一、引言
在C++中,“cin”和"cout"可以说是区别于C语言的一大亮点。
但是,它的自动识别类型,其本质不过是运算符重载。若真到了能够“自动识别”的那一天,人类大概也能进入新的纪元了罢。
对于我们自己写的类,想要用cout,cin,当然是可以的,我们只需自己写它的重载即可。
本文将以“cout”为例。
二、运算符重载
1、何为运算符重载
运算符重载:
函数名: operator操作符
返回类型: 看操作符运算后返回值是什么
参数:操作符有几个操作数,它就有几个参数
其中,有5 个符号是不能进行运算符重载的::: sizeof ?: . .*
2、日期类
下面我们以日期类为例,熟悉运算符重载:
众所周知,如果直接在类中进行运算符重载,那么第一个操作数必定是隐含的this指针。
这样就会产生一个问题:本应是“cout<<d”,如今却要写成“d<<cout”
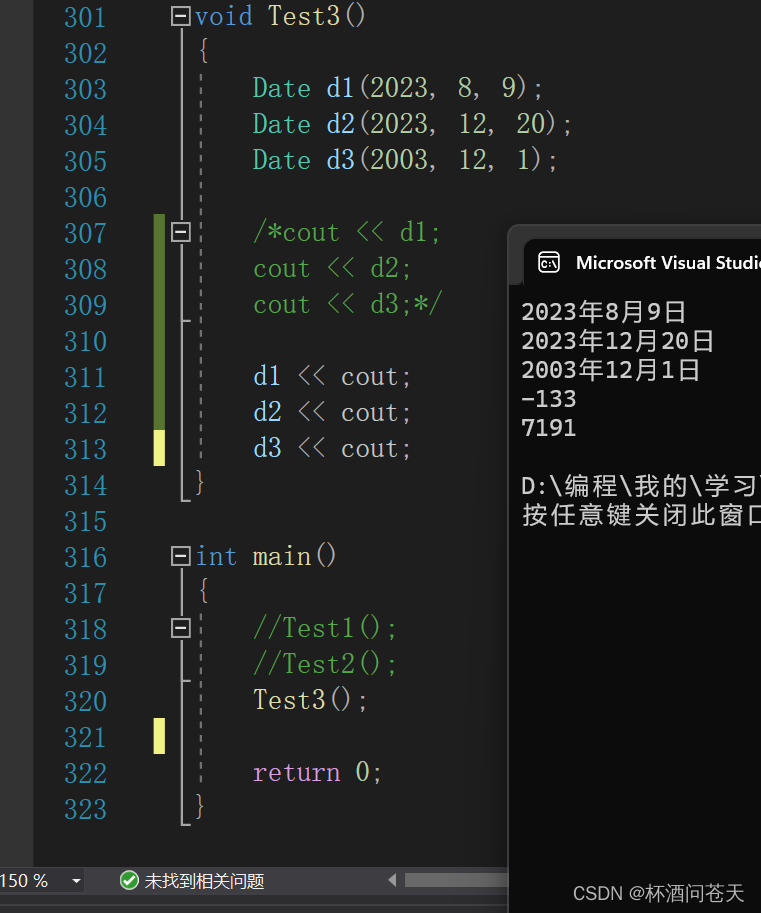
void Test3()
{
Date d1(2023, 8, 9);
Date d2(2023, 12, 20);
Date d3(2003, 12, 1);
d1 << cout;
d2 << cout;
d3 << cout;
}
int main()
{
Test3();
return 0;
}
class Date
{
friend void operator<< (ostream& out, const Date& d);
public:
// 获取某年某月的天数
int GetMonthDay(int year, int month)
{
int days[13] = { 0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31 };
if ((year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0) || year % 400 == 0)
{
days[2] = 29;
}
return days[month];
}
// 全缺省的构造函数
Date(int year = 1900, int month = 1, int day = 1)
{
_year = year;
_month = month;
_day = day;
if (month < 1 || month > 12 || day < 1 || day > GetMonthDay(year, month))
{
cout << "非法日期" << endl;
}
}
// 拷贝构造函数
// d2(d1)
Date(const Date& d)
{
_year = d._year;
_month = d._month;
_day = d._day;
}
// 赋值运算符重载
// d2 = d3 -> d2.operator=(&d2, d3)
Date& operator=(const Date& d)
{
_year = d._year;
_month = d._month;
_day = d._day;
return *this;
}
// 析构函数
~Date()
{
;
}
//打印
void Print() const
{
cout << _year << "年" << _month << "月" << _day << "日" << endl;
}
// 日期+=天数
Date& operator+=(int day)
{
if (day < 0)
{
*this -= (-day);
return *this;
}
_day += day;
while (_day > GetMonthDay(_year, _month))
{
_day -= GetMonthDay(_year, _month);
_month++;
if (_month > 12)
{
_year++;
_month = 1;
}
}
return *this;
}
// 日期+天数
Date operator+(int day)
{
Date tmp = *this;
tmp += day;
return tmp;
}
// 日期-天数
Date operator-(int day)
{
Date tmp = *this;
tmp -= day;
return tmp;
}
// 日期-=天数
Date& operator-=(int day)
{
if (day < 0)
{
*this += (-day);
return *this;
}
_day -= day;
while (_day <= 0)
{
_month--;
if (_month == 0)
{
_year--;
_month = 12;
}
_day += GetMonthDay(_year, _month);
}
return *this;
}
// 前置++
Date& operator++()
{
*this += 1;
return *this;
}
// 后置++
Date operator++(int)
{
Date tmp = *this;
*this += 1;
return tmp;
}
// 后置--
Date operator--(int)
{
Date tmp = *this;
*this -= 1;
return tmp;
}
// 前置--
Date& operator--()
{
*this -= 1;
return *this;
}
// >运算符重载
bool operator>(const Date& d)
{
if (_year > d._year)
{
return true;
}
else if(_year == d._year)
{
if (_month > d._month)
{
return true;
}
else if (_month == d._month)
{
if (_day > d._day)
{
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
// ==运算符重载
bool operator==(const Date& d)
{
return _year == d._year && _month == d._month && _day == d._day;
}
// >=运算符重载
bool operator >= (const Date& d)
{
return *this > d || *this == d;
}
// <运算符重载
bool operator < (const Date& d)
{
return !(*this >= d);
}
// <=运算符重载
bool operator <= (const Date& d)
{
return !(*this > d);
}
// !=运算符重载
bool operator != (const Date& d)
{
return !(*this == d);
}
// 日期-日期 返回天数
int operator-(const Date& d)
{
int num = 0;
Date max = *this;
Date min = d;
int flag = 1;
if (*this < d)
{
flag = -1;
max = d;
min = *this;
}
while (max > min)
{
num++;
min++;
}
return flag * num;
}
void operator<< (ostream& cout) const
{
cout << _year << "年" << _month << "月" << _day << "日" << endl;
}
private:
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
};3、“cout<<d”
要想使得代码是“cout<<d”而非“d<<cout”,
其实也很简单。我们将<<的重载写在类的外面,就没有了“隐含的this指针”的限制。
但是这样又会产生一个问题:如何访问Date类的私有成员呢?
这时,我们可以利用“友元”来解决问题。
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Date
{
//设置友元
friend void operator<< (ostream& out, const Date& d);
public:
// 获取某年某月的天数
int GetMonthDay(int year, int month)
{
int days[13] = { 0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31 };
if ((year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0) || year % 400 == 0)
{
days[2] = 29;
}
return days[month];
}
// 全缺省的构造函数
Date(int year = 1900, int month = 1, int day = 1)
{
_year = year;
_month = month;
_day = day;
if (month < 1 || month > 12 || day < 1 || day > GetMonthDay(year, month))
{
cout << "非法日期" << endl;
}
}
// 拷贝构造函数
// d2(d1)
Date(const Date& d)
{
_year = d._year;
_month = d._month;
_day = d._day;
}
// 赋值运算符重载
// d2 = d3 -> d2.operator=(&d2, d3)
Date& operator=(const Date& d)
{
_year = d._year;
_month = d._month;
_day = d._day;
return *this;
}
// 析构函数
~Date()
{
;
}
//打印
void Print() const
{
cout << _year << "年" << _month << "月" << _day << "日" << endl;
}
// 日期+=天数
Date& operator+=(int day)
{
if (day < 0)
{
*this -= (-day);
return *this;
}
_day += day;
while (_day > GetMonthDay(_year, _month))
{
_day -= GetMonthDay(_year, _month);
_month++;
if (_month > 12)
{
_year++;
_month = 1;
}
}
return *this;
}
// 日期+天数
Date operator+(int day)
{
Date tmp = *this;
tmp += day;
return tmp;
}
// 日期-天数
Date operator-(int day)
{
Date tmp = *this;
tmp -= day;
return tmp;
}
// 日期-=天数
Date& operator-=(int day)
{
if (day < 0)
{
*this += (-day);
return *this;
}
_day -= day;
while (_day <= 0)
{
_month--;
if (_month == 0)
{
_year--;
_month = 12;
}
_day += GetMonthDay(_year, _month);
}
return *this;
}
// 前置++
Date& operator++()
{
*this += 1;
return *this;
}
// 后置++
Date operator++(int)
{
Date tmp = *this;
*this += 1;
return tmp;
}
// 后置--
Date operator--(int)
{
Date tmp = *this;
*this -= 1;
return tmp;
}
// 前置--
Date& operator--()
{
*this -= 1;
return *this;
}
// >运算符重载
bool operator>(const Date& d)
{
if (_year > d._year)
{
return true;
}
else if(_year == d._year)
{
if (_month > d._month)
{
return true;
}
else if (_month == d._month)
{
if (_day > d._day)
{
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
// ==运算符重载
bool operator==(const Date& d)
{
return _year == d._year && _month == d._month && _day == d._day;
}
// >=运算符重载
bool operator >= (const Date& d)
{
return *this > d || *this == d;
}
// <运算符重载
bool operator < (const Date& d)
{
return !(*this >= d);
}
// <=运算符重载
bool operator <= (const Date& d)
{
return !(*this > d);
}
// !=运算符重载
bool operator != (const Date& d)
{
return !(*this == d);
}
// 日期-日期 返回天数
int operator-(const Date& d)
{
int num = 0;
Date max = *this;
Date min = d;
int flag = 1;
if (*this < d)
{
flag = -1;
max = d;
min = *this;
}
while (max > min)
{
num++;
min++;
}
return flag * num;
}
private:
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
};
//运算符重载
void operator<< (ostream& cout, const Date& d)
{
cout << d._year << "年" << d._month << "月" << d._day << "日" << endl;
}效果
void Test3()
{
Date d1(2023, 8, 9);
Date d2(2023, 12, 20);
Date d3(2003, 12, 1);
cout << d1;
cout << d2;
cout << d3;
}
int main()
{
Test3();
return 0;
}
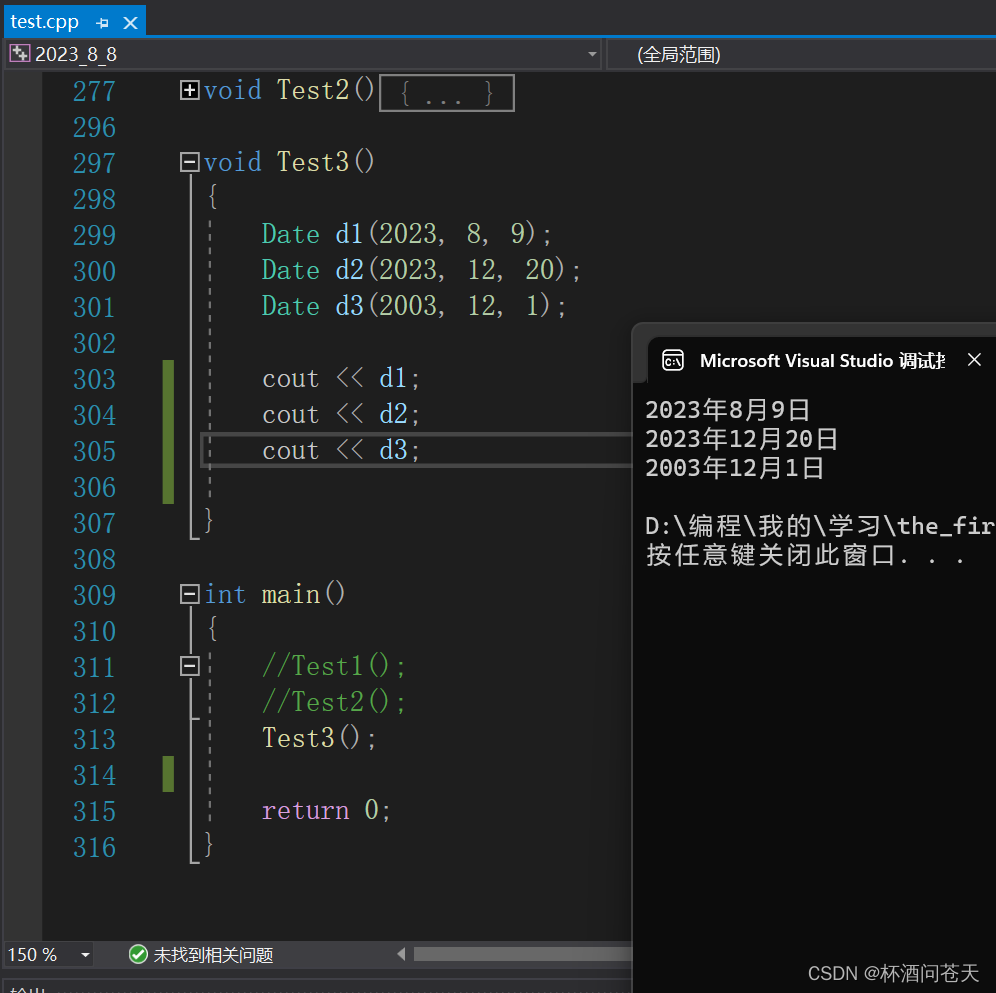
如此,我们就实现了将自定义的类使用cout输出了。

![[YAPI]导出API文档](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/6d228addf8e44806bbfdb5ba3e27f449.png)