一 : 什么是DFS和BFS?
转载自 : 什么是DFS和BFS?
简介: 深度优先遍历(Depth First Search, 简称 DFS) 与广度优先遍历(Breath First Search)是图论中两种非常重要的算法,生产上广泛用于拓扑排序,寻路(走迷宫),搜索引擎,爬虫等,也频繁出现在高频面试题中。
1.1 DFS
深度优先遍历主要思路是从图中一个未访问的顶点 V 开始,沿着一条路一直走到底,然后从这条路尽头的节点回退到上一个节点,再从另一条路开始走到底…,不断递归重复此过程,直到所有的顶点都遍历完成,它的特点是不撞南墙不回头,先走完一条路,再换一条路继续走。
树是图的一种特例(连通无环的图就是树),接下来我们来看看树用深度优先遍历该怎么遍历。
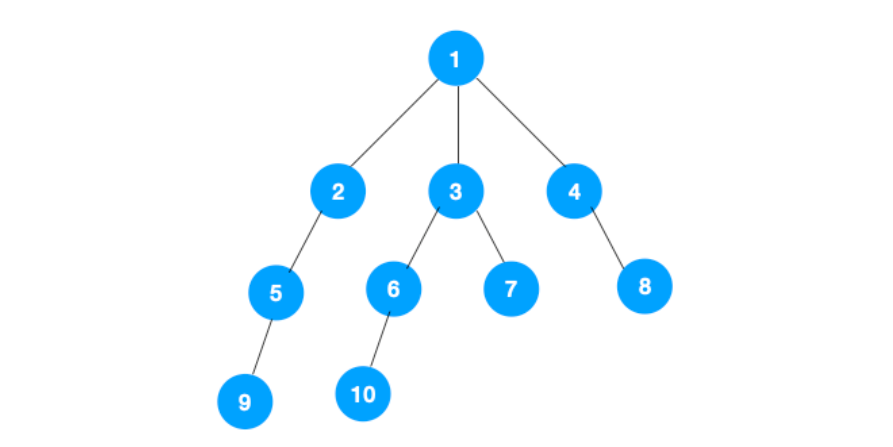
1、我们从根节点 1 开始遍历,它相邻的节点有 2,3,4,先遍历节点 2,再遍历 2 的子节点 5,然后再遍历 5 的子节点 9。
2、上图中一条路已经走到底了(9是叶子节点,再无可遍历的节点),此时就从 9 回退到上一个节点 5,看下节点 5 是否还有除 9 以外的节点,没有继续回退到 2,2 也没有除 5 以外的节点,回退到 1,1 有除 2 以外的节点 3,所以从节点 3 开始进行深度优先遍历,如下 :
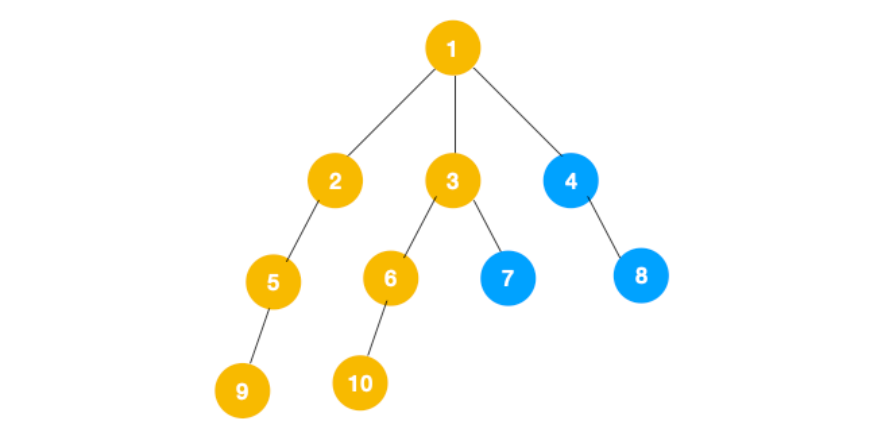
3、同理从 10 开始往上回溯到 6, 6 没有除 10 以外的子节点,再往上回溯,发现 3 有除 6 以外的子点 7,所以此时会遍历 7 :
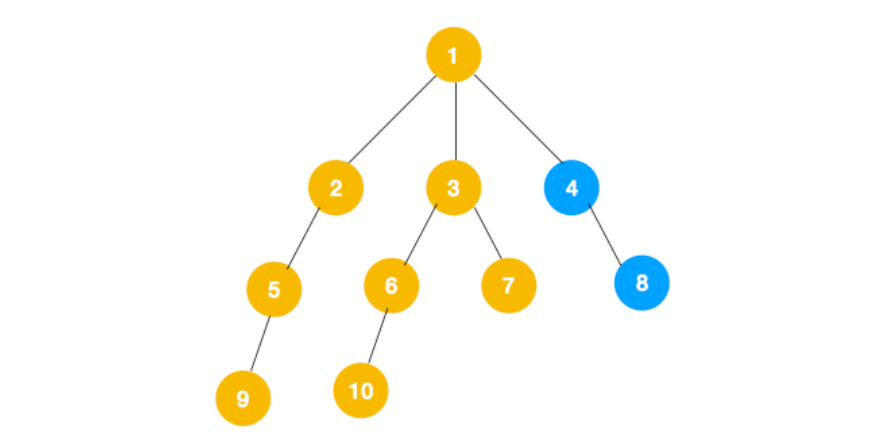
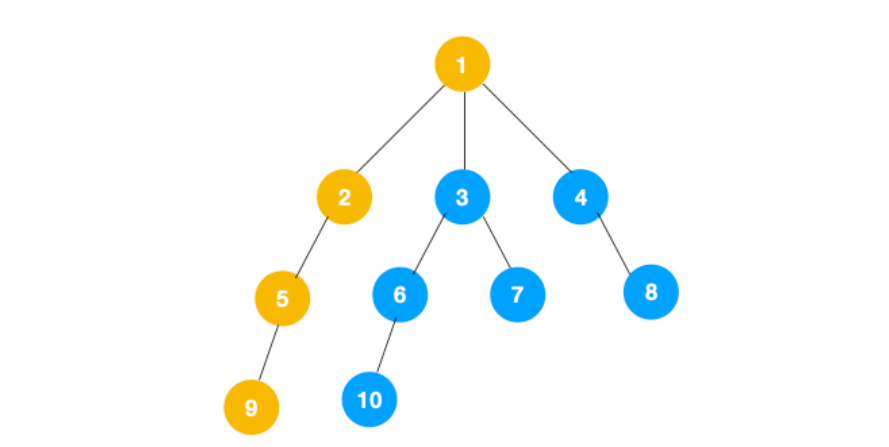
3、从 7 往上回溯到 3, 1,发现 1 还有节点 4 未遍历,所以此时沿着 4, 8 进行遍历,这样就遍历完成了
完整的节点的遍历顺序如下(节点上的的蓝色数字代表):
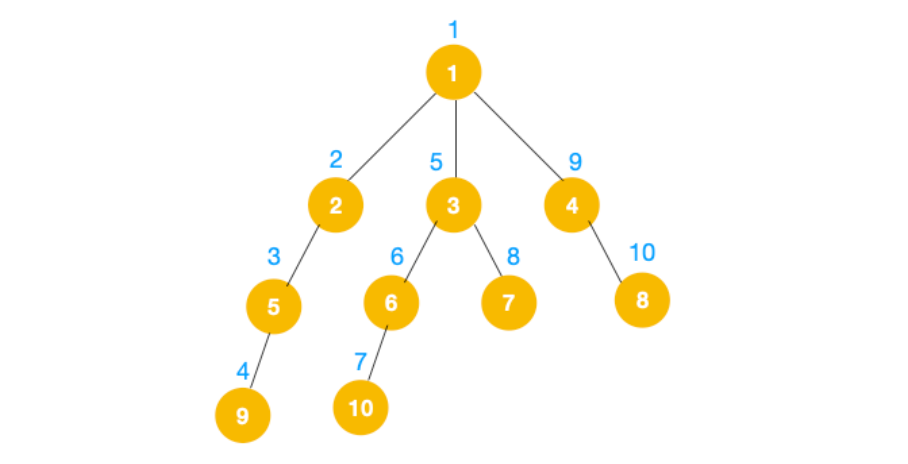
相信大家看到以上的遍历不难发现这就是树的前序遍历,实际上不管是前序遍历,还是中序遍历,亦或是后序遍历,都属于深度优先遍历。
那么深度优先遍历该怎么实现呢,有递归和非递归两种表现形式,接下来我们以二叉树为例来看下如何分别用递归和非递归来实现深度优先遍历。
1、递归实现
递归实现比较简单,由于是前序遍历,所以我们依次遍历当前节点,左节点,右节点即可,对于左右节点来说,依次遍历它们的左右节点即可,依此不断递归下去,直到叶节点(递归终止条件),代码如下 :
public class Solution {
private static class Node {
/**
* 节点值
*/
public int value;
/**
* 左节点
*/
public Node left;
/**
* 右节点
*/
public Node right;
public Node(int value, Node left, Node right) {
this.value = value;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
}
public static void dfs(Node treeNode) {
if (treeNode == null) {
return;
}
// 遍历节点
process(treeNode)
// 遍历左节点
dfs(treeNode.left);
// 遍历右节点
dfs(treeNode.right);
}
}
递归的表达性很好,也很容易理解,不过如果层级过深,很容易导致栈溢出。所以我们重点看下非递归实现 .
2、非递归实现
仔细观察深度优先遍历的特点,对二叉树来说,由于是先序遍历(先遍历当前节点,再遍历左节点,再遍历右节点),所以我们有如下思路 :
1、对于每个节点来说,先遍历当前节点,然后把右节点压栈,再压左节点(这样弹栈的时候会先拿到左节点遍历,符合深度优先遍历要求)
2、弹栈,拿到栈顶的节点,如果节点不为空,重复步骤 1, 如果为空,结束遍历。
我们以以下二叉树为例来看下如何用栈来实现 DFS。
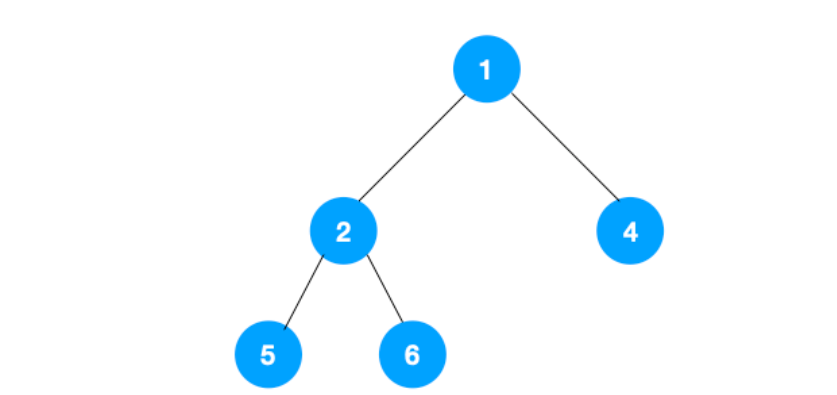
整体思路还是比较清晰的,使用栈来将要遍历的节点压栈,然后出栈后检查此节点是否还有未遍历的节点,有的话压栈,没有的话不断回溯(出栈),有了思路,不难写出如下用栈实现的二叉树的深度优先遍历代码 :
/**
* 使用栈来实现 dfs
* @param root
*/
public static void dfsWithStack(Node root) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<>();
// 先把根节点压栈
stack.push(root);
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
Node treeNode = stack.pop();
// 遍历节点
process(treeNode)
// 先压右节点
if (treeNode.right != null) {
stack.push(treeNode.right);
}
// 再压左节点
if (treeNode.left != null) {
stack.push(treeNode.left);
}
}
}
可以看到用栈实现深度优先遍历其实代码也不复杂,而且也不用担心递归那样层级过深导致的栈溢出问题。
1.2 BFS
广度优先遍历,指的是从图的一个未遍历的节点出发,先遍历这个节点的相邻节点,再依次遍历每个相邻节点的相邻节点。
上文所述树的广度优先遍历示意图如下,每个节点的值即为它们的遍历顺序。所以广度优先遍历也叫层序遍历,先遍历第一层(节点 1),再遍历第二层(节点 2,3,4),第三层(5,6,7,8),第四层(9,10)。
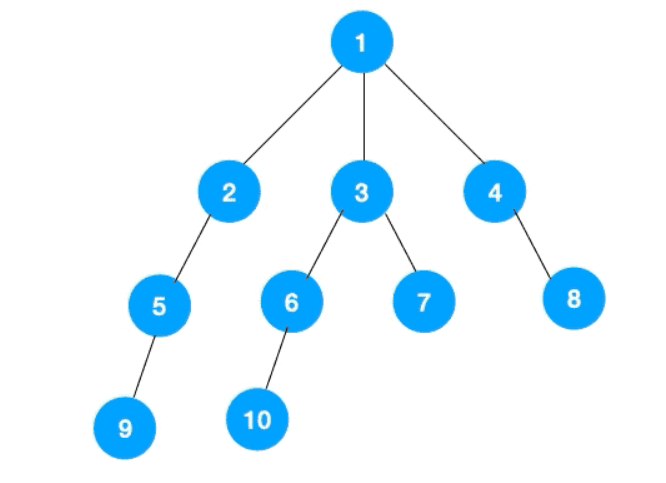
深度优先遍历用的是栈,而广度优先遍历要用队列来实现 , 具体代码如下 :
/**
* 使用队列实现 bfs
* @param root
*/
private static void bfs(Node root) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
Queue<Node> stack = new LinkedList<>();
stack.add(root);
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
Node node = stack.poll();
System.out.println("value = " + node.value);
Node left = node.left;
if (left != null) {
stack.add(left);
}
Node right = node.right;
if (right != null) {
stack.add(right);
}
}
}
下面是一些练习题目 .
二 : 红与黑
1.题目
有一间长方形的房子,地上铺了红色、黑色两种颜色的正方形瓷砖。你站在其中一块黑色的瓷砖上,只能向相邻的(上下左右四个方向)黑色瓷砖移动。请写一个程序,计算你总共能够到达多少块黑色的瓷砖。
2. 题解
2.1 DFS

我们可以使用一个标记数组 , 每当遍历过该黑色瓷砖 , 就将标记置为true .
具体代码如下 :
// write your code here
//DFS
import java.util.*;
public class Main{
public static int count = 0;
static int[][] direct = {{-1, 0},{1, 0},{0,-1},{0,1}};
private static void dfs(char[][] map,int m,int n,int x,int y,boolean[][] flags) {
if(flags[x][y]){
return;
}
if('#' == map[x][y]) {
return;
}
count++;
flags[x][y] = true;
for(int i=0; i<4; i++) {
int newx = x+direct[i][0];
int newy = y+direct[i][1];
if(newx >= 0 && newx < m && newy >= 0 && newy < n) {
dfs(map,m,n,newx,newy,flags);
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
while(sc.hasNext()){
int m = sc.nextInt();
int n = sc.nextInt();
char[][] map = new char[m][n];
boolean[][] flags =new boolean[m][n];
int x = 0;
int y = 0;
for(int i=0; i<m; i++) {
String s = sc.next();
for(int j=0; j<n; j++) {
map[i][j] = s.charAt(j);
if('@' == map[i][j]) {
x = i;
y = j;
}
}
}
//map中存储了瓷砖的所有信息
dfs(map,m,n,x,y,flags);
System.out.println(count);
count = 0;
}
}
}
进一步思考 , 每当遍历到黑色瓷砖 , 并将其"记录在册"后 , 就将该黑色瓷砖对应的位置标记为白色瓷砖 , 则下一次就不会遍历到这块瓷砖了 . 改进后的代码如下 :
// write your code here
//DFS
import java.util.*;
public class Main{
public static int count = 0;
static int[][] direct = {{-1, 0},{1, 0},{0,-1},{0,1}};
private static void dfs(char[][] map,int m,int n,int x,int y) {
if('#' == map[x][y]) {
return;
}
count++;
map[x][y] = '#';
for(int i=0; i<4; i++) {
int newx = x+direct[i][0];
int newy = y+direct[i][1];
if(newx >= 0 && newx < m && newy >= 0 && newy < n) {
dfs(map,m,n,newx,newy);
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
while(sc.hasNext()){
int m = sc.nextInt();
int n = sc.nextInt();
char[][] map = new char[m][n];
int x = 0;
int y = 0;
for(int i=0; i<m; i++) {
String s = sc.next();
for(int j=0; j<n; j++) {
map[i][j] = s.charAt(j);
if('@' == map[i][j]) {
x = i;
y = j;
}
}
}
//map中存储了瓷砖的所有信息
dfs(map,m,n,x,y);
System.out.println(count);
count = 0;
}
}
}
2.1 BFS
借助队列实现广度优先搜素 .
// write your code here
//DFS
import java.util.*;
public class Main{
static class Node{
int x, y;
public Node(int x, int y){
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
}
public static int count = 0;
static int[][] direct = {{-1, 0},{1, 0},{0,-1},{0,1}};
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
while(sc.hasNext()){
int m = sc.nextInt();
int n = sc.nextInt();
char[][] map = new char[m][n];
boolean[][] flags =new boolean[m][n];
int x = 0;
int y = 0;
Node cur = null;
for(int i=0; i<m; i++) {
String s = sc.next();
for(int j=0; j<n; j++) {
map[i][j] = s.charAt(j);
if('@' == map[i][j]) {
count++;
cur = new Node(i,j);
}
if('#' == map[i][j]) {
flags[i][j] = true;
}
}
}
//map中存储了瓷砖的所有信息
Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(cur);
flags[cur.x][cur.y] = true;
while(!queue.isEmpty()) {
Node node = queue.poll();
//搜索四个方向
for(int i=0; i<4; i++) {
Node next = new Node(node.x+direct[i][0],node.y+direct[i][1]);
if(next.x >= 0 && next.x < m &&
next.y >= 0 && next.y < n &&
!flags[next.x][next.y]) {
count++;
queue.offer(next);
flags[next.x][next.y] = true;
}
}
}
System.out.println(count);
count = 0;
}
}
}