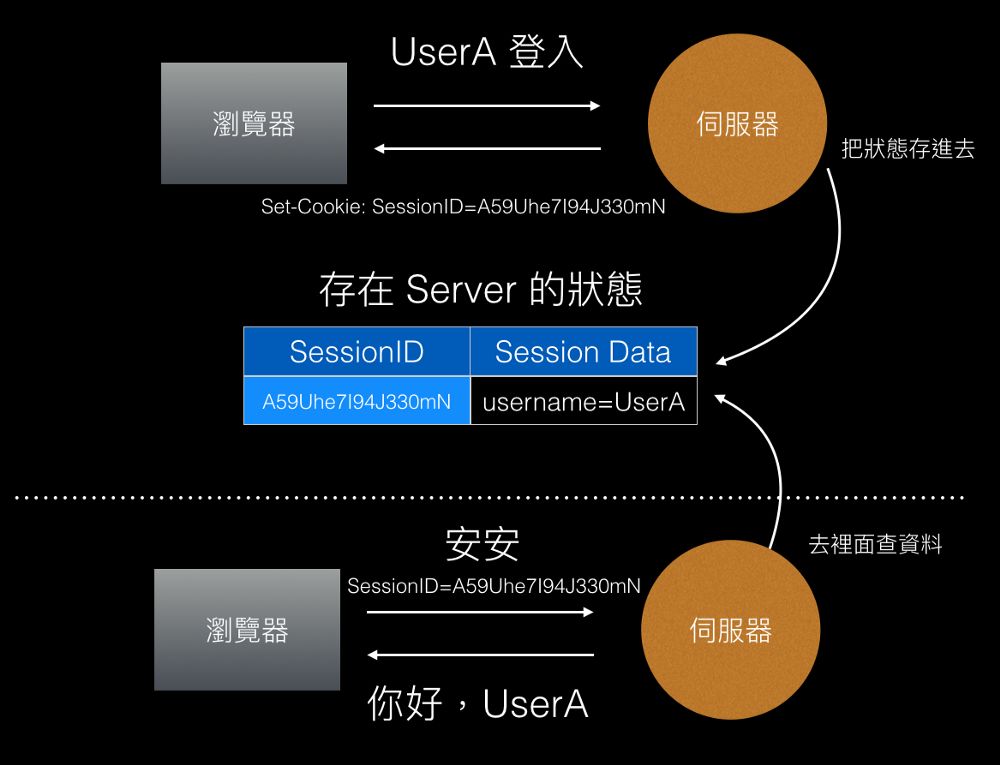
工程项目中,由于数据量不够,经常需要用到数据增强技术,尝试使用EDA进行数据增强。
1.EDA简介
EDA是一种简单但是非常有效的文本数据增强方法,是由美国Protago实验室发表于 EMNLP-IJCNLP 2019 会议。EDA来自论文《EDA: Easy Data Augmentation Techniques for Boosting Performance on Text Classification Tasks》
对于提高文本分类任务性能的简单数据增强技术,文中提出了四种数据增强技术方案,具体包括同义词替换,随机插入,随机交换,随机删除。并在深度学习模型RNN和CNN上用五个数据集做了文本分类实验的对比研究,实验中,作者根据数据集大小将训练集分为3种规模,用于比较EDA技术在训练数据集规模上的影响。实验也表明了,EDA提升了文本分类的效果。
2.增强方法
2-1. 同义词替换(Synonym Replacement, SR)
1.从文本中随机选取n个不属于停用词集的单词,并随机选择其同义词替换它们。
2.不考虑 stopwords,在句子中随机抽取n个词,然后从同义词词典中随机抽取同义词,并进行替换。关于同义词可以使用开源同义词表+领域自定义词表来建立。
注:需要借助synonyms库完成同义词的选择
def synonym_replacement(words, n):
new_words = words.copy()
random_word_list = list(set([word for word in words if word not in stop_words]))
random.shuffle(random_word_list)
num_replaced = 0
for random_word in random_word_list:
synonyms = get_synonyms(random_word)
if len(synonyms) >= 1:
synonym = random.choice(synonyms)
new_words = [synonym if word == random_word else word for word in new_words]
num_replaced += 1
if num_replaced >= n:
break
sentence = ' '.join(new_words)
new_words = sentence.split(' ')
return new_words
def get_synonyms(word):
return synonyms.nearby(word)[0]2-2.随机插入(Random Insertion, RI)
从文本中随机选择一个不在停用词表中的词,从它的同义词词集中随机选择一个词,插入到句子中的随机位置,并将该步骤重复 n 次。
def random_insertion(words, n):
new_words = words.copy()
for _ in range(n):
add_word(new_words)
return new_words
def add_word(new_words):
synonyms = []
counter = 0
while len(synonyms) < 1:
random_word = new_words[random.randint(0, len(new_words) - 1)]
synonyms = get_synonyms(random_word)
counter += 1
if counter >= 10:
return
random_synonym = random.choice(synonyms)
random_idx = random.randint(0, len(new_words) - 1)
new_words.insert(random_idx, random_synonym)2-3.随机交换(Random Swap, RS)
句子中,随机选择两个词,位置交换。该过程可以重复n次。 (swap_word 函数中随机产生两个序列下标,如果相同最多重新生成三次。)
def random_swap(words, n):
new_words = words.copy()
for _ in range(n):
new_words = swap_word(new_words)
return new_words
def swap_word(new_words):
random_idx_1 = random.randint(0, len(new_words) - 1)
random_idx_2 = random_idx_1
counter = 0
while random_idx_2 == random_idx_1:
random_idx_2 = random.randint(0, len(new_words) - 1)
counter += 1
if counter > 3:
return new_words
new_words[random_idx_1], new_words[random_idx_2] = new_words[random_idx_2], new_words[random_idx_1]
return new_words
2-4.随机删除(Random Deletion, RD)
用概率 p 随机删除文本中的单词。如果句子中只有一个单词,则直接返回。如果句子中所有单词都被删掉,则随机返回一个单词。
def random_deletion(words, p):
if len(words) == 1:
return words
new_words = []
for word in words:
r = random.uniform(0, 1)
if r > p:
new_words.append(word)
if len(new_words) == 0:
rand_int = random.randint(0, len(words) - 1)
return [words[rand_int]]
return new_words3.问题总结
3-1.若句子中有多个单词被改变了,那么句子的原始标签类别是否还会有效?
为了验证通过EDA方法产生的数据是否原数据特征一致,作者在Pro-Con数据集上进行数据的对比分析。
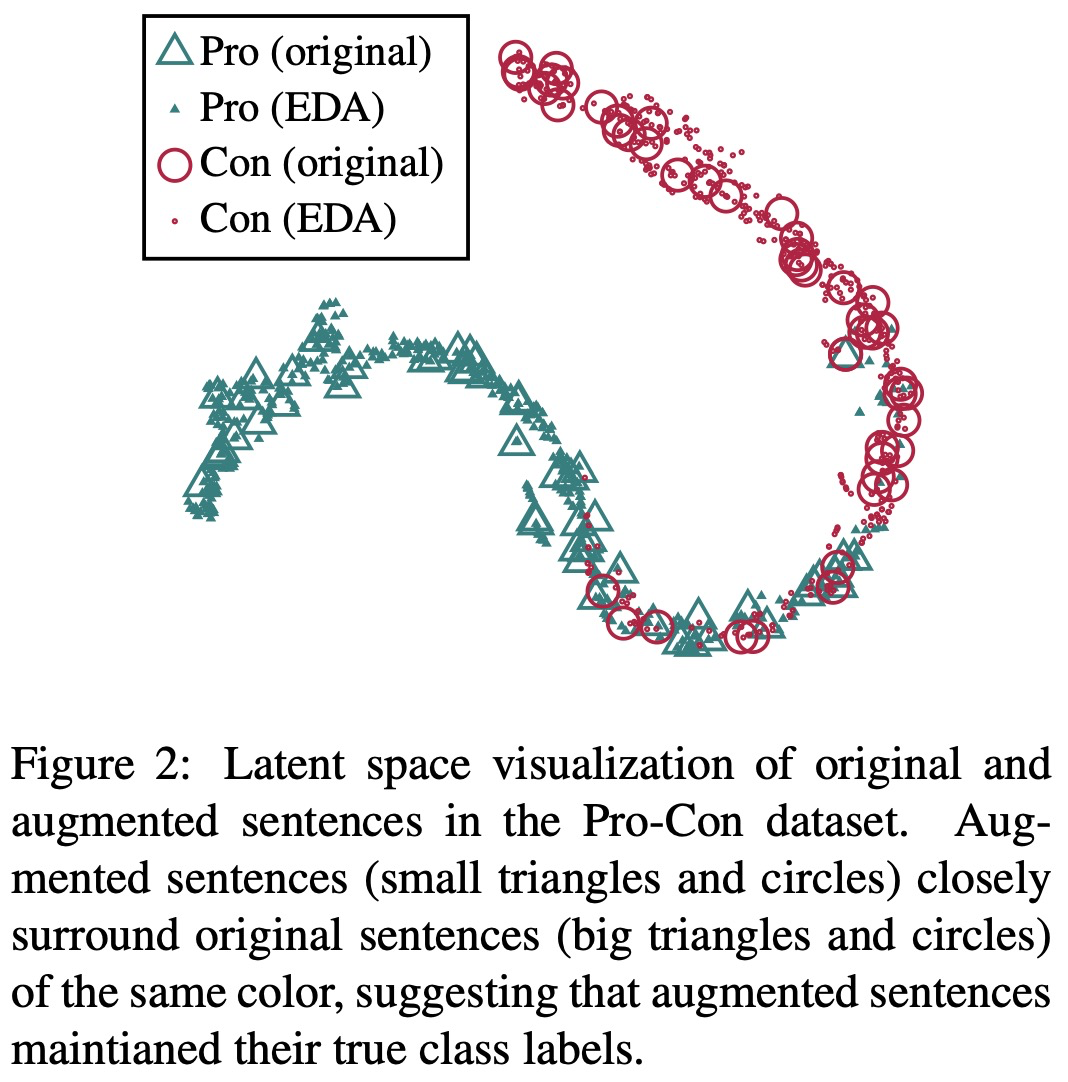
具体方法:首先,使用RNN在一未使用EDA过的数据集上进行训练;然后,对测试集进行EDA扩增,每个原始句子扩增出9个增强的句子,将这些句子作为测试集输入到RNN中;最后,从最后一个全连接层取出输出向量。应用t-SNE技术,将这些向量以二维的形式表示出来。如下图所示。下图中大三角和大圆圈都是原来的句子,小三角和小圆圈表示使用EDA技术进行数据增强的句子,可以看出来绝大多数原数据和EDA增强数据保持一致,即没有发生语义偏移,故而文中提出的4种数据增强技术不会影响文本的原始标签。
3-2.对于EDA中的每个方法,单独提升的效果如何?
为了确定性能的提升到底是由四种数据增强方式中哪一种,或哪几种方式起到的作用,以及哪种方式起到的作用比较大,作者做了消融研究——分别单独使用其中一种数据增强方式进行实验研究。并得到如下实验结果。

上图中,参数α表示四种数据增强方式里被改变的单词数量占原文本长度的比例,实验中取α={0.05,0.1,0.2,0.3,0.4,0.5}。
对于同义词替换(SR),当α较小时,实验性能提升明显,但是α变大时性能有所下降,可能是因为替换过多单词时改变了原文本的含义;
对于随机插入(RI),α在上述范围内的取值使得实验性能保持相对稳定,可能是因为随机插入的方法使得原文本中的单词顺序保持相对稳定;
对于随机交换(RS),当α≤0.2时实验性能提升明显,当α≥0.3时性能有所下降,因为过多的单词位置交换打乱了原文本的整体顺序,改变了文本含义;
对于随机删除(RD),当α较小时能够使得实验性能达到最高,但是α变大时能严重降低实验性能,因为删除过多单词时,句子难以理解,是的文本丢失语义信息。
消融实验得出的结论是,对于每个方法在小数据集上取得的效果更明显。 α如果太大的话,甚至会降低模型表现效果, α=0.1似乎是最佳值。
3-3.如何选取合适的增强语句个数?
在较小的数据集上,模型容易过拟合,因此生成多一点的语料能取得较好的效果。对于较大的数据集,每句话生成超过4个句子对于模型的效果提升就没有太大帮助。因此,作者推荐实际使用中的一些参数选取如下表所示。

naug :每个原始语句的增强语句个数;Ntrain :训练集大小
3-4.EDA提高文本分类的效果的原理是什么?
1.生成类似于原始数据的增强数据会引入一定程度的噪声,有助于防止过拟合;
2.使用EDA可以通过同义词替换和随机插入操作引入新的词汇,允许模型泛化到那些在测试集中但不在训练集中的单词;
4. EDA数据增强代码实现
4-1 说明
代码实现中是需要jieba分词,停用词表(默认使用哈工大停用词表),以及一个提供同义词的包(Synonyms)。
4-2 代码实现
import pandas as pd
import json
from tqdm import tqdm
# !/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import jieba
import re
import random
from random import shuffle
random.seed(2019)
import synonyms
# 停用词列表,默认使用哈工大停用词表
f = open('/home/zhenhengdong/WORk/Classfier/Dates/stopWord.json', encoding='utf-8')
stop_words = list()
for stop_word in f.readlines():
stop_words.append(stop_word[:-1])
# 文本清理
import re
def get_only_chars(line):
#1.清除所有的数字
########################################################################
# 同义词替换
# 替换一个语句中的n个单词为其同义词
########################################################################
def synonym_replacement(words, n):
new_words = words.copy()
random_word_list = list(set([word for word in words if word not in stop_words]))
random.shuffle(random_word_list)
num_replaced = 0
for random_word in random_word_list:
synonyms = get_synonyms(random_word)
if len(synonyms) >= 1:
synonym = random.choice(synonyms)
new_words = [synonym if word == random_word else word for word in new_words]
num_replaced += 1
if num_replaced >= n:
break
sentence = ' '.join(new_words)
new_words = sentence.split(' ')
return new_words
def get_synonyms(word):
return synonyms.nearby(word)[0]
########################################################################
# 随机插入
# 随机在语句中插入n个词
########################################################################
def random_insertion(words, n):
new_words = words.copy()
for _ in range(n):
add_word(new_words)
return new_words
def add_word(new_words):
synonyms = []
counter = 0
while len(synonyms) < 1:
random_word = new_words[random.randint(0, len(new_words) - 1)]
synonyms = get_synonyms(random_word)
counter += 1
if counter >= 10:
return
random_synonym = random.choice(synonyms)
random_idx = random.randint(0, len(new_words) - 1)
new_words.insert(random_idx, random_synonym)
########################################################################
# Random swap
# Randomly swap two words in the sentence n times
########################################################################
def random_swap(words, n):
new_words = words.copy()
for _ in range(n):
new_words = swap_word(new_words)
return new_words
def swap_word(new_words):
random_idx_1 = random.randint(0, len(new_words) - 1)
random_idx_2 = random_idx_1
counter = 0
while random_idx_2 == random_idx_1:
random_idx_2 = random.randint(0, len(new_words) - 1)
counter += 1
if counter > 3:
return new_words
new_words[random_idx_1], new_words[random_idx_2] = new_words[random_idx_2], new_words[random_idx_1]
return new_words
########################################################################
# 随机删除
# 以概率p删除语句中的词
########################################################################
def random_deletion(words, p):
if len(words) == 1:
return words
new_words = []
for word in words:
r = random.uniform(0, 1)
if r > p:
new_words.append(word)
if len(new_words) == 0:
rand_int = random.randint(0, len(words) - 1)
return [words[rand_int]]
return new_words
########################################################################
# EDA函数
def eda_func(sentence, alpha_sr = 0.35, alpha_ri = 0.35, alpha_rs = 0.35, p_rd = 0.35, num_aug = 12):
seg_list = jieba.cut(sentence)
seg_list = " ".join(seg_list)
words = list(seg_list.split())
num_words = len(words)
augmented_sentences = []
num_new_per_technique = int(num_aug / 4)
n_sr = max(1, int(alpha_sr * num_words))
n_ri = max(1, int(alpha_ri * num_words))
n_rs = max(1, int(alpha_rs * num_words))
# print(words, "\n")
# 同义词替换sr
for _ in range(num_new_per_technique):
a_words = synonym_replacement(words, n_sr)
augmented_sentences.append(''.join(a_words))
# 随机插入ri
for _ in range(num_new_per_technique):
a_words = random_insertion(words, n_ri)
augmented_sentences.append(''.join(a_words))
#
# 随机交换rs
for _ in range(num_new_per_technique):
a_words = random_swap(words, n_rs)
augmented_sentences.append(''.join(a_words))
#
#
# 随机删除rd
for _ in range(num_new_per_technique):
a_words = random_deletion(words, p_rd)
augmented_sentences.append(''.join(a_words))
# print(augmented_sentences)
shuffle(augmented_sentences)
if num_aug >= 1:
augmented_sentences = augmented_sentences[:num_aug]
else:
keep_prob = num_aug / len(augmented_sentences)
augmented_sentences = [s for s in augmented_sentences if random.uniform(0, 1) < keep_prob]
# augmented_sentences.append(seg_list)
def Data_Augmentation(item,num):
augmented_sentence_dataframe = pd.DataFrame()
for join_class in tqdm(stations_dict[item]):
for index in range(len(new_data)):
if new_data.loc[index].联合分类 == join_class:
augmented_sentences = eda_func(sentence = new_data.loc[index]['内容'])[:num]
for augmented_sentence in augmented_sentences:
creat_new_data = pd.DataFrame()
creat_new_data['内容'] = [augmented_sentence]
creat_new_data['反馈类型'] = [new_data.loc[index]['反馈类型']]
creat_new_data['一级分类'] = [new_data.loc[index]['一级分类']]
creat_new_data['二级分类'] = [new_data.loc[index]['二级分类']]
creat_new_data['联合分类'] = [new_data.loc[index]['联合分类']]
augmented_sentence_dataframe = pd.concat([augmented_sentence_dataframe, creat_new_data], ignore_index=True)
print(len(augmented_sentence_dataframe))
return augmented_sentence_dataframe
if __name__ == '__main__':
new_data = pd.read_csv('./Temp_data.csv')
stations_dict = {}
for index,key_values in enumerate(new_data.联合分类.value_counts().items()):
if 1500 > key_values[1] > 1000:
stations_dict.setdefault('1000', []).append(key_values[0])
if 1000 > key_values[1] > 800:
stations_dict.setdefault('800', []).append(key_values[0])
if 800 > key_values[1] > 600:
stations_dict.setdefault('600', []).append(key_values[0])
if 600 > key_values[1] > 500:
stations_dict.setdefault('500', []).append(key_values[0])
if 500 > key_values[1] > 400:
stations_dict.setdefault('400', []).append(key_values[0])
if 400 > key_values[1] > 300:
stations_dict.setdefault('300', []).append(key_values[0])
if 300 > key_values[1] > 0:
stations_dict.setdefault('0', []).append(key_values[0])
Temp_data = pd.DataFrame()
for item in stations_dict:
if item == '1000':#13642
augmented_sentence_dataframe = Data_Augmentation(item,num = 2)
Temp_data = pd.concat([Temp_data, augmented_sentence_dataframe], ignore_index=True)
if item == '800':#16503
augmented_sentence_dataframe = Data_Augmentation(item,num = 3)
Temp_data = pd.concat([Temp_data, augmented_sentence_dataframe], ignore_index=True)
if item == '600':#23684
augmented_sentence_dataframe = Data_Augmentation(item,num = 4)
Temp_data = pd.concat([Temp_data, augmented_sentence_dataframe], ignore_index=True)
if item == '500':#15186
augmented_sentence_dataframe = Data_Augmentation(item,num = 6)
Temp_data = pd.concat([Temp_data, augmented_sentence_dataframe], ignore_index=True)
if item == '400':#20400
augmented_sentence_dataframe = Data_Augmentation(item,num = 8)
Temp_data = pd.concat([Temp_data, augmented_sentence_dataframe], ignore_index=True)
if item == '300':#7137
augmented_sentence_dataframe = Data_Augmentation(item,num = 9)
Temp_data = pd.concat([Temp_data, augmented_sentence_dataframe], ignore_index=True)
if item == '0':#3897
augmented_sentence_dataframe = Data_Augmentation(item,num = 9)
Temp_data = pd.concat([Temp_data, augmented_sentence_dataframe], ignore_index=True)
#将合并的data存储
Temp_data.to_csv('./Temp_data_single_sample.csv',index = False,encoding='utf8')Reference:
1.https://www.zhihu.com/question/341361292/answer/2916784123
2.NLP中的数据增强:UDA、EDA_eda数据增强_快乐小码农的博客-CSDN博客