概述
二叉树的遍历是指按照某条搜索路径访问二叉树中的每个结点,使得每个结点均被访问一次,而且仅被访问一次。二叉树的遍历方式主要有:先序遍历、中序遍历、后序遍历、层次遍历。先序、中序、后序其实值得是父节点被访问的次序。若在遍历过程中,父节点均先于它的子节点被访问,就是先序遍历;若父节点被访问的次序在它的子节点被访问次序之间,就是中序遍历;若访问完左右孩子之后在访问父节点,就是后序遍历。无论是先序遍历、中序遍历还是后序遍历,左右孩子节点的相对访问次序是不会发生变化的,总是先访问左孩子,在访问右孩子节点。而层次遍历,就是按照从上到下,从左到右的顺序访问二叉树的每一个节点。

在介绍遍历算法之前,先定义一个二叉树的结构体,代码如下:
struct node{
int elem;//数据域
node *left;//左孩子节点指针
node *right;//有孩子指针节点
};
先序遍历
递归
使用递归,很容易写出遍历算法。代码如下:
void pre_order_r(const node* root, int(*visit)(const node*)){
//先序遍历,递归,root根结点,visit访问数据元素的函数指针
if(root == nullptr) return;
visit(root);//可以把这个理解成cout << root->elem
pre_order_r(root->left, visit);
pre_order_r(root->right, visit);
}
迭代
第一种迭代版本
代码如下:
void pre_order1(const node* root, int(*visit)(const node*)){
//先序遍历,非递归
const node *p;
stack<const node*>st;//辅助栈
p = root;
if(p != nullptr) st.push(p);//若根结点不为空,则令根结点进栈
while(!st.empty()){
p = st.top();
st.pop();
visit(p);
if(p->right != nullptr) st.push(p->right);
if(p->left != nullptr) st.push(p->left);
}
}
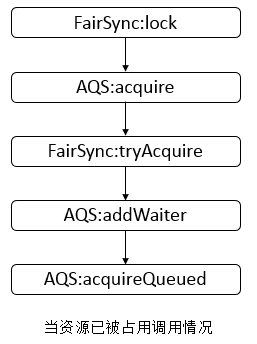
下面用一个实例来了解该迭代如何工作。

注:格子上面的元素表示已经被弹出并访问过。
这个二叉树的遍历过程如下:
- 初始化一个空栈和指针p指向根结点。
- 根结点不为空,入栈,此时将a入栈。
- 判断栈是否为空,不为空,循环开始,弹出并访问栈顶元素,此时栈顶元素为a。
- 如果a有右孩子,则将其右孩子节点入栈;如果有左孩子节点,则将左孩子节点入栈,此时栈中有b,c两个元素。
- 重复第三步骤,直至栈为空。遍历结束。
第2种迭代方式
来看一个规模更大,更具有一般性的二叉树:

这个二叉树的先序遍历序列是:abdheicfjkgl,也就是遵守下图所示的顺序:

进一步,我们把二叉树抽象成下图这样:,

a到e是二叉树的左侧链上的节点,i到f分别是a到d的有孩子。不难发现,二叉树的先序遍历就是先自上而下访问左子树上的节点,在自下而上访问左子树上的节点的右子树。我们第2中迭代就是根据这个思路来设计的。代码如下:
void pre_order2(const node* root, int(*visit)(const node*)){
const node *p;
stack<const node*> st;
p = root;
if(p != nullptr) st.push(p);
while( ! st.empty() ){
p = st.top();
st.pop();
while(p != nullptr){//从当前节点出发,逐批访问
visit(p);//访问当前节点
if(p->right != nullptr) st.push(p->right);//不为空的右孩子入栈
p = p->left;//沿左子树深入一层
}
}
}
中序遍历
递归
与先序遍历类似,不做过多解释。代码如下:
void in_order_r(const node* root, int(*visit)(const node*)){
//中序遍历,递归
if(root == nullptr) return;
in_order_r(root->left, visit);
visit(root);
in_order_r(root->right, visit);
}
迭代
对照先先序遍历第2种迭代版本,在宏观上,将中序遍历的顺序抽象为,先访问二叉树的左子树的最底层的节点,再访问该节点的右子树节点,再访问该节点的父节点,再访问该节点的父节点的右子树,直到全部节点都被访问结束。如下图:

按照这个思路可以实现中序遍历算法如下:
void in_order(const node* root, int(*visit)(const node*)){
//中序遍历,非递归
const node *p;
stack<const node *> st;
p= root;
while(!st.empty() ) {
if (p != nullptr){
st.push(p);
p = p->left;
}
else {
p = st.top();
st.pop();
visit(p);
p = p->right;
}
}
}
后序遍历
递归
与前面两个一样,直接上代码:
void post_order_r(const node* root, int(*visit)(const node*)){
//后序遍历,递归
if(root == nullptr) return;
post_order_r(root->left, visit);
post_order_r(root->right, visit);
visit(root);
}
迭代
要想使用迭代的方法实现后序遍历,则有一定难度,因为左右子树的递归遍历均严格不属于尾递归。但是我们可以套用前面的思想和方法,思考一下,后序遍历中,首先访问的是哪个节点?答案是二叉树的最高最左侧的叶子节点,这个最高最左测的叶子节点可能是左孩子节点,也可能是右孩子节点。

整个后序遍历可以分解为若干个片段,每个片段,分别起始于通路上的一个节点,并包括三步骤:访问当前节点,遍历以其右兄弟为根的子树,以及向上回溯到其父节点并转入下一个片段。基于这个理解,我们的代码如下:
void post_order(const node* root, int(*visit)(const node*)){
//后序遍历,非递归
const node *p, *q;//p正在访问的节点,q刚刚访问过的节点
stack<const node *> st;
p = root;
do {
while(p != nullptr){//往左走下去
st.push(p);
p = p->left;
}
q = nullptr;
while( !st.empty() ){
p = st.top();
st.pop();
if(p -> right == q) {//右孩子不存在或者已被访问过
visit(p);
q = p;//保存刚访问的节点
}
else{
st.push(p);//当前节点不能访问
p = p->right;//先处理右子树
break;
}
}
}while(! st.empty() );
}
我们对先序遍历的第一个实例进行后序遍历来了解这个迭代时如何工作的。

这个二叉树的遍历过程如下:
- 初始化一个空栈和指针p(表示正在访问的节点)q(刚刚访问过的节点)
- 从当前节点往左走,直到走到最后。
- 判断当前节点是否能被访问(即判断当前节点是否拥有右子树或是否已被访问),若当前节点没有右子树或者已被访问,则访问当前节点;反之将p指向当前节点的右子树,并返回第2步骤。
- 直至栈为空。遍历结束。
层次遍历
再开头对层次遍历的介绍中,我们说过层次遍历严格按照自上而下,自左向右的顺序访问二叉树的每一个节点。所以这里面我们需要队列作为辅助,代码如下:
void level_order(const node *root, int(*visit)(const node *)){
//层次遍历(BFS)
const node *p;
queue<const node *> qu;
p = root;
if(p != nullptr) qu.push(p);
while(! qu.empty() ) {
p = qu.front();
qu.pop();
visit(p);
if(p->left != nullptr) qu.push(p->left);
if(p->right != nullptr) qu.push(p->right);
}
}
完整代码
#include "iostream"
#include "queue"
#include "stack"
using namespace std;
struct node{
int elem;
node *left;
node *right;
};
void pre_order_r(const node* root, int(*visit)(const node*)){
//先序遍历,递归,root根结点,visit访问数据元素的函数指针
if(root == nullptr) return;
visit(root);
pre_order_r(root->left, visit);
pre_order_r(root->right, visit);
}
void in_order_r(const node* root, int(*visit)(const node*)){
//中序遍历,递归
if(root == nullptr) return;
in_order_r(root->left, visit);
visit(root);
in_order_r(root->right, visit);
}
void post_order_r(const node* root, int(*visit)(const node*)){
//后序遍历,递归
if(root == nullptr) return;
post_order_r(root->left, visit);
post_order_r(root->right, visit);
visit(root);
}
void pre_order1(const node* root, int(*visit)(const node*)){
//先序遍历,非递归
const node *p;
stack<const node*>st;
p = root;
if(p != nullptr) st.push(p);
while(!st.empty()){
p = st.top();
st.pop();
visit(p);
if(p->right != nullptr) st.push(p->right);
if(p->left != nullptr) st.push(p->left);
}
}
void pre_order2(const node* root, int(*visit)(const node*)){
const node *p;
stack<const node*> st;
p = root;
if(p != nullptr) st.push(p);
while( ! st.empty() ){
p = st.top();
st.pop();
while(p != nullptr){
visit(p);
if(p->right != nullptr) st.push(p->right);
p = p->left;
}
}
}
void in_order(const node* root, int(*visit)(const node*)){
//中序遍历,非递归
const node *p;
stack<const node *> st;
p= root;
while(!st.empty() ) {
if (p != nullptr){
st.push(p);
p = p->left;
}
else {
p = st.top();
st.pop();
visit(p);
p = p->right;
}
}
}
void post_order(const node* root, int(*visit)(const node*)){
//后序遍历,非递归
const node *p, *q;//p正在访问的节点,q刚刚访问过的节点
stack<const node *> st;
p = root;
do {
while(p != nullptr){//往左走下去
st.push(p);
p = p->left;
}
q = nullptr;
while( !st.empty() ){
p = st.top();
st.pop();
if(p -> right == q) {//右孩子不存在或者已被访问过
visit(p);
q = p;//保存刚访问的节点
}
else{
st.push(p);//当前节点不能访问
p = p->right;//先处理右子树
break;
}
}
}while(! st.empty() );
}
void level_order(const node *root, int(*visit)(const node *)){
//层次遍历(BFS)
const node *p;
queue<const node *> qu;
p = root;
if(p != nullptr) qu.push(p);
while(! qu.empty() ) {
p = qu.front();
qu.pop();
visit(p);
if(p->left != nullptr) qu.push(p->left);
if(p->right != nullptr) qu.push(p->right);
}
}