B - Hoppers
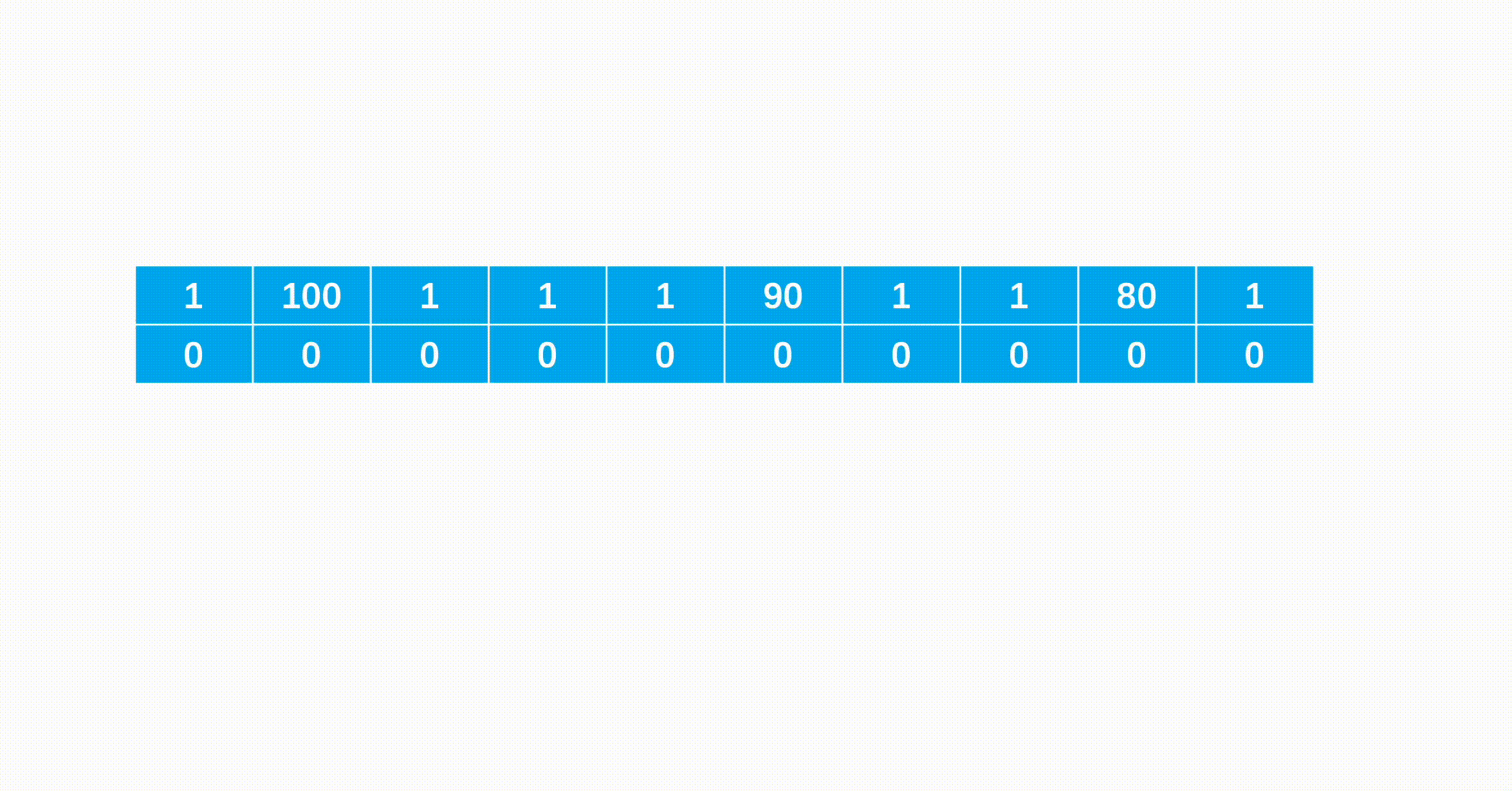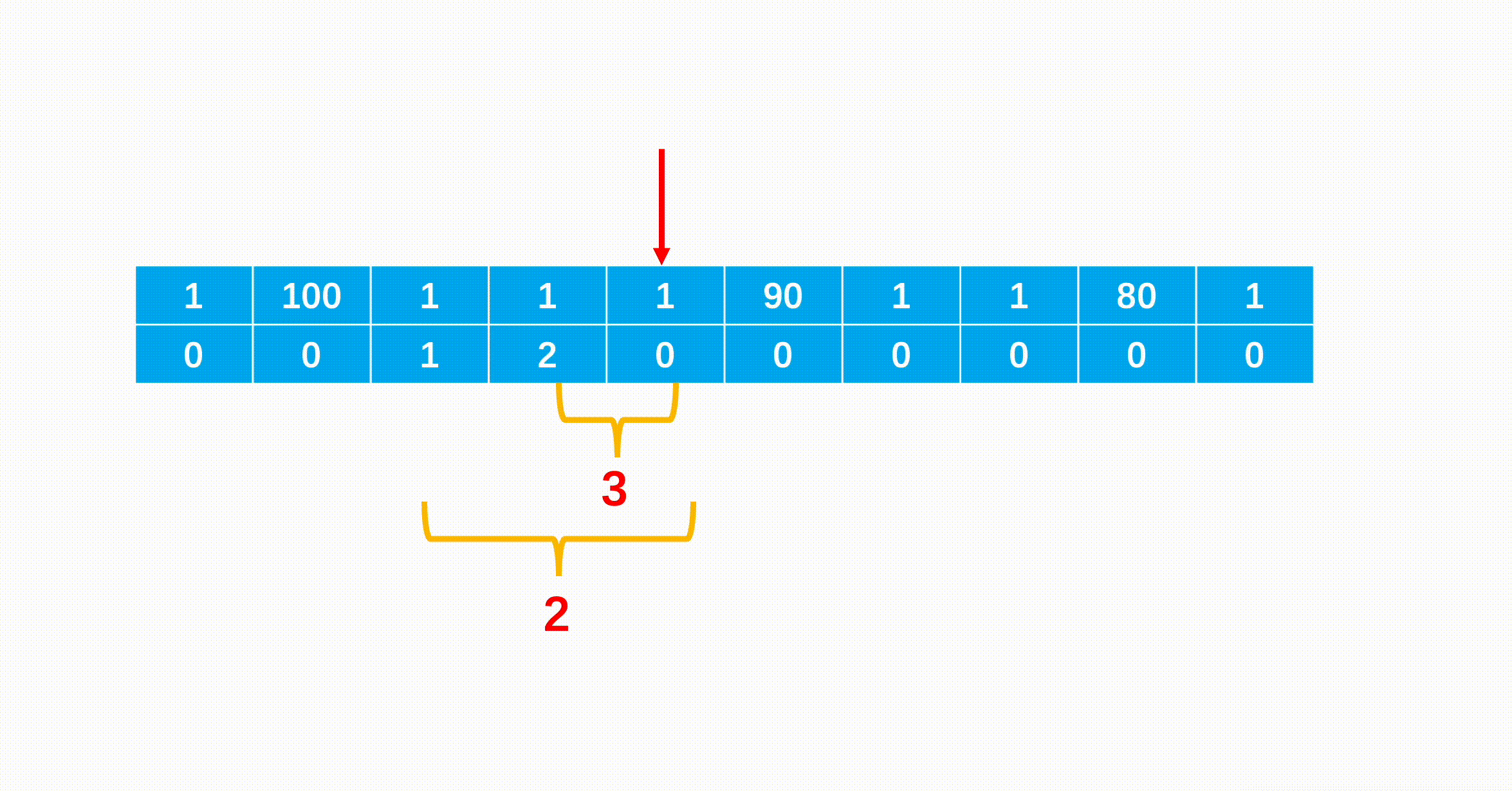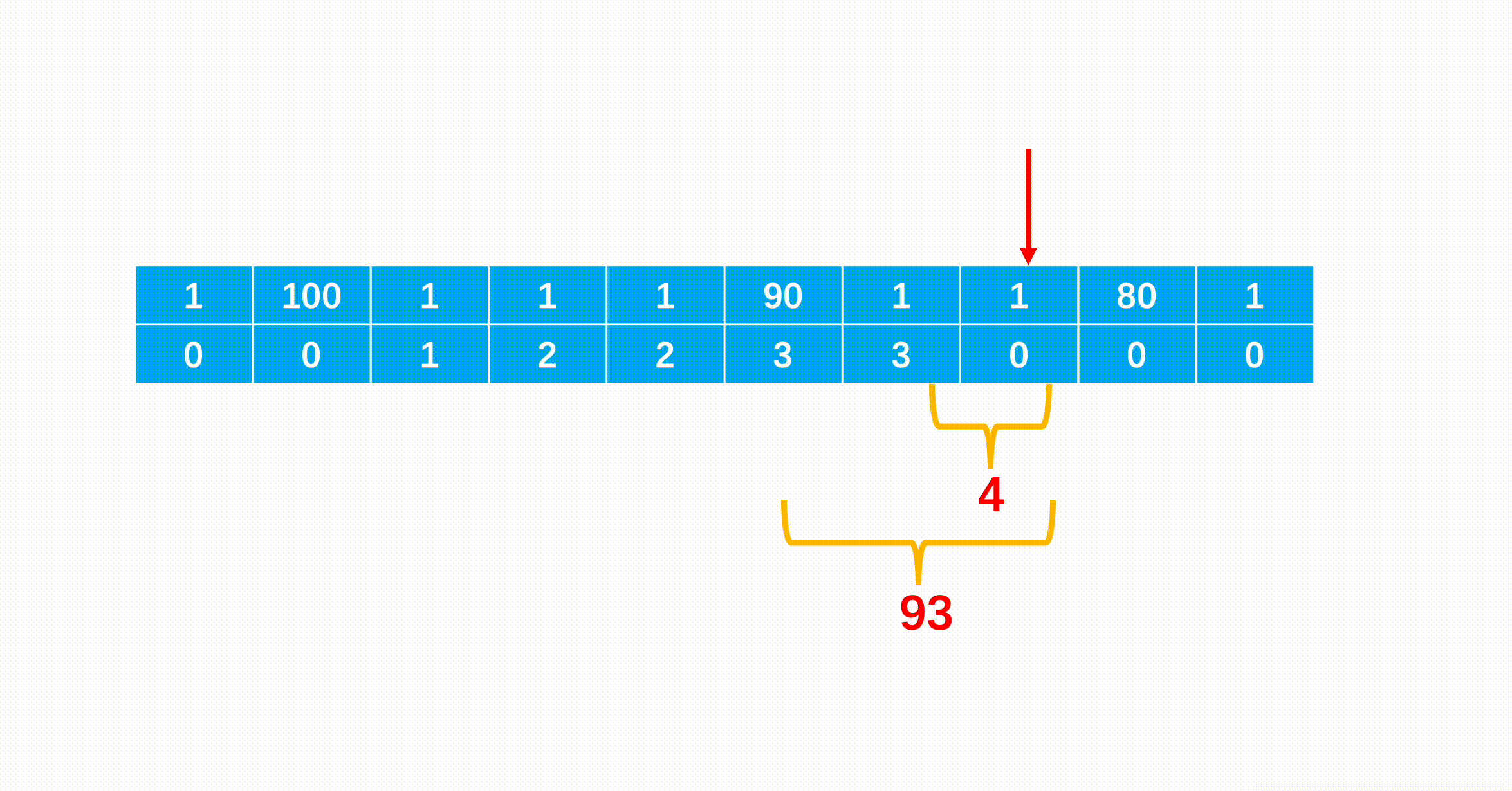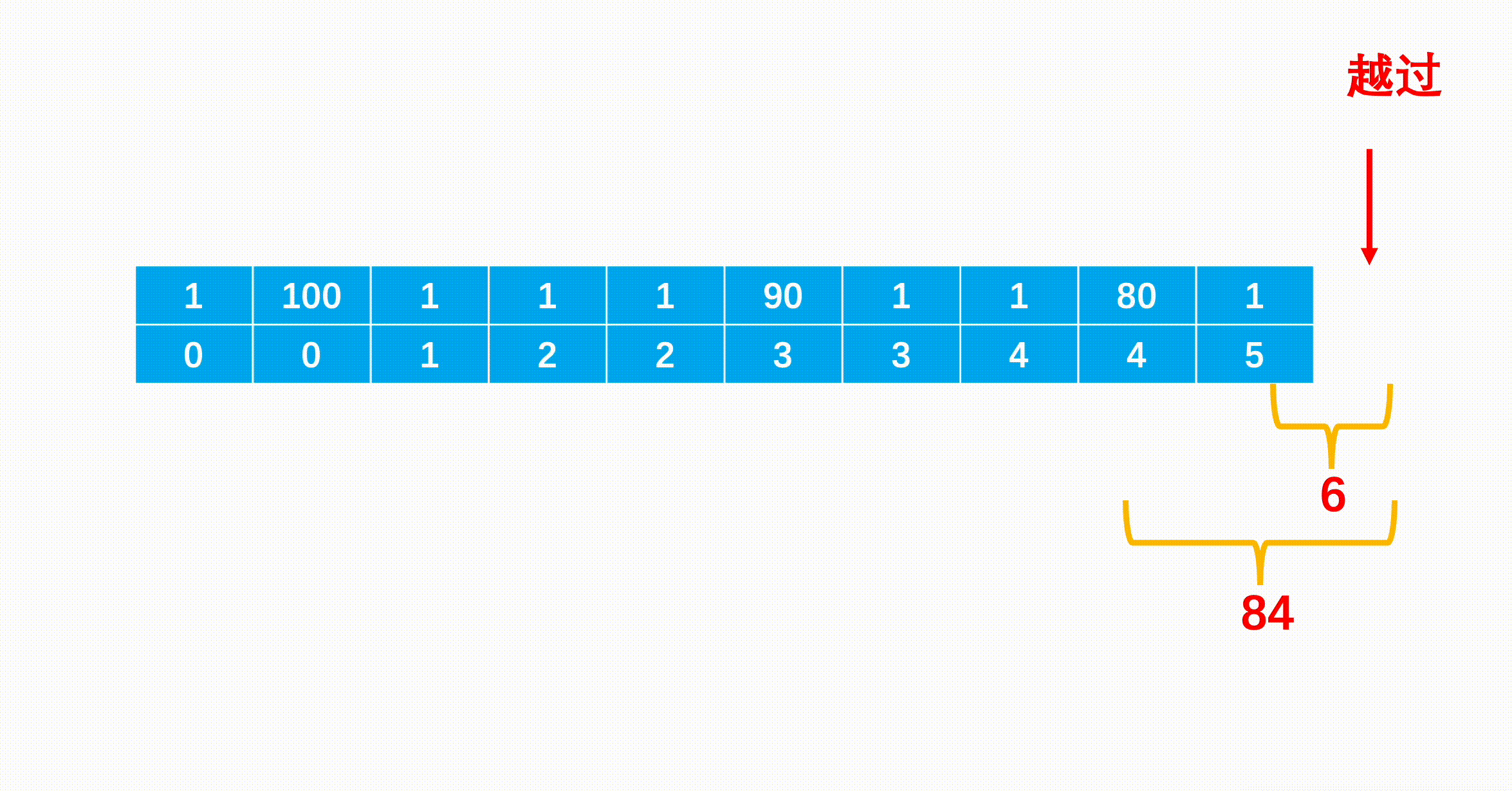
题意:给你一张无向图,可以选定一个点染色,随后距离为2的点都会被染色(可以传染)。求至少需要向图中添加几条边使得选定一个点染色后可以将整个图染色。(不一定是连通图)
思路:如果一个连通块是一个二分图,那么只能染色二分图的一部;如果一个连通块不是二分图,那么这个连通块可以被完全染色。(就是看有没有奇数环,二分图一定没有奇数环)
求出连通块的数量k以及是否有非二分图连通块,如果有非二分图那么只要用k-1条边把k个连通块连成一个非二分图连通块即可。如果没有非二分图那么用k-1条边连起来后还是个二分图连通块,需要再加一条边变成非二分连通块。
所以如果有非二分图(奇数环)ans=连通块数-1
否则ans=联通块数
这里写了两种方法,一个dfs,一个二分图染色(其实都差不多)
1:二分图染色
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define pi acos(-1)
#define xx first
#define yy second
#define endl "\n"
#define lowbit(x) x & (-x)
#define int long long
#define ull unsigned long long
#define pb push_back
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
typedef pair<double, double> PDD;
#define max(a, b) (((a) > (b)) ? (a) : (b))
#define min(a, b) (((a) < (b)) ? (a) : (b))
#define Ysanqian ios::sync_with_stdio(false), cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
const int N = 1e6 + 10, M = 1010, inf = 0x3f3f3f3f, mod = 18446, P = 13331;
const double eps = 1e-8;
int n, m;
bool flag;
int p[N];
int siz[N];
int st[N];
vector<int> g[N];
vector<int> now;
int find(int x)
{
if (x != p[x])
p[x] = find(p[x]);
return p[x];
}
void merge(int x, int y)
{
int a = find(x), b = find(y);
if (a != b)
{
p[b] = a;
siz[a] += siz[b];
}
}
bool dfs(int u, int c)
{
st[u] = c;
for (auto ed : g[u])
{
if (st[ed])
{
if (st[ed] == c)
return false;
}
else if (!dfs(ed, 3 - c))
return false;
}
return true;
}
void solve()
{
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
p[i] = i;
siz[i] = 1;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++)
{
int a, b;
cin >> a >> b;
g[a].pb(b);
g[b].pb(a);
merge(a, b);
}
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
if (p[i] == i)
ans++;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
if (!st[i])
{
if (!dfs(i, 1))
flag = 1;
}
}
if (flag)
cout << ans - 1 << endl;
else
cout << ans << endl;
}
signed main()
{
Ysanqian;
int T;
T = 1;
// cin >> T;
while (T--)
solve();
return 0;
}2:dfs
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define pi acos(-1)
#define xx first
#define yy second
#define endl "\n"
#define lowbit(x) x & (-x)
#define int long long
#define ull unsigned long long
#define pb push_back
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
typedef pair<double, double> PDD;
#define max(a, b) (((a) > (b)) ? (a) : (b))
#define min(a, b) (((a) < (b)) ? (a) : (b))
#define Ysanqian ios::sync_with_stdio(false), cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
const int N = 1e6 + 10, M = 1010, inf = 0x3f3f3f3f, mod = 18446, P = 13331;
const double eps = 1e-8;
int n, m;
bool flag;
int d[N];
vector<int> g[N];
void dfs(int u, int color)
{
d[u] = color;
for (auto ed: g[u])
{
if (!d[ed])
dfs(ed, -color);
else if (d[u] == d[ed])//临边有相同的颜色,即为非二分图,含有奇数环
flag = 1;
}
}
void solve()
{
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++)
{
int a, b;
cin >> a >> b;
g[a].pb(b);
g[b].pb(a);
}
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
if (!d[i])
{
dfs(i, 1);
ans++;
}
}
if (flag)
cout << ans - 1 << endl;
else
cout << ans << endl;
}
signed main()
{
Ysanqian;
int T;
T = 1;
// cin >> T;
while (T--)
solve();
return 0;
}C - SG Coin
题意:就是给你一个字符串的哈希值,以及一个计算字符串哈希值得函数,让你再构造两个串,可以满足这个函数,且其哈希值末尾有7个0
思路:我们根据其公式得知,我们得到其哈希值,要知道其牌号,和交易字符串,而这两个我们都不知道,那么我们其实可以只有构造一个交易字符串,在不加牌号得情况下求出其暂时的哈希值(mod1e9的意义下),但是我们还是不知道其牌号,其实这时候牌号就等于其变为后七位变为0减去其目前暂时哈希值(应为最终哈希值要后7位为0),这个操作可以通过令(x/1e7+1)*1e7得到后7位全为0得情况,减去x即为牌号,下一个构造同理
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define pi acos(-1)
#define xx first
#define yy second
#define endl "\n"
#define lowbit(x) x & (-x)
#define int long long
#define ull unsigned long long
#define pb push_back
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
typedef pair<double, double> PDD;
#define max(a, b) (((a) > (b)) ? (a) : (b))
#define min(a, b) (((a) < (b)) ? (a) : (b))
#define Ysanqian ios::sync_with_stdio(false), cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
const int N = 1e6 + 10, M = 1010, inf = 0x3f3f3f3f, mod = 18446, P = 13331;
const double eps = 1e-8;
int n;
string s1, s2, ans1, ans2;
int H(int last, string s)
{
int v = last;
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++)
{
v = (v * 31 + s[i]) % 1000000007;
}
return (v * 7 ) % 1000000007;
}
void solve()
{
s1 = "charlie-pays-to-eve-9-sg-coins";
s2 = "icpc-sg-2018-at-nus";
cin >> n;
int x1 = H(n, s1);
int g = ((int)(x1 / 1e7) + 1) * 1e7;
cout << s1 << ' ';
cout << g - x1 << endl;
int x2 = H(g, s2);
g = ((int)(x2 / 1e7) + 1) * 1e7;
cout << s2 << ' ';
cout << g - x2 << endl;
}
signed main()
{
Ysanqian;
int T;
T = 1;
// cin >> T;
while (T--)
solve();
return 0;
}L - Non-Prime Factors
题意:n次询问,每次询问给出一个x,求x得约数里有多少个不是质因数
思路:看到这个数据量,跑不了是预处理了,但是我们预处理所有得质因数,没次分解约数(根号n)的复杂度我们也接受不了,既然我们用筛法来求质因数了,不难想到用同一思想来与预处理答案
对于任意一个整数,它必定可以被拆成两个整数的乘积。所以我们可以枚举因数,然后把2~2e6的数的结果在时间复杂度内计算出来
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define pi acos(-1)
#define xx first
#define yy second
#define endl "\n"
#define lowbit(x) x & (-x)
#define int long long
#define ull unsigned long long
#define pb push_back
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
typedef pair<double, double> PDD;
#define max(a, b) (((a) > (b)) ? (a) : (b))
#define min(a, b) (((a) < (b)) ? (a) : (b))
#define Ysanqian ios::sync_with_stdio(false), cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
const int N = 2e6 + 10, M = 1010, inf = 0x3f3f3f3f, mod = 18446, P = 13331;
const double eps = 1e-8;
int n, m, cnt;
int ans[N], prime[N];
bool st[N], p[N];
void is_prime()
{
st[1] = 1;
for (int i = 2; i <= N; i++)
{
if (!st[i])
prime[cnt++] = i;
for (int j = 0; prime[j] <= N / i; j++)
{
st[i * prime[j]] = 1;
if (i % prime[j] == 0)
break;
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= 2e6; i++)
{
if (!st[i])
continue;
for (int j = i; j <= 2e6; j += i) // 每个数都有其较小的约数线性筛出来
{
ans[j]++;
}
}
}
void solve()
{
cin >> n;
cout << ans[n] << endl;
}
signed main()
{
Ysanqian;
int T;
T = 1;
is_prime();
cin >> T;
while (T--)
solve();
return 0;
}