前言
面经:
针对链表的题目,对于笔试可以不太在乎空间复杂度,以时间复杂度为主(能过就行,对于任何题型都一样,笔试能过就行);对于面试,时间复杂度依然处在第一位,但要力求空间复杂度最低的算法(突出亮点);
链表题的重要技巧包括:使用额外的数据结构记录(例如哈希表等),使用快慢指针的思想;
1--反转单向链表

笔试解法:
借助栈先进后出,可以遍历把结点存到栈中,然后不断出栈,这样结点的顺序就反转了;
时间复杂度为O(n),空间复杂度为O(n);
#include <iostream>
#include <stack>
struct ListNode {
int val;
ListNode *next;
ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
};
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {
if(head == NULL) return head;
std::stack<ListNode*> st;
while(head != NULL){
st.push(head);
head = head->next;
}
ListNode *new_head = new ListNode(0);
ListNode *tmp = new_head;
while(!st.empty()){
tmp->next = st.top();
st.pop();
tmp = tmp->next;
}
tmp->next = NULL;
return new_head->next;
}
};
int main(int argc, char *argv[]){
ListNode *Node1 = new ListNode(1);
ListNode *Node2 = new ListNode(2);
ListNode *Node3 = new ListNode(3);
ListNode *Node4 = new ListNode(4);
ListNode *Node5 = new ListNode(5);
Node1->next = Node2;
Node2->next = Node3;
Node3->next = Node4;
Node4->next = Node5;
Solution S1;
ListNode *res = S1.reverseList(Node1);
while(res != NULL){
std::cout << res->val << " ";
res = res->next;
}
return 0;
}面试解法:
不借助栈或递归,通过迭代将空间复杂度优化为O(1);
利用一个额外的前驱结点 pre 来存储当前结点 cur 的前一个结点,不断更新 pre 和 cur即可;
#include <iostream>
#include <stack>
struct ListNode {
int val;
ListNode *next;
ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
};
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {
if(head == NULL) return head;
ListNode *pre = NULL;
ListNode *cur = head;
while(cur != NULL){
ListNode* next = cur->next;
cur->next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = next;
}
return pre;
}
};
int main(int argc, char *argv[]){
ListNode *Node1 = new ListNode(1);
ListNode *Node2 = new ListNode(2);
ListNode *Node3 = new ListNode(3);
ListNode *Node4 = new ListNode(4);
ListNode *Node5 = new ListNode(5);
Node1->next = Node2;
Node2->next = Node3;
Node3->next = Node4;
Node4->next = Node5;
Solution S1;
ListNode *res = S1.reverseList(Node1);
while(res != NULL){
std::cout << res->val << " ";
res = res->next;
}
return 0;
}2--反转单向链表-II
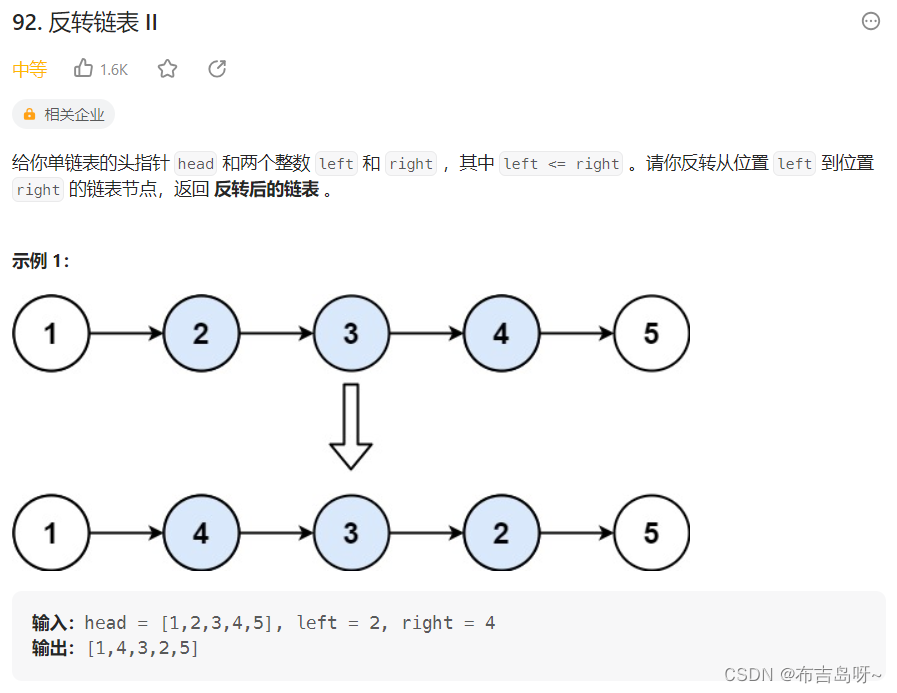
主要思路:
使用三个指针,指针 pre 指向反转区域外的第一个节点,即上图中的 1;指针 cur 指向当前指针,指针 next 指向 cur 的下一个指针;
遍历链表,每次将 next 指针头插,具体过程可以参考官方题解;
#include <iostream>
struct ListNode {
int val;
ListNode *next;
ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
};
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseBetween(ListNode* head, int left, int right) {
ListNode *dummyNode = new ListNode(-1);
dummyNode->next = head;
ListNode *pre = dummyNode;
ListNode *cur;
ListNode *next;
// 经过循环之后,pre指向反转区域前的第一个节点
for(int i = 0; i < left - 1; i++){
pre = pre->next;
}
cur = pre->next; // cur指向反转区域的第一个节点
for(int i = 0; i < right - left; i++){
next = cur->next;
cur->next = next->next; // cur指向next的下一个节点,因为next节点要头插到pre节点后面
next->next = pre->next; // next节点头插,指向原来的第一个节点
pre->next = next; // next节点头插到pre节点后面
}
return dummyNode->next;
}
};
int main(){
ListNode *Node1 = new ListNode(1);
ListNode *Node2 = new ListNode(2);
ListNode *Node3 = new ListNode(3);
ListNode *Node4 = new ListNode(4);
ListNode *Node5 = new ListNode(5);
Node1->next = Node2;
Node2->next = Node3;
Node3->next = Node4;
Node4->next = Node5;
Solution S1;
int left = 2, right = 4;
ListNode *res = S1.reverseBetween(Node1, left, right);
while(res != NULL){
std::cout << res->val << " ";
res = res->next;
}
return 0;
}3--反转双向链表
主要思路:
与反转单向链表类似,使用 pre,cur 和 next 指向前一个节点,当前节点和后一个节点,不断遍历更新三个指针所指向的节点即可,并修改对应的前驱指针和后驱指针;
#include <iostream>
#include <stack>
struct ListNode {
int val;
ListNode *pre;
ListNode *next;
ListNode() : val(0), pre(nullptr), next(nullptr) {}
ListNode(int x) : val(x), pre(nullptr), next(nullptr) {}
ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), pre(nullptr), next(next) {}
};
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {
if(head == NULL) return head;
ListNode *pre = NULL;
ListNode *cur = head;
while(cur != NULL){
ListNode* next = cur->next;
cur->next = pre;
cur->pre = next;
pre = cur;
cur = next;
}
return pre;
}
};
int main(int argc, char *argv[]){
ListNode *Node1 = new ListNode(1);
ListNode *Node2 = new ListNode(2);
ListNode *Node3 = new ListNode(3);
ListNode *Node4 = new ListNode(4);
ListNode *Node5 = new ListNode(5);
Node1->next = Node2;
Node2->next = Node3;
Node3->next = Node4;
Node4->next = Node5;
Node2->pre = Node1;
Node3->pre = Node2;
Node4->pre = Node3;
Node5->pre = Node4;
Solution S1;
ListNode *res = S1.reverseList(Node1);
while(res != NULL){
std::cout << res->val << " ";
if(res->pre != NULL) std::cout << res->pre->val;
std::cout << std::endl;
res = res->next;
}
return 0;
}4--打印两个有序链表的公共部分
给定两个有序链表的头指针 head1 和 head2,打印两个链表的公共部分;要求时间复杂度为O(n),额外空间复杂度要求为 O(1);
主要思路:
类似于归并排序,由于两个链表时有序的,因此可以使用两个指针 i 和 j 分别指向两个链表;
对于小的链表节点,指针后移;
当比较到两个指针相等时,打印节点的值,两个指针 i 和 j 同时后移;
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
struct ListNode {
int val;
ListNode *next;
ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
};
class Solution {
public:
std::vector<ListNode*> printlist(ListNode* head1, ListNode* head2) {
std::vector<ListNode*> res;
if(head1 == NULL || head2 == NULL) return res;
ListNode *i = head1;
ListNode *j = head2;
while(i != NULL && j != NULL){
// 小的后移
if(i->val < j->val) i = i->next;
else if(i->val > j->val) j = j->next;
else{ // 相等同时后移
res.push_back(i);
i = i->next;
j = j->next;
}
}
return res;
}
};
int main(int argc, char *argv[]){
ListNode *Node1 = new ListNode(1);
ListNode *Node2 = new ListNode(2);
ListNode *Node3 = new ListNode(5);
ListNode *Node4 = new ListNode(0);
ListNode *Node5 = new ListNode(2);
ListNode *Node6 = new ListNode(3);
ListNode *Node7 = new ListNode(5);
Node1->next = Node2;
Node2->next = Node3;
Node4->next = Node5;
Node5->next = Node6;
Node6->next = Node7;
Solution S1;
std::vector<ListNode *> res = S1.printlist(Node1, Node4);
for(ListNode * node : res) std::cout << node->val << " ";
return 0;
}