C++ 11;
C++ 14;
C++ 17;
C++ 20;
1、为什么要多线程
任务分解
耗时的操作,任务分解,实时响应
数据分解
充分利用多核CPU处理数据
数据流分解
读写分离,解耦合设计
2、相关代码
1、初步: join(),detach()
#include <thread>
#include <iostream>
// Linux -lpthread //linux系统
using namespace std;
bool is_exit = false;//子线程是否退出
void ThreadMain()
{
cout << "begin sub thread main" << this_thread::get_id() << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{//等待10秒
if (is_exit)
{
break;
}
printf("thread:%d\n",i);
//this_thread::sleep_for(10ms);//1000ms
this_thread::sleep_for(chrono::seconds(1));// 两种方法都可以
}
cout << "end sub thread main" << this_thread::get_id() << endl;
}
int main()
{
cout << "main thread ID" << this_thread::get_id() << endl;//获取线程ID
{
thread th(ThreadMain);
this_thread::sleep_for(chrono::seconds(5));// 两种方法都可以
is_exit = true;
cout << "主线程阻塞,等待子线程退出" << endl;
th.join();//阻塞
cout << "子线程退出" << endl;
}
//{
// thread th(ThreadMain);
// th.detach();//子线程与主线程分离,守护线程;这里需要注意坑
// //坑:主线程退出后,子线程不一定退出,如果这时候子线程访问退出的主线程变量,则会异常
//}
getchar();
return 0;
}
2、实体传参代码:
#include <thread>
#include <iostream>
// Linux -lpthread //linux系统
using namespace std;
class Para
{
public:
Para() { cout << "Crate Para" << endl; }
Para(const Para& p) {//重定义拷贝构造函数,覆盖原始的拷贝构造函数
cout << "Copy Para" << endl;
this->name = p.name;
}
~Para() { cout << "Drop Para" << endl; }
string name;
};
void ThreadMain(int p1,float p2,string str, Para p4)
{
this_thread::sleep_for(100ms);
cout << "Thread main:" <<p1<<" "<<p2<<" "<< str.c_str()<<" "<<p4.name.c_str()<< endl;
}
int main()
{
cout << "main thread ID" << this_thread::get_id() << endl;//获取线程ID
thread th;
{
float f1 = 12.1f;
Para p;
p.name = "Test para class";
//所有参数做复制
th = thread(ThreadMain, 101, f1, "test string param",p);
}
th.join();
getchar();
return 0;
}
实体传参,创建一次,复制了两次,销毁了3次

3、指针、引用传参
#include <thread>
#include <iostream>
// Linux -lpthread //linux系统
using namespace std;
class Para
{
public:
Para() { cout << "Crate Para" << endl; }
Para(const Para& p) {//重定义拷贝构造函数,覆盖原始的拷贝构造函数
cout << "Copy Para" << endl;
this->name = p.name;
}
~Para() { cout << "Drop Para" << endl; }
string name;
};
void ThreadMain(int p1,float p2,string str, Para p4)
{//普通传参
this_thread::sleep_for(100ms);
cout << "Thread main:" <<p1<<" "<<p2<<" "<< str.c_str()<<" "<<p4.name.c_str()<< endl;
}
void ThreadMainPtr(Para*p)
{//传递指针
this_thread::sleep_for(100ms);
cout << "ThreadMain Prt name=" << p->name.c_str() << endl;
}
void ThreadMainRef(Para&p)
{//传递引用
this_thread::sleep_for(100ms);
cout << "ThreadMain Ref name=" << p.name.c_str() << endl;
}
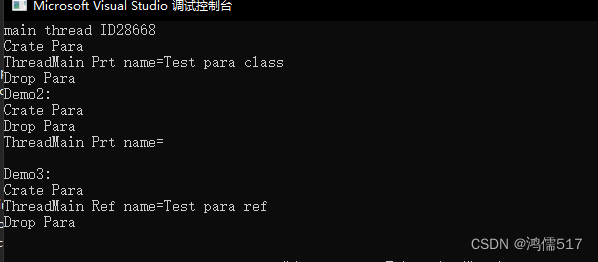
int main()
{
cout << "main thread ID" << this_thread::get_id() << endl;//获取线程ID
//正常情况
{
Para p;//调用初始化
p.name = "Test para class";
thread th(ThreadMainPtr,&p);
th.join();
}//调用销毁
printf("Demo2:\n");
{//异常情况演示,主程序结束了,参数p也销毁了,所以子线程中访问不到
Para p;
p.name = "Test para detach";
thread th(ThreadMainPtr, &p);
th.detach();//主线程与子线程分离,守护线程
}
getchar();
printf("Demo3:\n");
{//传递引用
Para p;
p.name = "Test para ref";
thread th(ThreadMainRef, ref(p));//传递引用需要在外面增加ref()标记引用类型,否则编译会报错
th.join();
}
getchar();
return 0;
}
指针、引用传参,创建一次,复制了两次,销毁了3次
4、成员函数作为子线程传入
//演示成员函数进行传参
#include <thread>
#include<iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class MyThread
{
public:
//入口线程函数
void Main()
{
cout << "MyThread Main:" << name.c_str() << " : "<< age << endl;
}
string name="";
int age = 100;
};
class XThread
{
public:
virtual void Start() //虚函数,可以在子函数中重载它
{
is_exit_ = false;//不退出
th_ = std::thread(&XThread::Main,this);//创建线程
}
virtual void Wait()
{
if (th_.joinable())
{
th_.join();
}
}
virtual void Stop()
{
is_exit_ = true;//退出
Wait();
}
bool is_exit() { return is_exit_; }//谷歌的编码标准
private:
virtual void Main() = 0;//定义纯虚函数,纯虚函数在子函数中必须实现,否则报错
std::thread th_;
bool is_exit_ = false;//是否退出线程循环
};
class TestXThread :public XThread//继承
{
public:
void Main() override//增加 override 检查重写父类的函数
{
cout << "Begin:TestThread Main ,name:"<<name << endl;
while (!is_exit())
{
this_thread::sleep_for(100ms);
cout << "." << flush;
}
cout << "TestThread Main end!" << endl;
}
string name;
};
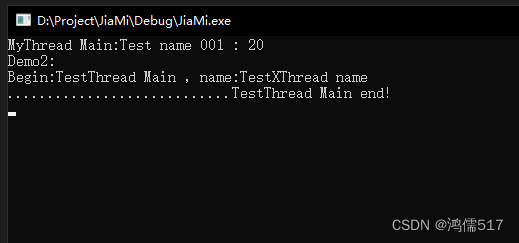
int main()
{
{
MyThread myth;
myth.name = "Test name 001";
myth.age = 20;
thread th(&MyThread::Main, &myth);//以成员函数方式
th.join();
}
printf("Demo2:\n");
TestXThread testth;
testth.name = "TestXThread name";
testth.Start();
//getchar();
this_thread::sleep_for(3s);
testth.Stop();//
//testth.Wait();//
getchar();
return 0;
}
5、Lambda匿名(临时)函数多线程
#include <thread>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class TestLambda
{
public:
void Start()
{
thread th([this]() {cout << "name=" << name << endl; });//成员的匿名线程函数
th.join();
}
string name = "test lambda in Class";
};
int main()
{
thread th([](int i) {cout << "test lambda" << i << endl; }, 123);
th.join();
TestLambda test;
test.Start();
return 0;
}

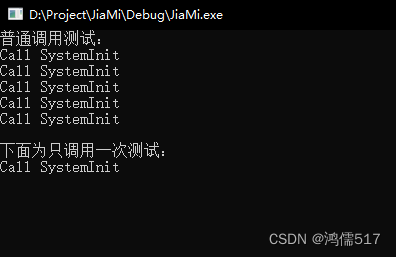
6、call_once多线程调用函数,但是函数只进入一次
#include <thread>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <mutex>
using namespace std;
void SystemInit()
{
cout << "Call SystemInit" << endl;
}
void SystemInitOne()
{//C++ 11
static std::once_flag flag;
std::call_once(flag,SystemInit);
}
int main()
{
printf("普通调用测试:\n");
SystemInit();
SystemInit();
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
thread th(SystemInit);
th.detach();
}
getchar();
printf("下面为只调用一次测试:\n");
SystemInitOne();
SystemInitOne();
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
thread th(SystemInitOne);
th.detach();
}
getchar();
return 0;
}