文章目录
- 前言
- 一、如何实现?
- 1、数值转成分数
- 2、Row+Flexible布局横向
- 3、Column+Flexible布局纵向
- 二、完整代码
- 三、使用示例
- 1、基本用法
- 2、四分屏
- 3、六分屏
- 4、八分屏
- 5、九分屏
- 6、414分屏
- 总结
前言
做视频监控项目时需要需要展示多分屏,比如2x2、3x3、414等等,如果每一种分屏都单独实现会很麻烦,而且不能支持用户定制。最好的方式还是实现一个通用的分屏容器,而且采样比例计算位置大小,可以适配任意尺寸。
一、如何实现?
最直观的实现方式是获取控件宽高然后按比例计算,但是flutter在build的时候无法获取位置宽高信息,只有绘制之后才能获取,所以这种方式并不容易实现,比较简单的方式应该是使用Row、Column结合Flexible。
1、数值转成分数
需要转换的数值
final Rect rect; //子控件位置大小,比例值范围0-1
定义一个分数对象
//分数
class Rational {
int den = 1; //分母
int num = 0; //分子
Rational(this.num, this.den);
//通过double构造,accuracy小数点后精度
factory Rational.fromDouble(double d, {int accuracy = 5}) {
int den = 1;
while (d > d.toInt() && accuracy-- > 0) {
d *= 10;
den *= 10;
}
return Rational(d.toInt(), den);
}
}
转成分数并对齐分母
//将位置大小转成分数
final width = Rational.fromDouble(rect.width);
final x = Rational.fromDouble(rect.left);
final height = Rational.fromDouble(rect.height);
final y = Rational.fromDouble(rect.top);
//对齐分母
if (width.den != x.den) {
final den = width.den;
width.den *= x.den;
width.num *= x.den;
x.den *= den;
x.num *= den;
}
//对齐分母
if (height.den != y.den) {
final den = height.den;
height.den *= y.den;
height.num *= y.den;
y.den *= den;
y.num *= den;
}
2、Row+Flexible布局横向
我们利用Row的自动布局,以及Flexible的比例布局的特性,根据上面的分数计算出控件比例的位置大小对应的flex值即可。
Row(
children: [
Flexible(
flex: x.num,
child: Container(),
),
Flexible(
flex: width.num,
child: child/*子控件,加上纵向布局则是Column*/
),
Flexible(flex: width.den - width.num - x.num, child: Container()),
],
);
}
3、Column+Flexible布局纵向
我们利用Column的自动布局,以及Flexible的比例布局的特性,根据上面的分数计算出控件比例的位置大小对应的flex值即可。
Column(
children: [
Flexible(
flex: y.num,
child: Container(),
),
Flexible(flex: height.num, child: child/*子控件*/),
Flexible(
flex: height.den - height.num - y.num,
child: Container(),
),
],
)
二、完整代码
proportion.dart
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
//比例布局控件,
class Proportion extends StatelessWidget {
final Rect rect; //位置大小,比例值范围0-1
final Widget child;
const Proportion({
super.key,
this.rect = const Rect.fromLTWH(0, 0, 1, 1),
required this.child,
});
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
//实现按比例显示布局
final width = Rational.fromDouble(rect.width);
final x = Rational.fromDouble(rect.left);
final height = Rational.fromDouble(rect.height);
final y = Rational.fromDouble(rect.top);
if (width.den != x.den) {
final den = width.den;
width.den *= x.den;
width.num *= x.den;
x.den *= den;
x.num *= den;
}
if (height.den != y.den) {
final den = height.den;
height.den *= y.den;
height.num *= y.den;
y.den *= den;
y.num *= den;
}
return Row(
children: [
Flexible(
flex: x.num,
child: Container(),
),
Flexible(
flex: width.num,
child: Column(
children: [
Flexible(
flex: y.num,
child: Container(),
),
Flexible(flex: height.num, child: child),
Flexible(
flex: height.den - height.num - y.num,
child: Container(),
),
],
),
),
Flexible(flex: width.den - width.num - x.num, child: Container()),
],
);
}
}
//分数
class Rational {
int den = 1; //分母
int num = 0; //分子
Rational(this.num, this.den);
//通过double构造,accuracy小数点后精度
factory Rational.fromDouble(double d, {int accuracy = 5}) {
int den = 1;
while (d > d.toInt() && accuracy-- > 0) {
d *= 10;
den *= 10;
}
return Rational(d.toInt(), den);
}
}
常用布局(可选)
proportions.dart
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
import 'proportion.dart';
//常用布局,需配合stack作为父容器使用
class Proportions {
Proportions._();
//全屏
static List<Proportion> fullScreen({
required Widget child,
}) =>
[
Proportion(
rect: const Rect.fromLTWH(0, 0, 1, 1),
child: child,
)
];
//二分屏
static List<Proportion> halfScreen({
required Widget left,
required Widget right,
}) =>
[
Proportion(
rect: const Rect.fromLTWH(0, 0, 0.5, 1),
child: left,
),
Proportion(
rect: const Rect.fromLTWH(0.5, 0, 0.5, 1),
child: right,
),
];
//四分屏
static List<Proportion> quadScreen({
required List<Widget> children,
}) {
return [
Proportion(
rect: const Rect.fromLTWH(0, 0, 0.5, 0.5),
child: children[0],
), //左上
Proportion(
rect: const Rect.fromLTWH(0.5, 0, 0.5, 0.5),
child: children[1],
), //右上
Proportion(
rect: const Rect.fromLTWH(0, 0.5, 0.5, 0.5),
child: children[2],
), //左下
Proportion(
rect: const Rect.fromLTWH(0.5, 0.5, 0.5, 0.5),
child: children[3],
), //右下
];
}
//6 分屏
static List<Proportion> sixScreen({
required List<Widget> children,
}) {
return [
Proportion(
rect: const Rect.fromLTWH(0, 0, 0.666, 0.666),
child: children[0],
), //左上
Proportion(
rect: const Rect.fromLTWH(0.666, 0, 0.333, 0.333),
child: children[1],
), //右上
Proportion(
rect: const Rect.fromLTWH(0.666, 0.333, 0.333, 0.333),
child: children[2],
), //右中
Proportion(
rect: const Rect.fromLTWH(0.666, 0.666, 0.333, 0.333),
child: children[3],
), //右下
Proportion(
rect: const Rect.fromLTWH(0.333, 0.666, 0.333, 0.333),
child: children[4],
), //中下
Proportion(
rect: const Rect.fromLTWH(0, 0.666, 0.333, 0.333),
child: children[5],
), //左下
];
}
//8 分屏
static List<Proportion> eightScreen({
required List<Widget> children,
}) {
return [
Proportion(
rect: const Rect.fromLTWH(0, 0, 0.75, 0.75),
child: children[0],
), //左上
Proportion(
rect: const Rect.fromLTWH(0.75, 0, 0.25, 0.25),
child: children[1],
), //右上
Proportion(
rect: const Rect.fromLTWH(0.75, 0.25, 0.25, 0.25),
child: children[2],
), //右中1
Proportion(
rect: const Rect.fromLTWH(0.75, 0.5, 0.25, 0.25),
child: children[3],
), //右中2
Proportion(
rect: const Rect.fromLTWH(0.75, 0.75, 0.25, 0.25),
child: children[4],
), //右下
Proportion(
rect: const Rect.fromLTWH(0.5, 0.75, 0.25, 0.25),
child: children[5],
), //中下2
Proportion(
rect: const Rect.fromLTWH(0.25, 0.75, 0.25, 0.25),
child: children[6],
), //中下1
Proportion(
rect: const Rect.fromLTWH(0, 0.75, 0.25, 0.25),
child: children[7],
), //左下
];
}
//9 分屏
static List<Proportion> nightScreen({
required List<Widget> children,
}) {
int n = 0;
return [
...children.getRange(0, 9).map(
(element) {
final i = n++;
return Proportion(
rect: Rect.fromLTWH(
(i % 3) * 0.333,
(i ~/ 3) * 0.333,
0.333,
0.333,
),
child: element,
);
},
)
];
}
//16 分屏
static List<Proportion> sixteenScreen({
required List<Widget> children,
}) {
int n = 0;
return [
...children.getRange(0, 16).map(
(element) {
final i = n++;
return Proportion(
rect: Rect.fromLTWH((i % 4) * 0.25, (i ~/ 4) * 0.25, 0.25, 0.25),
child: element,
);
},
)
];
}
//414分屏
static List<Proportion> fourOneFourScreen({
required List<Widget> children,
}) {
int n = 0;
return [
//左4
...children.getRange(0, 4).map(
(element) {
final i = n++;
return Proportion(
rect: Rect.fromLTWH((i ~/ 4) * 0.25, (i % 4) * 0.25, 0.25, 0.25),
child: element,
);
},
),
//中间
Proportion(
rect: const Rect.fromLTWH(0.25, 0, 0.5, 1),
child: children[4],
),
//右边4
...children.getRange(5, 9).map(
(element) {
final i = n++ + 8;
return Proportion(
rect: Rect.fromLTWH((i ~/ 4) * 0.25, (i % 4) * 0.25, 0.25, 0.25),
child: element,
);
},
)
];
}
}
三、使用示例
1、基本用法
设置子控件位置大小。一般配合stack作为父容器使用
Proportion(
rect: Rect.fromLTRB(0, 0, 0.5, 0.5), //子控件位置大小,(0, 0, 0.5, 0.5)表示左上1/4的区域
child: ColoredBox(color: Colors.red), //子控件
);
2、四分屏
final List<int> _nums = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9];
Stack(
children: Proportions.quadScreen(children: [
..._nums.map((e) => Container(
constraints: const BoxConstraints.expand(),
decoration: BoxDecoration(
border: Border.all(color: Colors.deepPurple.shade300)),
child: Center(child: Text("video $e")),
))

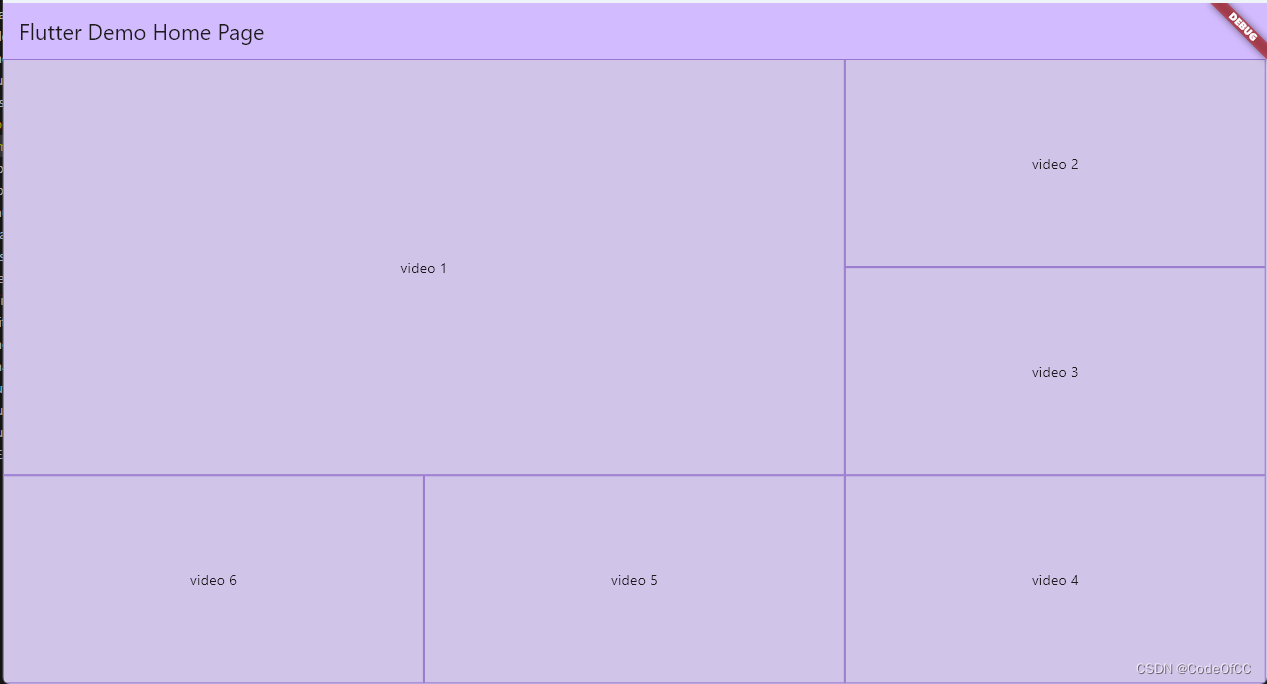
3、六分屏
final List<int> _nums = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9];
Stack(
children: Proportions.sixScreen(children: [
..._nums.map((e) => Container(
constraints: const BoxConstraints.expand(),
decoration: BoxDecoration(
border: Border.all(color: Colors.deepPurple.shade300)),
child: Center(child: Text("video $e")),
))
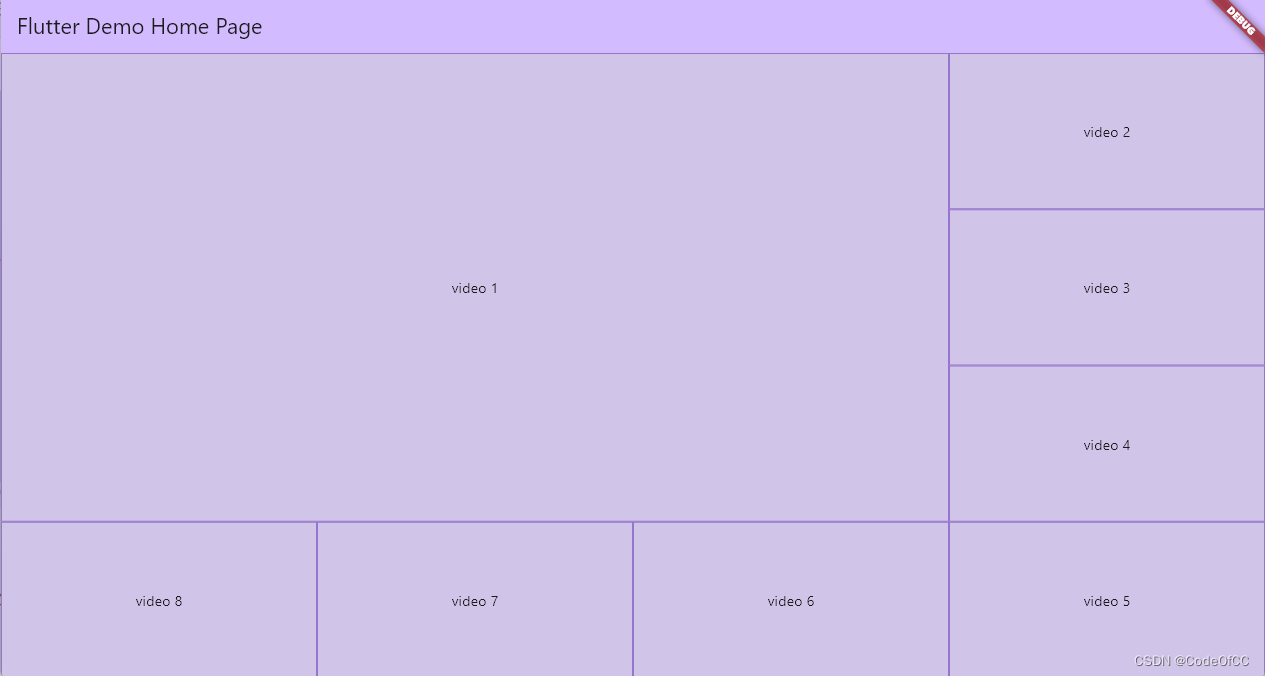
4、八分屏
final List<int> _nums = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9];
Stack(
children: Proportions.eightScreen(children: [
..._nums.map((e) => Container(
constraints: const BoxConstraints.expand(),
decoration: BoxDecoration(
border: Border.all(color: Colors.deepPurple.shade300)),
child: Center(child: Text("video $e")),
))

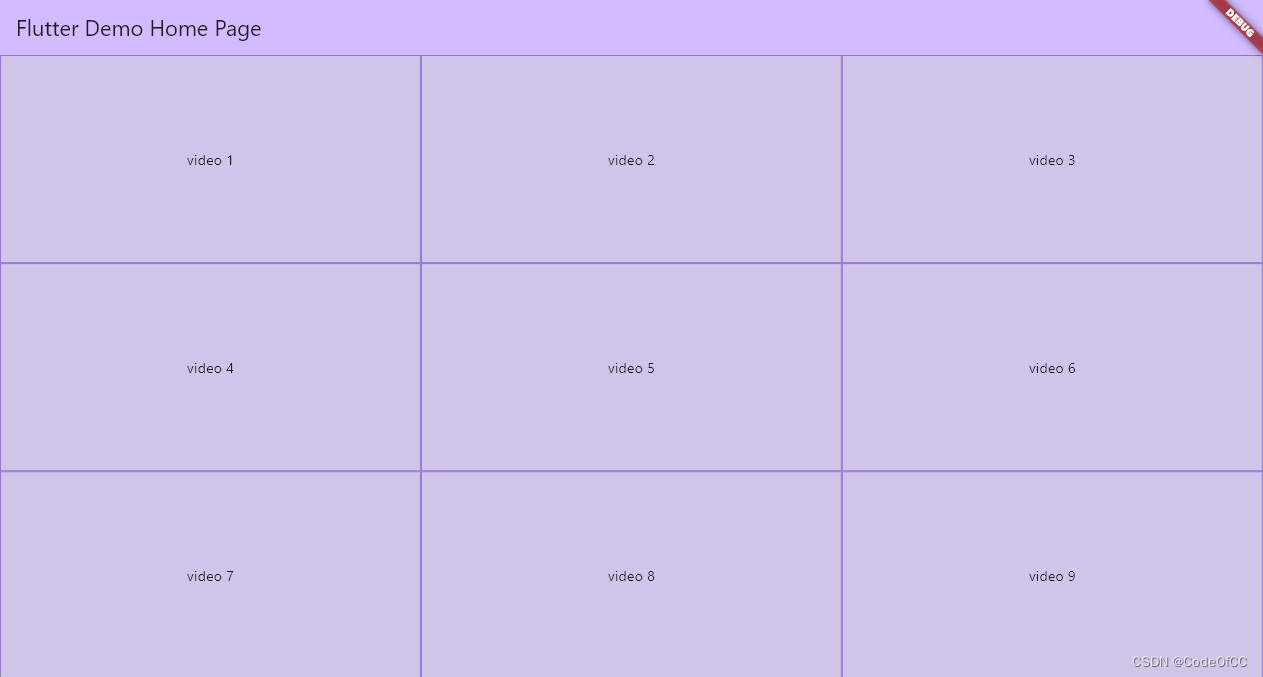
5、九分屏
final List<int> _nums = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9];
Stack(
children: Proportions.nightScreen(children: [
..._nums.map((e) => Container(
constraints: const BoxConstraints.expand(),
decoration: BoxDecoration(
border: Border.all(color: Colors.deepPurple.shade300)),
child: Center(child: Text("video $e")),
))
6、414分屏
final List<int> _nums = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9];
Stack(
children: Proportions.fourOneFourScreen(children: [
..._nums.map((e) => Container(
constraints: const BoxConstraints.expand(),
decoration: BoxDecoration(
border: Border.all(color: Colors.deepPurple.shade300)),
child: Center(child: Text("video $e")),
))

始终保持比例

总结
以上就是今天要讲的内容,本文用的是比较简单的方式实现了比例布局控件,其主要特点是可以灵活使用,尤其是方便视频分屏预览的实现。本质上也是对一类布局规则的总结得出的一个通用的控件,因为考虑到2x2、3x3还是可以写死的,但是到了4x4、5x5写死则需要16、25个参数,那就必须改用数组,也就意味着需要根据规则计算位置,那和本文一样了。所以本文的控件是有实际使用意义的。