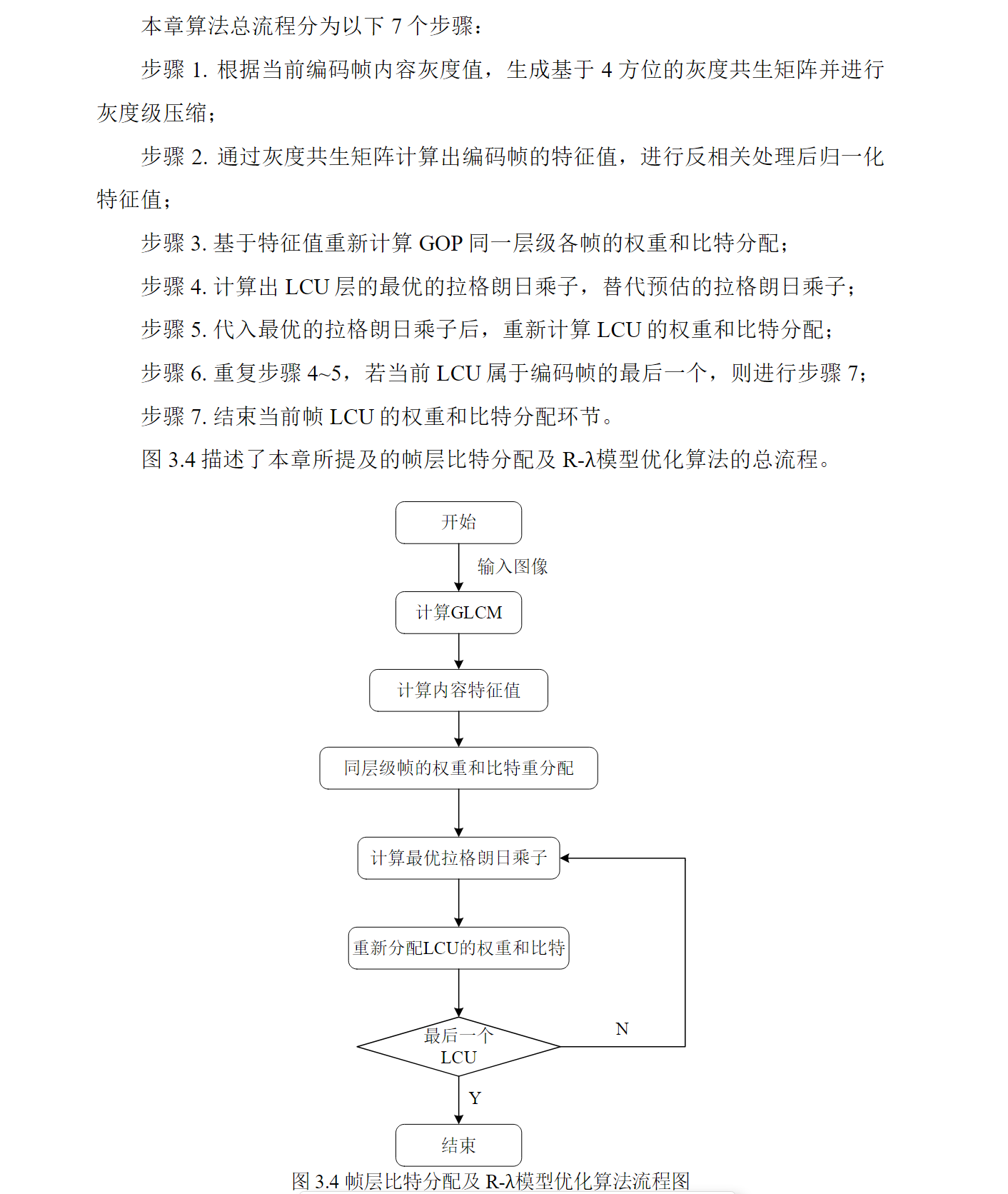
通篇全文都是不开启事务,不开启多线程,只有主线程去执行
借鉴 Redis源码与设计剖析 – 18.Redis网络连接库分析
客户端与集群之间数据的交互
- IO多路复用与客户端、输出缓冲区和读取缓冲区之间的关系
- 一、读取缓冲区
- 1、新客户端连接时注册从socket读取事件到server.eventLoop
- (1)新的客户端连接服务端时,服务端要创建一个client信息存储在服务端,
- (2)通过connSocketSetReadHandler设置客户端的读取事件
- (3) 通过aeCreateFileEvent把文件事件写入server.eventLoop
- 2、服务端启动最后一步是主线程循环遍历server.eventLoop,停止条件是server.eventLoop为0
- 3、读取事件的实现函数readQueryFromClient
- (1)主线程首先把socket中的数据写入到client缓冲区
- (2) 遍历缓冲区
- 1) 每次取缓冲区中完整一条命令到client中的argv数组中
- 2) 如果client中的argv数组大于0,则主线程会执行命令
- 二、主线程执行命令processCommand,
- 1、call()由主线程执行命令
- (1)主线程在执行命令的函数内,有结果了会同步把结果返回到输出缓冲区
- 2、把事务请求缓存在客户端事务数组中,等待后面的事务提交命令exec让主线程执行第一步的call()
- 三、输出缓冲区
- 1、主线程执行命令后通过addReply写入输出缓冲区和回复列表
- 2、在EventLoop增加一个可以从输出缓冲区写入到socket的事件前置函数beforeSleep
- (1)beforeSleep函数在循环事件执行函数aeProcessEvents代码中的位置
- (2)beforeSleep中有调用从输出缓冲区输出到客户端的方法writeToClient
- (3)存在主从节点的集群,只有主节点执行把数据从输出缓冲区输出到客户端
- (3)如果输出缓冲区执行了一次写入到客户端操作发现输出缓冲区还有数据,则会注册文件事件
IO多路复用与客户端、输出缓冲区和读取缓冲区之间的关系
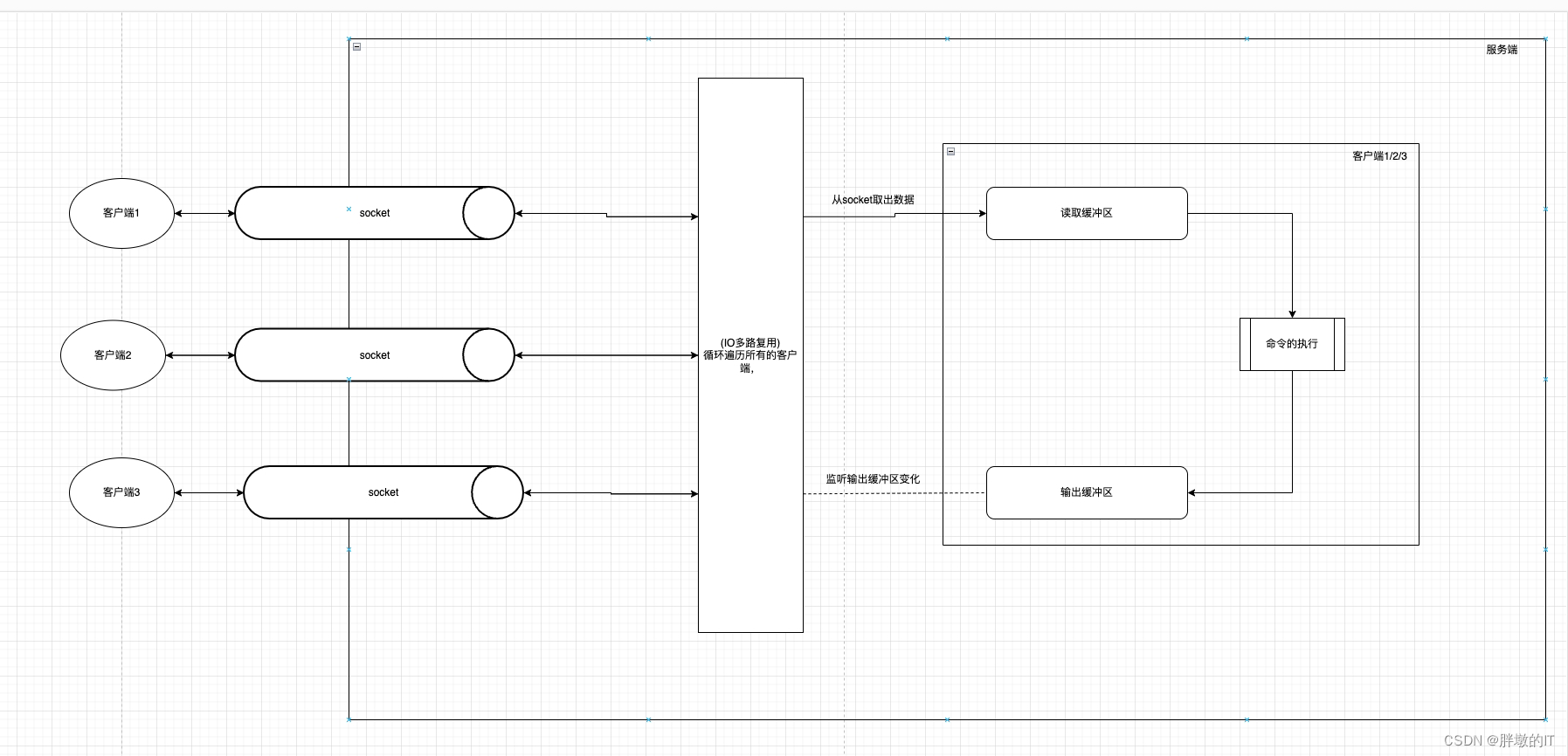
一、读取缓冲区
1、新客户端连接时注册从socket读取事件到server.eventLoop
typedef struct client{
......//删除干扰字段
// client的套接字
int fd; /* Client socket. */
......//删除干扰字段
// 保存指向数据库的ID
int dictid; /* ID of the currently SELECTed DB. */
......//删除干扰字段
// 输入缓冲区
sds querybuf; /* Buffer we use to accumulate client queries. */
// 输入缓存的峰值
size_t querybuf_peak; /* Recent (100ms or more) peak of querybuf size. */
// client输入命令时,参数的数量
int argc; /* Num of arguments of current command. */
// client输入命令的参数列表
robj **argv; /* Arguments of current command. */
// 事物状态
multiState mstate; /* MULTI/EXEC state */
......//删除干扰字段
// 回复缓存列表,用于发送大于固定回复缓冲区的回复:保存命令回复的链表. 因为静态缓冲区大小固定,主要保存固定长度的命令回复,当处理一些返回大量回复的命令,则会将命令回复以链表的形式连接起来
list *reply; /* List of reply objects to send to the client. */
// 已发送的字节数或对象的字节数
size_t sentlen; /* Amount of bytes already sent in the current*/
// 回复缓存列表对象的总字节数:保存回复链表的字节数
unsigned long long reply_bytes
/* Response buffer */
// 回复固定缓冲区的偏移量:记录静态缓冲区的偏移量,也就是buf数组已经使用的字节数
int bufpos;
// 回复固定缓冲区:char buf[16*1024]:保存执行完命令所得命令回复信息的静态缓冲区,它的大小是固定的,所以主要保存的是一些比较短的回复. 分配client结构空间时,就会分配一个16K的大小
char buf[PROTO_REPLY_CHUNK_BYTES];
}
(1)新的客户端连接服务端时,服务端要创建一个client信息存储在服务端,
client *createClient(connection *conn) {
client *c = zmalloc(sizeof(client));
/* passing NULL as conn it is possible to create a non connected client.
* This is useful since all the commands needs to be executed
* in the context of a client. When commands are executed in other
* contexts (for instance a Lua script) we need a non connected client. */
if (conn) {
connEnableTcpNoDelay(conn);
if (server.tcpkeepalive)
connKeepAlive(conn,server.tcpkeepalive);
//注册这个客户端的读事件,readQueryFromClient这个函数则是执行从socket读取数据的函数
connSetReadHandler(conn, readQueryFromClient);
connSetPrivateData(conn, c);
}
......//删除干扰代码行
}
//内联函数
static inline int connSetReadHandler(connection *conn, ConnectionCallbackFunc func) {
return conn->type->set_read_handler(conn, func);
}
/* Register a read handler, to be called when the connection is readable.
* If NULL, the existing handler is removed.
*/
//通过这个知道set_read_handler的实现是connSocketSetReadHandler方法
.set_read_handler = connSocketSetReadHandler,
(2)通过connSocketSetReadHandler设置客户端的读取事件
static int connSocketSetReadHandler(connection *conn, ConnectionCallbackFunc func) {
if (func == conn->read_handler) return C_OK;
//将新传入的函数指针`func`设置为当前连接的读处理器。
conn->read_handler = func;
if (!conn->read_handler)
aeDeleteFileEvent(server.el,conn->fd,AE_READABLE);
else
//读处理器存在,代码将尝试创建一个新的文件事件
if (aeCreateFileEvent(server.el,conn->fd,
AE_READABLE,conn->type->ae_handler,conn) == AE_ERR) return C_ERR;
return C_OK;
}
//给socket事件
static void connSocketEventHandler(struct aeEventLoop *el, int fd, void *clientData, int mask)
{
......//删除干扰代码行
int call_write = (mask & AE_WRITABLE) && conn->write_handler;
int call_read = (mask & AE_READABLE) && conn->read_handler;
/* Handle normal I/O flows 正常触发读事件*/
if (!invert && call_read) {
if (!callHandler(conn, conn->read_handler)) return;
}
/* Fire the writable event. 触发写事件,*/
if (call_write) {
if (!callHandler(conn, conn->write_handler)) return;
}
/* If we have to invert the call, fire the readable event now
* after the writable one. 如果是翻转调用,比如先写,后读,则一定要执行下面的*/
if (invert && call_read) {
if (!callHandler(conn, conn->read_handler)) return;
}
}
(3) 通过aeCreateFileEvent把文件事件写入server.eventLoop
int aeCreateFileEvent(aeEventLoop *eventLoop, int fd, int mask,
aeFileProc *proc, void *clientData)
{
if (fd >= eventLoop->setsize) {
errno = ERANGE;
return AE_ERR;
}
aeFileEvent *fe = &eventLoop->events[fd];
if (aeApiAddEvent(eventLoop, fd, mask) == -1)
return AE_ERR;
fe->mask |= mask;
if (mask & AE_READABLE) fe->rfileProc = proc;
if (mask & AE_WRITABLE) fe->wfileProc = proc;
fe->clientData = clientData;
if (fd > eventLoop->maxfd)
eventLoop->maxfd = fd;
return AE_OK;
}
2、服务端启动最后一步是主线程循环遍历server.eventLoop,停止条件是server.eventLoop为0
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
.......//删除影响理解的代码行
//开始进入循环,在个方法里会一直while触发eventLoop
aeMain(server.el);
//删除所有的EventLoop:只有上面aeMain方法结束才执行这个
aeDeleteEventLoop(server.el);
return 0;
void aeMain(aeEventLoop *eventLoop) {
eventLoop->stop = 0;
while (!eventLoop->stop) {
aeProcessEvents(eventLoop, AE_ALL_EVENTS|
AE_CALL_BEFORE_SLEEP|
AE_CALL_AFTER_SLEEP);
}
}
3、读取事件的实现函数readQueryFromClient
(1)主线程首先把socket中的数据写入到client缓冲区
void readQueryFromClient(connection *conn) {
.......//删除影响理解的代码行
//首先,代码调用connRead函数从连接中读取数据,并将读取的数据存储在c->querybuf+qblen中。nread变量记录了读取的字节数。
nread = connRead(c->conn, c->querybuf+qblen, readlen);
//如果nread等于-1,表示读取数据时发生了错误。此时,代码首先检查连接的状态是否是已连接状态(CONN_STATE_CONNECTED)。如果是已连接状态,说明错误是临时的,代码直接返回。如果不是已连接状态,说明连接已经断开,代码会记录错误日志并释放客户端的资源,然后跳转到done标签处继续执行后续逻辑。
if (nread == -1) {
if (connGetState(conn) == CONN_STATE_CONNECTED) {
return;
} else {
serverLog(LL_VERBOSE, "Reading from client: %s",connGetLastError(c->conn));
freeClientAsync(c);
goto done;
}
} else if (nread == 0) {
//如果nread等于0,表示客户端关闭了连接。代码会根据服务器的日志级别判断是否需要记录客户端关闭连接的日志,然后释放客户端的资源,最后跳转到done标签处继续执行后续逻辑。
if (server.verbosity <= LL_VERBOSE) {
sds info = catClientInfoString(sdsempty(), c);
serverLog(LL_VERBOSE, "Client closed connection %s", info);
sdsfree(info);
}
freeClientAsync(c);
goto done;
}
//将客户端的输入缓冲区的长度增加 nread。
sdsIncrLen(c->querybuf,nread);
//获取客户端输入缓冲区的当前长度。
qblen = sdslen(c->querybuf);
if (c->querybuf_peak < qblen) c->querybuf_peak = qblen;
.......//删除影响理解的代码行
/* There is more data in the client input buffer, continue parsing it
* and check if there is a full command to execute. */
//客户端输入缓冲区中有更多数据,继续解析并检查是否有完整的命令要执行
if (processInputBuffer(c) == C_ERR)
c = NULL;
.......//删除影响理解的代码行
}
(2) 遍历缓冲区
int processInputBuffer(client *c) {
/* Keep processing while there is something in the input buffer */
//当输入缓冲区中有内容时继续处理
while(c->qb_pos < sdslen(c->querybuf)) {
//处理请求,把请求拆分,放入到c中,方便执行processCommandAndResetClient时可以通过c得到此次请求的全部内容,这个是单条
if (c->reqtype == PROTO_REQ_INLINE) {
if (processInlineBuffer(c) != C_OK) break;
} else if (c->reqtype == PROTO_REQ_MULTIBULK) {
//这个是多条批量
if (processMultibulkBuffer(c) != C_OK) break;
} else {
serverPanic("Unknown request type");
}
/* Multibulk processing could see a <= 0 length. */
if (c->argc == 0) {
resetClient(c);
} else {
.......//删除影响理解的代码行
//主线程执行命令
/* We are finally ready to execute the command. */
if (processCommandAndResetClient(c) == C_ERR) {
return C_ERR;
}
}
}
}
1) 每次取缓冲区中完整一条命令到client中的argv数组中
int processInlineBuffer(client *c) {
/* Search for end of line */
//搜索行尾
newline = strchr(c->querybuf+c->qb_pos,'\n');
.......//删除影响理解的代码行
/* Split the input buffer up to the \r\n */
querylen = newline-(c->querybuf+c->qb_pos);
//创建了一个新的sds字符串,这个字符串存储了查询命令。
aux = sdsnewlen(c->querybuf+c->qb_pos,querylen);
//把sds字符串中的查询命令拆分为单独的参数,这些参数存储在argv中,参数数量则存储在argc中。
argv = sdssplitargs(aux,&argc);
.......//删除影响理解的代码行
/* Setup argv array on client structure */
//在客户端结构上设置 argv 数组
if (argc) {
if (c->argv) zfree(c->argv);
c->argv_len = argc;
c->argv = zmalloc(sizeof(robj*)*c->argv_len);
c->argv_len_sum = 0;
}
/* Create redis objects for all arguments. */
//遍历所有传入的参数,为它们创建Redis对象,并存储在客户端的`argv`数组中
for (c->argc = 0, j = 0; j < argc; j++) {
c->argv[c->argc] = createObject(OBJ_STRING,argv[j]);
c->argc++;
c->argv_len_sum += sdslen(argv[j]);
}
zfree(argv);
return C_OK;
}
2) 如果client中的argv数组大于0,则主线程会执行命令
int processCommandAndResetClient(client *c) {
int deadclient = 0;
client *old_client = server.current_client;
server.current_client = c;
if (processCommand(c) == C_OK) {
.......//删除影响理解的代码行
}
.......//删除影响理解的代码行
}
二、主线程执行命令processCommand,
int processCommand(client *c) {
......//删除干扰代码
/* Exec the command */
//通过判断`c->cmd->proc`来分开此次请求是不是事务请求、是不是事务提交请求
if (c->flags & CLIENT_MULTI &&
c->cmd->proc != execCommand &&
c->cmd->proc != discardCommand &&
c->cmd->proc != multiCommand &&
c->cmd->proc != watchCommand &&
c->cmd->proc != quitCommand &&
c->cmd->proc != resetCommand)
{
// 如果正在执行事务,
// 并且新命令不是 EXEC / DISCARD / MULTI / WATCH
// 那么将它们追加到事务队列,
//c->cmd->proc是execCommand时,就是提交事务,直接走下面的else语句中的call执行execCommand
queueMultiCommand(c, cmd_flags);
//返回给客户端QUEUED
addReply(c,shared.queued);
} else {
//主线程执行命令的逻辑,
int flags = CMD_CALL_FULL;
if (client_reprocessing_command) flags |= CMD_CALL_REPROCESSING;
//实际执行
call(c,flags);
if (listLength(server.ready_keys))
handleClientsBlockedOnKeys();
}
return C_OK;
}
1、call()由主线程执行命令
void call(client *c, int flags) {
......//删除干扰代码
//开始执行增删改查命令
c->cmd->proc(c);
//退出执行单元
exitExecutionUnit();
......//删除干扰代码
}
这里proc( c )实际执行的是命令,通过上面的processCommand函数中,就知道调用的是***Command这种函数
在server.h文件中,就有很多这种命令
(1)主线程在执行命令的函数内,有结果了会同步把结果返回到输出缓冲区
举一个例子:以setCommand函数为例子
/* SET key value [NX] [XX] [KEEPTTL] [GET] [EX <seconds>] [PX <milliseconds>]
* [EXAT <seconds-timestamp>][PXAT <milliseconds-timestamp>] */
void setCommand(client *c) {
robj *expire = NULL;
int unit = UNIT_SECONDS;
int flags = OBJ_NO_FLAGS;
//通过client中的argv数组的命令内容
c->argv[2] = tryObjectEncoding(c->argv[2]);
setGenericCommand(c,flags,c->argv[1],c->argv[2],expire,unit,NULL,NULL);
}
void setGenericCommand(client *c, int flags, robj *key, robj *val, robj *expire, int unit, robj *ok_reply, robj *abort_reply) {
......//删除干扰代码
found = (lookupKeyWrite(c->db,key) != NULL);
......//删除干扰代码
if ((flags & OBJ_SET_NX && found) ||
(flags & OBJ_SET_XX && !found))
{
if (!(flags & OBJ_SET_GET)) {
//把结果写入到输出缓冲区
addReply(c, abort_reply ? abort_reply : shared.null[c->resp]);
}
return;
}
......//删除干扰代码
if (!(flags & OBJ_SET_GET)) {
//把结果写入到输出缓冲区
addReply(c, ok_reply ? ok_reply : shared.ok);
}
......//删除干扰代码
}
其他函数类似
2、把事务请求缓存在客户端事务数组中,等待后面的事务提交命令exec让主线程执行第一步的call()
这里要认识一个类multiState,根据上面知道client中有一个字段是multiState,保存每一个客户端的事务状态,而这个事务状态数据结果如下面
typedef struct multiState {
//这是一个数组,存的是事务命令,一个事务内可能有多条命令
multiCmd *commands; /* Array of MULTI commands */
int count; /* Total number of MULTI commands */
int cmd_flags; /* The accumulated command flags OR-ed together.
So if at least a command has a given flag, it
will be set in this field. */
int cmd_inv_flags; /* Same as cmd_flags, OR-ing the ~flags. so that it
is possible to know if all the commands have a
certain flag. */
size_t argv_len_sums; /* mem used by all commands arguments */
int alloc_count; /* total number of multiCmd struct memory reserved. */
} multiState;
/* Add a new command into the MULTI commands queue */
void queueMultiCommand(client *c, uint64_t cmd_flags) {
multiCmd *mc;
/* No sense to waste memory if the transaction is already aborted.
* this is useful in case client sends these in a pipeline, or doesn't
* bother to read previous responses and didn't notice the multi was already
* aborted. */
if (c->flags & (CLIENT_DIRTY_CAS|CLIENT_DIRTY_EXEC))
return;
if (c->mstate.count == 0) {
/* If a client is using multi/exec, assuming it is used to execute at least
* two commands. Hence, creating by default size of 2. */
c->mstate.commands = zmalloc(sizeof(multiCmd)*2);
c->mstate.alloc_count = 2;
}
//如果mstate.count等于mstate.alloc_count,即队列已满,那么将mstate.commands数组的大小扩展为原来的两倍,直到不超过INT_MAX的限制。
if (c->mstate.count == c->mstate.alloc_count) {
c->mstate.alloc_count = c->mstate.alloc_count < INT_MAX/2 ? c->mstate.alloc_count*2 : INT_MAX;
c->mstate.commands = zrealloc(c->mstate.commands, sizeof(multiCmd)*(c->mstate.alloc_count));
}
//将待执行的命令信息存储在mstate.commands数组中的下一个空闲位置
mc = c->mstate.commands+c->mstate.count;
mc->cmd = c->cmd;
mc->argc = c->argc;
mc->argv = c->argv;
mc->argv_len = c->argv_len;
c->mstate.count++;
c->mstate.cmd_flags |= cmd_flags;
c->mstate.cmd_inv_flags |= ~cmd_flags;
c->mstate.argv_len_sums += c->argv_len_sum + sizeof(robj*)*c->argc;
/* Reset the client's args since we copied them into the mstate and shouldn't
* reference them from c anymore. */
c->argv = NULL;
c->argc = 0;
c->argv_len_sum = 0;
c->argv_len = 0;
}
三、输出缓冲区
输出缓冲区由主线程的事件驱动监听输出缓冲区,如果有数据就会把输出缓冲区中的数据放入客户端的socket中
1、主线程执行命令后通过addReply写入输出缓冲区和回复列表
每一个客户端的输出缓冲区只有16k大小,如果比这个大,就要存回复列表里,
//将结果返回一些区域
void addReply(client *c, robj *obj) {
if (prepareClientToWrite(c) != C_OK) return;
if (sdsEncodedObject(obj)) {
_addReplyToBufferOrList(c,obj->ptr,sdslen(obj->ptr));
} else if (obj->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_INT) {
/* For integer encoded strings we just convert it into a string
* using our optimized function, and attach the resulting string
* to the output buffer. */
char buf[32];
size_t len = ll2string(buf,sizeof(buf),(long)obj->ptr);
_addReplyToBufferOrList(c,buf,len);
} else {
serverPanic("Wrong obj->encoding in addReply()");
}
}
//写入到输出缓冲区和回复链表
void _addReplyToBufferOrList(client *c, const char *s, size_t len) {
.....//删除干扰代码
size_t reply_len = _addReplyToBuffer(c,s,len);
if (len > reply_len) _addReplyProtoToList(c,c->reply,s+reply_len,len-reply_len);
}
//写入到客户端的输出缓冲区
size_t _addReplyToBuffer(client *c, const char *s, size_t len) {
size_t available = c->buf_usable_size - c->bufpos;
/* If there already are entries in the reply list, we cannot
* add anything more to the static buffer. */
if (listLength(c->reply) > 0) return 0;
size_t reply_len = len > available ? available : len;
memcpy(c->buf+c->bufpos,s,reply_len);
c->bufpos+=reply_len;
/* We update the buffer peak after appending the reply to the buffer */
if(c->buf_peak < (size_t)c->bufpos)
c->buf_peak = (size_t)c->bufpos;
return reply_len;
}
2、在EventLoop增加一个可以从输出缓冲区写入到socket的事件前置函数beforeSleep
在
main->initServer中会往EventLoop加入beforeSleep函数,记住不是注册成事件,而是一个前置函数
void initServer(void) {
......//删除干扰代码
/* Register a readable event for the pipe used to awake the event loop
* from module threads. */
//初始化AE_READABLE到server.el
if (aeCreateFileEvent(server.el, server.module_pipe[0], AE_READABLE,
modulePipeReadable,NULL) == AE_ERR) {
serverPanic(
"Error registering the readable event for the module pipe.");
}
/* Register before and after sleep handlers (note this needs to be done
* before loading persistence since it is used by processEventsWhileBlocked. */
//aeSetBeforeSleepProc里有connSocketSetWriteHandler,通过aeCreateFileEvent(server.el,conn->fd,AE_WRITABLE,conn->type->ae_handler,conn)注册AE_WRITABLE
aeSetBeforeSleepProc(server.el,beforeSleep);
......//删除干扰代码
}
(1)beforeSleep函数在循环事件执行函数aeProcessEvents代码中的位置
//使用一个轮询机制来处理事件,并根据事件的类型和标志位来触发相应的事件处理器。
int aeProcessEvents(aeEventLoop *eventLoop, int flags)
{
int processed = 0, numevents;
/* Nothing to do? return ASAP */
//根据eventLoop的maxfd和标志位判断是否需要等待事件,如果不需要等待,则立即返回
if (!(flags & AE_TIME_EVENTS) && !(flags & AE_FILE_EVENTS)) return 0;
......//删除干扰代码
if (eventLoop->maxfd != -1 ||
((flags & AE_TIME_EVENTS) && !(flags & AE_DONT_WAIT))) {
//在进入等待事件触发之前,可以调用beforesleep回调函数
if (eventLoop->beforesleep != NULL && (flags & AE_CALL_BEFORE_SLEEP))
eventLoop->beforesleep(eventLoop);
......//删除干扰代码
/* Call the multiplexing API, will return only on timeout or when
* some event fires. */
//调用aeApiPoll(eventLoop, tvp)来等待事件的发生,该函数将在超时或某个事件触发时返回。
numevents = aeApiPoll(eventLoop, tvp);
......//删除干扰代码
}
}
......//删除干扰代码
}
(2)beforeSleep中有调用从输出缓冲区输出到客户端的方法writeToClient
void beforeSleep(struct aeEventLoop *eventLoop) {
......//删除干扰代码
/* Handle writes with pending output buffers. */
//处理具有挂起输出缓冲区的写入。
//调用了handleClientsWithPendingWritesUsingThreads从缓冲区输出客户端
handleClientsWithPendingWritesUsingThreads();
......//删除干扰代码
}
因为这篇文章通篇讲的是不开启多线程,所以像下面这样,直接调用handleClientsWithPendingWrites
int handleClientsWithPendingWritesUsingThreads(void) {
int processed = listLength(server.clients_pending_write);
if (processed == 0) return 0; /* Return ASAP if there are no clients. */
/* If I/O threads are disabled or we have few clients to serve, don't
* use I/O threads, but the boring synchronous code. */
//不开启多线程
if (server.io_threads_num == 1 || stopThreadedIOIfNeeded()) {
return handleClientsWithPendingWrites();
}
......//删除干扰代码
}
因为是主线程执行,所以主线程会遍历所有输出缓冲区有数据要输出的客户端
int handleClientsWithPendingWrites(void) {
listIter li;
listNode *ln;
int processed = listLength(server.clients_pending_write);
//遍历等待写出客户端列表,循环把所有需要把
listRewind(server.clients_pending_write,&li);
while((ln = listNext(&li))) {
client *c = listNodeValue(ln);
c->flags &= ~CLIENT_PENDING_WRITE;
......//删除干扰代码
if (writeToClient(c,0) == C_ERR) continue;
/* If after the synchronous writes above we still have data to
* output to the client, we need to install the writable handler. */
//如果在上面的同步写入之后,我们仍然有数据要输出到客户端,我们需要注册输出事件
if (clientHasPendingReplies(c)) {
installClientWriteHandler(c);
}
}
return processed;
}
int writeToClient(client *c, int handler_installed) {
//删除干扰代码......
while(clientHasPendingReplies(c)) {
int ret = _writeToClient(c, &nwritten);
//删除干扰代码......
}
//删除干扰代码......
}
(3)存在主从节点的集群,只有主节点执行把数据从输出缓冲区输出到客户端
int _writeToClient(client *c, ssize_t *nwritten) {
*nwritten = 0;
//判断客户端类型是否为从机(slave)。如果是从机,则执行下面的操作
//主要内容是处理从节点的复制操作,并确保逐个块地发送复制缓冲区的数据
if (getClientType(c) == CLIENT_TYPE_SLAVE) {
//删除干扰代码
return C_OK;
}
/* When the reply list is not empty, it's better to use writev to save us some
* system calls and TCP packets. */
//下面是向客户端socket发送的逻辑,根据要回复数据的大小,选择不同的处理方式,并进行相应的处理。
if (listLength(c->reply) > 0) {
//如果回复列表中大于0,则执行下面的逻辑
int ret = _writevToClient(c, nwritten);
if (ret != C_OK) return ret;
/* If there are no longer objects in the list, we expect
* the count of reply bytes to be exactly zero. */
if (listLength(c->reply) == 0)
serverAssert(c->reply_bytes == 0);
} else if (c->bufpos > 0) {
//如果回复列表没有数据,但是输出缓冲区有数据,则执行下面的逻辑
*nwritten = connWrite(c->conn, c->buf + c->sentlen, c->bufpos - c->sentlen);
if (*nwritten <= 0) return C_ERR;
c->sentlen += *nwritten;
/* If the buffer was sent, set bufpos to zero to continue with
* the remainder of the reply. */
if ((int)c->sentlen == c->bufpos) {
c->bufpos = 0;
c->sentlen = 0;
}
}
return C_OK;
}
(3)如果输出缓冲区执行了一次写入到客户端操作发现输出缓冲区还有数据,则会注册文件事件
void installClientWriteHandler(client *c) {
//删除干扰代码
if (connSetWriteHandlerWithBarrier(c->conn, sendReplyToClient, ae_barrier) == C_ERR) {
freeClientAsync(c);
}
}
.set_write_handler = connSocketSetWriteHandler,
static inline int connSetWriteHandlerWithBarrier(connection *conn, ConnectionCallbackFunc func, int barrier) {
return conn->type->set_write_handler(conn, func, barrier);
}
connSocketSetWriteHandler 会往server.el添加文件事件,由最开始的aeMain函数执行
static int connSocketSetWriteHandler(connection *conn, ConnectionCallbackFunc func, int barrier) {
if (!conn->write_handler)
aeDeleteFileEvent(server.el,conn->fd,AE_WRITABLE);
else
if (aeCreateFileEvent(server.el,conn->fd,AE_WRITABLE,
conn->type->ae_handler,conn) == AE_ERR) return C_ERR;
return C_OK;
}






![SSM(Vue3+ElementPlus+Axios+SSM前后端分离)--搭建Vue 前端工程[一]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/43e0cc595418c536362a57e2dd1fc6bd.png)