React 基础巩固(三十二)——Redux的三大原则
一、Redux的三大原则
-
单一数据源
- 整个应用程序的state被存储在一颗object tree 中,并且这个object tree 只存储在一个store中;
- Redux并没有强制让我们不能创建多个Store,但是那样做不利于数据维护;
- 单一的数据源可以让整个应用程序的state变得方便维护、追踪、修改;
-
State是只读的
-
唯一修改State的方法一定是触发action,不要试图在其他地方通过任何的方式来修改State;
-
这样就确保了View或网络请求都不能直接修改state,它们只能通过action来描述自己想要如何修改state;
-
这样可以保证所有的修改都被集中化处理,并且按照严格的顺序来执行,所以不需要担心reace condition(竞态)的问题;
-
-
使用纯函数来执行修改
- 通过reducer将旧state和actions联系在一起,并且返回一个新的state;
- 随着应用程序的复杂度增加,我们可以将reducer拆分成多个小的reducers,分别操作不同state tree 的一部分;
- 但是所有的reducer都应该是纯函数,不能产生任何的副作用;
二、Redux的使用流程
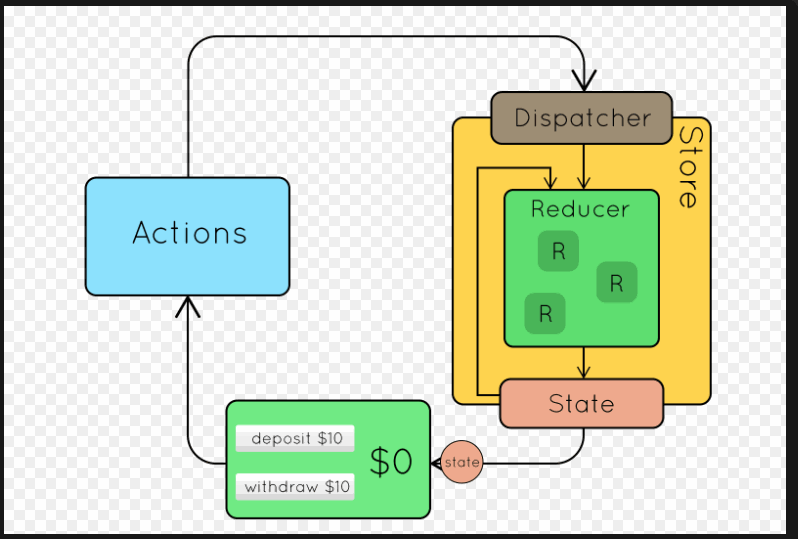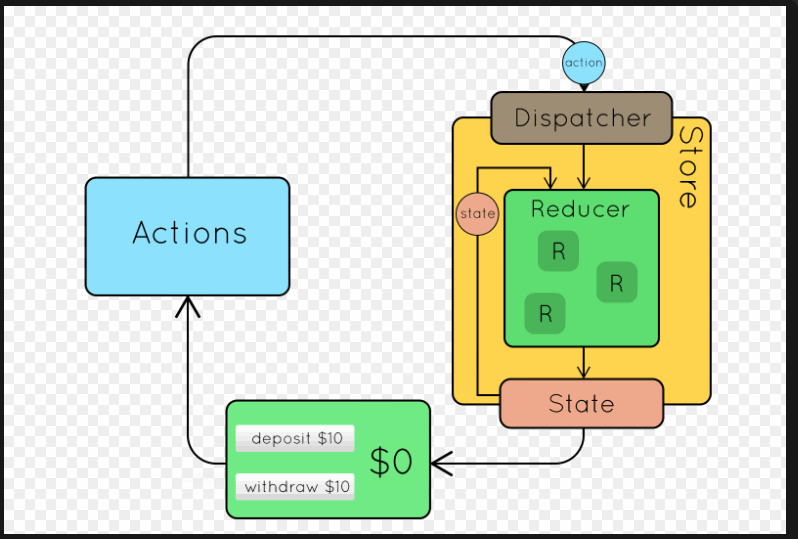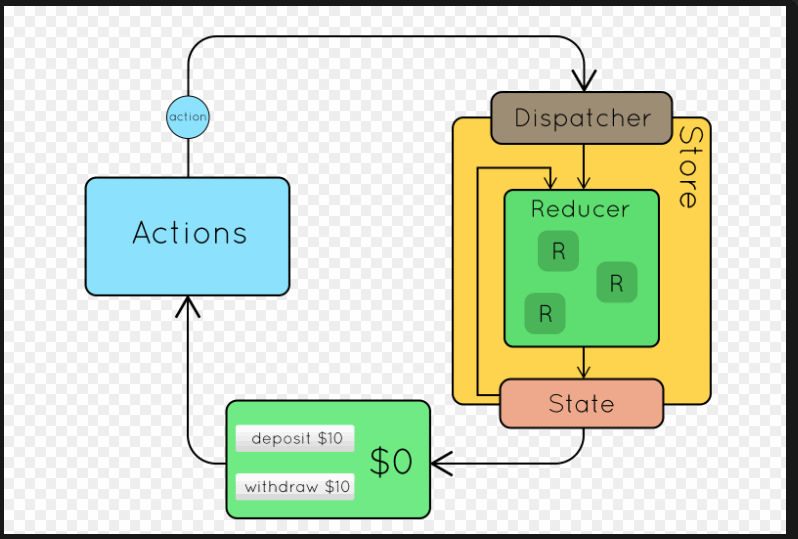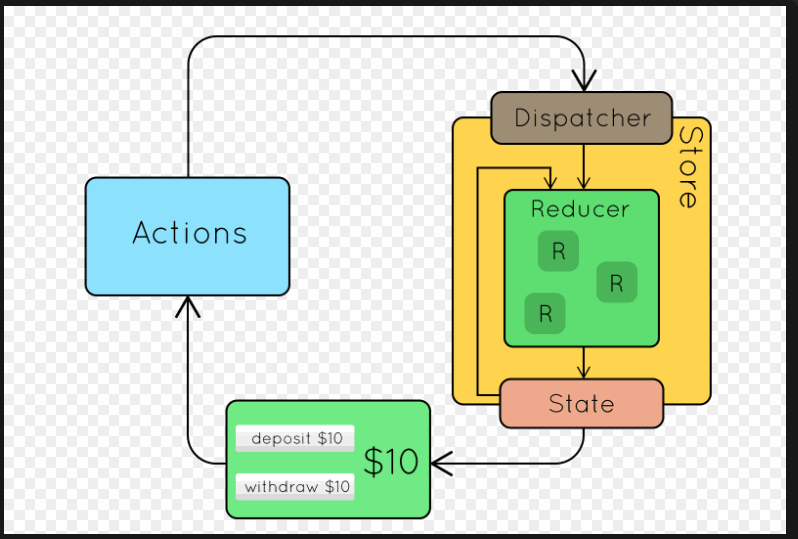
三、Redux的基本使用(计数器小案例)
-
构建react项目
# 创建新的react项目 create-react-app redux-learn # 创建成功后cd进入文件夹,随后安装redux npm install redux -
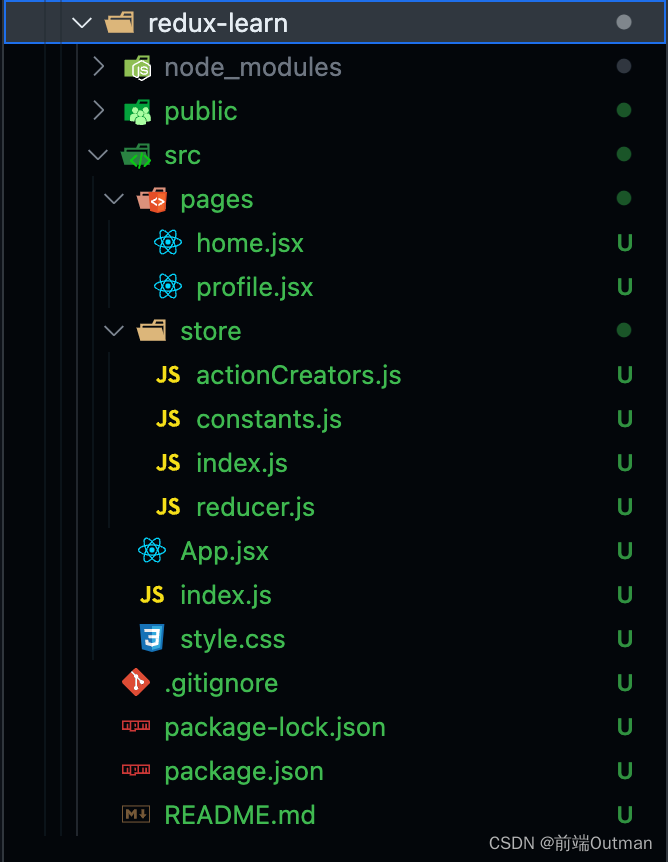
删除暂时无关文件,构建store相关文件,并引用store至所需页面中
- 目录
-
store/constants.js
export const ADD_NUMBER = "add_number"; export const SUB_NUMBER = "sub_number"; -
store/reducer.js
import * as actionTypes from "./constants"; const initialState = { counter: 111, }; function reducer(state = initialState, action) { switch (action.type) { case actionTypes.ADD_NUMBER: return { ...state, counter: state.counter + action.num }; case actionTypes.SUB_NUMBER: return { ...state, counter: state.counter - action.num }; default: return state; } } export default reducer; -
store/actionCreators.js
import * as actionTypes from "./constants"; export const addNumberAction = (num) => ({ type: actionTypes.ADD_NUMBER, num, }); export const subNumberAction = (num) => ({ type: actionTypes.SUB_NUMBER, num, }); -
store/index.js
import { createStore } from "redux"; import reducer from "./reducer"; const store = createStore(reducer); export default store; -
pages/home.jsx
import React, { PureComponent } from "react"; import store from "../store"; import { addNumberAction } from "../store/actionCreators"; export class home extends PureComponent { constructor() { super(); this.state = { counter: store.getState().counter, }; } componentDidMount() { store.subscribe(() => { const state = store.getState(); this.setState({ counter: state.counter, }); }); } addNumber(num) { store.dispatch(addNumberAction(num)); } render() { const { counter } = this.state; return ( <div> home counter:{counter} <div> <button onClick={(e) => this.addNumber(1)}>+1</button> <button onClick={(e) => this.addNumber(5)}>+5</button> <button onClick={(e) => this.addNumber(8)}>+8</button> </div> </div> ); } } export default home; -
pages/profile.jsx
import React, { PureComponent } from "react"; import store from "../store"; import { subNumberAction } from "../store/actionCreators"; export class profile extends PureComponent { constructor() { super(); this.state = { counter: store.getState().counter, }; } componentDidMount() { store.subscribe(() => { const state = store.getState(); this.setState({ counter: state.counter, }); }); } subNumber(num) { store.dispatch(subNumberAction(num)); } render() { const { counter } = this.state; return ( <div> profile counter:{counter} <div> <button onClick={(e) => this.subNumber(1)}>-1</button> <button onClick={(e) => this.subNumber(5)}>-5</button> <button onClick={(e) => this.subNumber(8)}>-8</button> </div> </div> ); } } export default profile; -
App.jsx
import React, { PureComponent } from "react"; import Home from "./pages/home"; import Profile from "./pages/profile"; import "./style.css"; import store from "./store"; export class App extends PureComponent { constructor() { super(); this.state = { counter: store.getState().counter, }; } componentDidMount() { store.subscribe(() => { const state = store.getState(); this.setState({ counter: state.counter, }); }); } render() { const { counter } = this.state; return ( <div> <h2>App Counter: {counter}</h2> <div className="pages"> <Home /> <Profile /> </div> </div> ); } } export default App;
- 运行结果

至此,代码仍较为复杂,代码将在React 基础巩固(三十三)中得到优化