目录
一、什么是虚拟主机
二、编写虚拟主机代码
🍅 1、准备工作
🍅 2、实现exchange相关操作
🎄实现创建交换机exchangeDeclare
🎄 实现 删除交换机exchangeDelete
🍅 3、实现queue相关操作
🎄实现创建队列queueDeclare
🎄实现删除队列queueDelete
🍅 4、实现binding相关操作
🎄 实现交换机的转发规则
🎄 创建绑定queueBind
🎄 删除绑定queueUnbind
🍅 5、实现basicPublish
🎄实现basicPublish类
🎄 完善router类中的代码
三、测试routeTopic
🍅 1、准备工作和收尾工作
🍅 2、编写测试方法
一、什么是虚拟主机
虚拟主机,就类似于MySQL的database,把交换机,队列,绑定,消息等进行逻辑上的隔离。
这里只实现单个虚拟主机,不仅要管理数据,还要提供一些核心API,供上层代码进行调用。
这里的核心API,主要就是要把之前写的内存中的数据管理和硬盘的数据管理穿起来。
核心API:
(1)创建交换机 exhcangeDeclare
(2)删除交换机 exchangeDelete
(3)创建队列 queueDeckare
(4)删除队列 queueDelete
(5)创建绑定 queueBind
(6)删除绑定 queueUnbind
(7)发送消息 basicPublish
(8)订阅消息 basicCosume
(9)确认消息 basicAck
二、编写虚拟主机代码
🍅 1、准备工作
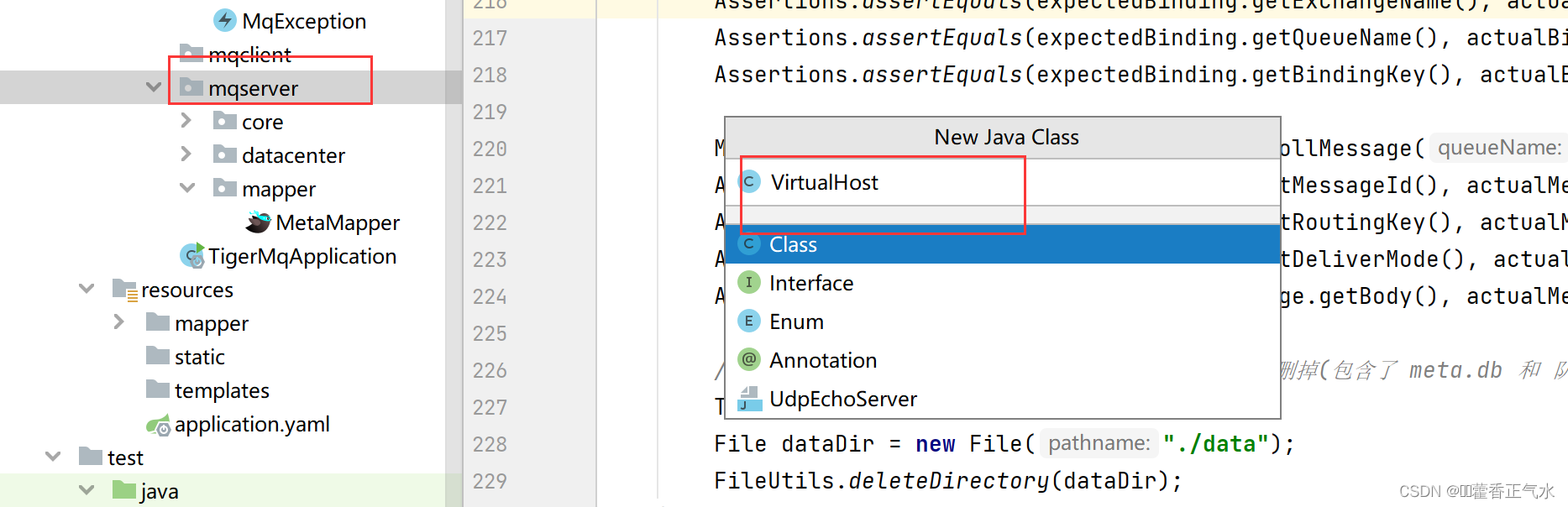
创建一个VirtualHost表示虚拟主机,其中每一个虚拟主机都管理着自己的交换机、队列、绑定、消息和数据,并且提供了一些api供上层使用。
/*
* 表示虚拟主机
* 每个虚拟主机都相当于一个消息队列,管理者自己的交换机、队列、绑定....
* 提供了api供上层调用
* */
@Data
public class VirtualHost {
private String vitualHostName;
private MemoryDataCenter memoryDataCenter = new MemoryDataCenter();
private DiskDataCenter diskDataCenter = new DiskDataCenter();
/*
* 创建构造方法
* */
public VirtualHost(String name){
this.vitualHostName = name;
// MemoryDataCenter只需要new对象
// DiskDataCenter需要进行初始化操作,建库建表和初始数据的设定
diskDataCenter.init();
// 还需要针对硬盘的数据进行恢复到内存中
try{
memoryDataCenter.recovery(diskDataCenter);
}catch (IOException | MqException | ClassNotFoundException e ){
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("[VirtualHost]恢复内存数据失败");
}
}
}注意:有关创建、删除等操作,无法避免的在多线程环境下面进行,所以后续为了保证线程安全,对一些操作还需要加锁。
这里创建一个统一的锁对象,在上面的代码中还新增几条成员变量:
//作为交换机的锁对象
private final Object exchangeLocker = new Object();
//针对队列的锁对象
private final Object queueLocker = new Object();🍅 2、实现exchange相关操作
表示交换机和虚拟主机之间的关系:使用虚拟主机的名字 + 交换机的真实名字
🎄实现创建交换机exchangeDeclare
public boolean exchangeDeclare(String exchangeName, ExchangeType exchangeType, boolean durable){
// 1、把交换机的名字,加上虚拟主机作为前缀
exchangeName = virtualHostName + exchangeName;
try{
synchronized (exchangeLocker){
// 1.判定交换机是否存在,直接通过内存查询
Exchange existsExchange = memoryDataCenter.getExchange(exchangeName);
if (existsExchange != null){
// 该交换机已经存在
System.out.println("[VirtualHost]交换机已经存在!exchangeName = "+ exchangeName);
return true;
}
// 2、创建交换机,先构造Exchange对象
Exchange exchange = new Exchange();
exchange.setName(exchangeName);
exchange.setType(exchangeType);
exchange.setDurable(durable);
// 3、把交换机对象写入硬盘
if (durable){
diskDataCenter.insertExchange(exchange);
}
// 4、把交换机对象写入内存
memoryDataCenter.insertExchange(exchange);
System.out.println("[VirtualHost] 交换机创建完成!exchangeName = " + exchangeName);
}
return true;
}catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("[VirtualHost]交换机创建失败!exchangName = " + exchangeName );
e.printStackTrace();
return false;
}
}🎄 实现 删除交换机exchangeDelete
public boolean exchangeDelete(String exchangeName){
exchangeName = virtualHostName + exchangeName;
try{
synchronized (exchangeLocker){
// 1.先找到对应的交换机
Exchange toDelete = memoryDataCenter.getExchange(exchangeName);
if (toDelete == null){
throw new MqException("[VirtualHost]交换机不存在无法删除");
}
// 2、删除硬盘上的数据
if (toDelete.isDurable()){
diskDataCenter.deleteExchange(exchangeName);
}
// 3、删除内存中的交换数据
memoryDataCenter.deleteExchange(exchangeName);
System.out.println("[VirtualHost] 交换机删除成功!exchangeName = " + exchangeName);
}
return true;
} catch (Exception e){
System.out.println("[VirtualHost] 交换机删除失败!exchangeName = " + exchangeName);
e.printStackTrace();
return false;
}
}🍅 3、实现queue相关操作
表示队列和虚拟主机之间的关系:使用虚拟主机的名字 + 队列的真实名字
🎄实现创建队列queueDeclare
// 创建队列
public boolean queueDeclare(String queueName,boolean durable){
// 把队列的名字,拼接上虚拟主机的名字
queueName = virtualHostName + queueName;
try {
synchronized (queueLocker){
//1、判定队列是否存在
MSGQueue exixtsQueue = memoryDataCenter.getQueue(queueName);
if (exixtsQueue != null){
System.out.println("[VirtualHost]队列已经存在!queueName = " + queueName);
return true;
}
// 2、创建队列对象
MSGQueue queue = new MSGQueue();
queue.setName(queueName);
queue.setDurable(durable);
// 3、写硬盘
if(durable){
diskDataCenter.insertQueue(queue);
}
// 4、写内容
memoryDataCenter.insertQueue(queue);
System.out.println("[VirtualHost]队列创建成功!queueName = " + queueName);
}
return true;
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("[VirtualHost]队列创建失败!queueName = " + queueName);
e.printStackTrace();
return false;
}
}🎄实现删除队列queueDelete
public Boolean queueDelete(String queueName){
queueName = virtualHostName + queueName;
try{
synchronized (queueLocker){
// 1、根据队列名字,查询当前队列对象
MSGQueue queue = memoryDataCenter.getQueue(queueName);
if (queue == null){
throw new MqException("[VirtualHost]队列不存在!无法删除,queueName = " + queueName);
}
// 2、删除硬盘数据
if (queue.isDurable()){
diskDataCenter.deleteQueue(queueName);
}
// 3、删除内存数据
memoryDataCenter.deleteQueue(queueName);
System.out.println("[VirtualHost]删除队列成功!queueName = " + queueName);
}
return true;
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("[VirtualHost]删除队列失败!queueName = " + queueName);
e.printStackTrace();
return false;
}
}🍅 4、实现binding相关操作
🎄 实现交换机的转发规则
创建 一个Router类,验证bindingKey是否合法,合法返回true没不合法返回false。
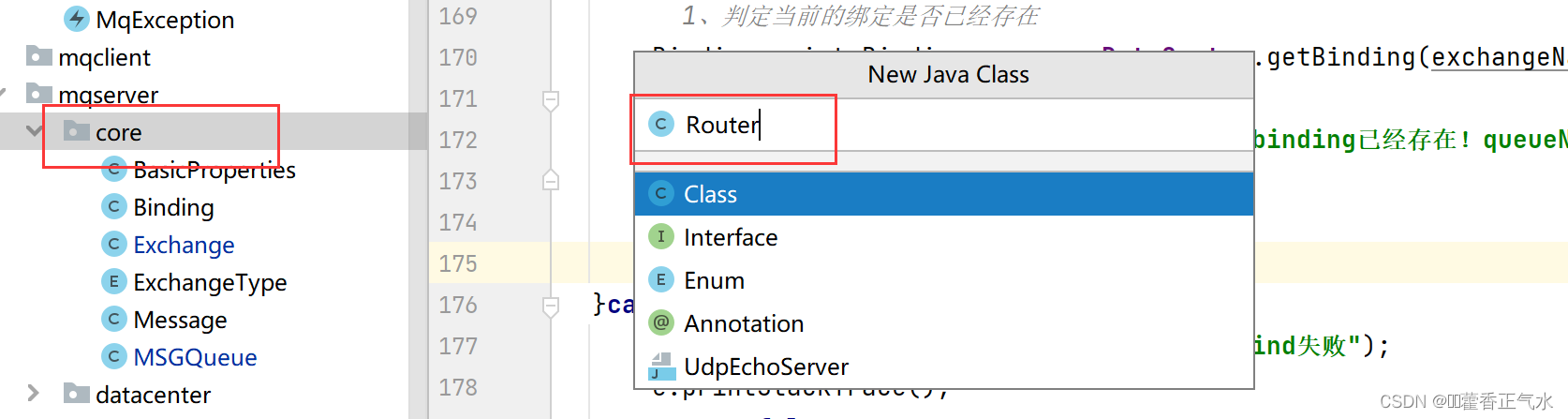
public class Router {
public boolean checkBindingKey(String bindingKey){
// 这里暂时不会写具体的步骤,等后面需要了再添加
return true;
}
}
然后再VirtualHost里面新增一条成员变量:
private Router router = new Router();🎄 创建绑定queueBind
public boolean queueBind(String queueName,String exchangeName,String bindingKey){
queueName = virtualHostName + queueName;
exchangeName = virtualHostName + exchangeName;
try {
synchronized (exchangeLocker){
synchronized (queueLocker){
// 1、判定当前的绑定是否已经存在
Binding existsBinding = memoryDataCenter.getBinding(exchangeName,queueName);
if (existsBinding != null){
throw new MqException("[VirtualHost]binding已经存在!queueName = " + queueName + ",exchangeName = " + exchangeName);
}
// 2、验证bindingKey是否合法
if (!router.checkBindingKey(bindingKey)){
throw new MqException("[VirtualHost]bindingKey非法!bindingkey = " + bindingKey);
}
// 3.创建Binding对象
Binding binding = new Binding();
binding.setExchangeName(exchangeName);
binding.setQueueName(queueName);
binding.setBindingKey(bindingKey);
// 4、获取对应的交换机和队列,如果交换机或者队列不存在,这样的绑定也是无法创建的
MSGQueue queue = memoryDataCenter.getQueue(queueName);
if (queue == null){
throw new MqException("[VirtualHost]队列不存在!queueName = " + queueName);
}
Exchange exchange = memoryDataCenter.getExchange(exchangeName);
if (exchange == null){
throw new MqException("[VirtualHost]交换机不存在!exchangeName = " + exchangeName);
}
// 5、将binding写入写硬盘
if(queue.isDurable() && exchange.isDurable()){
diskDataCenter.insertBinding(binding);
}
// 6、将binding写入内存
memoryDataCenter.insertBinding(binding);
}
}
System.out.println("[VirtualHost]绑定创建成功! exchangeName = " + exchangeName + "queueName = " + queueName);
return true;
}catch(Exception e){
System.out.println("[VirtualHost]绑定创建失败! exchangeName = " + exchangeName + "queueName = " + queueName);
e.printStackTrace();
return false;
}
}🎄 删除绑定queueUnbind
注意点:删除绑定时,按照之前删除队列和交换机的设定一样,校验绑定的交换机和队列是否为空,为空就抛出异常,删除绑定失败。但是,如果在进行删除时,发现在删除绑定之前,就已经删了交换机或者队列了,但是绑定还在,此时前面那个逻辑就有问题了。
所以这里,我们就不校验绑定的交换机或者队列是否存在,直接就尝试删除。
// 删除绑定
public boolean queueUnbind(String queueName,String exchangeName) {
queueName = virtualHostName + queueName;
exchangeName = virtualHostName + exchangeName;
try{
synchronized (exchangeLocker){
synchronized (queueLocker){
// 1、获取绑定看是否已经存在
Binding binding = memoryDataCenter.getBinding(exchangeName,queueName);
if (binding == null){
throw new MqException("[VirtualHost]删除绑定失败!绑定不存在!exchangeName = " + exchangeName + ",queueName = " + queueName);
}
//
// 2、删除硬盘上面的数据
diskDataCenter.deleteBinding(binding);
// 3、删除内存上的数据
memoryDataCenter.deleteBinding(binding);
System.out.println("[VirtualHost]删除绑定成功");
}
}
return true;
}catch(Exception e){
System.out.println("[VirtualHost]删除绑定失败!exchangeName = " + exchangeName + ",queueName = " + queueName);
e.printStackTrace();
return false;
}
}🍅 5、实现basicPublish
这一块比较复杂哈~
这个API主作用是发送消息到指定的的交换机中,然后再由交换机转发给队列。
关于交换机,这里有三种交换机:
* Direct 直接交换机 (发送时指定队列名发送)
* Fanout 扇出交换机(每个队列都发送)
* Topic 主题交换机(指定bindingKey和RoutingKey)
需求分析里面也提到了这三种交换机,看到这里忘记了的小伙伴建议看看,参考博客项目实战 — 消息队列(1) {需求分析}_️藿香正气水的博客-CSDN博客
🎄实现basicPublish类
主要分以下几步:
(1)转换交换机的名字:虚拟机名 + 交换机名
(2)检查routingkey是否合法
(3)根据交换机的名字查找交换机对象
(4)判断交换机的类型,编写具体的转发规则
🎊 以直接交换机(direct)的方式转发消息
a. 构造消息对象;
b. 查找该队列对应的对象,并判断队列是否为空
c. 队列存在就给队列写入消息
🎊 以扇出交换机(fanout)和主题交换机(topic)的方式转发消息
a. 获取到绑定对象,判断对应的队列是否存在
b. 构造下消息对象
c. 判断消息是否能转发给队列
d. 转发消息给队列
首先我们再Router类中编写再几个方法,先搭个架子,不具体实现,避免basicPublish类报错
public class Router {
// 判断routingKey和BindingKey是否合法
public boolean checkBindingKey(String bindingKey){
return true;
}
public boolean checkRoutingKey(String routingKey){
return true;
}
// 该方法用来判定该消息是否用来转发给绑定的队列
public boolean route(ExchangeType exchangeType,Binding binding,Message message) throws MqException {
return true;
}
private boolean routeTopic(Binding binding,Message message){
return true;
}
}编写basicPublish
// 发送消息到指定的交换机或者队列中
public boolean basicPublish(String exchangeName,String routingKey,BasicProperties basicProperties,byte body[]){
try {
// 1、转换交换机的名字
exchangeName = virtualHostName + exchangeName;
// 2、检查这里的routingKey是否合法
if (router.checkRoutingKey(routingKey)){
throw new MqException("[VirtualHost]routingKey非法!routingKey = " + routingKey);
}
// 3.根据交换机的名字查找到交换机对象
Exchange exchange = memoryDataCenter.getExchange(exchangeName);
if (exchange == null){
throw new MqException("[VirtualHost]交换机不存在!exchangeName = " + exchangeName);
}
// 4、判断交换机的类型
if(exchange.getType() == ExchangeType.DIRECT){
// 按照直接交换机的方式转发消息
// 以routingKey作为队列的名字,直接把消息写入到指定的队列中
String queueName = virtualHostName + routingKey;
// 5、构造消息对象
Message message = Message.createMessageWithId(routingKey,basicProperties,body);
// 6、查找该队列对应的对象
MSGQueue queue = memoryDataCenter.getQueue(queueName);
if (queue == null) {
throw new MqException("[VirtualHost]队列不存在!queuename = " + queueName);
}
// 7、队列存在,直接给队列中写入消息
sendMessage(queue,message);
}else {
// 按照fanout和topic的方式来转发
// 找到该交换机的所有绑定,并且遍历这些绑定消息
ConcurrentHashMap<String ,Binding> bindingsMap = memoryDataCenter.getBindings(exchangeName);
for (Map.Entry<String ,Binding> entry : bindingsMap.entrySet()){
// (1)获取到该绑定对象,判断对应的队列是否存在
Binding binding = entry.getValue();
MSGQueue queue = memoryDataCenter.getQueue(binding.getQueueName());
if (queue == null){
// 存在多个队列,这里为了避免因为一个队列的失败影响到其他队列的消息传输
// 这里就不抛异常
System.out.println("[VirtualHost]basicPublish发送消息时间,发现队列不存在!queueName = " + binding.getQueueName());
continue;
}
// (2)构造消息对象
Message message = Message.createMessageWithId(routingKey,basicProperties,body);
// (3)判定这个消息是否能转发给该队列
如果fanout,所有的绑定队列都要转发
如果式topic。还需要判定bindingKey和routingKey是不是匹配
if(!router.route(exchange.getType(),binding,message)){
continue;
}
// (4)转发消息给队列
sendMessage(queue,message);
}
}
return true;
}catch (Exception e){
System.out.println("[VirtualHost]消息发送失败");
e.printStackTrace();
return false;
}
}
// 编写sendMessage
public void sendMessage(MSGQueue queue,Message message) throws IOException, MqException {
// 把消息写入到 硬盘 和 内存 中去
// 判定持久化
int deliverMode = message.getDeliverMode();
// deliverMode为1,不持久化,deliverMode 为2 表示持久化
if(deliverMode == 2){
// 写入硬盘
diskDataCenter.sendMessage(queue,message);
}
// 写入内存
memoryDataCenter.sendMessage(queue,message);
}
🎄 完善router类中的代码
首先编写route()方法,判断该消息是否需要用来转发给绑定的队列。
public boolean route(ExchangeType exchangeType,Binding binding,Message message) throws MqException {
// 根据不同的exchangeType使用不同的判定转发规则
if (exchangeType == ExchangeType.FANOUT){
// 如果是fanout类型,那么所有队列都需要转发
}else if(exchangeType == ExchangeType.TOPIC){
// 如果是topic主题交换机
return routeTopic(binding,message);
}else {
throw new MqException("[Router]交换机类型非法! exchangeType = " + exchangeType);
}
return true;
}然后编写有关topic中的一套转发规则。
首先检测routingKey和bindingKey是否合法:
有关routingKey和bindingKey的一套命名规则:
🎊 routingKey
(1)数字、字母、下划线
(2)使用“.”点号,将routingKey分割程多个部分,形如aaa.bbb.ccc
🎊 bindingKey
(1)数字、字母、下划线
(2)使用" . "点号,把整个bindingKey分成了多个部分
(3)支持两种特殊的通配符:“ * ” 和“ # ” 。* 和 #必须是作为被分割出来的独立部分, 由" . "分割。形如aaa.*.bbb
“ * ”代表可以匹配任何一个独立的部分;
“ # ”代表可以匹配任何0个或者多个独立的部分。
第一种情况(bindingKey中没有 * 和 #):此时必须要求routingKey和bindingKey一 模一样,才能够匹配成功。这种就相当于直接交换机。
第二种情况(bindingKey中有“ * ”):
设定bindingKey:aaa.*.ccc,此时如果是aaa.bbb.ccc或者aaa.b.ccc这种形式的 routingKey都能匹配成功,但是,如果是aaa.b.ccc这种就会匹配失败
第三种情况(bindingKey中有#):相当于fanout交换机。
设定bindingKey:aaa.#.ccc,
如果routingKey是以下的形式:
aaa.bbb.ccc(匹配成功)
aaa.b.b.ccc(匹配成功)
aaa.ccc(匹配成功)
aaa.b.b(匹配失败)
所以,综上所述,直接交换机和扇出交换机属于主题交换机的特例。
// routingKey构造规则:数字\字母\下划线\使用 . 分割
public boolean checkRoutingKey(String routingKey){
if (routingKey.length() == 0){
// 空字符串,routingKey为0,可能就是使用的fanout交换机
return true;
}
for (int i = 0; i < routingKey.length(); i++) {
char ch = routingKey.charAt(i);
// 判定该字符是否是大写字母
if (ch >= 'A' && ch <= 'Z'){
continue;
}
// 判定该字母是否是小写字母
if (ch >= 'a' && ch <= 'z'){
continue;
}
// 判断字母是否是阿拉伯数字
if (ch >= '0' && ch <= '9'){
continue;
}
// 判定是否是 _ 或者 .
if(ch == '_' || ch == '.'){
continue;
}
// 上面的条件不符合
return false;
}
return true;
}
// bindingKey构造规则:数字\字母\下划线\使用 . 分割\允许存在 * 和 # 作为通配符
public boolean checkBindingKey(String bindingKey){
if (bindingKey.length() == 0){
// 合法,使用直接交换机和扇出交换机,可以为空,因为此时用不到bindingKey
return true;
}
// 检查是否存在不合法字符
for (int i = 0; i < bindingKey.length(); i++) {
char ch = bindingKey.charAt(i);
if (ch >= 'A' && ch <= 'Z'){
continue;
}
if (ch >= 'a' && ch <= 'z'){
continue;
}
if (ch >= '0' && ch <= '9'){
continue;
}
if (ch == '_' || ch == '.' || ch == '*' || ch == '#'){
continue;
}
return false;
}
// 检查*或者#的位置是否正确(被 . 进行分割)
// 为什么写作\\. ,因为,在正则表达式种,"\."和"."都是特殊的字符,所以需要双\\转义
String[] words = bindingKey.split("\\.");
for (String word : words){
// 如果word为*或者#,那么长度不会大于1
if (word.length() > 1 && (word.contains("*") || word.contains("#"))){
return false;
}
}
// 约定,通配符之间的相邻关系
// 1.aaa.#.#.bbb => 非法
// 2.aaa.#.*.bbb => 非法
// 3.aaa.*.#.bbb => 非法
// 4.aaa.*.*.bbb => 合法
for (int i = 0; i < words.length; i++) {
// #.#
if(words[i].equals("#") && words[i+1].equals("#")){
return false;
}
// #.*
if (words[i].equals("#") && words[i+1].equals("*")){
return false;
}
// *.#
if (words[i].equals("*") && words[i+1].equals("#")){
return false;
}
}
return true;
}编写routeTopic()方法,考虑routingKey和bindingKey之间的匹配规则
采用双指针:
根据bindingKey的下标,判定当前下标指向的部分。
(1)指向的是普通字符串,此时要求和routingKey对应的下标指向的内容完全一致
(2)指向的是 * ,此时无论routingKey指向的是什么,指针都是前进
(3)遇到了 # ,并且如果#后面没有其他内容了,匹配上了,直接返回true
(4)遇到了#,#后面仍然有其他内容,然后拿着#后面的部分,去routingKey种找是否有相同的部分,没找到就返回fasle。如果找到了,就把routingkey的箭头指向该位置,指针继续往后走。按照前面的方式,走到末尾为止
(5)移动过程种,如果同时到达末尾,就返回true;否则返回false。
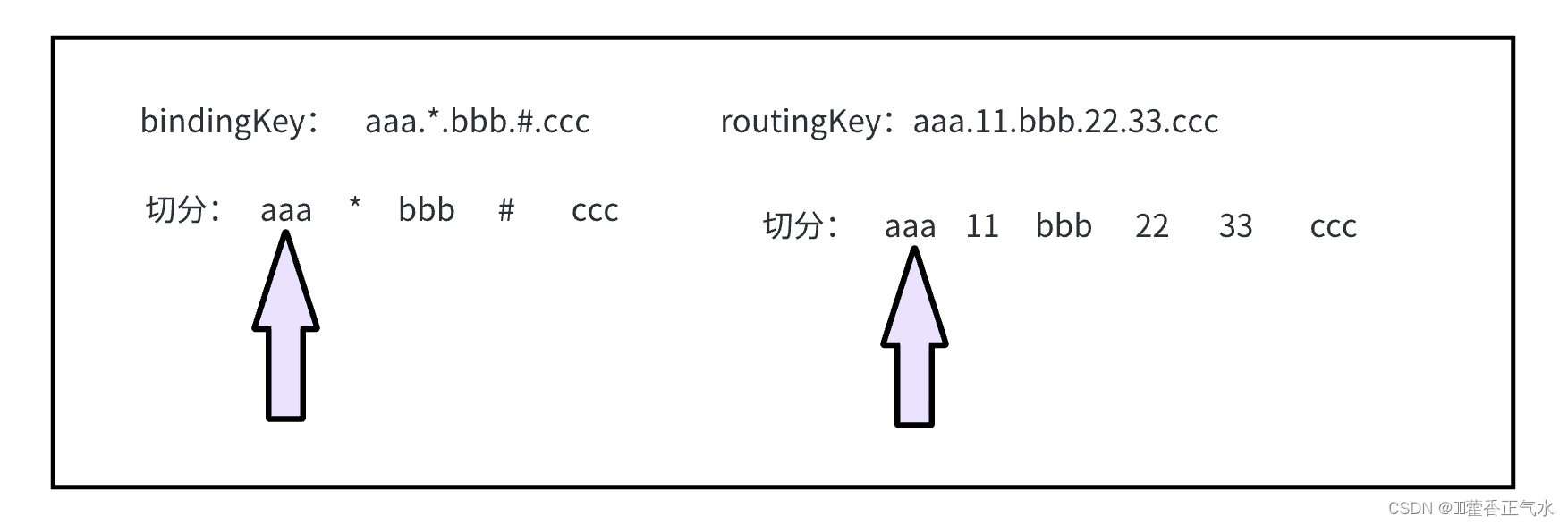
private boolean routeTopic(Binding binding,Message message){
// 1.进行切分
String[] bindingTokens = binding.getBindingKey().split("\\.");
String[] routingTokens = message.getRoutingKey().split("\\.");
// 2.引入两个下标,指向两个数组的0下标
int bindingIndex = 0;
int routingIndex = 0;
// 3.进行循环
while (bindingIndex < bindingTokens.length && routingIndex < routingTokens.length){
if (bindingTokens[bindingIndex].equals("*")){
// [1]如果遇见*,直接进入下一轮,*可以匹配到任何一个部分
bindingIndex++;
routingIndex++;
continue;
} else if (bindingTokens[bindingIndex].equals("#")){
// 如果遇到#,看还有没有下一个为止
bindingIndex++;
if (bindingIndex == bindingTokens.length){
// [3]直接到了末尾
return true;
}
// [4] #后面还有内容,继续向后
// findNextMatch用来查找该部分在routingKey的位置,返回改下标,没找到就返回-1
routingIndex = findNextMatch(routingTokens,routingIndex,bindingTokens[bindingIndex]);
if(routingIndex == -1){
// 没找到匹配的结果,匹配失败
return false;
}
// 找到了匹配的结果,继续向后匹配
bindingIndex++;
routingIndex++;
} else {
// [1]如果遇见了普通的字符串(不含#和*),如果一样就返回true
if (!bindingTokens[bindingIndex].equals(routingTokens[routingIndex])){
return false;
}
bindingIndex++;
routingIndex++;
}
}
// [5]判断是否双方同时到达末尾
if(bindingIndex == bindingTokens.length && routingIndex == routingTokens.length){
return true;
}
return true;
}
private int findNextMatch(String[] routingTokens, int routingIndex, String bindingToken) {
for (int i = routingIndex; i < routingTokens.length ; i++) {
if (routingTokens[i].equals(bindingToken)){
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
三、测试routeTopic
🍅 1、准备工作和收尾工作
创建测试类routerTests
@SpringBootTest
public class RouterTests {
private Router router = new Router();
private Binding binding = null;
private Message message = null;
@BeforeEach
public void setUp(){
binding = new Binding();
message = new Message();
}
@AfterEach
public void tearDown(){
binding = null;
message = null;
}
}以下是一些测试用例
[测试用例]
binding key routing key result
1 aaa aaa true
2 aaa.bbb aaa.bbb true
3 aaa.bbb aaa.bbb.ccc false
4 aaa.bbb aaa.ccc false
5 aaa.bbb.ccc aaa.bbb.ccc true
6 aaa.* aaa.bbb true
7 aaa.*.bbb aaa.bbb.ccc false
8 *.aaa.bbb aaa.bbb false
9 # aaa.bbb.ccc true
10 aaa.# aaa.bbb true
11 aaa.# aaa.bbb.ccc true
12 aaa.#.ccc aaa.ccc true
13 aaa.#.ccc aaa.bbb.ccc true
14 aaa.#.ccc aaa.aaa.bbb.ccc true
15 #.ccc ccc true
16 #.ccc aaa.bbb.ccc true🍅 2、编写测试方法
根据上面的测试用例编写16个测试方法
@Test
public void test1() throws MqException {
binding.setBindingKey("aaa");
message.setRoutingKey("aaa");
Assertions.assertTrue(router.route(ExchangeType.TOPIC,binding,message));
}
@Test
public void test2() throws MqException {
binding.setBindingKey("aaa.bbb");
message.setRoutingKey("aaa.bbb");
Assertions.assertTrue(router.route(ExchangeType.TOPIC,binding,message));
}
@Test
public void test3() throws MqException {
binding.setBindingKey("aaa.bbb");
message.setRoutingKey("aaa.bbb.ccc");
Assertions.assertTrue(router.route(ExchangeType.TOPIC,binding,message));
}
@Test
public void test4() throws MqException {
binding.setBindingKey("aaa.bbb");
message.setRoutingKey("aaa.ccc");
Assertions.assertFalse(router.route(ExchangeType.TOPIC,binding,message));
}
@Test
public void test5() throws MqException {
binding.setBindingKey("aaa.bbb.ccc");
message.setRoutingKey("aaa.bbb.ccc");
Assertions.assertTrue(router.route(ExchangeType.TOPIC,binding,message));
}
@Test
public void test6() throws MqException {
binding.setBindingKey("aaa.*");
message.setRoutingKey("aaa.bbb");
Assertions.assertTrue(router.route(ExchangeType.TOPIC,binding,message));
}
@Test
public void test7() throws MqException {
binding.setBindingKey("aaa.*.bbb");
message.setRoutingKey("aaa.bbb.ccc");
Assertions.assertFalse(router.route(ExchangeType.TOPIC,binding,message));
}
@Test
public void test8() throws MqException {
binding.setBindingKey("*.aaa.bbb");
message.setRoutingKey("aaa.bbb");
Assertions.assertFalse(router.route(ExchangeType.TOPIC,binding,message));
}
@Test
public void test9() throws MqException {
binding.setBindingKey("#");
message.setRoutingKey("aaa.bbb.ccc");
Assertions.assertTrue(router.route(ExchangeType.TOPIC,binding,message));
}
@Test
public void test10() throws MqException {
binding.setBindingKey("aaa.#");
message.setRoutingKey("aaa.bbb");
Assertions.assertTrue(router.route(ExchangeType.TOPIC,binding,message));
}
@Test
public void test11() throws MqException {
binding.setBindingKey("aaa.#");
message.setRoutingKey("aaa.bbb.ccc");
Assertions.assertTrue(router.route(ExchangeType.TOPIC,binding,message));
}
@Test
public void test12() throws MqException {
binding.setBindingKey("aaa.#.ccc");
message.setRoutingKey("aaa.ccc");
Assertions.assertTrue(router.route(ExchangeType.TOPIC,binding,message));
}
@Test
public void test13() throws MqException {
binding.setBindingKey("aaa.#.ccc");
message.setRoutingKey("aaa.bbb.ccc");
Assertions.assertTrue(router.route(ExchangeType.TOPIC,binding,message));
}
@Test
public void test14() throws MqException {
binding.setBindingKey("aaa.#.ccc");
message.setRoutingKey("aaa.aaa.bbb.ccc");
Assertions.assertTrue(router.route(ExchangeType.TOPIC,binding,message));
}
@Test
public void test15() throws MqException {
binding.setBindingKey("#.ccc");
message.setRoutingKey("ccc");
Assertions.assertTrue(router.route(ExchangeType.TOPIC,binding,message));
}
@Test
public void test16() throws MqException {
binding.setBindingKey("#.ccc");
message.setRoutingKey("aaa.bbb.ccc");
Assertions.assertTrue(router.route(ExchangeType.TOPIC,binding,message));
}