文章目录
- 两个链表的第一个重合节点
- 判断回文链表
两个链表的第一个重合节点
同LeetCode 160.相交链表
解法一:Hash和Set(集合),此处用Set合适。
把其中一个链表的所有节点引用放入set,再从头遍历另一个链表第一次重合的地方就是答案。
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
Set<ListNode> set = new HashSet<>();
while(headA != null){
set.add(headA);
headA = headA.next;
}
while(headB != null){
if(set.contains(headB)) return headB;
headB = headB.next;
}
return null;
}
解法二:使用栈
同解法一思路,只不过出栈的时候判断的是最后一个相同引用。
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
Stack<ListNode> stackA = new Stack<>();
Stack<ListNode> stackB = new Stack<>();
while (headA != null) {
stackA.push(headA);
headA = headA.next;
}
while (headB != null) {
stackB.push(headB);
headB = headB.next;
}
ListNode cur = null;
while (!stackA.isEmpty() && !stackB.isEmpty()) {
if (stackA.peek() == stackB.peek()) {
cur = stackA.pop();
stackB.pop();
} else break;
}
return cur;
}
前两种解法利用了数据结构的特点,下面两种则是将两个链表的长度设法弄成一样的,之后节点映射对比。
解法三:拼接
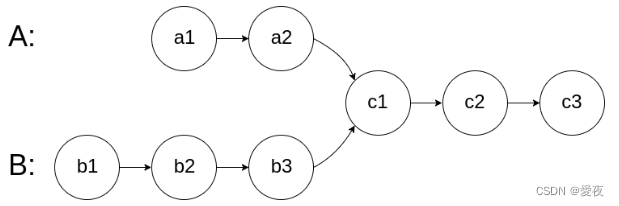
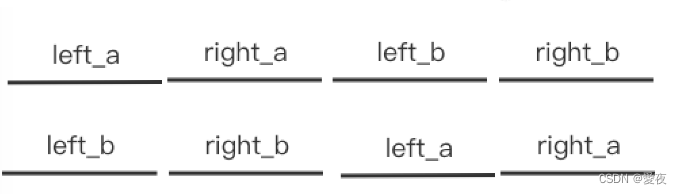
如图AB两个链表如果有重合部分,则可以把AB链表分成 left 和 right 部分,易知 right_a = right_b 。将AB两个链表按照AB、BA两种方式拼接得到的结果可以看到有重合部分,这样两个链表长度相等,则可以映射对比。
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
if(headA==null || headB==null) return null;
ListNode node1 = headA;
ListNode node2 = headB;
while (node1 != node2){
node1 = node1.next;
node2 = node2.next;
if(node1 == node2) break;
// 因为两个合并链表长度一定相等,也就是说遍历完合并链表一定能得到答案。这个判断是对AB链表无交集情况的判断,防止死循环。
if (node1!=node2) {
if(node1==null) node1 = headB;
if(node2==null) node2 = headA;
}
}
return node1;
}
解法四:消余
同思路三都是让链表长度相等再遍历。这个方法就是让长的链表遍历到和短链表长度相等时比较。
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
if(headA==null || headB==null) return null;
ListNode node1 = headA;
ListNode node2 = headB;
int l1 = 0, l2 = 0;
while (node1!=null){
l1++;
node1 = node1.next;
}
while (node2!=null){
l2++;
node2 = node2.next;
}
int l = Math.abs(l1-l2);
if(l1>l2){
while (l!=0){
headA = headA.next;
l--;
}
}else {
while (l!=0){
headB = headB.next;
l--;
}
}
while (headA!=headB){
headA = headA.next;
headB = headB.next;
}
return headA;
}
判断回文链表
同LeetCode 234.回文链表
解法一:入栈对比。
ublic boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {
Stack<ListNode> stack = new Stack<>();
ListNode cur = head;
int l = 0;
// 将全部元素入栈
while (cur != null){
stack.push(cur);
cur = cur.next;
l++;
}
// 比价一半长度即可
l /= 2;
while (l!=0) {
if(head.val != stack.pop().val) return false;
head = head.next;
l--;
}
return true;
}
解法二:翻转链表。
使用快慢指针遍历(也可以遍历求长度,然后遍历到链表的中间),然后翻转链表后半部分,再与原链表对比。
public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head;
while (fast!=null && fast.next!=null){
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
fast = reverse(slow);
while (fast!=null){
if(fast.val!= head.val) return false;
fast = fast.next;
head = head.next;
}
return true;
}
private ListNode reverse(ListNode head) {
ListNode cur = head.next;
head.next = null;
while (cur!=null){
ListNode curNext = cur.next;
cur.next = head;
head = cur;
cur = curNext;
}
return head;
}




![[VRTK4.0]添加一个Curved Pointer](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/3f68296d6f594f26bccdf0cefbb76956.png)