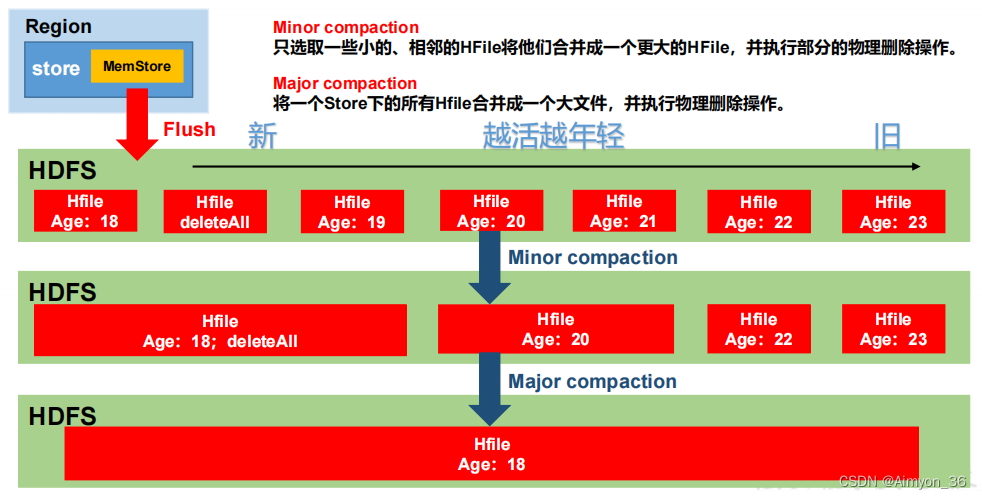
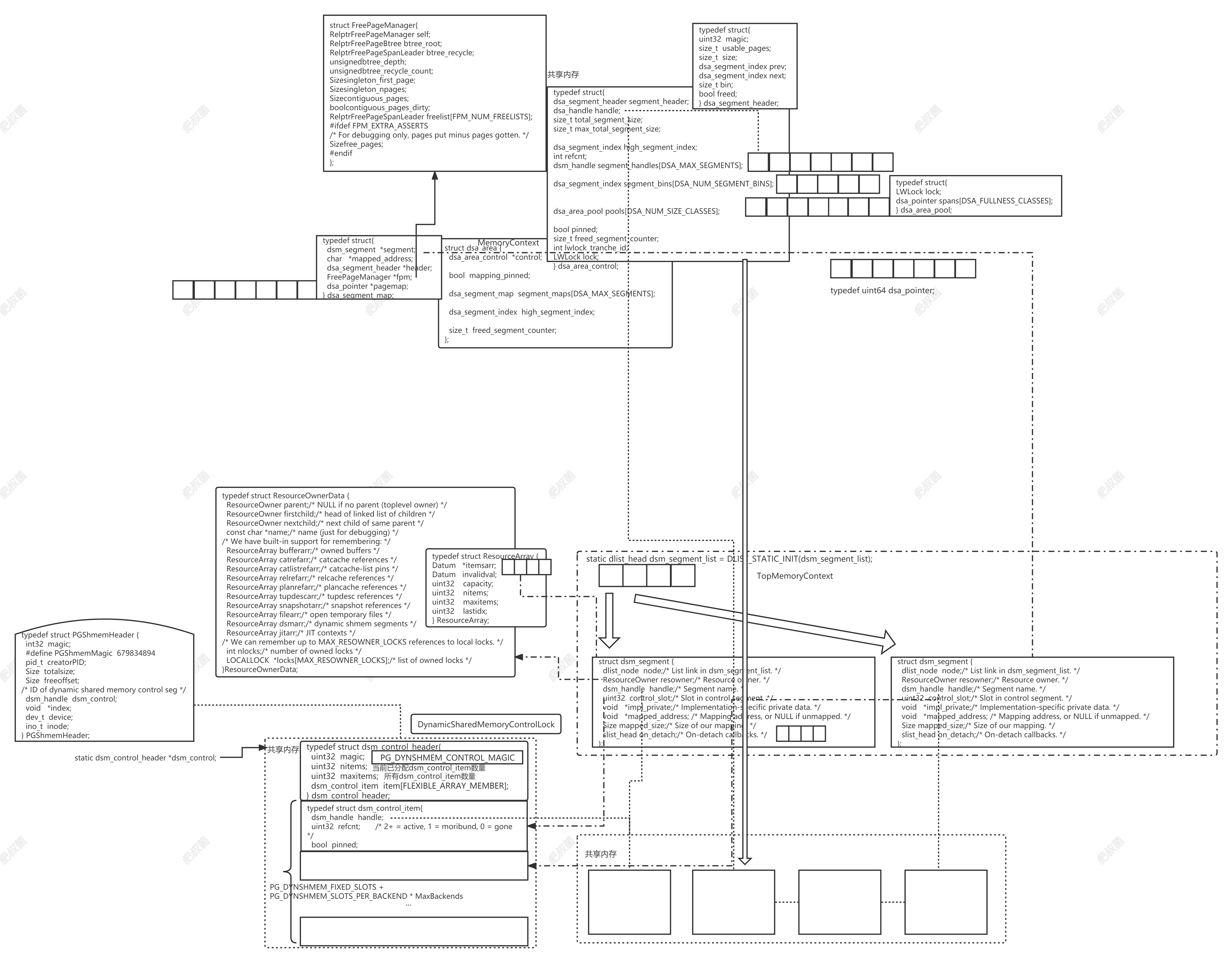
dsm.c提供的功能允许创建后端进程间共享的共享内存段。DSA利用多个DSM段提供共享内存heap;DSA可以利用已经存在的共享内存(DSM段)也可以创建额外的DSM段。和系统heap使用指针不同的是,DSA提供伪指针,可以转换为backend-local指针,但是该伪指针可以在后端进程之间共享,可以用于构建共享数据结构。
每个DSA管理多个DSM段,可以向其中添加新段,不需要时detach它们。每个段包含多个4KB页,一个free page manager(用于跟踪空闲页的连续运行)以及一个页面映射page map(用于跟踪分配给每个页面的对象的来源)。分配超过8KB的空间请求通过通过选择一个段并在其空闲页管理器中查找连续的空闲页来处理。较小的分配请求使用选定大小的对象池来处理。每个池由多个16页(64KB)超级块组成,以与大型对象相同的方式分配。大型对象和新超级块的分配由单个LWLock进行串行化,但从预先存在的超级块分配小型对象时,每个池使用一个LWLock。目前,每个大小类有一个池,因此有一个锁。提高并发性的每核心池和减少由此产生的碎片的策略是未来研究的领域。每个超级块都用一个“span”来管理,它跟踪超级块的空闲列表。自由请求是通过查看页面映射来处理的,以查找分配地址的跨度,这样小对象就可以返回到适当的自由列表中,大对象页面可以直接返回到自由页面映射中。在分配时,用于选择段和超级块的简单启发式方法试图鼓励集中占用的内存,从而增加了整个超级块变为空并返回到空闲页管理器的可能性,而整个段变为空并且返回到操作系统的可能性。Each DSA area manages a set of DSM segments, adding new segments as required and detaching them when they are no longer needed. Each segment contains a number of 4KB pages, a free page manager for tracking consecutive runs of free pages, and a page map for tracking the source of objects allocated on each page. Allocation requests above 8KB are handled by choosing a segment and finding consecutive free pages in its free page manager. Allocation requests for smaller sizes are handled using pools of objects of a selection of sizes. Each pool consists of a number of 16 page (64KB) superblocks allocated in the same way as large objects. Allocation of large objects and new superblocks is serialized by a single LWLock, but allocation of small objects from pre-existing superblocks uses one LWLock per pool. Currently there is one pool, and therefore one lock, per size class. Per-core pools to increase concurrency and strategies for reducing the resulting fragmentation are areas for future research. Each superblock is managed with a ‘span’, which tracks the superblock’s freelist. Free requests are handled by looking in the page map to find which span an address was allocated from, so that small objects can be returned to the appropriate free list, and large object pages can be returned directly to the free page map. When allocating, simple heuristics for selecting segments and superblocks try to encourage occupied memory to be concentrated, increasing the likelihood that whole superblocks can become empty and be returned to the free page manager, and whole segments can become empty and be returned to the operating system.
dsa_create/dsa_create_in_place
dsa_create函数在新的一个DSM段中创建一个新的shared area。dsa_create_in_place函数在已经存在的共享内存空间上创建一个新的shared area。
dsa_area *dsa_create(int tranche_id){
dsm_segment *segment = dsm_create(DSA_INITIAL_SEGMENT_SIZE, 0); /* Create the DSM segment that will hold the shared control object and the first segment of usable space. */
dsm_pin_segment(segment); /* All segments backing this area are pinned, so that DSA can explicitly control their lifetime (otherwise a newly created segment belonging to this area might be freed when the only backend that happens to have it mapped in ends, corrupting the area). */
/* Create a new DSA area with the control object in this segment. */
dsa_area *area = create_internal(dsm_segment_address(segment), DSA_INITIAL_SEGMENT_SIZE, tranche_id, dsm_segment_handle(segment), segment);
/* Clean up when the control segment detaches. */
on_dsm_detach(segment, &dsa_on_dsm_detach_release_in_place, PointerGetDatum(dsm_segment_address(segment)));
return area;
}
dsa_area *dsa_create_in_place(void *place, size_t size,int tranche_id, dsm_segment *segment){
dsa_area *area = create_internal(place, size, tranche_id, DSM_HANDLE_INVALID, NULL);
/* Clean up when the control segment detaches, if a containing DSM segment was provided. */
if (segment != NULL)
on_dsm_detach(segment, &dsa_on_dsm_detach_release_in_place, PointerGetDatum(place));
return area;
}
dsa_attach/dsa_attach_in_place
dsa_allocate dsa_free