文章目录
- 一、优先级队列简介
- 二、优先级队列的接口说明
- 1.基本介绍及其使用
- 2.构造函数
- 3.求数组中第k个最大的元素
- 三、手撕优先级队列
- 四、仿函数
- 1.仿函数介绍
- 2.优先级队列添加仿函数
- 3.需要自己写仿函数的情形
- 五、优先级队列完整代码
一、优先级队列简介
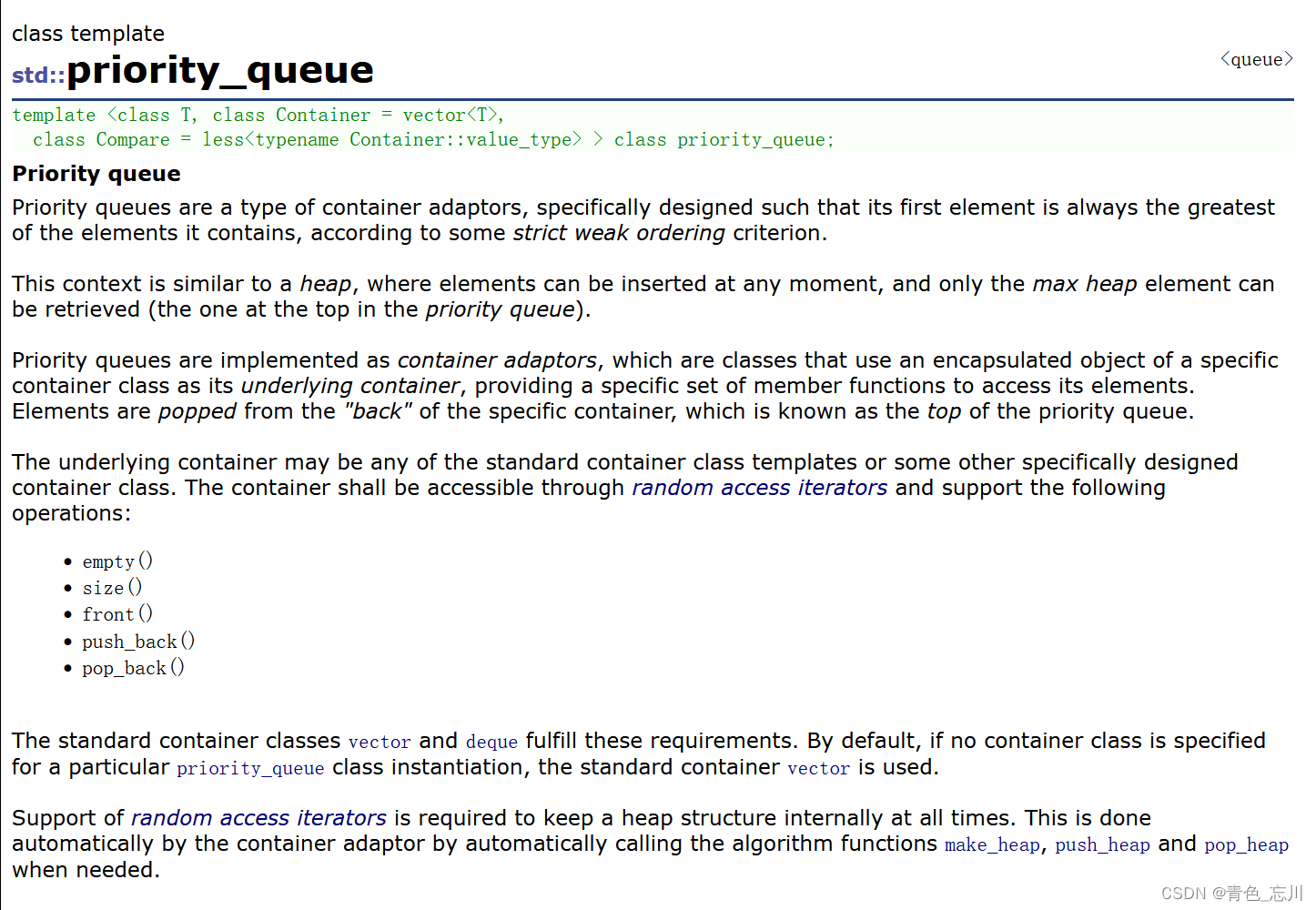
优先级队列是一种容器适配器,根据某种严格的弱排序标准,它的第一个元素总是它所包含的元素中最大的。
此上下文类似于堆,在堆中可以随时插入元素,并且只能检索最大的堆元素(优先级队列中位于顶部的元素)。
优先级队列是作为容器适配器实现的,这些适配器是使用特定容器类的封装对象作为其底层容器的类,提供一组特定的成员函数来访问其元素。元素从特定容器的“后面”弹出,这被称为优先级队列的顶部。
底层容器可以是任何标准容器类模板或其他特定设计的容器类。容器必须可以通过随机访问迭代器访问,并支持以下功能操作:empty、size、front、push_back、pop_back
标准容器类vector和deque满足这些要求。默认情况下,如果没有为特定的priority_queue类实例化指定容器类,则使用标准容器向量。
为了始终在内部保持堆结构,需要支持随机访问迭代器。这是由容器适配器在需要时自动调用算法函数make_heap、push_heap和pop_heap自动完成的。
二、优先级队列的接口说明
1.基本介绍及其使用
优先级队列的接口有如下几种。对于优先级队列我们默认是它的大的数优先级高。其底层是一个堆。也就是说,我们默认是大堆,所以大的数优先级高。如果是一个小堆,那么就是小的优先级高。
我们来简单的使用一下这些接口
void test_priority_queue()
{
priority_queue<int> pq;
pq.push(1);
pq.push(10);
pq.push(2);
pq.push(51);
pq.push(4);
while (!pq.empty())
{
cout << pq.top() << " ";
pq.pop();
}
cout << endl;
}
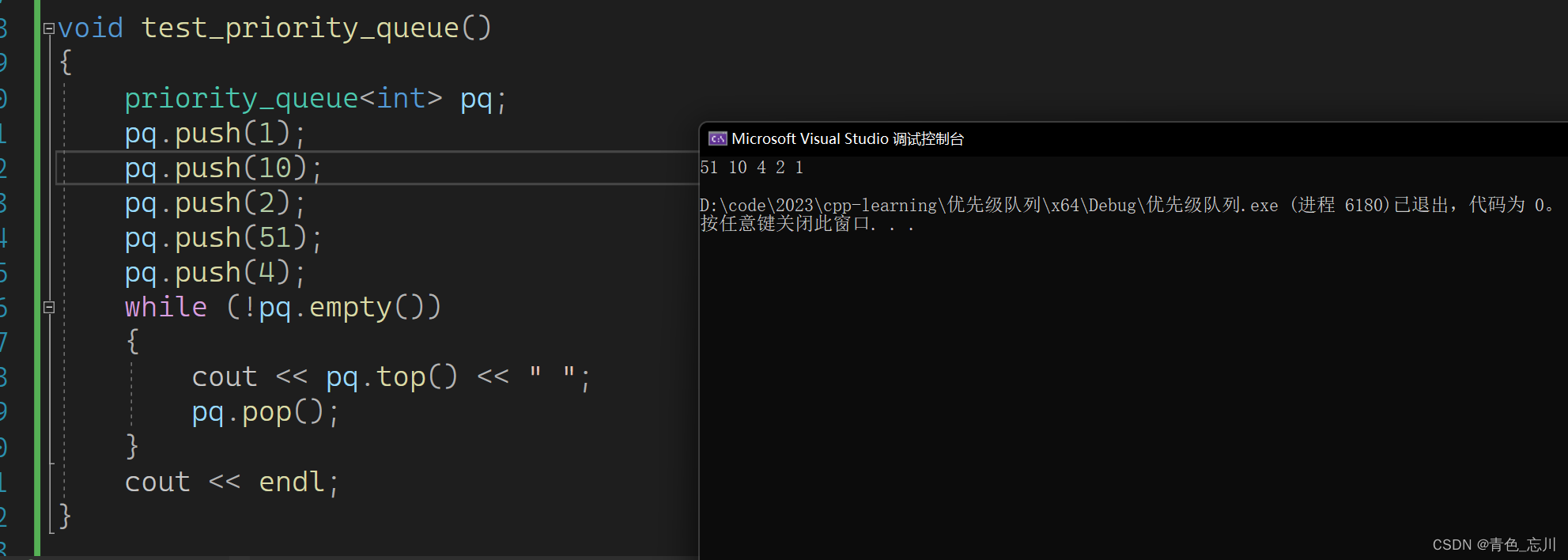
可以看到,默认是一个大堆,但是我们会注意到,它库里面默认传的是less,但是却是一个大堆,这里需要额外注意一下。

所以我们如果想要是一个小堆的话,我们需要将这个less替换为greater
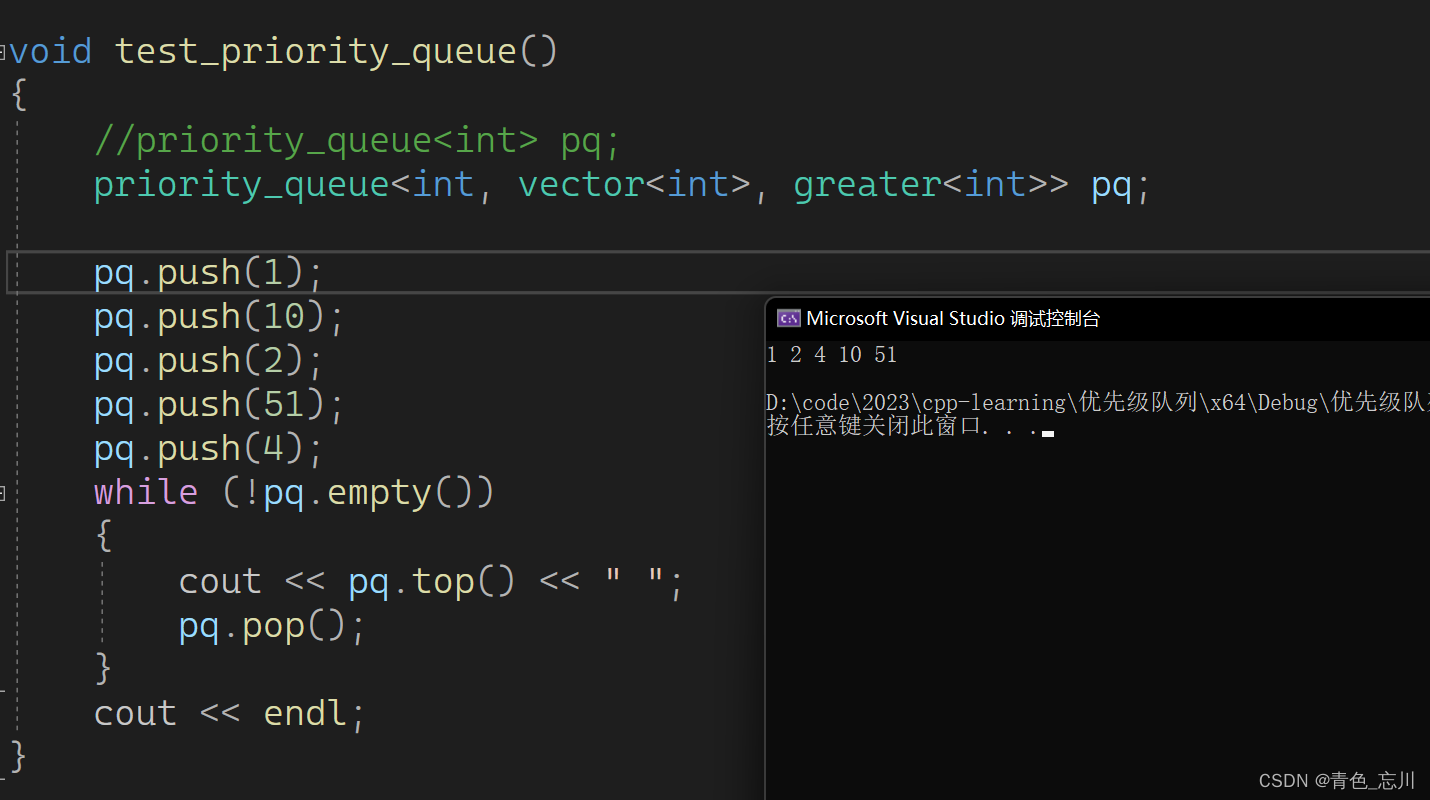
在这里我们传的less,greater这些也称之为仿函数。也就是说,通过仿函数控制实现大小堆.
除此之外,这里除了可以传vector以外,还可以传递deque,但是由于堆需要大量访问[]运算符,所以deque的效率不高。
2.构造函数
对于它的构造函数也是比较简单的,如下所示,可以无参构造,也可以用迭代器区间进行初始化。
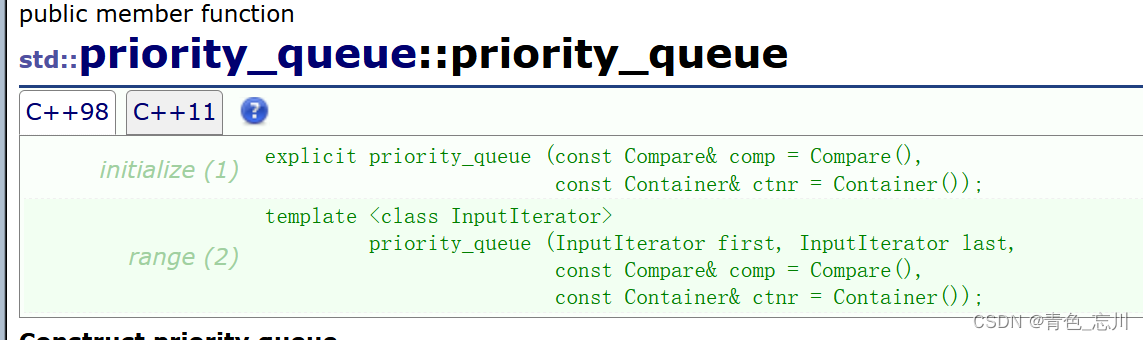
3.求数组中第k个最大的元素
题目链接:数组中第k个最大元素
这道题其实就是top-k问题,由于优先级队列就是一个堆,所以我们直接使用优先级队列可以很轻松的完成这道题
下面是建大堆的方法
class Solution {
public:
int findKthLargest(vector<int>& nums, int k) {
priority_queue<int> pq(nums.begin(),nums.end());
while(--k)
{
pq.pop();
}
return pq.top();
}
};
下面是建小堆的方法,注意我们的模板参数。
class Solution {
public:
int findKthLargest(vector<int>& nums, int k) {
priority_queue<int,vector<int>,greater<int>> pq(nums.begin(),nums.begin()+k);
for(int i=k;i<nums.size();i++)
{
if(nums[i]>pq.top())
{
pq.pop();
pq.push(nums[i]);
}
}
return pq.top();
}
};
三、手撕优先级队列
如下代码所示,对于优先级队列,主要还是堆的逻辑的实现。即堆的构造,向上调整和向下调整。
template<class T, class Container = vector<T>>
class priority_queue
{
private:
void AdjustDown(int parent)
{
int child = parent * 2 + 1;
while (child<_con.size())
{
if (child + 1 < _con.size() && _con[child] < _con[child + 1])
{
child++;
}
if (_con[child] > _con[parent])
{
swap(_con[child], _con[parent]);
parent = child;
child = parent * 2 + 1;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
void AdjustUp(int child)
{
int parent = (child - 1) / 2;
while (child > 0)
{
if (_con[child] > _con[parent])
{
swap(_con[child], _con[parent]);
child = parent;
parent = (child - 1) / 2;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
public:
template<class InputIterator>
priority_queue(InputIterator first, InputIterator last)
{
while (first != last)
{
_con.push_back(*first);
first++;
}
for (int i = (_con.size() - 1 - 1) / 2; i >= 0; i--)
{
AdjustDown(i);
}
}
priority_queue()
{}
void pop()
{
swap(_con[0], _con[_con.size() - 1]);
_con.pop_back();
AdjustDown(0);
}
void push(const T& val)
{
_con.push_back(val);
AdjustUp(_con.size() - 1);
}
const T& top()
{
return _con[0];
}
bool empty()
{
return _con.empty();
}
size_t size()
{
return _con.size();
}
private:
Container _con;
};
四、仿函数
1.仿函数介绍
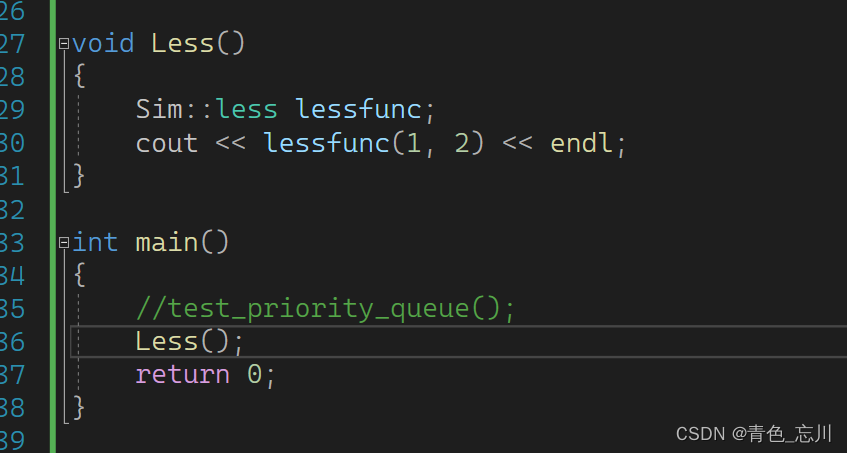
我们知道对于优先级队列可以用仿函数改变其是大堆还是小堆。根据底层逻辑可知,仿函数应该就是改变了大小比较。才改变的行为。我们可以写一个简单的仿函数类
如下所示就是一个最简单的仿函数
class less
{
public:
bool operator()(int x, int y)
{
return x < y;
}
};
这样我们就可以类似于一个函数一样进行比较大小了,仿函数即函数对象,可以让类对象像函数一样使用
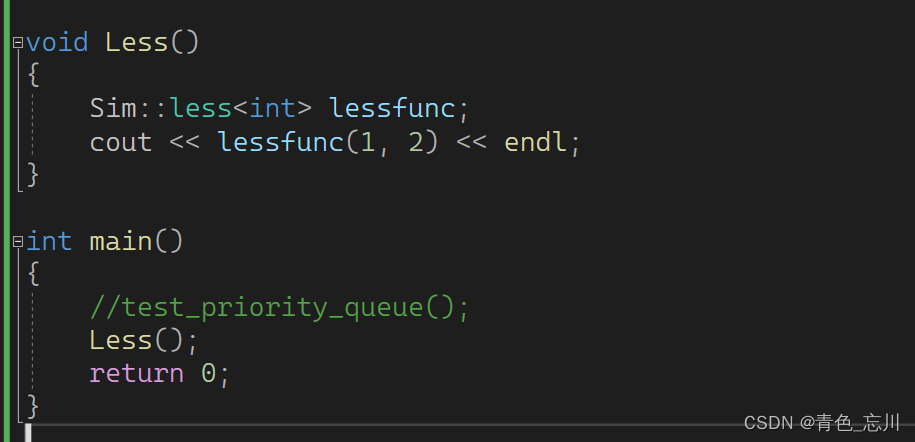
我们可以继续将这个仿函数扩展成模板,如下所示,这样更加贴近于我们的使用
template<class T>
class less
{
public:
bool operator()(const T& x, const T& y)
{
return x < y;
}
};
有了仿函数,我们就可以在前面的优先级队列中使用仿函数来切换大堆小堆了。在C语言中,我们想要实现这个功能只有使用函数指针。而这个仿函数就刚好可以替换掉函数指针。因为函数指针的弊端太明显了,它太过于复杂了,可读性不好。
2.优先级队列添加仿函数
#pragma once
namespace Sim
{
template<class T, class Container = vector<T>, class Compare = less<T>>
class priority_queue
{
private:
void AdjustDown(int parent)
{
Compare com;
int child = parent * 2 + 1;
while (child<_con.size())
{
if (child + 1 < _con.size() && com(_con[child], _con[child + 1]))
{
child++;
}
if (com(_con[parent], _con[child]))
{
swap(_con[child], _con[parent]);
parent = child;
child = parent * 2 + 1;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
void AdjustUp(int child)
{
Compare com;
int parent = (child - 1) / 2;
while (child > 0)
{
if (com(_con[parent], _con[child]))
{
swap(_con[child], _con[parent]);
child = parent;
parent = (child - 1) / 2;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
public:
template<class InputIterator>
priority_queue(InputIterator first, InputIterator last)
{
while (first != last)
{
_con.push_back(*first);
first++;
}
for (int i = (_con.size() - 1 - 1) / 2; i >= 0; i--)
{
AdjustDown(i);
}
}
priority_queue()
{}
void pop()
{
swap(_con[0], _con[_con.size() - 1]);
_con.pop_back();
AdjustDown(0);
}
void push(const T& val)
{
_con.push_back(val);
AdjustUp(_con.size() - 1);
}
const T& top()
{
return _con[0];
}
bool empty()
{
return _con.empty();
}
size_t size()
{
return _con.size();
}
private:
Container _con;
};
template<class T>
class less
{
public:
bool operator()(const T& x, const T& y)
{
return x < y;
}
};
template<class T>
class greater
{
public:
bool operator()(const T& x, const T& y)
{
return x > y;
}
};
}
接下来我们可以去测试一下我们的优先级队列,用内置类型是没有什么问题的,我们可以使用自定义类型来进行测试,比如将我们之前所写的日期类给导入进来
这里直接给出我们的代码
Date.h
#pragma once
#include<iostream>
#include<assert.h>
using namespace std;
class Date
{
//友元函数声明
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const Date& d);
friend istream& operator>>(istream& in, Date& d);
public:
Date(int year = 1, int month = 1, int day = 1);
void Print() const
{
cout << _year << '-' << _month << '-' << _day << endl;
}
bool operator<(const Date& x) const;
bool operator==(const Date& x) const;
bool operator<=(const Date& x) const;
bool operator>(const Date& x) const;
bool operator>=(const Date& x) const;
bool operator!=(const Date& x) const;
int GetMonthDay(int year, int month) const;
Date& operator+=(int day);
Date& operator-=(int day);
Date operator+(int day) const;
Date operator-(int day) const;
Date& operator++();
Date operator++(int);
Date& operator--();
Date operator--(int);
int operator-(const Date& d) const;
private:
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
};
ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const Date& d);
istream& operator>>(istream& in, Date& d);
Date.cpp
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include"Date.h"
Date::Date(int year, int month, int day)
{
if (month > 0 && month < 13
&& day>0 && day <= GetMonthDay(year, month))
{
_year = year;
_month = month;
_day = day;
}
else
{
cout << "非法日期" << endl;
assert(false);
}
}
bool Date::operator<(const Date& x) const
{
if (_year < x._year)
{
return true;
}
else if (_year == x._year && _month < x._month)
{
return true;
}
else if (_year == x._year && _month == x._month && _day < x._day)
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
bool Date::operator==(const Date& x) const
{
return (_year == x._year) &&
(_month == x._month) &&
(_day == x._day);
}
bool Date::operator<=(const Date& x) const
{
return (*this < x) || (*this == x);
}
bool Date::operator>(const Date& x) const
{
return !(*this <= x);
}
bool Date::operator>=(const Date& x) const
{
return !(*this < x);
}
bool Date::operator!=(const Date& x) const
{
return !(*this == x);
}
int Date::GetMonthDay(int year, int month) const
{
if (month <= 12 && month >= 1)
{
const static int ArrDay[13] = { 0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31 };
if (month == 2 && ((year % 4 == 0) && (year % 100 != 0) || (year % 400 == 0)))
{
return 29;
}
return ArrDay[month];
}
cout << "非法日期" << endl;
return -1;
}
Date& Date::operator+=(int day)
{
if (day < 0)
{
return *this -= -day;
}
_day += day;
while (_day > GetMonthDay(_year, _month))
{
_day -= GetMonthDay(_year, _month);
_month++;
if (_month > 12)
{
_month -= 12;
_year++;
}
}
return *this;
}
Date& Date::operator-=(int day)
{
if (day < 0)
{
return *this += -day;
}
_day -= day;
while (_day <= 0)
{
_month--;
if (_month <= 0)
{
_month += 12;
_year--;
}
_day += GetMonthDay(_year, _month);
}
return *this;
}
Date Date::operator+(int day) const
{
Date tmp = *this;
return tmp += day;
}
Date Date::operator-(int day) const
{
Date tmp = *this;
return tmp -= day;
}
Date& Date::operator++()
{
*this += 1;
return *this;
}
Date Date::operator++(int)
{
Date tmp = *this;
*this += 1;
return tmp;
}
Date& Date::operator--()
{
*this -= 1;
return *this;
}
Date Date::operator--(int)
{
Date tmp = *this;
*this -= 1;
return tmp;
}
int Date::operator-(const Date& d) const
{
Date max = *this;
Date min = d;
int flag = 1;
if (max < min)
{
max = d;
min = *this;
flag = -1;
}
int n = 0;
while (max != min)
{
min++;
n++;
}
return flag * n;
}
//流插入不能写成成员函数
//因为Date对象默认占用第一个参数,就是做了左操作数
//写出来就是下面的样子,不符合我们的使用习惯
//d1<<cout;
ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const Date& d)
{
out << d._year << "年" << d._month << "月" << d._day << "日" << endl;
return out;
}
istream& operator>>(istream& in, Date& d)
{
int year, month, day;
in >> year >> month >> day;
if (month > 0 && month < 13
&& day>0 && day <= d.GetMonthDay(year, month))
{
d._year = year;
d._month = month;
d._day = day;
}
else
{
cout << "非法日期" << endl;
assert(false);
}
return in;
}
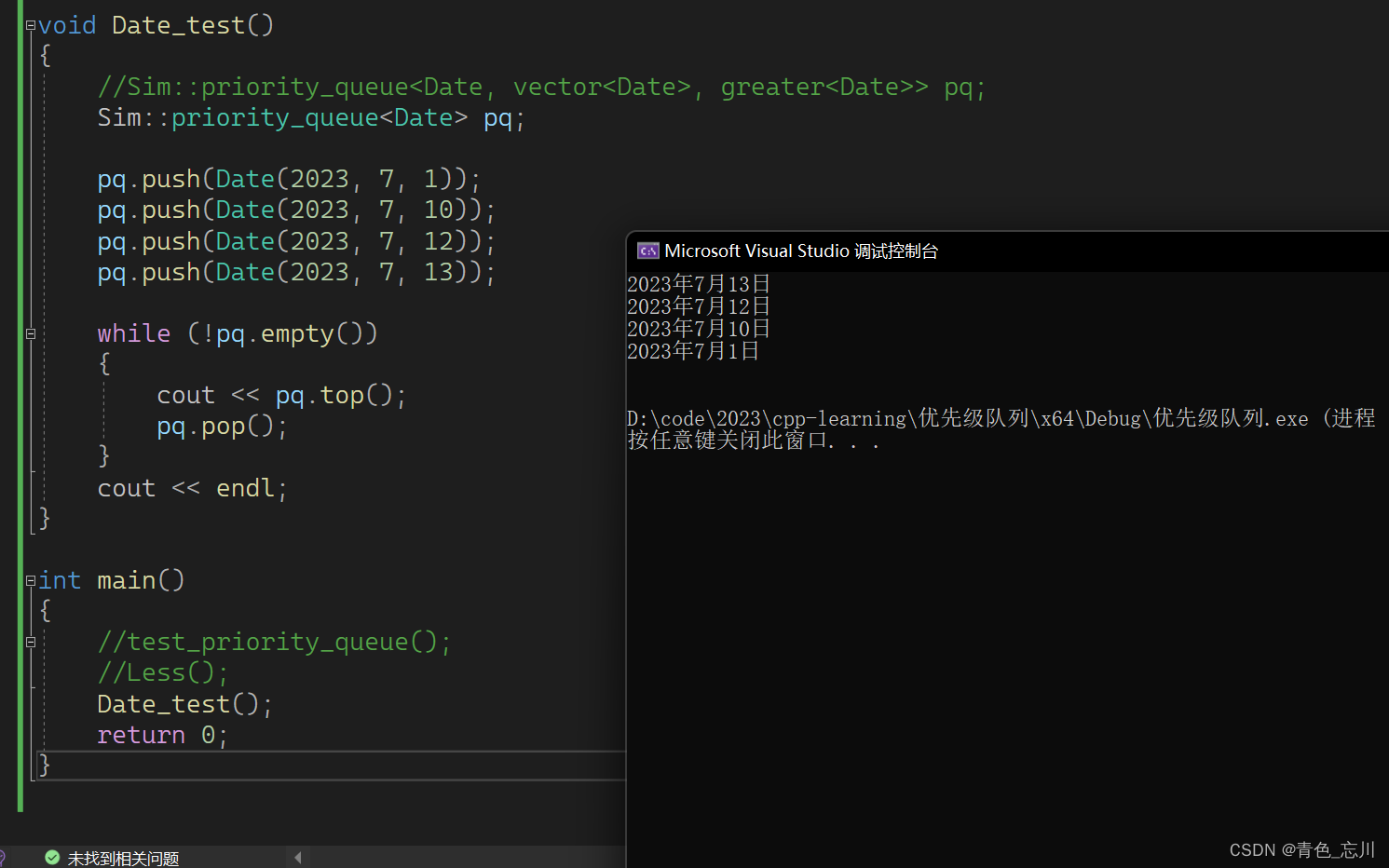
然后我们用下面的代码进行测试
void Date_test()
{
//Sim::priority_queue<Date, vector<Date>, greater<Date>> pq;
Sim::priority_queue<Date> pq;
pq.push(Date(2023, 7, 1));
pq.push(Date(2023, 7, 10));
pq.push(Date(2023, 7, 12));
pq.push(Date(2023, 7, 13));
while (!pq.empty())
{
cout << pq.top();
pq.pop();
}
cout << endl;
}
符合我们的预期
3.需要自己写仿函数的情形
我们的上面的仿函数是模拟库里面的行为,上面的仿函数在库里面早已给出,我们无需自己动手写。但是有时候我们也需要自己去写一个仿函数。
如下测试用例,我们此时存储的是一个指针,而不是一个对象
void Date_test1()
{
//Sim::priority_queue<Date, vector<Date>, greater<Date*>> pq;
Sim::priority_queue<Date*> pq;
pq.push(new Date(2023, 7, 1));
pq.push(new Date(2023, 7, 10));
pq.push(new Date(2023, 7, 12));
pq.push(new Date(2023, 7, 13));
while (!pq.empty())
{
cout << *(pq.top());
pq.pop();
}
cout << endl;
}
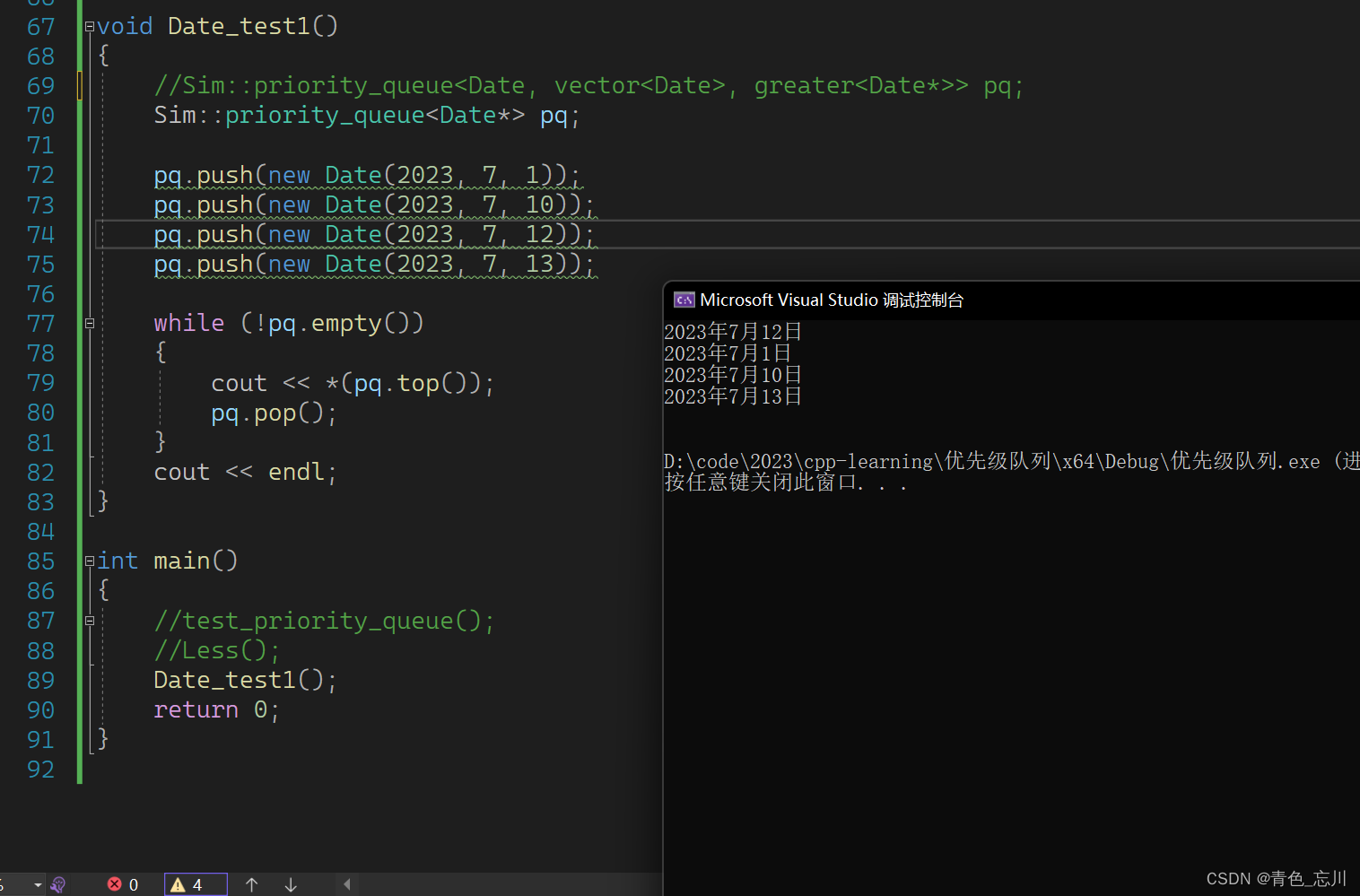
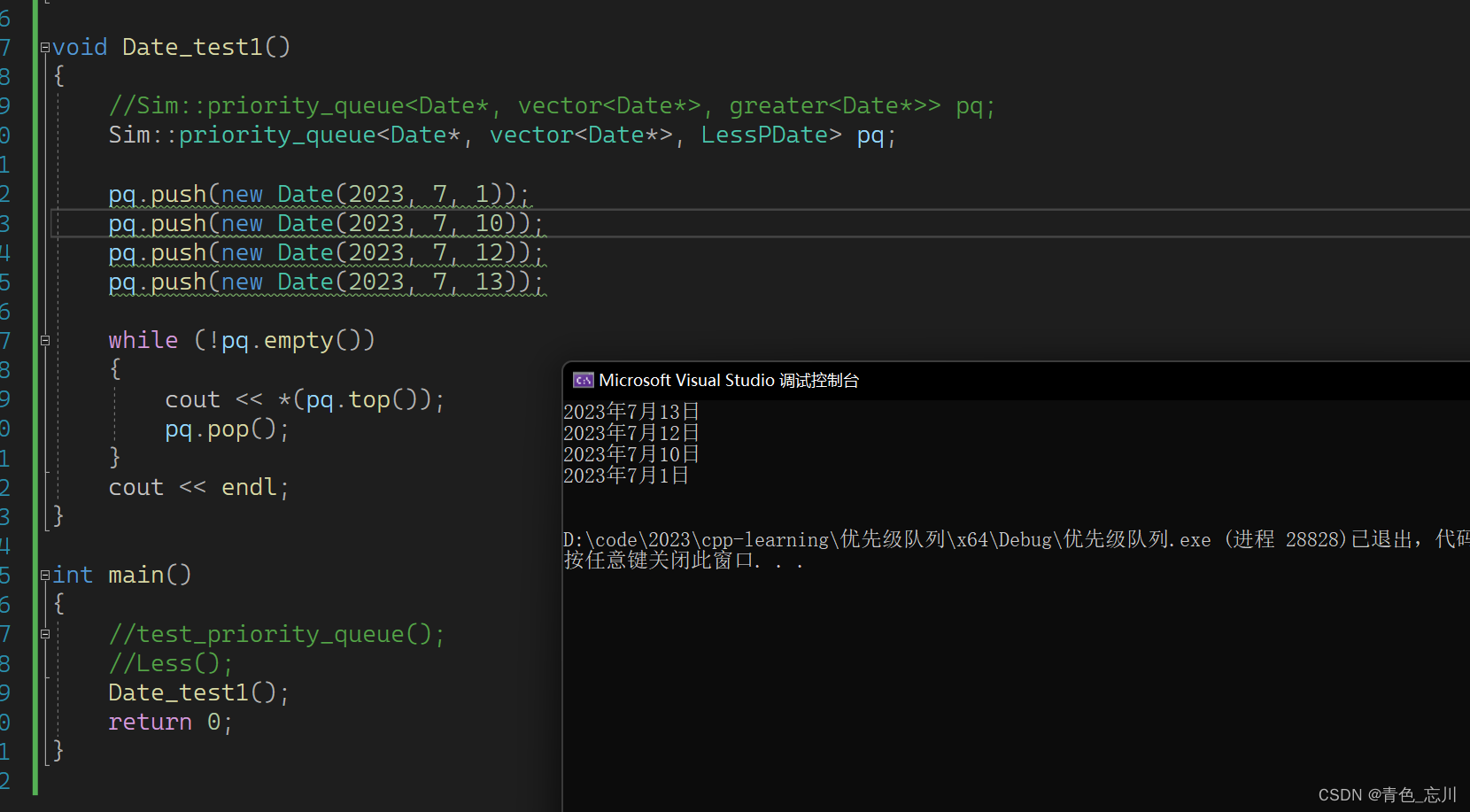
这时候我们的比较逻辑就会出问题,我们只能自己写一个去比较指针指向的内容
如下代码所示
struct LessPDate
{
bool operator()(Date* x, Date* y)
{
return *x < *y;
}
};
五、优先级队列完整代码
#pragma once
namespace Sim
{
template<class T, class Container = vector<T>, class Compare = less<T>>
class priority_queue
{
private:
void AdjustDown(int parent)
{
Compare com;
int child = parent * 2 + 1;
while (child<_con.size())
{
if (child + 1 < _con.size() && com(_con[child], _con[child + 1]))
{
child++;
}
if (com(_con[parent], _con[child]))
{
swap(_con[child], _con[parent]);
parent = child;
child = parent * 2 + 1;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
void AdjustUp(int child)
{
Compare com;
int parent = (child - 1) / 2;
while (child > 0)
{
if (com(_con[parent], _con[child]))
{
swap(_con[child], _con[parent]);
child = parent;
parent = (child - 1) / 2;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
public:
template<class InputIterator>
priority_queue(InputIterator first, InputIterator last)
{
while (first != last)
{
_con.push_back(*first);
first++;
}
for (int i = (_con.size() - 1 - 1) / 2; i >= 0; i--)
{
AdjustDown(i);
}
}
priority_queue()
{}
void pop()
{
swap(_con[0], _con[_con.size() - 1]);
_con.pop_back();
AdjustDown(0);
}
void push(const T& val)
{
_con.push_back(val);
AdjustUp(_con.size() - 1);
}
const T& top()
{
return _con[0];
}
bool empty()
{
return _con.empty();
}
size_t size()
{
return _con.size();
}
private:
Container _con;
};
template<class T>
class less
{
public:
bool operator()(const T& x, const T& y)
{
return x < y;
}
};
template<class T>
class greater
{
public:
bool operator()(const T& x, const T& y)
{
return x > y;
}
};
}
好了,本期内容就到这里了
如果对你有帮助,不要忘记点赞加收藏哦!!!