1.文件IO
最直观的系统调用
1.1打开文件
int open(const char *pathname, int flags, mode_t mode);
功能:打开/创建后打开一个文件
返回值:成功返回文件描述符,失败-1
0 —— 标准输入 1 —— 标准输出 2 —— 标准出错
参数说明:
pathname:要打开的某个文件
flags:打开文件的方式
O_RDONLY:只读
O_WRONLY:只写
O_RDWR:读写
O_APPEND:在文件末尾追加
O_CREAT:文件不存在则创建,文件存在则不管
O_EXCL:和O_CREAT,文件不存在则会创建,文件存在则直接报错
O_TRUNC:文件存在就清空
mode:创建文件时的权限,只有写了O_CREAT的时候才生效,如0666
最后文件的权限会使用 mode和~umask相与
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
// 打开文件,并以只写方式创建文件,权限设置为0644
int fileDescriptor = open("example.txt", O_CREAT | O_WRONLY, 0644);
if (fileDescriptor == -1) {
perror("open");
return 1;
}
// 写入内容到文件
write(fileDescriptor, "Hello, this is a file example!\n", 30);
// 关闭文件
close(fileDescriptor);
return 0;
}
1.2读文件
#include <unistd.h>
ssize_t read(int fd, void *buf, size_t count);
功能:从fd里读取内容存放到buf
返回值:成功返回实际读到的字节数,失败返回-1
参数说明:
fd:已经打开的文件描述符
buf:要存放的缓冲区
count:预计要读的字节数,不能超过buf的大小
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main() {
// 打开文件,并以只读方式打开
int fileDescriptor = open("example.txt", O_RDONLY | O_CREAT , 0644);
if (fileDescriptor == -1) {
perror("open");
return 1;
}
// 读取文件内容到缓冲区
char buffer[256];
ssize_t bytesRead = read(fileDescriptor, buffer, sizeof(buffer) - 1);
if (bytesRead == -1) {
perror("read");
return 1;
}
buffer[bytesRead] = '\0'; // Null-terminate the buffer
printf("Read %ld bytes: %s\n", bytesRead, buffer);
// 关闭文件
close(fileDescriptor);
return 0;
}
一种简单的图片加密方式
1.3写文件
ssize_t write(int fd, const void *buf, size_t count);
功能:往fd里写内容
返回值:成功返回实际写入的字节数,失败返回-1
参数说明:
fd:已经打开的文件描述符
buf:存放的要写入的内容的缓冲区
count:预计要写的字节数,不能超过buf的大小
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
int main() {
int fd_src = open("open.c", O_RDONLY);
if(fd_src < 0){
perror("open1");
return -1;
}
int fd_dest = open("xxx", O_WRONLY | O_CREAT | O_TRUNC, 0666);
if(fd_dest < 0){
perror("open2");
return -1;
}
char buf[64];
int ret;
while(1){
memset(buf, 0, sizeof(buf));
ret = read(fd_src, buf, sizeof(buf));
if(ret <= 0){
perror("read");
return -1;
}
write(fd_dest, buf, ret);
}
// 关闭文件
close(fd_src);
return 0;
}
2.时间函数
#include <time.h>
time_t time(time_t *tloc);
功能:统计现在的系统时间(从1970-1-1 00:00:00到现在所过的秒数)
返回值:成功就返回这个秒数,失败返回-1
参数说明:
tloc:用于存放这个秒数的变量地址
time_t tm;
tm = time(NULL); <==> time(&tm);
struct tm {
int tm_sec; /* Seconds (0-60) */
int tm_min; /* Minutes (0-59) */
int tm_hour; /* Hours (0-23) */
int tm_mday; /* Day of the month (1-31) */
int tm_mon; /* Month (0-11) */
int tm_year; /* Year - 1900 */
int tm_wday; /* Day of the week (0-6, Sunday = 0) */
int tm_yday; /* Day in the year (0-365, 1 Jan = 0) */
int tm_isdst; /* Daylight saving time */
};
struct tm *gmtime(const time_t *timep);
功能:将统计的秒数转换成时间结构体的形式
返回值:成功返回时间结构体的地址,失败返回NULL
参数说明:
timep:time()的返回值
struct tm *localtime(const time_t *timep);
功能:将统计的秒数转换成时间结构体的形式
返回值:成功返回时间结构体的地址,失败返回NULL
参数说明:
timep:time()的返回值
char *asctime(const struct tm *tm);
功能:把系统时间按照固定格式转换成字符串
返回值:成功返回字符串的首地址,失败返回NULL
参数说明:
tm:转换秒数后的时间结构体
char *ctime(const time_t *timep);
功能:把系统时间按照固定格式转换成字符串
返回值:成功返回字符串的首地址,失败返回NULL
参数说明:
timep:直接转换秒数到固定字符串格式
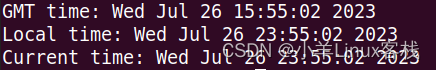
#include <stdio.h>
#include <time.h>
int main() {
// 获取当前系统时间
time_t currentTime;
time(¤tTime);
// 转换为GMT时间
struct tm *timeInfo = gmtime(¤tTime);
// 打印GMT时间
printf("GMT time: %s", asctime(timeInfo));
// 转换为本地时间
struct tm *localTimeInfo = localtime(¤tTime);
// 打印本地时间
printf("Local time: %s", asctime(localTimeInfo));
// 直接打印当前系统时间
printf("Current time: %s", ctime(¤tTime));
return 0;
}
3.文件属性
int stat(const char *pathname, struct stat *statbuf);
功能:获取文件的属性
返回值:成功返回0,失败返回-1
pathname:要查看的文件
statbuf:用于存放信息的结构体地址
struct stat {
dev_t st_dev; /* ID of device containing file */
ino_t st_ino; /* Inode number */
mode_t st_mode; /* File type and mode */
nlink_t st_nlink; /* Number of hard links */
uid_t st_uid; /* User ID of owner */
gid_t st_gid; /* Group ID of owner */
dev_t st_rdev; /* Device ID (if special file) */
off_t st_size; /* Total size, in bytes */
blksize_t st_blksize; /* Block size for filesystem I/O */
blkcnt_t st_blocks; /* Number of 512B blocks allocated */
struct timespec st_atim; /* Time of last access */
struct timespec st_mtim; /* Time of last modification */
struct timespec st_ctim; /* Time of last status change */
#define st_atime st_atim.tv_sec /* Backward compatibility */
#define st_mtime st_mtim.tv_sec
#define st_ctime st_ctim.tv_sec
};
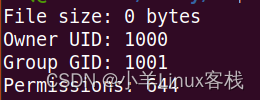
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
int main() {
// 获取文件属性
struct stat fileStat;
if (stat("example.txt", &fileStat) == -1) {
perror("stat");
return 1;
}
// 打印文件属性
printf("File size: %ld bytes\n", fileStat.st_size);
printf("Owner UID: %d\n", fileStat.st_uid);
printf("Group GID: %d\n", fileStat.st_gid);
printf("Permissions: %o\n", fileStat.st_mode & 0777);
return 0;
}
ls-a功能
#include <stdio.h>
#include <dirent.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
DIR *dirp = opendir(".");
if(dirp == NULL){
perror("opendir:");
return -1;
}
struct dirent *dp = NULL;
while(1){
dp = readdir(dirp);
if(dp == NULL){
break;
}else if(dp->d_name[0] != '.'){
printf("%s\t",dp->d_name);
}
}
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
ls-l功能
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <dirent.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <pwd.h>
#include <grp.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <libgen.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
if(argc < 2){
printf("请输入路径%s <src>\n",argv[0]);
return -1;
}
DIR* dirp = opendir(argv[1]);
if(dirp == NULL){
perror("opendir:");
return -1;
}
struct dirent* dp = NULL;
struct stat st;
char pathname[1024];
while((dp = readdir(dirp)) != NULL){
if (strcmp(dp->d_name, ".") == 0 || strcmp(dp->d_name, "..") == 0) {
continue;
}
sprintf(pathname, "%s/%s", argv[1], dp->d_name);
if (lstat(pathname, &st) < 0) {
perror("lstat:");
break;
}
switch(st.st_mode & S_IFMT){
case S_IFSOCK: printf("s");break;
case S_IFLNK: printf("l");break;
case S_IFREG: printf("-");break;
case S_IFBLK: printf("b");break;
case S_IFDIR: printf("d");break;
case S_IFCHR: printf("c");break;
case S_IFIFO: printf("p");break;
}
int n = 8;
while(n > 0){
if(st.st_mode & 1 << n){
switch(n%3){
case 2:printf("r");break;
case 1:printf("w");break;
case 0:printf("x");break;
}
}else{
printf("-");
}
n--;
}
struct passwd *u_uid = getpwuid(st.st_uid);
printf(" %s",u_uid->pw_name);
struct group* g_uid = getgrgid(st.st_gid);
printf(" %s",g_uid->gr_name);
printf(" %8ld",st.st_size);
struct tm *time = localtime(&st.st_mtime);
int month = time->tm_mon+1;
switch(month)
{
case 1: printf(" 一月"); break;
case 2: printf(" 二月"); break;
case 3: printf(" 三月"); break;
case 4: printf(" 四月"); break;
case 5: printf(" 五月"); break;
case 6: printf(" 六月"); break;
case 7: printf(" 七月"); break;
case 8: printf(" 八月"); break;
case 9: printf(" 九月"); break;
case 10: printf(" 十月"); break;
case 11: printf(" 十一月"); break;
case 12: printf(" 十二月"); break;
}
printf(" %2d %d:%02d %s",time->tm_mday,time->tm_hour,time->tm_min,dp->d_name);
printf("\n");
}
closedir(dirp);
return 0;
}
ls-l功能源文件
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <dirent.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <pwd.h>
#include <grp.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <libgen.h>
void printPermissions(mode_t mode) {
printf((S_ISDIR(mode)) ? "d" : "-");
printf((mode & S_IRUSR) ? "r" : "-");
printf((mode & S_IWUSR) ? "w" : "-");
printf((mode & S_IXUSR) ? "x" : "-");
printf((mode & S_IRGRP) ? "r" : "-");
printf((mode & S_IWGRP) ? "w" : "-");
printf((mode & S_IXGRP) ? "x" : "-");
printf((mode & S_IROTH) ? "r" : "-");
printf((mode & S_IWOTH) ? "w" : "-");
printf((mode & S_IXOTH) ? "x" : "-");
}
void printFileInfo(const char *filename) {
struct stat fileStat;
if (stat(filename, &fileStat) < 0) {
perror("stat");
return;
}
// 打印文件权限
printPermissions(fileStat.st_mode);
printf(" ");
// 打印硬链接数
printf("%ld ", fileStat.st_nlink);
// 打印所有者用户名
struct passwd *pw = getpwuid(fileStat.st_uid);
printf("%-2s ", pw->pw_name);
// 打印所有者所属组名
struct group *gr = getgrgid(fileStat.st_gid);
printf("%-2s ", gr->gr_name);
// 打印文件大小
printf("%5ld ", fileStat.st_size);
// 打印最后修改时间
struct tm *timeinfo;
char timeString[80];
timeinfo = localtime(&fileStat.st_mtime);
strftime(timeString, sizeof(timeString), "%Y年%m月%d日 %H:%M", timeinfo);
printf("%s ", timeString);
// 打印文件名
printf("%s\n", basename((char*)filename));
}
int main() {
char cwd[1024];
if (getcwd(cwd, sizeof(cwd)) == NULL) {
perror("getcwd");
return 1;
}
DIR *dir = opendir(cwd);
if (!dir) {
perror("opendir");
return 1;
}
int blocksize = 0;
struct dirent *entry;
while ((entry = readdir(dir)) != NULL) {
// 忽略以'.'开头的文件(隐藏文件)
if (entry->d_name[0] == '.')
continue;
char path[PATH_MAX];
snprintf(path, sizeof(path), "%s/%s", cwd, entry->d_name);
struct stat fileStat;
if (stat(path, &fileStat) < 0) {
perror("stat");
continue;
}
blocksize += fileStat.st_blocks;
}
closedir(dir);
// 打印总用量(总块数)
printf("总用量:%d\n", blocksize / 2);
dir = opendir(cwd);
if (!dir) {
perror("opendir");
return 1;
}
while ((entry = readdir(dir)) != NULL) {
if (entry->d_name[0] == '.')
continue;
char path[PATH_MAX];
snprintf(path, sizeof(path), "%s/%s", cwd, entry->d_name);
printFileInfo(path);
}
closedir(dir);
return 0;
}
4.库的制作
4.1静态库
①.生成二进制文件
gcc -c linkstack.c -o linkstack.o
②.制作静态库文件(把.o文件转换成.a文件)
ar crs libmykun.a hello.o //生成libmykun.a这个静态库文件
③.编译时链接
gcc linkstack_main.c -L. -llinkstack //-L表示指定库路径,-l表示指定具体的库

4.2动态库
①.生成地址无关二进制文件
gcc -fPIC -c linkstack.c
②.制作动态库文件
gcc -shared -o liblinkstack.so linkstack.o

③.编译时链接
gcc linkstack_main.c -L. -llinkstack //-L表示指定库路径,-l表示指定具体的库

注:动态库程序运行时需要去默认路径加载库
1.把动态库文件拷贝到/lib或者/usr/lib目录下
或
2.配置动态库搜索文件
2.1、sudo vi /etc/ld.so.conf.d/my.conf(新建一个my.conf)将你的.so文件路径复制进去进行
2.2、把动态库路径存放进文件(再次刷新)
sudo ldconfig /etc/ld.so.conf.d/my.conf