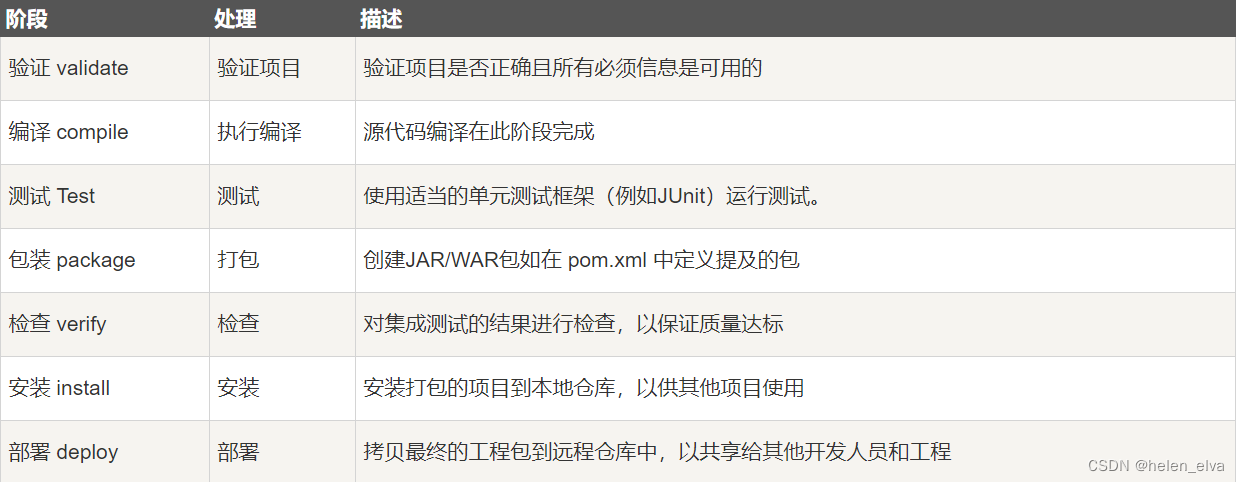
二叉树
二叉树的概念
- 树有很多种,每个节点最多只能有两个子节点的一种形式称为二叉树。
- 二叉树的子节点分为左节点和右节点。

- 如果该二叉树的所有叶子节点都在最后一层,并且节点总数 = 2^n - 1,n 为层数,则我们称为满二叉树。
- 如果该二叉树的所有叶子节点都在最后一层或者倒数第二层,而且最后一层的叶子节点在左边连续,倒数第二层的叶子节点在右边连续,我们称为完全二叉树。

二叉树的前序、中序和后序遍历
使用前序,中序,后序对二叉树进行遍历。
- 前序遍历:先输出父节点,再遍历左子树和右子树。
- 中序遍历:先遍历左子树,再输出父节点,再遍历右子树。
- 后序遍历:先遍历左子树,再遍历右子树,最后输出父节点。
小结:看输出父节点的顺序,就确定是前序,中序还是后序。
前序遍历
遍历步骤:
- 创建二叉树
- 前序遍历
- 先输出当前节点(初始的时候是root节点)
- 如果左子节点不为空,则递归继续前序遍历
- 如果右子节点不为空,则递归继续前序遍历
中序遍历
遍历步骤:
- 创建二叉树
- 中序遍历
- 如果当前节点的左子节点不为空,则递归中序遍历
- 输出当前节点
- 如果当前节点的右子节点不为空,则递归中序遍历
后序遍历
遍历步骤:
- 创建二叉树
- 后序遍历
- 如果当前节点的左子节点不为空,则递归后序遍历
- 如果当前节点的右子节点不为空,则递归后序遍历
- 输出当前节点
代码演示:
public class BinaryTreeDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建二叉树
BinaryTree binaryTree = new BinaryTree();
// 创建需要的节点
HeroNode root = new HeroNode(1,"宋江");
HeroNode node2 = new HeroNode(2,"吴用");
HeroNode node3 = new HeroNode(3,"卢俊义");
HeroNode node4 = new HeroNode(4,"林冲");
HeroNode node5 = new HeroNode(5,"关胜");
// 先手动创建二叉树
root.setLeft(node2);
root.setRight(node3);
node3.setLeft(node5);
node3.setRight(node4);
binaryTree.setRoot(root);
// 测试
System.out.println("前序遍历");
binaryTree.preOrder();
System.out.println("中序遍历");
binaryTree.infixOrder();
System.out.println("后序遍历");
binaryTree.postOrder();
}
}
// 定义 BinaryTree 二叉树
class BinaryTree {
private HeroNode root;
public void setRoot(HeroNode root) {
this.root = root;
}
// 前序遍历
public void preOrder() {
if (this.root != null) {
this.root.preOrder();
} else {
System.out.println("二叉树为空,无法遍历");
}
}
// 中序遍历
public void infixOrder() {
if (this.root != null) {
this.root.infixOrder();
} else {
System.out.println("二叉树为空,无法遍历");
}
}
// 后序遍历
public void postOrder() {
if (this.root != null) {
this.root.postOrder();
} else {
System.out.println("二叉树为空,无法遍历");
}
}
}
// 创建 HeroNode 节点
class HeroNode {
private int no;
private String name;
private HeroNode left;
private HeroNode right;
public HeroNode(int no, String name) {
this.no = no;
this.name = name;
}
public int getNo() {
return no;
}
public void setNo(int no) {
this.no = no;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public HeroNode getLeft() {
return left;
}
public void setLeft(HeroNode left) {
this.left = left;
}
public HeroNode getRight() {
return right;
}
public void setRight(HeroNode right) {
this.right = right;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "HeroNode{" +
"no=" + no +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
// 编写前序遍历的方法
public void preOrder() {
// 想输出父节点
System.out.println(this);
// 递归向左子树前序遍历
if (this.left != null) {
this.left.preOrder();
}
// 递归向右子树前序遍历
if (this.right != null) {
this.right.preOrder();
}
}
// 中序遍历
public void infixOrder() {
// 递归向左子树中序遍历
if (this.left != null) {
this.left.infixOrder();
}
// 输出父类节点
System.out.println(this);
// 递归向右子树中序遍历
if (this.right != null) {
this.right.infixOrder();
}
}
// 后序遍历
public void postOrder() {
// 递归向左子树后序遍历
if (this.left != null) {
this.left.postOrder();
}
// 递归向右子树后序遍历
if (this.right != null) {
this.right.postOrder();
}
// 输出父节点
System.out.println(this);
}
}
二叉树的前序、中序和后序查找
前序查找
查找步骤:
- 先判断当前节点的 no 是否等于要查找的 no
- 如果相等,则返回当前节点
- 如果不等,则判断当前节点的左子节点是否为空,如果不为空,则递归前序查找
- 如果左递归前序查找,找到节点,则返回,否则继续判断,当前节点的右子节点是否为空,如果不为空,则继续向右递归前序查找
中序查找
查找步骤:
- 先判断当前节点的左子节点是否为空,如果不为空,则递归中序查找
- 如果找到,则返回;如果没有找到,就和当前节点比较,如果是,则返回当前节点,如果不是,继续进行右递归中序查找
- 如果右递归中序查找找到就返回,否则返回 null
后序查找
查找步骤:
- 判断当前节点的左子节点是否为空,如果不为空,则递归后序查找
- 如果找到,就返回,如果没有找到,就判断当前节点的右子节点是否为空,如果不为空,则右递归进行后序查找,如果找到,就返回
- 如果没有找到就和当前节点进行比较,如果是则返回,否则返回 null
代码演示:
主方法:
System.out.println("前序查找");
HeroNode resNode1 = binaryTree.preOrderSearch(5);
if (resNode1 != null) {
System.out.printf("找到了,信息为 no=%d name=%s\n", resNode1.getNo(), resNode1.getName());
} else {
System.out.printf("没有找到 no=%d 的英雄\n", 5);
}
System.out.println("中序查找");
HeroNode resNode2 = binaryTree.infixOrderSearch(4);
if (resNode2 != null) {
System.out.printf("找到了,信息为 no=%d name=%s\n", resNode2.getNo(), resNode2.getName());
} else {
System.out.printf("没有找到 no=%d 的英雄\n", 4);
}
System.out.println("后序查找");
HeroNode resNode3 = binaryTree.postOrderSearch(3);
if (resNode3 != null) {
System.out.printf("找到了,信息为 no=%d name=%s\n", resNode3.getNo(), resNode3.getName());
} else {
System.out.printf("没有找到 no=%d 的英雄\n", 3);
}
BinaryTree 类:
// 前序查找
public HeroNode preOrderSearch(int no) {
if (root != null) {
return root.preOrderSearch(no);
} else {
return null;
}
}
// 中序查找
public HeroNode infixOrderSearch(int no) {
if (root != null) {
return root.infixOrderSearch(no);
} else {
return null;
}
}
// 后序查找
public HeroNode postOrderSearch(int no) {
if (root != null) {
return root.postOrderSearch(no);
} else {
return null;
}
}
HeroNode 类:
/**
* 前序查找
*
* @param no 查找的 no
* @return 如果找到就返回该 Node,否则就返回 null
*/
public HeroNode preOrderSearch(int no) {
// 比较当前节点
if (this.no == no) {
return this;
}
// 1. 判断当前节点的左子节点是否为空,如果不为空,则递归前序查找
// 2. 如果左递归前序查找,找到节点,则返回
HeroNode resNode = null;
if (this.left != null) {
resNode = this.left.preOrderSearch(no);
}
if (resNode != null) { // 说明在左子树找到
return resNode;
}
// 继续判断,当前节点的右子节点是否为空,如果不为空,则继续向右递归前序查找
if (this.right != null) {
resNode = this.right.preOrderSearch(no);
}
return resNode;
}
/**
* 中序查找
*
* @param no 查找的 no
* @return 如果找到就返回该 Node,否则就返回 null
*/
public HeroNode infixOrderSearch(int no) {
// 判断当前节点的左子节点是否为空,如果不为空,则递归中序查找
HeroNode resNode = null;
if (this.left != null) {
resNode = this.left.infixOrderSearch(no);
}
if (resNode != null) {
return resNode;
}
// 如果没有找到,就和当前节点比较
if (this.no == no) {
return this;
}
// 1. 继续进行右递归中序查找
// 2. 如果右递归中序查找找到就返回,否则返回 null
if (this.right != null) {
resNode = this.right.infixOrderSearch(no);
}
return resNode;
}
/**
* 后序查找
*
* @param no 查找的 no
* @return 如果找到就返回该 Node,否则就返回 null
*/
public HeroNode postOrderSearch(int no) {
// 判断当前节点的左子节点是否为空,如果不为空,则递归后序查找
HeroNode resNode = null;
if (this.left != null) {
resNode = this.left.postOrderSearch(no);
}
if (resNode != null) {
return resNode;
}
// 判断当前节点的右子节点是否为空,如果不为空,则右递归进行后序查找
if (this.right != null) {
resNode = this.right.postOrderSearch(no);
}
if (resNode != null) {
return resNode;
}
// 和当前节点进行比较,如果是则返回,否则返回 null
if (this.no == no) {
return this;
}
return resNode;
}
删除节点
要求:
- 如果删除的节点是叶子节点,则删除该节点。
- 如果删除的节点是非叶子节点,则删除该子树。
思路:
- 首先,考虑如果树是空树 root,如果只有一个 root 节点,则等价将二叉树置空。
- 因为我们的二叉树是单向的,所以我们判断当前节点的子节点是否需要删除节点,而不能去判断当前这个节点是不是需要删除的节点。
- 如果当前节点的左子节点不为空,并且左子节点及时需要删除的节点,就将 this.left = null;并且返回(结束递归删除)。
- 如果当前节点的右子节点不为空,并且右子节点及时需要删除的节点,就将 this.right = null;并且返回(结束递归删除)。
- 如果第 3 步和第 4 步没有删除节点,那么我们就需要向左子树进行递归删除。
- 如果第 5 步也没有删除节点,那么我们就需要向右子树进行递归删除。
代码演示:
主方法:
System.out.println("删除前");
binaryTree.preOrder();
binaryTree.delNode(5);
System.out.println("删除后");
binaryTree.preOrder();
BinaryTree 类:
// 删除节点
public void delNode(int no) {
if (root != null) {
// 如果只有一个 root 节点,这里立即判断 root 是不是就是要删除的节点
if (root.getNo() == no) {
root = null;
} else {
// 递归删除
root.delNode(no);
}
} else {
System.out.println("空树,不能删除~");
}
}
HeroNode 类:
/**
* 递归删除节点
* 1. 如果删除的节点是叶子结点,则删除该节点
* 2. 如果删除的节点是非叶子节点,则删除该子树
*
* @param no 需要删除的 no
*/
public void delNode(int no) {
// 如果当前节点的左子节点不为空,并且左子节点及时需要删除的节点,就将 this.left = null;并且返回(结束递归删除)。
if (this.left != null && this.left.no == no) {
this.left = null;
return;
}
// 如果当前节点的右子节点不为空,并且右子节点及时需要删除的节点,就将 this.right = null;并且返回(结束递归删除)。
if (this.right != null && this.right.no == no) {
this.right = null;
return;
}
// 如果第 3 步和第 4 步没有删除节点,那么我们就需要向左子树进行递归删除。
if (this.left != null) {
this.left.delNode(no);
}
// 如果第 5 步也没有删除节点,那么我们就需要向右子树进行递归删除。
if (this.right != null) {
this.right.delNode(no);
}
}