SQL3:distinct
查询结果去重,返回所有不同的university
方法一:distinct关键字。(注意:这个关键字实际上是 select distinct,如果是多列,多列作为一个组合然后 distinct 去重)
方法二:巧用group by
select distinct university
from user_profileselect university
from user_profile
group by universitySQL4:limit
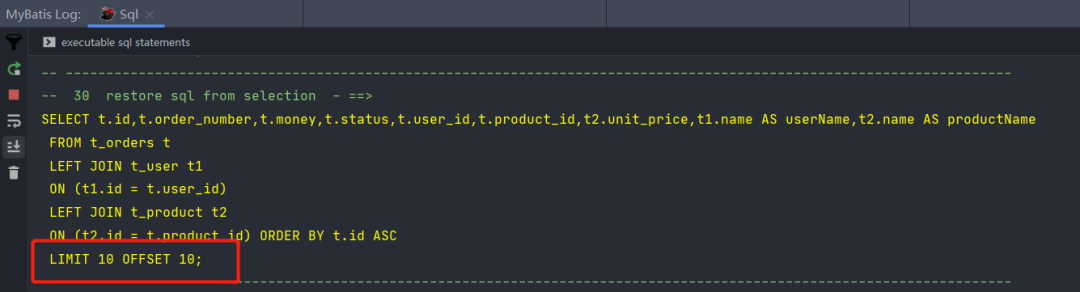
返回前两行id
limit n:表示返回前 n 行
limit m,n:表示从下标 m 开始,返回长度 n 行
select device_id
from user_profile
limit 2SQL5:as
接着上一题,用as将输出列改别名
select device_id as user_infos_example
from user_profile
limit 2注意:有时候子查询表不用 as 起名字可能会编译报错,有时候则不会,尽量养成好习惯as一下,当然,能看懂报错告诉要 as 一下自然也没问题。
SQL8:between and
where age between 2 and 3 等价于 where age>=2 and age<=3
where age not between 2 and 3 等价于 where age<2 or age>3
mysql是这样的,有些数据库可能取等不一样。因此我不建议用between,了解即可。
SQL10:is null
where age is null / is not null
SQL13:in
in/not in:相当于多个等于条件用 or 连接
where university in ('北京大学','复旦大学','山东大学')
SQL15:like
like+正则表达式,%表示任意串,.或_表示任意字符,另外注意 like 的正则表达式并不包含正则表达式的全部功能
SQL16:max、round、all
复旦大学GPA的最大值,要求保留一位小数。
方法一:max函数。方法二:排序。方法三:利用 all 函数
注意点:
①保留一位小数 round(xxx,1)(测试数据太弱,已经是一位,所以不用也过了)
②max(xxx)聚合后列名会变,有必要时需 as 一下
select max(gpa)
from user_profile
where university='复旦大学'select gpa
from user_profile
where university='复旦大学'
order by gpa desc
limit 1select distinct gpa
from user_profile
where university='复旦大学' and gpa>=all(
select gpa from user_profile where university='复旦大学'
)与 all 相对的是 any
这里 all 实际上也等价于把子查询里 select gpa 换成 select max(gpa)
SQL17:count、avg
男性的个数及平均gpa
select count(*),avg(gpa)
from user_profile
where gender='male'SQL18:group by多个属性
每个学校的每个性别的聚合情况。在 group by 里直接逗号相连即可
select gender,university,count(*),avg(active_days_within_30),avg(question_cnt)
from user_profile
group by university,genderSQL19:聚合的比较用 group by+having,而不能where
sql执行顺序:from->where->group by->having->select->order by
having 里可以用别名,也可以用聚合函数,order by也可,聚合函数或其别名没有区别,是等价的
但是注意where里不能用聚合或其别名,这是取决于执行顺序的,where 的时候还没有分组
因此请一定注意聚合时的执行顺序问题
select university,
round(avg(question_cnt),3) as avg_question_cnt,
round(avg(answer_cnt),3) as avg_answer_cnt
from user_profile
group by university
having avg(question_cnt)<5 or avg(answer_cnt)<20SQL21:两表联查、子查询 或 join on
device_id 是用户表主码,问题表外码。要查的内容在问题表,需要筛选用户表中'浙江大学'的项
法一:子查询
select device_id,question_id,result
from question_practice_detail
where device_id in (select device_id
from user_profile
where university='浙江大学')
order by question_id法二:join,注意命名冲突(注:join 默认表示 inner join)
select u.device_id,question_id,result
from question_practice_detail as q
join user_profile as u
where q.device_id=u.device_id and u.university='浙江大学'
order by question_id需要注意的是完整写法应当是
from a join b on a.id=b.id
省略 on 时,默认按属性名相同的所有属性。但有时候会不好用,养成好习惯,不准省略on!
四种 join 类型:(join 默认 inner join)
①outer join:a有m项,b有n项,则结果有 m*n 项,符合 a.id=b.id 的将会填上 a、b 的其他内容,不符合的将会把缺的全填null
(注:mysql中实际上没有 outer join,可以把 left join 和 right join 的结果 union all 一下)
②inner join:仅保留 a.id=b.id 的笛卡尔乘积项
③left join/right join:以left join为例,保留 a 的 m 项,对 b 内容,如果 a.id=b.id,则补充上b的内容,如果不等,则用 null 补充上 b 的内容
另注:join不会让 a.id、b.id 合成一个 id,二者在结果中皆是存在的
SQL22:技巧:count(distinct xxx)

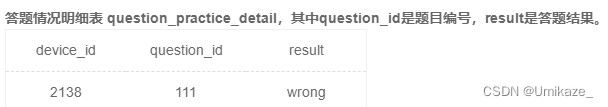
device_id是第一个表主码,第二个表外码,求每个学校的平均答题数
法一:第二个表聚合每个device_id的答题数后,再join求平均
select university,avg(cnt)
from user_profile as u join(
select device_id,count(*) as cnt
from question_practice_detail
group by device_id
)as q
on u.device_id=q.device_id
group by university
order by university法二:技巧:count(distinct xxx) 大法
select university,count(u.device_id)/count(distinct u.device_id)
from user_profile as u join question_practice_detail as q
on u.device_id=q.device_id
group by university
order by universitySQL23:多表join
无需括号,继续join即可,每个表都可以独立地用名字.属性
select university,difficult_level,count(*)/count(distinct u.device_id)
from user_profile as u
join question_practice_detail as qp
on u.device_id=qp.device_id
join question_detail as qd
on qp.question_id=qd.question_id
group by university,difficult_levelSQL25:Intersect、Union、Except
返回山东大学或男性的数据,要求先显示山东大学,再显示男性,且结果不去重。
直接用 where or 无法保证结果有序
请注意 Intersect、Union、Except 交、并、补,可以保证结果有序
请注意 Intersect、Union、Except 会对结果去重,重复的可能来自 a,也可能来自 b 或 a op b
比如 id、name:1、a;2、b;3、a,那么 select name,如果用交并补计算,将会是 a、b
使用 Intersect all、Union all、Except all,不去重,上例中即 a、b、a
select device_id,gender,age,gpa
from user_profile
where university='山东大学'
union all
select device_id,gender,age,gpa
from user_profile
where gender='male'SQL26:select 实值 或 IF + group by
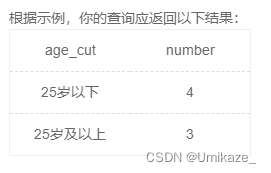
法一:
select '25岁以下' as age_cut,count(*) as number
from user_profile
where age<25 or age is null
union
select '25岁及以上' as age_cut,count(*) as number
from user_profile
where age>=25法二:
select if(age<25 or age is null,'25岁以下','25岁及以上') as age_cut,
count(*) as number
from user_profile
group by age_cutSQL27:Case When Then Else End (和IF一样也可联用 group by)
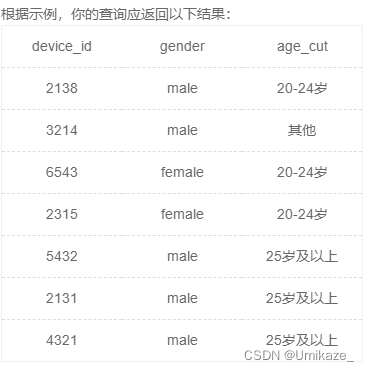
age为null返回其他
注意每个 when then 后没有逗号
select device_id,gender,
case
when age<20 then '20岁以下'
when age<=24 then '20-24岁'
when age>=25 then '25岁及以上'
else '其他'
end as age_cut
from user_profileSQL28:year、month、day函数
2021年8月,每日的数量
select day(date) as day,count(*) as question_cnt
from question_practice_detail as q
where year(date)=2021 and month(date)=8
group by day(date)实际上date也可以用like做,但是这三个函数对date类型明显简单
SQL29:left join+自连接 或 over开窗函数+lead
统计用户某天做题后,下一天还会做题的概率
法一:
由于用户可以一天内反复做题,因此先去重
由于需要 q1 表长度做分母,因此左连接
连接 q2 时,on条件设置了 date等于+1 才能连接,这样不满足+1的就会填null,因此可以count(q2.date)得到符合条件的数量,即分子
count()的数量不包含null,是个很重要的特性
select count(q2.date)/count(*) as avg_ret
from (select distinct device_id,date
from question_practice_detail) as q1
left join (select distinct device_id,date
from question_practice_detail) as q2
on q1.device_id=q2.device_id and q2.date=q1.date+1法二:
开窗函数格式:分析函数() over(partition by xxx order by yyy)
其中,分数函数必需,partition by/order by任选其一或都用
作用是开了一个新列,然后partition by name,按各个name分组,然后组内 order by score,按成绩排序,然后该新列每行的值由分析函数()在组内计算得到
这里请注意组内 order by score,不是新列按score排序后拼上,而是带着空的新列,组里所有整个行已经进行了排序。最后的整个表此时已经是按组内有序的了。而且是按组放在一起输出的。
rank()同排名会为之后累计人数,dense_rank()不会,row_number()是行号,用于排名则是无同排名
例如三个人分数是 10、10、9
select rank() over(order by score desc) 得到 1、1、3
dense_rank() 得到 1、1、2
row_number() 得到 1、2、3
常用的分析函数还有:
percent_rank()、count()等聚合函数、first_value()、last_value、
ratio_to_report(xxx):新列返回的是xxx除以order by属性的结果、
lead(xxx):新列返回 xxx 向上推一行的结果,空则补None、
lag(xxx):同上,xxx向下推一行
此题往上推之前,一是和法一一样,要先注意去重
第二,题中日期可能无序,有序的时候向上推一下才有意义。
select avg(if(date2=date1+1,1,0)) as avg_ret
from (
select device_id,
date as date1,
lead(date) over (partition by device_id order by date) as date2
from (select distinct device_id, date
from question_practice_detail
) as q1
) as q2SQL30:substring_index等字符串函数
格式如图,统计每种性别人数

substring_index(s,分隔符,i),表示第 i 个分隔符左侧的所有内容,i为负时,则是倒数第i个右侧所有内容(i表示第几个,从1开始)
例如 www.baidu.com
substring_index(s,'.',2) 表示 www.baidu
substring_index(s,'.',-2) 表示 baidu.com
当然此题也可用like,但是还是这样简单
select substring_index(profile,',',-1) as gender,
count(*) as number
from user_submit
group by gender补充:
substring_index是索引子串,除此之外还有:
substr(s,begin,len),begin从1开始。
replace(s,s1,s2),将 s 中的模式串 s1 的部分替换为 s2
trim(s1 from s),去掉模式串 s1 后的 s。
SQL33:和29类似,over函数
找出每个学校GPA最低的所有同学
最低的可能不止一个学生,而且还需要他的其他属性,因此不能直接 group by 然后 min
很容易想到<=all子查询,或者<=子查询的min,或者用 in 也有办法解决。也有 left join 然后自连接的方法,类比于 SQL29。
类比于SQL29,自然也可以用开窗函数over,值得练习,代码如下
select device_id,university,gpa
from(select *,
rank() over(partition by university order by gpa) as r
from user_profile
) as u
where r=1
order by universitySQL34
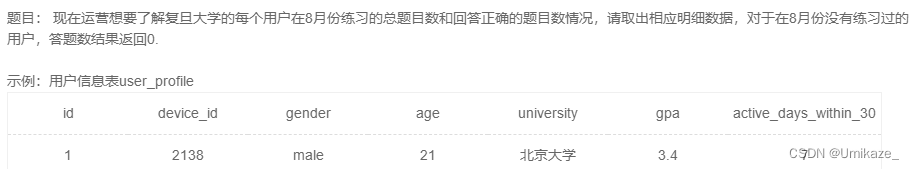
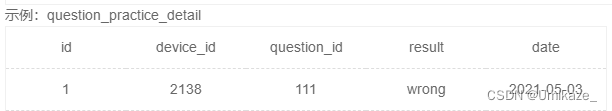
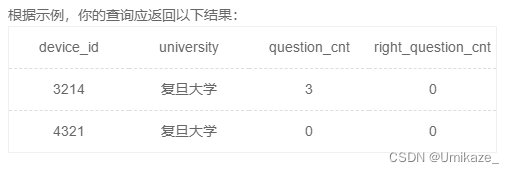
首先注意这个题意,叙述的可能不太清楚。这里练习的总题目数指的是练习了多少条,同一道题反复做每做一次都算一次的。同样地,正确数也是,同一题目反复AC也是每次AC都算。
练习过前面的题之后,其实会发现这题并不难,left join就秒了,但是注意月份=8月应该写在哪
不答题的,我们需要它的答题记录为null,从而统计出0
注意8月没答题,如果你用where筛选,那么这一条就没了,也就没有统计null的机会了
因此请注意要在 on 条件里判断等于 8 月。
select u.device_id,university,
count(result) as question_cnt,
sum(if(result='right',1,0)) as right_question_cnt
from user_profile as u
left join question_practice_detail as q
on u.device_id=q.device_id and month(date)=8
where university='复旦大学'
group by u.device_idSQL35
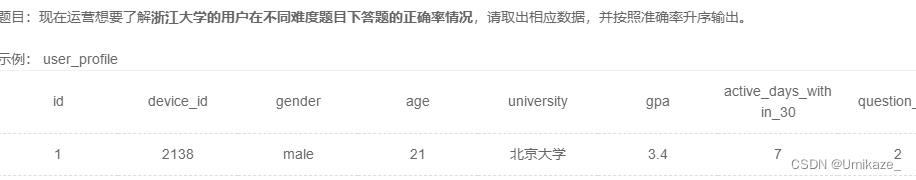
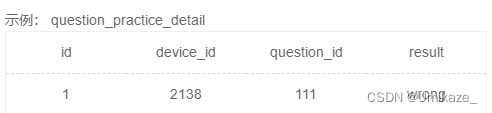
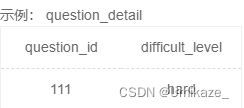
和上一题一个道理,重复做题每次都算独立的一次
于是这个题完全就是白给,难度困难,名不副实,直接看代码就好
select difficult_level,avg(if(result='right',1,0)) as correct_rate
from user_profile as u
join question_practice_detail as qp
on u.device_id=qp.device_id
join question_detail as qd
on qp.question_id=qd.question_id
where university='浙江大学'
group by difficult_level
order by correct_rate![[oeasy]python0028_直接运行_修改py文件执行权限_设置py文件打开方式](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/0b387a7e4585d2722586c8b1e0376447.png)