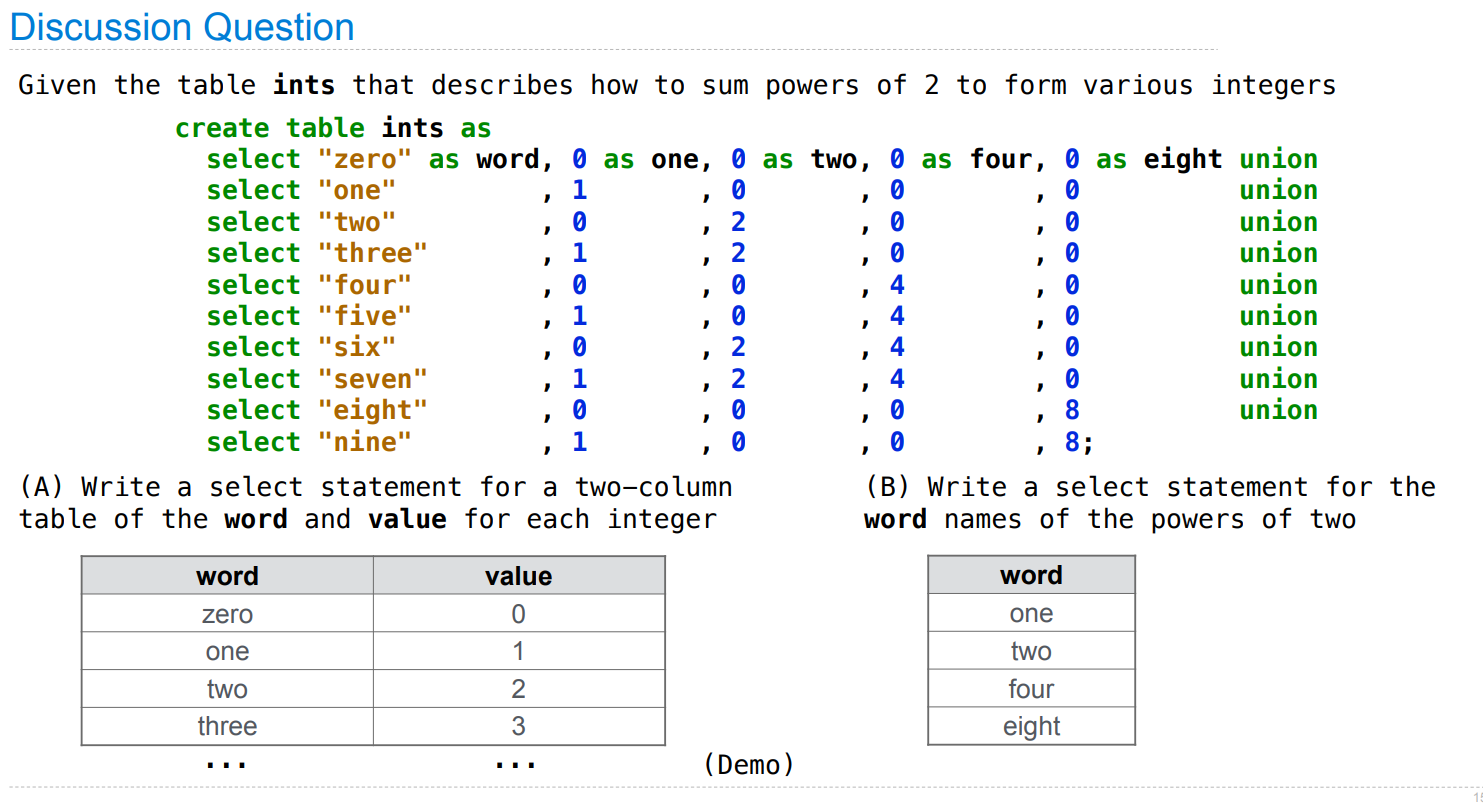
Arithmetic
Lecture 35
Tables
Joining Tables
表的连接(得好好复习一下数据库了,先就大致听一下,不是本课程的重点)
Aliases and Dot Expressions
别名和点表达式
Two tables may share a column name; dot expressions and aliases disambiguate column values
SELECT [columns] FROM [table] WHERE [condition] ORDER BY [order];
[table] is a comma-separated list of table names with optional aliases
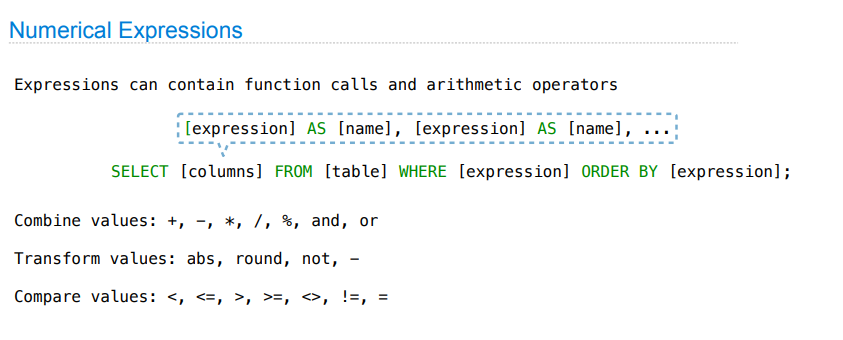
Numerical Expressions
String Expressions

Lecture 36
Aggregation (Video Only)
(聚合)继续讲 SQL
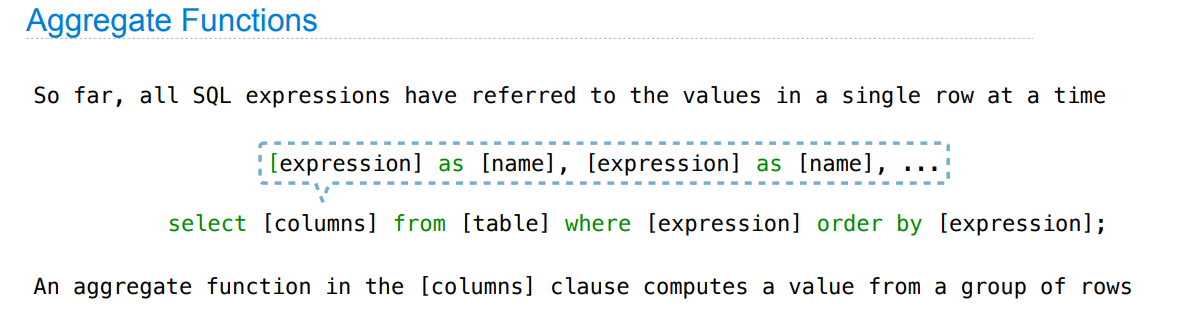

Groups
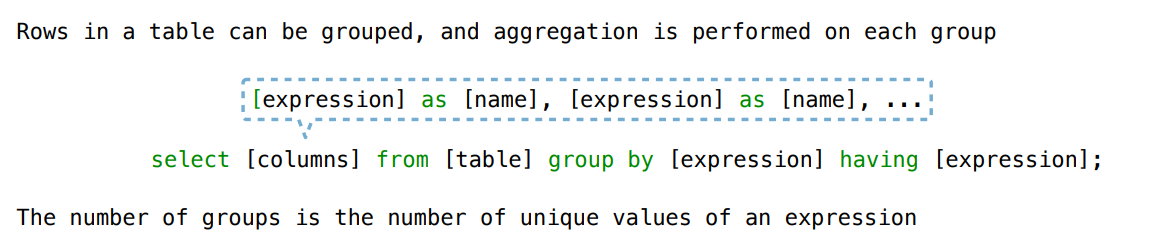
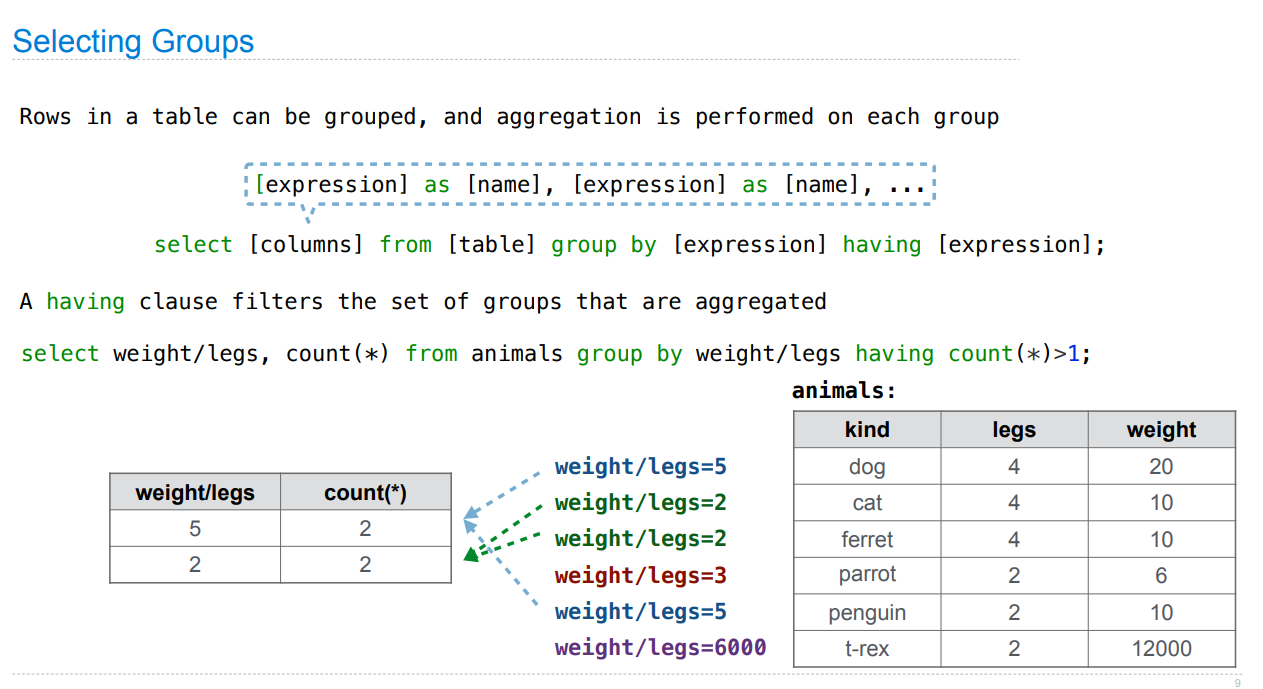
Lecture 37
Databases (Optional)
继续数据库原理
与 python 的 sqlite3 的一些对数据库的交互
Lecture 38
Final Examples
How to Design Programs
From Problem Analysis to Data Definitions Identify the information that must be represented and how it is represented in the chosen programming language. Formulate data definitions and illustrate them with examples.
Signature, Purpose Statement, Header State what kind of data the desired function consumes and produces. Formulate a concise answer to the question what the function computes. Define a stub that lives up to the signature.
Functional Examples Work through examples that illustrate the function’s purpose.
Function Template Translate the data definitions into an outline of the function.
Function Definition Fill in the gaps in the function template. Exploit the purpose statement and the examples.
Testing Articulate the examples as tests and ensure that the function passes all. Doing so discovers mistakes. Tests also supplement examples in that they help others read and understand the definition when the need arises—and it will arise for any serious program.
从问题分析到数据定义 确定必须表示的信息,以及如何在所选择的编程语言中表示这些信息。拟定数据定义,并举例说明。
签名、目的声明、标题 说明所需的函数会消耗和产生什么样的数据。对函数计算的问题提出一个简洁的答案。定义一个符合签名的存根。
功能实例 通过实例来说明函数的目的。
函数模板 将数据定义转化为函数的大纲。
函数定义 填补函数模板中的空白。利用目的声明和例子。
测试 将例子阐述为测试,并确保函数通过所有测试。这样做可以发现错误。测试也是对例子的补充,因为它们可以帮助其他人在需要时阅读和理解定义–任何严肃的程序都会出现这种情况。
Lecture 39
Conclusion
没有录像只有 slides 😭
之后就是 RRR week (Reading, Review, and Recitation)
其他参考
课程给出的提纲:
61a-mt1-study-guide.key (cs61a.org)
61a-mt2-study-guide.key (cs61a.org)
他人的笔记与感想:
最好的CS入门课:CS61a学后感 - 知乎 (zhihu.com)
分章节来说,CS61a主要教了以下这些内容:
用函数构建抽象关系
- 函数与函数设计
- 控制
- 高级函数
- 递归函数
用数据构建抽象关系
- 数据抽象
- 可变数据
- 面向对象编程
解释(interpreting)计算机程序
- 函数式编程
- 异常
- 解释器的开发
数据处理
- 声明式编程




![[附源码]Python计算机毕业设计SSM基于web的烟草售卖系统(程序+LW)](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/4920850550de4b04a964e055cef6261a.png)



![[附源码]Node.js计算机毕业设计电影推荐系统Express](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/a56f0ca3043f4465b792709fd622392a.png)