动态规划
Dynamic Programming
简写为 DP,是运筹学的一个分支,是求解决策过程最优化的过程。20世纪50年代初,美国数学家贝尔曼(R.Bellman)等人在研究多阶段决策过程的优化问题时,提出了著名的最优化原理,从而创立了动态规划。动态规划的应用极其广泛,包括工程技术、经济、工业生产、军事以及自动化控制等领域,并在背包问题、生产经营问题、资金管理问题、资源分配问题、最短路径问题和复杂系统可靠性问题等中取得了显著的效果。
动态规划算法的基本步骤包括:
- 确定状态:确定需要求解的状态,并将其表示为变量。
- 确定状态转移方程:根据问题的特定约束条件和目标函数,确定状态之间的转移关系,并将其表示为数学公式。
- 初始化:为初始状态赋初值,并将其表示为初始条件。
- 递推计算:根据状态转移方程,使用循环依次计算各个状态的解,并将其保存在数组或表中。
- 求解最终结果:根据问题的目标,从计算得到的解中得出最终结果。
动态规划算法可以用于解决各种问题,例如最短路径问题、背包问题、最长公共子序列问题等。在实现动态规划算法时,需要根据具体问题的特点进行设计和调整,以确保算法的正确性和效率。
适用条件
任何思想方法都有一定的局限性,超出了特定条件,它就失去了作用。同样,动态规划也并不是万能的。适用动态规划的问题必须满足最优化原理和无后效性。
最优化原理(最优子结构性质)
最优化原理可这样阐述:一个最优化策略具有这样的性质,不论过去状态和决策如何,对前面的决策所形成的状态而言,余下的诸决策必须构成最优策略。简而言之,一个最优化策略的子策略总是最优的。一个问题满足最优化原理又称其具有最优子结构性质 [8] 。
无后效性
将各阶段按照一定的次序排列好之后,对于某个给定的阶段状态,它以前各阶段的状态无法直接影响它未来的决策,而只能通过当前的这个状态。换句话说,每个状态都是过去历史的一个完整总结。这就是无后向性,又称为无后效性 [8] 。
子问题的重叠性
动态规划算法的关键在于解决冗余,这是动态规划算法的根本目的。动态规划实质上是一种以空间换时间的技术,它在实现的过程中,不得不存储产生过程中的各种状态,所以它的空间复杂度要大于其他的算法。选择动态规划算法是因为动态规划算法在空间上可以承受,而搜索算法在时间上却无法承受,所以我们舍空间而取时间。
真题举例(2)
70. 爬楼梯
假设你正在爬楼梯。需要 n 阶你才能到达楼顶。
每次你可以爬 1 或 2 个台阶。你有多少种不同的方法可以爬到楼顶呢?
注意:给定 n 是一个正整数。
示例 1:
输入: 2 输出: 2 解释: 有两种方法可以爬到楼顶。 1. 1 阶 + 1 阶 2. 2 阶
示例 2:
输入: 3 输出: 3 解释: 有三种方法可以爬到楼顶。 1. 1 阶 + 1 阶 + 1 阶 2. 1 阶 + 2 阶 3. 2 阶 + 1 阶
代码1:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class Solution
{
public:
int climbStairs(int n)
{
if (n == 1)
{
return 1;
}
int first = 1;
int second = 2;
for (int i = 3; i <= n; i++)
{
int third = first + second;
first = second;
second = third;
}
return second;
}
};
int main()
{
Solution s;
cout << s.climbStairs(2) << endl;
cout << s.climbStairs(3) << endl;
return 0;
} 代码2:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class Solution
{
public:
int climbStairs(int n)
{
vector<int> res(n + 1, 0);
res[1] = 1;
res[2] = 2;
for (int i = 3; i <= n; i++)
res[i] = res[i - 1] + res[i - 2];
return res[n];
}
};
int main()
{
Solution s;
cout << s.climbStairs(2) << endl;
cout << s.climbStairs(3) << endl;
return 0;
} 代码3:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class Solution
{
public:
int climbStairs(int n)
{
vector<int> s;
s.push_back(1);
s.push_back(2);
if (n == 1)
return 1;
if (n == 2)
return 2;
for (int i = 2; i < n; i++)
{
s.push_back(s[i - 1] + s[i - 2]);
}
return s[n - 1];
}
};
int main()
{
Solution s;
cout << s.climbStairs(2) << endl;
cout << s.climbStairs(3) << endl;
return 0;
} 72. 编辑距离
给你两个单词 word1 和 word2,请你计算出将 word1 转换成 word2 所使用的最少操作数 。
你可以对一个单词进行如下三种操作:
- 插入一个字符
- 删除一个字符
- 替换一个字符
示例 1:
输入:word1 = "horse", word2 = "ros" 输出:3 解释:horse -> rorse (将 'h' 替换为 'r')rorse -> rose (删除 'r')rose -> ros (删除 'e')
示例 2:
输入:word1 = "intention", word2 = "execution" 输出:5 解释:intention -> inention (删除 't')inention -> enention (将 'i' 替换为 'e')enention -> exention (将 'n' 替换为 'x')exention -> exection (将 'n' 替换为 'c')exection -> execution (插入 'u')
提示:
0 <= word1.length, word2.length <= 500word1和word2由小写英文字母组成
代码1:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class Solution
{
public:
int minDistance(string word1, string word2)
{
int m = word1.size(), n = word2.size();
if (m == 0)
return n;
if (n == 0)
return m;
int dp[m][n];
bool w1 = false, w2 = false;
if (word1[0] == word2[0])
{
w1 = true;
w2 = true;
dp[0][0] = 0;
}
else
dp[0][0] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i < m; i++)
{
if (!w1 && word1[i] == word2[0])
{
w1 = true;
dp[i][0] = dp[i - 1][0];
}
else
dp[i][0] = dp[i - 1][0] + 1;
}
for (int j = 1; j < n; j++)
{
if (!w2 && word1[0] == word2[j])
{
w2 = true;
dp[0][j] = dp[0][j - 1];
}
else
dp[0][j] = dp[0][j - 1] + 1;
}
for (int i = 1; i < m; i++)
for (int j = 1; j < n; j++)
if (word1[i] == word2[j])
dp[i][j] = min(min(dp[i][j - 1], dp[i - 1][j]) + 1, dp[i - 1][j - 1]);
else
dp[i][j] = min(min(dp[i][j - 1], dp[i - 1][j]), dp[i - 1][j - 1]) + 1;
return dp[m - 1][n - 1];
}
};
int main()
{
Solution s;
string word1 = "horse", word2 = "ros";
cout << s.minDistance(word1, word2) << endl;
word1 = "intention", word2 = "execution";
cout << s.minDistance(word1, word2) << endl;
return 0;
} 代码2:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class Solution
{
public:
int minDistance(string word1, string word2)
{
int n = word1.size();
int m = word2.size();
if (n * m == 0)
{
return n + m;
}
int d[n + 1][m + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < n + 1; ++i)
{
d[i][0] = i;
}
for (int i = 0; i < m + 1; ++i)
{
d[0][i] = i;
}
for (int i = 1; i < n + 1; ++i)
{
for (int j = 1; j < m + 1; ++j)
{
int left = d[i - 1][j] + 1;
int down = d[i][j - 1] + 1;
int left_down = d[i - 1][j - 1];
if (word1[i - 1] != word2[j - 1])
{
left_down += 1;
}
d[i][j] = min(left, min(down, left_down));
}
}
return d[n][m];
}
};
int main()
{
Solution s;
string word1 = "horse", word2 = "ros";
cout << s.minDistance(word1, word2) << endl;
word1 = "intention", word2 = "execution";
cout << s.minDistance(word1, word2) << endl;
return 0;
} 代码3:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class Solution
{
public:
int minDistance(string word1, string word2)
{
int m = word1.size(), n = word2.size();
vector<vector<int>> dp(m + 1, vector<int>(n + 1, 0));
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
dp[0][i] = dp[0][i - 1] + 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= m; ++i)
dp[i][0] = dp[i - 1][0] + 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= m; ++i)
{
for (int j = 1; j <= n; ++j)
{
if (word1[i - 1] == word2[j - 1])
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1];
else
dp[i][j] = min(min(dp[i - 1][j - 1], dp[i - 1][j]), dp[i][j - 1]) + 1;
}
}
return dp[m][n];
}
};
int main()
{
Solution s;
string word1 = "horse", word2 = "ros";
cout << s.minDistance(word1, word2) << endl;
word1 = "intention", word2 = "execution";
cout << s.minDistance(word1, word2) << endl;
return 0;
} 代码4:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
int minDistance(string word1, string word2) {
int len1 = word1.size();
int len2 = word2.size();
int **dp = new int *[len1 + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < len1 + 1; i++)
dp[i] = new int[len2 + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < len1 + 1; i++)
dp[i][0] = i;
for (int i = 0; i < len2 + 1; i++)
dp[0][i] = i;
for (int i = 1; i < len1 + 1; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j < len2 + 1; j++) {
if (word1[i - 1] == word2[j - 1])
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1];
else
dp[i][j] = (min(dp[i - 1][j - 1], min(dp[i - 1][j], dp[i][j - 1])) + 1);
}
}
int res = dp[len1][len2];
for (int i = 0; i < len1 + 1; i++)
delete[] dp[i];
delete[] dp;
return res;
}
};
int main()
{
Solution s;
string word1 = "horse", word2 = "ros";
cout << s.minDistance(word1, word2) << endl;
word1 = "intention", word2 = "execution";
cout << s.minDistance(word1, word2) << endl;
return 0;
} 85. 最大矩形
给定一个仅包含 0 和 1 、大小为 rows x cols 的二维二进制矩阵,找出只包含 1 的最大矩形,并返回其面积。
示例 1:
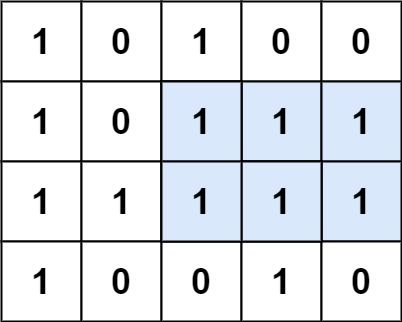
输入:matrix = [["1","0","1","0","0"],["1","0","1","1","1"],["1","1","1","1","1"],["1","0","0","1","0"]] 输出:6 解释:最大矩形如上图所示。
示例 2:
输入:matrix = [] 输出:0
示例 3:
输入:matrix = [["0"]] 输出:0
示例 4:
输入:matrix = [["1"]] 输出:1
示例 5:
输入:matrix = [["0","0"]] 输出:0
提示:
rows == matrix.lengthcols == matrix[0].length0 <= row, cols <= 200matrix[i][j]为'0'或'1'
代码1:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class Solution
{
public:
int maximalRectangle(vector<vector<char>> &matrix)
{
if (matrix.size() == 0)
{
return 0;
}
int maxarea = 0;
int dp[matrix.size()][matrix[0].size()];
memset(dp, 0, sizeof(dp));
for (int i = 0; i < matrix.size(); ++i)
{
for (int j = 0; j < matrix[0].size(); ++j)
{
if (matrix[i][j] == '1')
{
dp[i][j] = j == 0 ? 1 : dp[i][j - 1] + 1;
int width = dp[i][j];
for (int k = i; k >= 0; k--)
{
width = min(width, dp[k][j]);
maxarea = max(maxarea, width * (i - k + 1));
}
}
}
}
return maxarea;
}
};
int main()
{
Solution s;
vector<vector<char>> matrix = {
{'1','0','1','0','0'},
{'1','0','1','1','1'},
{'1','1','1','1','1'},
{'1','0','0','1','0'}};
cout << s.maximalRectangle(matrix) << endl;
matrix = {};
cout << s.maximalRectangle(matrix) << endl;
matrix = {{'0'}};
cout << s.maximalRectangle(matrix) << endl;
matrix = {{'1'}};
cout << s.maximalRectangle(matrix) << endl;
matrix = {{'0','0'}};
cout << s.maximalRectangle(matrix) << endl;
return 0;
} 代码2:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class Solution
{
public:
int maximalRectangle(vector<vector<char>> &matrix)
{
int res = 0;
vector<int> height;
for (int i = 0; i < matrix.size(); ++i)
{
height.resize(matrix[i].size());
for (int j = 0; j < matrix[i].size(); ++j)
{
height[j] = matrix[i][j] == '0' ? 0 : (1 + height[j]);
}
res = max(res, largestRectangleArea(height));
}
return res;
}
int largestRectangleArea(vector<int> &heights)
{
if (heights.empty())
return 0;
stack<int> st;
heights.push_back(0);
int res0 = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < heights.size(); i++)
{
while (!st.empty() && heights[i] < heights[st.top()])
{
int curHeight = heights[st.top()];
st.pop();
int width = st.empty() ? i : i - st.top() - 1;
if (width * curHeight > res0)
res0 = width * curHeight;
}
st.push(i);
}
return res0;
}
};
int main()
{
Solution s;
vector<vector<char>> matrix = {
{'1','0','1','0','0'},
{'1','0','1','1','1'},
{'1','1','1','1','1'},
{'1','0','0','1','0'}};
cout << s.maximalRectangle(matrix) << endl;
matrix = {};
cout << s.maximalRectangle(matrix) << endl;
matrix = {{'0'}};
cout << s.maximalRectangle(matrix) << endl;
matrix = {{'1'}};
cout << s.maximalRectangle(matrix) << endl;
matrix = {{'0','0'}};
cout << s.maximalRectangle(matrix) << endl;
return 0;
} 代码3:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class Solution
{
public:
int largestRectangleArea(vector<int> &heights)
{
stack<int> h;
heights.push_back(0);
int ans = 0, hsize = heights.size();
for (int i = 0; i < hsize; i++)
{
while (!h.empty() && heights[h.top()] > heights[i])
{
int top = h.top();
h.pop();
ans = max(ans, heights[top] * (h.empty() ? i : (i - h.top())));
}
h.push(i);
}
return ans;
}
int maximalRectangle(vector<vector<char>> &matrix)
{
if (matrix.empty())
return 0;
int n = matrix.size(), m = matrix[0].size(), ans = 0;
vector<vector<int>> num(n, vector<int>(m, 0));
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++)
{
num[0][j] = (matrix[0][j] == '0') ? 0 : 1;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
num[i][j] = (matrix[i][j] == '0') ? 0 : num[i - 1][j] + 1;
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
int area = largestRectangleArea(num[i]);
ans = max(ans, area);
}
return ans;
}
};
int main()
{
Solution s;
vector<vector<char>> matrix = {
{'1','0','1','0','0'},
{'1','0','1','1','1'},
{'1','1','1','1','1'},
{'1','0','0','1','0'}};
cout << s.maximalRectangle(matrix) << endl;
matrix = {};
cout << s.maximalRectangle(matrix) << endl;
matrix = {{'0'}};
cout << s.maximalRectangle(matrix) << endl;
matrix = {{'1'}};
cout << s.maximalRectangle(matrix) << endl;
matrix = {{'0','0'}};
cout << s.maximalRectangle(matrix) << endl;
return 0;
} 87. 扰乱字符串
使用下面描述的算法可以扰乱字符串 s 得到字符串 t :
- 如果字符串的长度为 1 ,算法停止
- 如果字符串的长度 > 1 ,执行下述步骤:
- 在一个随机下标处将字符串分割成两个非空的子字符串。即,如果已知字符串
s,则可以将其分成两个子字符串x和y,且满足s = x + y。 - 随机 决定是要「交换两个子字符串」还是要「保持这两个子字符串的顺序不变」。即,在执行这一步骤之后,
s可能是s = x + y或者s = y + x。 - 在
x和y这两个子字符串上继续从步骤 1 开始递归执行此算法。
- 在一个随机下标处将字符串分割成两个非空的子字符串。即,如果已知字符串
给你两个 长度相等 的字符串 s1 和 s2,判断 s2 是否是 s1 的扰乱字符串。如果是,返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。
示例 1:
输入:s1 = "great", s2 = "rgeat" 输出:true 解释:s1 上可能发生的一种情形是: "great" --> "gr/eat" // 在一个随机下标处分割得到两个子字符串 "gr/eat" --> "gr/eat" // 随机决定:「保持这两个子字符串的顺序不变」 "gr/eat" --> "g/r / e/at" // 在子字符串上递归执行此算法。两个子字符串分别在随机下标处进行一轮分割 "g/r / e/at" --> "r/g / e/at" // 随机决定:第一组「交换两个子字符串」,第二组「保持这两个子字符串的顺序不变」 "r/g / e/at" --> "r/g / e/ a/t" // 继续递归执行此算法,将 "at" 分割得到 "a/t" "r/g / e/ a/t" --> "r/g / e/ a/t" // 随机决定:「保持这两个子字符串的顺序不变」 算法终止,结果字符串和 s2 相同,都是 "rgeat" 这是一种能够扰乱 s1 得到 s2 的情形,可以认为 s2 是 s1 的扰乱字符串,返回 true
示例 2:
输入:s1 = "abcde", s2 = "caebd" 输出:false
示例 3:
输入:s1 = "a", s2 = "a" 输出:true
提示:
s1.length == s2.length1 <= s1.length <= 30s1和s2由小写英文字母组成
代码1:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class Solution
{
public:
bool isScramble(string s1, string s2)
{
if (s1.size() != s2.size())
return false;
if (s1 == s2)
return true;
vector<int> hash(26, 0);
for (int i = 0; i < s1.size(); i++)
hash.at(s1[i] - 'a')++;
for (int j = 0; j < s2.size(); j++)
hash.at(s2[j] - 'a')--;
for (int k = 0; k < 26; k++)
{
if (hash.at(k) != 0)
return false;
}
for (int i = 1; i < s1.size(); i++)
{
if (
(isScramble(s1.substr(0, i), s2.substr(0, i)) && isScramble(s1.substr(i, s1.size() - i), s2.substr(i, s1.size() - i))) || (isScramble(s1.substr(0, i), s2.substr(s1.size() - i)) && isScramble(s1.substr(i), s2.substr(0, s1.size() - i))))
return true;
}
return false;
}
};
int main()
{
Solution s;
cout << s.isScramble("great", "rgeat") << endl;
cout << s.isScramble("abcde", "caebd") << endl;
cout << s.isScramble("a", "a") << endl;
return 0;
} 代码2:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class Solution
{
public:
bool isScramble(string s1, string s2)
{
int n1 = s1.length(), n2 = s2.length();
if (n1 != n2)
return false;
vector<vector<vector<bool>>> dp(n1 + 1, vector<vector<bool>>(n1 + 1, vector<bool>(n1 + 1, false)));
int i, j, k;
for (i = 1; i <= n1; i++)
{
for (j = 1; j <= n1; j++)
{
dp[i][j][1] = (s1[i - 1] == s2[j - 1]);
}
}
for (int len = 2; len <= n1; len++)
{
for (i = 1; i <= n1 && i + len <= n1 + 1; i++)
{
for (j = 1; j <= n1 && j + len <= n1 + 1; j++)
{
for (k = 1; k < len; k++)
{
if (dp[i][j][k] && dp[i + k][j + k][len - k])
{
dp[i][j][len] = true;
break;
}
if (dp[i][j + len - k][k] && dp[i + k][j][len - k])
{
dp[i][j][len] = true;
break;
}
}
}
}
}
return dp[1][1][n1];
}
};
int main()
{
Solution s;
cout << s.isScramble("great", "rgeat") << endl;
cout << s.isScramble("abcde", "caebd") << endl;
cout << s.isScramble("a", "a") << endl;
return 0;
} 代码3:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class Solution
{
public:
bool isScramble(string s1, string s2)
{
if (s1.size() != s2.size())
return false;
if (s1 == s2)
return true;
string str1 = s1, str2 = s2;
sort(str1.begin(), str1.end());
sort(str2.begin(), str2.end());
if (str1 != str2)
return false;
for (int i = 1; i < s1.size(); ++i)
{
string s11 = s1.substr(0, i);
string s12 = s1.substr(i);
string s21 = s2.substr(0, i);
string s22 = s2.substr(i);
if (isScramble(s11, s21) && isScramble(s12, s22))
return true;
s21 = s2.substr(s2.size() - i);
s22 = s2.substr(0, s2.size() - i);
if (isScramble(s11, s21) && isScramble(s12, s22))
return true;
}
return false;
}
};
int main()
{
Solution s;
cout << s.isScramble("great", "rgeat") << endl;
cout << s.isScramble("abcde", "caebd") << endl;
cout << s.isScramble("a", "a") << endl;
return 0;
} 91. 解码方法
一条包含字母 A-Z 的消息通过以下映射进行了 编码 :
'A' -> 1'B' -> 2...'Z' -> 26
要 解码 已编码的消息,所有数字必须基于上述映射的方法,反向映射回字母(可能有多种方法)。例如,"11106" 可以映射为:
"AAJF",将消息分组为(1 1 10 6)"KJF",将消息分组为(11 10 6)
注意,消息不能分组为 (1 11 06) ,因为 "06" 不能映射为 "F" ,这是由于 "6" 和 "06" 在映射中并不等价。
给你一个只含数字的 非空 字符串 s ,请计算并返回 解码 方法的 总数 。
题目数据保证答案肯定是一个 32 位 的整数。
示例 1:
输入:s = "12" 输出:2 解释:它可以解码为 "AB"(1 2)或者 "L"(12)。
示例 2:
输入:s = "226" 输出:3 解释:它可以解码为 "BZ" (2 26), "VF" (22 6), 或者 "BBF" (2 2 6) 。
示例 3:
输入:s = "0" 输出:0 解释:没有字符映射到以 0 开头的数字。含有 0 的有效映射是 'J' -> "10" 和 'T'-> "20" 。由于没有字符,因此没有有效的方法对此进行解码,因为所有数字都需要映射。
示例 4:
输入:s = "06" 输出:0 解释:"06" 不能映射到 "F" ,因为字符串含有前导 0("6" 和 "06" 在映射中并不等价)。
提示:
1 <= s.length <= 100s只包含数字,并且可能包含前导零。
代码1:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class Solution
{
public:
int numDecodings(string s)
{
vector<int> nums(s.size());
if (s[0] == '0')
{
return 0;
}
nums[0] = 1;
if (s.size() > 1)
{
if (s[1] != '0')
{
nums[1] += 1;
}
if ((s[0] - '0') * 10 + (s[1] - '0') <= 26)
{
nums[1] += 1;
}
}
for (int i = 2; i < s.size(); i++)
{
if (s[i] != '0')
{
nums[i] += nums[i - 1];
}
if (s[i - 1] != '0' && ((s[i - 1] - '0') * 10 + (s[i] - '0') <= 26))
{
nums[i] += nums[i - 2];
}
}
return nums[s.size() - 1];
}
};
int main()
{
Solution s;
cout << s.numDecodings("12") << endl;
cout << s.numDecodings("226") << endl;
cout << s.numDecodings("0") << endl;
cout << s.numDecodings("06") << endl;
return 0;
} 代码2:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class Solution
{
public:
int numDecodings(string s)
{
int n = s.size();
if (s.empty())
return 0;
if (s[0] == '0')
return 0;
vector<int> info(n + 1, 0);
info[0] = 1;
info[1] = 1;
for (int i = 2; i < n + 1; ++i)
{
if (s[i - 1] != '0')
info[i] += info[i - 1];
if (s.substr(i - 2, 2) <= "26" && s.substr(i - 2, 2) >= "10")
info[i] += info[i - 2];
}
return info[n];
}
};
int main()
{
Solution s;
cout << s.numDecodings("12") << endl;
cout << s.numDecodings("226") << endl;
cout << s.numDecodings("0") << endl;
cout << s.numDecodings("06") << endl;
return 0;
} 代码3:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class Solution
{
public:
int dp(string &s, int i, int j)
{
int n = j - i + 1;
if (n == 0)
return 0;
if (n == 1)
return s[i] == '0' ? 0 : 1;
if (n == 2)
{
if (s[i] == '0')
return 0;
if (s[i] > '2')
return s[j] == '0' ? 0 : 1;
if (s[i] == '2' && s[j] > '6')
return 1;
if (s[j] == '0')
return 1;
return 2;
}
if (s[i] > '2')
return dp(s, i + 1, j);
if (s[i] == '2')
{
if (s[i + 1] == '0')
return dp(s, i + 2, j);
else if (s[i + 1] < '7')
return dp(s, i + 1, j) + dp(s, i + 2, j);
else
return dp(s, i + 1, j);
}
if (s[i] == '0')
return 0;
if (s[i + 1] == '0')
return dp(s, i + 2, j);
return dp(s, i + 1, j) + dp(s, i + 2, j);
}
int numDecodings(string s)
{
return dp(s, 0, s.size() - 1);
}
};
int main()
{
Solution s;
cout << s.numDecodings("12") << endl;
cout << s.numDecodings("226") << endl;
cout << s.numDecodings("0") << endl;
cout << s.numDecodings("06") << endl;
return 0;
} 代码4:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
int numDecodings(string s) {
int n = s.size();
vector<int> f(n + 1);
f[0] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
if (s[i - 1] != '0') {
f[i] += f[i - 1];
}
if (i > 1 && s[i - 2] != '0' && ((s[i - 2] - '0') * 10 + (s[i - 1] - '0') <= 26)) {
f[i] += f[i - 2];
}
}
return f[n];
}
};
int main()
{
Solution s;
cout << s.numDecodings("12") << endl;
cout << s.numDecodings("226") << endl;
cout << s.numDecodings("0") << endl;
cout << s.numDecodings("06") << endl;
return 0;
} 代码5:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class Solution
{
public:
int numDecodings(string s)
{
if (s.empty() || s[0] == '0')
return 0;
vector<int> dp(s.size() + 1, 0);
dp[0] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i < dp.size(); ++i)
{
dp[i] = (s[i - 1] == '0') ? 0 : dp[i - 1];
if (i > 1 && (s[i - 2] == '1' || (s[i - 2] >= '2' && s[i - 1] <= '6')))
dp[i] += dp[i - 2];
}
return dp[s.size()];
}
};
int main()
{
Solution s;
cout << s.numDecodings("12") << endl;
cout << s.numDecodings("226") << endl;
cout << s.numDecodings("0") << endl;
cout << s.numDecodings("06") << endl;
return 0;
} 代码6:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class Solution
{
public:
int numDecodings(string s) {
if (s.empty() || s[0] == '0') {
return 0;
}
vector<int> dp(s.size() + 1, 1);
for (int i = 2; i < dp.size(); ++i){
dp[i] = ((s[i-1] == '0') ? 0 : dp[i-1]);
if (s[i-2] == '1' || (s[i-2] == '2' && s[i-1] <= '6')){
dp[i] += dp[i-2];
}
}
return dp.back();
}
};
int main()
{
Solution s;
cout << s.numDecodings("12") << endl;
cout << s.numDecodings("226") << endl;
cout << s.numDecodings("0") << endl;
cout << s.numDecodings("06") << endl;
return 0;
} 前:https://hannyang.blog.csdn.net/article/details/129287197



![【算法心得】C++map用不着map.find(arr[j])!=map.end();js的map是map不是哈希;编译器选GNU](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/bc215a913e954f7cb2ea4750a17ce251.png)