进程创建时发生了什么
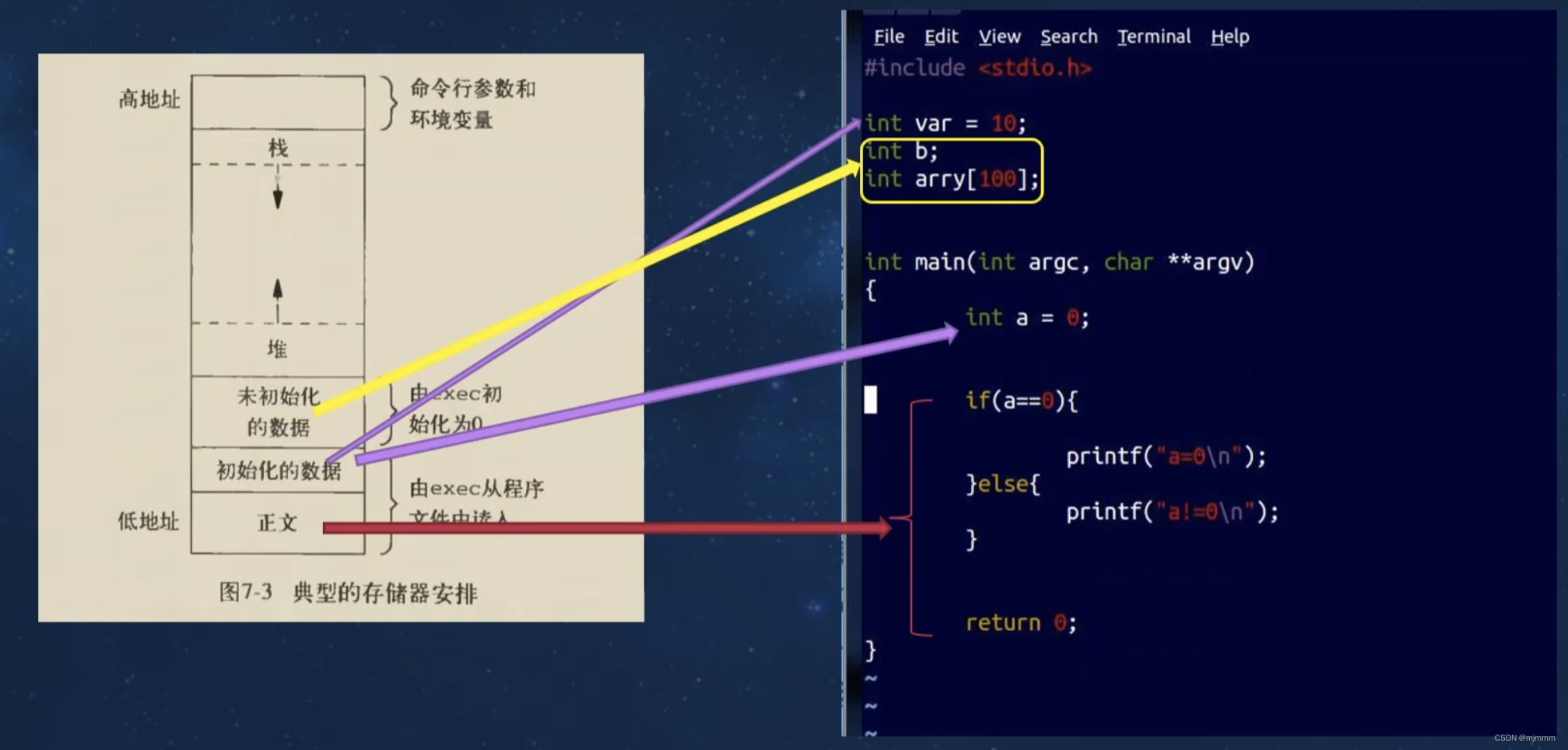
回顾上节关于存储空间分配的图片:
当程序运行到 fork() 函数了之后:
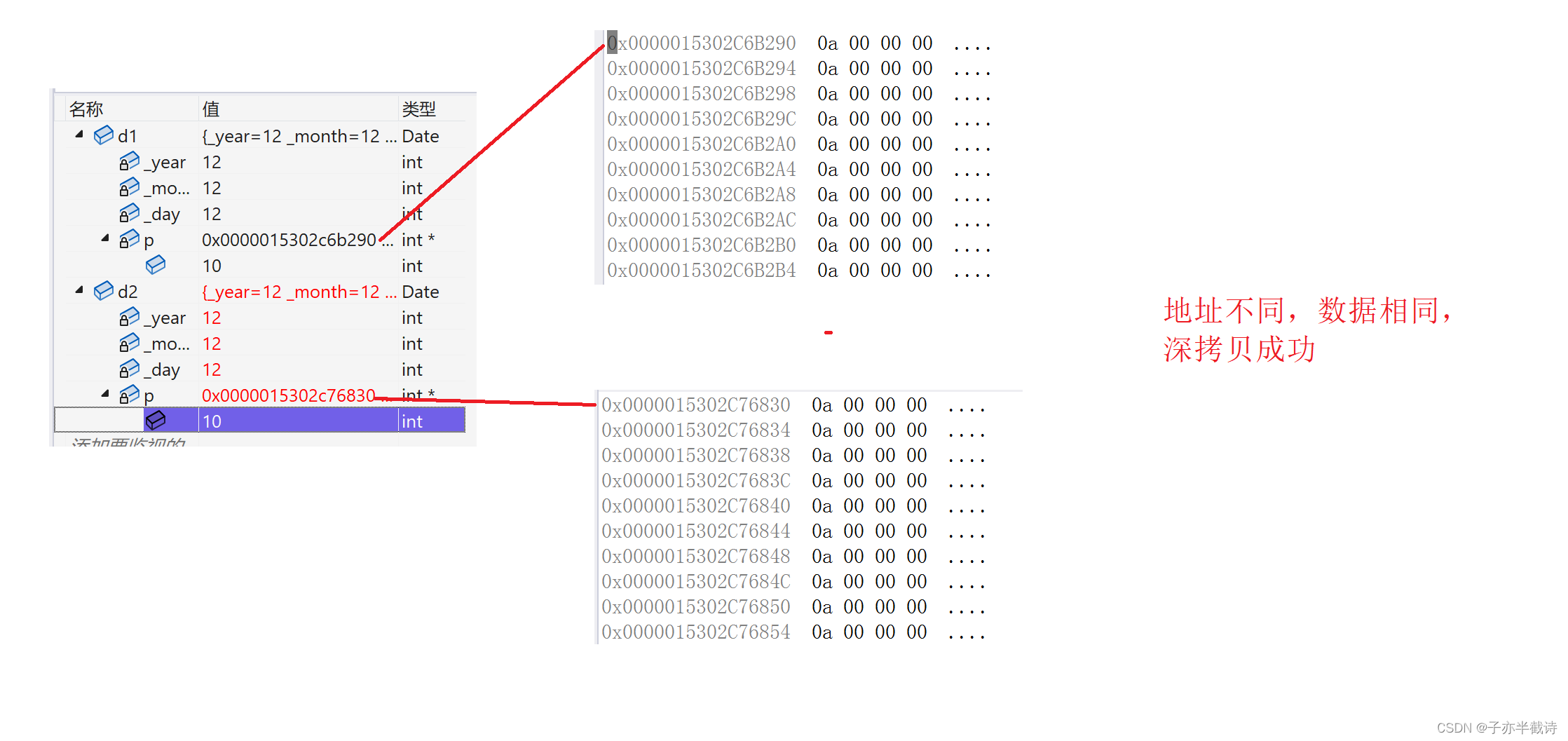
- 在早期的Linux中,系统会将fork之前所有的数据段,代码段,堆,栈等对应的全部的存储空间拷贝一份,作为子进程的数据段,并共享正文段,称为全拷贝
- 在之后,系统经过优化,fork函数执行后,对于没有修改过的数据,采用了共享存储空间的方法,只将变化部分的代码拷贝,同时也共享正文段,称为写时拷贝(Copy-On-Write, COW)
创建子进程的目的

创建进程使用的函数
fork函数:
需要添加的库:
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
函数原型:
pid_t fork(void);- 如果fork函数调用成功,则返回两次:
- 返回值为0,代表当前进程为子进程
- 返回值为非负数,代表当前进程为父进程
- 如果fork函数调用失败,则返回-1
实操演示
在Linux环境中的"./home"下创建“JC”文件夹,关于进程学习的代码都放在这里:
demo1.c:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main()
{
pid_t pid;
pid_t fork_return;
pid = getpid();
printf("before fork, PID = %d\n",pid);
fork_return = fork();
if(fork_return > 0){
printf("This is the father JC,PID = %d\n",getpid()); //这句话父进程会执行
}else{
printf("This is the son JC,PID = %d\n",getpid()); //这句话子进程会执行
}
return 0;
}运行代码:

由此可见,在fork之前,只有一个进程,在fork之后,原来的进程变成了父进程,并创建了一个子进程,所以在fork之后的代码父子进程都会执行,并根据fork的返回值来打印不同的语句。
而如果打印fork函数返回的“fork_return”,就会发现,父进程打印的fork_return其实就是子进程的PID号,而子进程打印的fork_return就是0。侧面印证了fork函数的返回值,大于0对应父进程。
vfork函数:
vfork 和 fork 的区别:
- vfork直接使用父进程的存储空间,不进行拷贝
- vfork保证子进程先运行,当子进程调用exit退出后,父进程才进行
需要添加的库:(和fork相同)
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
函数原型:(除了名字都和fork相同)
pid_t vfork(void);- 如果vfork函数调用成功,则返回两次:
- 返回值为0,代表当前进程为子进程
- 返回值为非负数,代表当前进程为父进程
- 如果vfork函数调用失败,则返回-1
实操演示
demo2.c:
为了展示区别,先用fork写一段代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main()
{
pid_t pid;
pid_t fork_return;
pid = getpid();
printf("before fork, PID = %d\n",pid);
fork_return = fork();
if(fork_return > 0){
while(1){
printf("This is the father JC,PID = %d\n",getpid());
sleep(2);
}
}else{
while(1){
printf("This is the son JC,PID = %d\n",getpid());
sleep(2);
}
}
return 0;
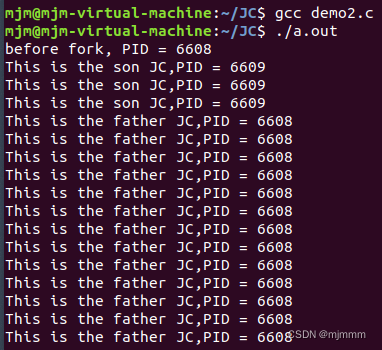
}运行代码1:

可见,父子进程基本交替在运行。
此时,修改demo2, 将fork改为vfork。
fork_return = vfork();运行代码2:

可见,由于子进程没有exit,所以父进程不会进行,只有子进程一直在运行。
而此时在子进程中添加退出的代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
pid_t pid;
pid_t fork_return;
int cnt = 0;
pid = getpid();
printf("before fork, PID = %d\n",pid);
fork_return = vfork();
if(fork_return > 0){
while(1){
printf("This is the father JC,PID = %d\n",getpid());
sleep(2);
}
}else{
while(1){
printf("This is the son JC,PID = %d\n",getpid());
sleep(2);
cnt++;
if(cnt == 3){
exit(-1);
}
}
}
return 0;
}运行代码3:
此时,子进程运行三次之后就会自动退出,父进程就会开始一直运行。