文章目录
- 多线程
- C++
- 创建线程
- join 和detach
- this_thread
- 线程操作
- 锁
- lock_guard
- unique_lock
- 条件变量 condition_variable
- wait
- waitfor
- C语言
- 线程创建
- 线程同步
- 参考
多线程
传统的C++(C++11标准之前)中并没有引入线程这个概念,在C++11出来之前,如果我们想要在C++中实现多线程,需要借助操作系统平台提供的API,比如Linux的<pthread.h>,或者windows下的<windows.h> 。
C++11提供了语言层面上的多线程,包含在头文件中。它解决了跨平台的问题,提供了管理线程、保护共享数据、线程间同步操作、原子操作等类。
C++
在 C++ 中,线程操作由标准库提供支持,主要涉及以下几个头文件:
#include <thread> // 线程相关的库
#include <mutex> // 互斥量相关的库
#include <condition_variable> // 条件变量相关的库
创建线程
当线程启动后,一定要在和线程相关联的thread销毁前,确定以何种方式等待线程执行结束。
- detach方式,启动的线程自主在后台运行,当前的代码继续往下执行,不等待新线程结束。
- join方式,等待启动的线程完成,才会继续往下执行。
可以使用joinable判断是join模式还是detach模式。
if (myThread.joinable()) foo.join();
在 C++ 中,使用 std::thread 类创建新线程。创建线程的基本形式为:
std::thread t1(func, args...);
其中 func 是线程执行的函数,args… 是函数的参数列表。
示例:
#include <iostream>
#include <thread>
using namespace std;
void threadFunc1() {
std::cout << "Thread ID: " << std::this_thread::get_id() << std::endl;
}
void threadFunc2(int n) {
std::cout << "Thread ID: " << std::this_thread::get_id()
<< ", n = " << n << std::endl;
}
int main(){
// 方式1:无参 void thread_fun()
thread t1(threadFunc1);
t1.join();
//方式2:有参数 void thread_fun(int x)
thread t2(threadFunc2, 10);
t2.join();
//方式3:直接创建线程,没有名字
thread(threadFunc2, 100).join();
return 0;
}
join 和detach
(1)join举例
下面的代码,join后面的代码不会被执行,除非子线程结束。
#include <iostream>
#include <thread>
using namespace std;
void thread_1()
{
while(1)
{
//cout<<"子线程1111"<<endl;
}
}
void thread_2(int x)
{
while(1)
{
//cout<<"子线程2222"<<endl;
}
}
int main()
{
thread first ( thread_1); // 开启线程,调用:thread_1()
thread second (thread_2,100); // 开启线程,调用:thread_2(100)
first.join(); // pauses until first finishes 这个操作完了之后才能destroyed
second.join(); // pauses until second finishes//join完了之后,才能往下执行。
while(1)
{
std::cout << "主线程\n";
}
return 0;
}
(2)detach举例
下列代码中,主线程不会等待子线程结束。如果主线程运行结束,程序则结束。
#include <iostream>
#include <thread>
using namespace std;
void thread_1()
{
while(1)
{
cout<<"子线程1111"<<endl;
}
}
void thread_2(int x)
{
while(1)
{
cout<<"子线程2222"<<endl;
}
}
int main()
{
thread first ( thread_1); // 开启线程,调用:thread_1()
thread second (thread_2,100); // 开启线程,调用:thread_2(100)
first.detach();
second.detach();
for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
std::cout << "主线程\n";
}
return 0;
}
this_thread
this_thread是一个类,它有4个功能函数,具体如下:
| 函数 | 使用 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| get_id | std::this_thread::get_id() | 获取线程id |
| yield | std::this_thread::yield() | 放弃线程执行,回到就绪状态 |
| sleep_for | std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::seconds(1)) | 暂停1秒 |
| sleep_until | 如下 | 一分钟后执行吗,如下 |
using std::chrono::system_clock;
std::time_t tt = system_clock::to_time_t(system_clock::now());
struct std::tm * ptm = std::localtime(&tt);
cout << "Waiting for the next minute to begin...\n";
++ptm->tm_min; //加一分钟
ptm->tm_sec = 0; //秒数设置为0 暂停执行,到下一整分执行
this_thread::sleep_until(system_clock::from_time_t(mktime(ptm)));
线程操作
锁
文主要讨论 c++11 中的两种锁:lock_guard 和 unique_lock。这两种锁都可以对std::mutex进行封装,实现RAII的效果。绝大多数情况下这两种锁是可以互相替代的,区别是unique_lock比lock_guard能提供更多的功能特性(但需要付出性能的一些代价)
lock_guard
lock_guard 通常用来管理一个 std::mutex 类型的对象,通过定义一个 lock_guard 一个对象来管理 std::mutex 的上锁和解锁。在 lock_guard 初始化的时候进行上锁,然后在 lock_guard 析构的时候进行解锁。这样避免了人为的对 std::mutex 的上锁和解锁的管理。
template<class Mutex> class lock_guard;
它的特点如下:
- (1) 创建即加锁,作用域结束自动析构并解锁,无需手工解锁
- (2) 不能中途解锁,必须等作用域结束才解锁
- (3) 不能复制
注意:lock_guard 并不管理 std::mutex 对象的声明周期,也就是说在使用 lock_guard 的过程中,如果 std::mutex 的对象被释放了,那么在 lock_guard 析构的时候进行解锁就会出现空指针错误。
示例代码如下:
#include <thread>
#include <mutex>
#include <iostream>
int g_i = 0;
std::mutex g_i_mutex;
void safe_increment()
{
const std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(g_i_mutex);
++g_i;
std::cout << std::this_thread::get_id() << ": " << g_i << '\n';
}
int main()
{
std::cout << "main: " << g_i << '\n';
std::thread t1(safe_increment);
std::thread t2(safe_increment);
t1.join();
t2.join();
std::cout << "main: " << g_i << '\n';
}
输出:
main: 0
140641306900224: 1
140641298507520: 2
main: 2
unique_lock
nique_lock 和 lock_guard 一样,对 std::mutex 类型的互斥量的上锁和解锁进行管理,一样也不管理 std::mutex 类型的互斥量的声明周期。但是它的使用更加的灵活。支持的构造函数如下:
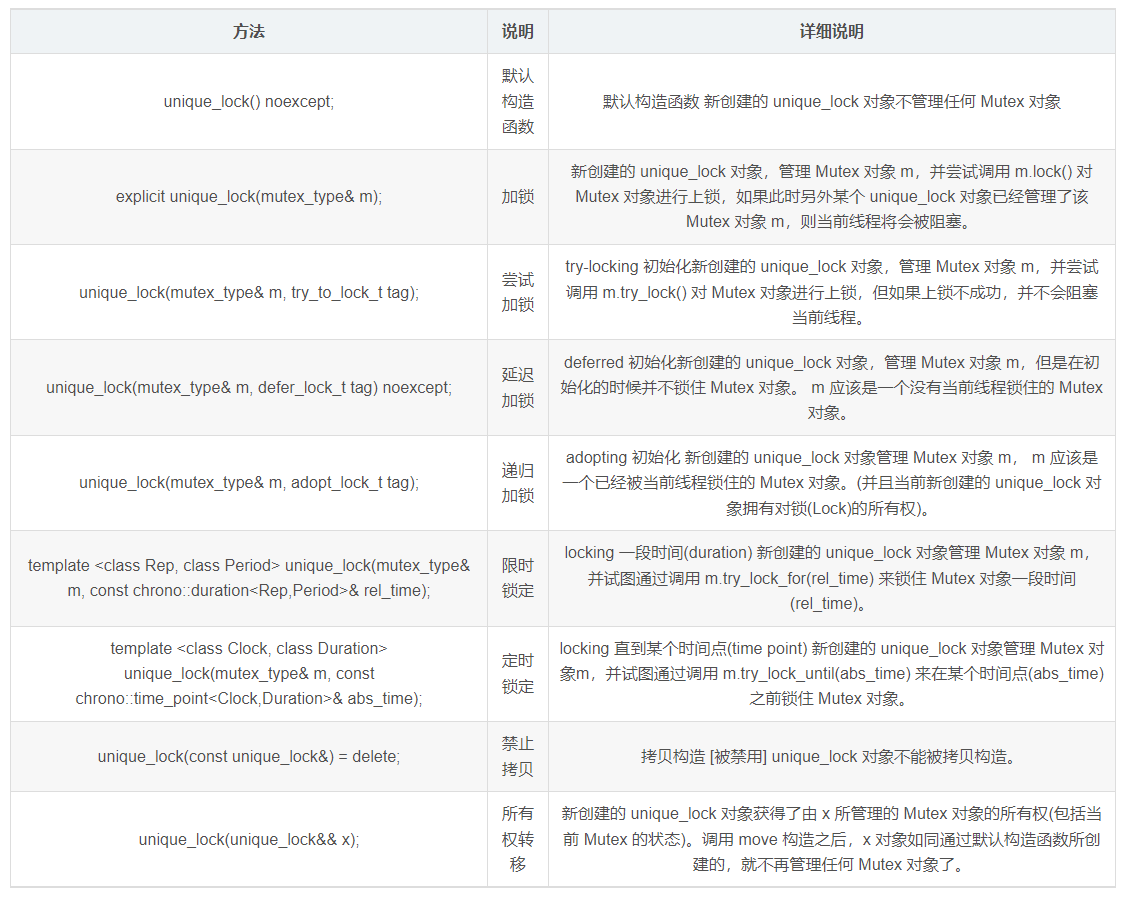
简单地讲,unique_lock 是 lock_guard 的升级加强版,它具有 lock_guard 的所有功能,同时又具有其他很多方法,使用起来更强灵活方便,能够应对更复杂的锁定需要。需要使用锁的时候,首先考虑使用 lock_guard。它简单、明了、易读。如果用它完全 ok,就不要考虑其他了。如果现实不允许,再使用 unique_lock 。
特点如下:
- 创建时可以不锁定(通过指定第二个参数为 std::defer_lock),而在需要时再锁定
- 可以随时加锁解锁
- 作用域规则同 lock_grard,析构时自动释放锁
- 不可复制,可移动
- 条件变量需要该类型的锁作为参数(此时必须使用 unique_lock)
示例代码:
一个线程减的数据加到另一个线程中去。
#include <mutex>
#include <thread>
#include <chrono>
struct Box {
explicit Box(int num) : num_things{num} {}
int num_things;
std::mutex m;
};
void transfer(Box &from, Box &to, int num)
{
std::unique_lock<std::mutex> lock1(from.m, std::defer_lock);
std::unique_lock<std::mutex> lock2(to.m, std::defer_lock);
std::lock(lock1, lock2);
from.num_things -= num;
to.num_things += num;
}
int main()
{
Box acc1(100);
Box acc2(50);
std::thread t1(transfer, std::ref(acc1), std::ref(acc2), 10);
std::thread t2(transfer, std::ref(acc2), std::ref(acc1), 5);
t1.join();
t2.join();
}
条件变量 condition_variable
condition_variable头文件有两个variable类,一个是condition_variable,另一个是condition_variable_any。condition_variable必须结合unique_lock使用。condition_variable_any可以使用任何的锁。下面以condition_variable为例进行介绍。
condition_variable条件变量可以阻塞(wait、wait_for、wait_until)调用的线程直到使用(notify_one或notify_all)通知恢复为止。condition_variable是一个类,这个类既有构造函数也有析构函数,使用时需要构造对应的condition_variable对象,调用对象相应的函数来实现上面的功能。
| 类型 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| condition_variable | 构建对象 |
| 析构 | 删除 |
| wait | Wait until notified |
| wait_for | Wait for timeout or until notified |
| wait_until | Wait until notified or time point |
| notify_one | 解锁一个线程,如果有多个,则未知哪个线程执行 |
| notify_all | 解锁所有线程 |
| cv_status | 这是一个类,表示variable 的状态,如下所示 |
enum class cv_status { no_timeout, timeout };
wait
当前线程调用 wait() 后将被阻塞(此时当前线程应该获得了锁(mutex),不妨设获得锁 lck),直到另外某个线程调用 notify_* 唤醒了当前线程。在线程被阻塞时,该函数会自动调用 lck.unlock() 释放锁,使得其他被阻塞在锁竞争上的线程得以继续执行。另外,一旦当前线程获得通知(notified,通常是另外某个线程调用 notify_* 唤醒了当前线程),wait()函数也是自动调用 lck.lock(),使得lck的状态和 wait 函数被调用时相同。代码示例:
#include <iostream>
#include <thread>
#include <mutex>
#include <condition_variable>
std::mutex mtx; // 定义互斥量
std::condition_variable cv; // 定义条件变量
bool ready = false; // 条件变量状态标志
void threadFunc(int n) {
std::unique_lock<std::mutex> lock(mtx);
while (!ready) { // 等待条件变量
cv.wait(lock);
}
std::cout << "Thread ID: " << std::this_thread::get_id()
<< ", n = " << n << std::endl;
}
int main() {
std::thread t1(threadFunc, 10);
std::thread t2(threadFunc, 20);
// 设置条件变量状态标志
std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::seconds(2));
ready = true;
cv.notify_all(); // 唤醒所有等待条件变量的线程
t1.join();
t2.join();
return 0;
}
在上述代码中,std::condition_variable 类型的 cv 对象用于实现线程等待条件变量的功能。在 threadFunc 函数中,使用 cv.wait(lock) 等待条件变量。在 main 函数中,先等待一段时间后设置条件变量状态标志 ready 为 true,再通过 cv.notify_all() 唤醒所有等待条件变量的线程。
waitfor
与std::condition_variable::wait() 类似,不过 wait_for可以指定一个时间段,在当前线程收到通知或者指定的时间 rel_time 超时之前,该线程都会处于阻塞状态。而一旦超时或者收到了其他线程的通知,wait_for返回,剩下的处理步骤和 wait()类似。
template <class Rep, class Period>
cv_status wait_for (unique_lock<mutex>& lck,
const chrono::duration<Rep,Period>& rel_time);
另外,wait_for 的重载版本的最后一个参数pred表示 wait_for的预测条件,只有当 pred条件为false时调用 wait()才会阻塞当前线程,并且在收到其他线程的通知后只有当 pred为 true时才会被解除阻塞。
template <class Rep, class Period, class Predicate>
bool wait_for (unique_lock<mutex>& lck,
const chrono::duration<Rep,Period>& rel_time, Predicate pred);
代码示例:
#include <iostream> // std::cout
#include <thread> // std::thread
#include <chrono> // std::chrono::seconds
#include <mutex> // std::mutex, std::unique_lock
#include <condition_variable> // std::condition_variable, std::cv_status
std::condition_variable cv;
int value;
void read_value()
{
std::cin >> value;
cv.notify_one();
}
int main ()
{
std::cout << "Please, enter an integer (I'll be printing dots): \n";
std::thread th (read_value);
std::mutex mtx;
std::unique_lock<std::mutex> lck(mtx);
while (cv.wait_for(lck,std::chrono::seconds(3))==std::cv_status::timeout)
{
std::cout << '.' << std::endl;
}
std::cout << "You entered: " << value << '\n';
th.join();
return 0;
}
通知或者超时都会解锁,所以主线程会一直打印。示例中只要过去3秒,就会不断的打印。
C语言
在 C语言中,可以通过 pthread 库来创建线程。pthread 库是一个 POSIX 标准的线程库,可以在 Linux、Unix 等操作系统上使用。
线程创建
线程的创建需要用到 pthread_create 函数,它的原型如下:
int pthread_create(pthread_t *thread, const pthread_attr_t *attr, void *(*start_routine) (void *), void *arg);
参数说明:
- thread:指向 pthread_t 类型的指针,用于存储新创建的线程的 ID;
- attr:指向 pthread_attr_t 类型的指针,用于设置线程的属性,一般可以设置为 NULL;
- start_routine:指向线程的函数指针,该函数用于执行新线程的任务;
- arg:传递给线程函数的参数。
下面是一个简单的线程创建示例代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <pthread.h>
void *thread_func(void *arg) {
printf("This is a new thread!\n");
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
int main() {
pthread_t tid;
pthread_create(&tid, NULL, thread_func, NULL);
printf("This is the main thread!\n");
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
运行结果:
This is the main thread!
This is a new thread!
可以看到,在 main 函数中调用 pthread_create 函数创建了一个新线程,然后在新线程中执行了 thread_func 函数,并打印出"This is a new thread!“。同时,主线程也继续执行,并打印出"This is the main thread!”。
需要注意的是,在使用 pthread 库时,main 函数必须调用 pthread_exit 函数来结束程序,否则可能会出现线程无法正常退出的情况。
线程同步
在多线程编程中,由于多个线程同时执行,可能会出现资源竞争的情况。为了避免这种情况,需要对线程进行同步。在 C语言中,可以使用互斥锁、条件变量等机制来实现线程同步。
- 互斥锁
互斥锁是一种用于保护共享资源的锁,只有获得锁的线程才能访问共享资源。
在 C语言中,可以使用 pthread 库中的 pthread_mutex_init、pthread_mutex_lock、pthread_mutex_unlock、pthread_mutex_destroy 函数来实现互斥锁。其中,pthread_mutex_init 函数用于初始化互斥锁,pthread_mutex_lock 函数用于加锁,pthread_mutex_unlock 函数用于解锁,pthread_mutex_destroy 函数用于销毁互斥锁。
下面是一个使用互斥锁的示例代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <pthread.h>
int counter = 0;
pthread_mutex_t mutex;
void *thread_func(void *arg) {
int i;
for (i = 0; i < 1000000; i++) {
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
counter++;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
}
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
int main() {
pthread_t tid1, tid2;
pthread_mutex_init(&mutex, NULL);
pthread_create(&tid1, NULL, thread_func, NULL);
pthread_create(&tid2, NULL, thread_func, NULL);
pthread_join(tid1, NULL);
pthread_join(tid2, NULL);
pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex);
printf("counter = %d\n", counter);
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
运行结果:
counter = 2000000
可以看到,在 main 函数中创建了两个线程 tid1 和 tid2,它们的任务是分别对 counter 变量进行 1000000 次累加操作。由于 counter 变量是一个共享资源,因此需要使用互斥锁来保护它。
在线程函数中,首先调用 pthread_mutex_lock 函数获得锁,然后对 counter 变量进行操作,最后调用 pthread_mutex_unlock 函数释放锁。在 main 函数中,使用 pthread_join 函数等待线程 tid1 和 tid2 执行完毕,然后销毁互斥锁并打印出 counter 的最终值。
- 条件变量
条件变量是一种用于线程间通信的机制,可以用于实现线程的等待和唤醒操作。
在 C语言中,可以使用 pthread 库中的 pthread_cond_init、pthread_cond_wait、pthread_cond_signal、pthread_cond_broadcast、pthread_cond_destroy 函数来实现条件变量。
其中,pthread_cond_init 函数用于初始化条件变量,pthread_cond_wait 函数用于等待条件变量,pthread_cond_signal 函数用于唤醒等待条件变量的线程,pthread_cond_broadcast 函数用于唤醒所有等待条件变量的线程,pthread_cond_destroy 函数用于销毁条件变量。
下面是一个使用条件变量的示例代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <pthread.h>
int buffer = 0;
pthread_mutex_t mutex;
pthread_cond_t cond;
void *producer(void *arg) {
int i;
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
buffer++;
printf("Producer produced %d\n", buffer);
pthread_cond_signal(&cond);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
sleep(1);
}
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
void *consumer(void *arg) {
int i;
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
while (buffer == 0) {
pthread_cond_wait(&cond, &mutex);
}
buffer--;
printf("Consumer consumed %d\n", buffer);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
sleep(1);
}
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
int main() {
pthread_t tid1, tid2;
pthread_mutex_init(&mutex, NULL);
pthread_cond_init(&cond, NULL);
pthread_create(&tid1, NULL, producer, NULL);
pthread_create(&tid2, consumer, NULL);
pthread_join(tid1, NULL);
pthread_join(tid2, NULL);
pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex);
pthread_cond_destroy(&cond);
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
运行结果:
Producer produced 1
Consumer consumed 0
Producer produced 1
Consumer consumed 0
Producer produced 1
Consumer consumed 0
Producer produced 1
Consumer consumed 0
Producer produced 1
Consumer consumed 0
Producer produced 1
Consumer consumed 0
Producer produced 1
Consumer consumed 0
Producer produced 1
Consumer consumed 0
Producer produced 1
Consumer consumed 0
Producer produced 1
Consumer consumed 0
可以看到,该程序中有一个生产者线程和一个消费者线程,它们共享一个缓冲区变量 buffer。生产者线程负责将 buffer 逐个增加,消费者线程负责将 buffer 逐个减少。当 buffer 为 0 时,消费者线程将进入等待状态,等待生产者线程将 buffer 增加后发出信号唤醒自己。当 buffer 不为 0 时,生产者线程将向消费者线程发送一个信号,通知其可以开始消费。通过使用条件变量和互斥锁,生产者和消费者线程可以保证对 buffer 变量的操作是互斥的。
参考
- C++多线程详解(全网最全)
- C++ 线程操作
- lock_guard和unique_lock
- C语言多线程编程










![[深入理解NAND Flash] 闪存(NAND Flash) 学习指南](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/a2555b3d39a44b1d9c5b1a22d01ceaa2.png)

