概述
延迟分配delay allocation是ext4非常重要的特性,启用该特性write系统将用户空间buffer写入内存page cache中即返回,此时也不会真正进行磁盘block分配,而是延迟到磁盘回写时(比如dirty ratio达到一定值,定时刷新,主动sync等) 才开始映射磁盘block(map block)进行块分配,好处就是可以将连续的块进行合并merge,结合ext4的mballoc多块分配机制,可以一次性分配多个物理block,降低cpu使用率和碎片化问题。本文将根据内核源码分析ext4的delay allocation机制,脏页达到阈值后台writeback场景分析,其调用栈:
remote Thread 1 In: ext4_writepages Line: 2634 PC: 0xffffffff8155cc91
#0 ext4_writepages (mapping=0xffff8880062459d0, wbc=0xffff888000a27a60) at fs/ext4/inode.c:2634
#1 0xffffffff8134255a in do_writepages (mapping=0xffff8880062459d0, wbc=0xffff888000a27a60) at mm/page-writeback.c:2352
#2 0xffffffff814697c5 in __writeback_single_inode (inode=0xffff888006245858, wbc=0xffff888000a27a60) at fs/fs-writeback.c:1461
#3 0xffffffff8146a06c in writeback_sb_inodes (sb=<optimized out>, wb=0xffff88800442e060, work=0xffff888000a27d50) at fs/fs-writeback.c:1721
#4 0xffffffff8146a4ff in __writeback_inodes_wb (wb=0xffff88800442e060, work=0xffff888000a27d50) at fs/fs-writeback.c:1790
#5 0xffffffff8146a9d9 in wb_writeback (wb=0xffff88800442e060, work=0xffff888000a27d50) at fs/fs-writeback.c:1896
#6 0xffffffff8146c865 in wb_check_background_flush (wb=<optimized out>) at fs/fs-writeback.c:1964
#7 wb_do_writeback (wb=<optimized out>) at fs/fs-writeback.c:2052
#8 wb_workfn (work=0xffff88800442e1f0) at fs/fs-writeback.c:2080
#9 0xffffffff81196a32 in process_one_work (worker=0xffff8880009f0400, work=0xffff88800442e1f0) at kernel/workqueue.c:2269
#10 0xffffffff81196de9 in worker_thread (__worker=0xffff8880009f0400) at kernel/workqueue.c:2415
#11 0xffffffff811a0a89 in kthread (_create=<optimized out>) at kernel/kthread.c:292
数据结构
writeback_control
/*
* A control structure which tells the writeback code what to do. These are
* always on the stack, and hence need no locking. They are always initialised
* in a manner such that unspecified fields are set to zero.
*/
struct writeback_control {
long nr_to_write; /* Write this many pages, and decrement
this for each page written */
long pages_skipped; /* Pages which were not written */
/*
* For a_ops->writepages(): if start or end are non-zero then this is
* a hint that the filesystem need only write out the pages inside that
* byterange. The byte at `end' is included in the writeout request.
*/
loff_t range_start;
loff_t range_end;
enum writeback_sync_modes sync_mode;
unsigned for_kupdate:1; /* A kupdate writeback */
unsigned for_background:1; /* A background writeback */
unsigned tagged_writepages:1; /* tag-and-write to avoid livelock */
unsigned for_reclaim:1; /* Invoked from the page allocator */
unsigned range_cyclic:1; /* range_start is cyclic */
unsigned for_sync:1; /* sync(2) WB_SYNC_ALL writeback */
/*
* When writeback IOs are bounced through async layers, only the
* initial synchronous phase should be accounted towards inode
* cgroup ownership arbitration to avoid confusion. Later stages
* can set the following flag to disable the accounting.
*/
unsigned no_cgroup_owner:1;
unsigned punt_to_cgroup:1; /* cgrp punting, see __REQ_CGROUP_PUNT */
...
};1.sync_mode字段
/*
* fs/fs-writeback.c
*/
enum writeback_sync_modes {
WB_SYNC_NONE, /* Don't wait on anything */
WB_SYNC_ALL, /* Wait on every mapping */
};源码备注很清晰,WB_SYNC_NONE : 不需要等待数据真正落盘返回,WB_SYNC_ALL需要等待数据落盘完成返回,sync调用使用。
2. range_cyclic 字段
值为 1 表示当前任务的回写范围为整个 inode,并且从上次完成的位置作为起始位置进行循环回写。值为 0 则根据 struct writeback_control wbc 的 range_start 以及 range_end 作为回写的范围。
static int ext4_writepages(struct address_space *mapping,
struct writeback_control *wbc) {
...
if (wbc->range_cyclic) {
writeback_index = mapping->writeback_index;
if (writeback_index)
cycled = 0;
mpd.first_page = writeback_index;
mpd.last_page = -1;
} else {
mpd.first_page = wbc->range_start >> PAGE_SHIFT;
mpd.last_page = wbc->range_end >> PAGE_SHIFT;
}
...
}
3. for_update字段
值为 1 表示当前任务是定期回写任务,用于回写已经至脏超过指定时间的脏页。通过get_nr_dirty_pages获取回写的page数量。
static long wb_check_old_data_flush(struct bdi_writeback *wb)
{
unsigned long expired;
long nr_pages;
/*
* When set to zero, disable periodic writeback
*/
if (!dirty_writeback_interval)
return 0;
expired = wb->last_old_flush +
msecs_to_jiffies(dirty_writeback_interval * 10);
if (time_before(jiffies, expired))
return 0;
wb->last_old_flush = jiffies;
nr_pages = get_nr_dirty_pages();
if (nr_pages) {
struct wb_writeback_work work = {
.nr_pages = nr_pages,
.sync_mode = WB_SYNC_NONE,
.for_kupdate = 1,
.range_cyclic = 1,
.reason = WB_REASON_PERIODIC,
};
return wb_writeback(wb, &work);
}
return 0;
}
4. for_background 字段
值为 1 表示当前任务是阈值回写任务,当脏页比例超过阈值后才会触发。
static long wb_check_background_flush(struct bdi_writeback *wb)
{
if (wb_over_bg_thresh(wb)) {
struct wb_writeback_work work = {
.nr_pages = LONG_MAX,
.sync_mode = WB_SYNC_NONE,
.for_background = 1,
.range_cyclic = 1,
.reason = WB_REASON_BACKGROUND,
};
return wb_writeback(wb, &work);
}
return 0;
}5. for_sync字段
值为 1 表示当前任务是阈值回写任务 sync 系统调用手动触发的回写任务。
/**
* sync_inodes_sb - sync sb inode pages
* @sb: the superblock
*
* This function writes and waits on any dirty inode belonging to this
* super_block.
*/
void sync_inodes_sb(struct super_block *sb)
{
DEFINE_WB_COMPLETION_ONSTACK(done);
struct wb_writeback_work work = {
.sb = sb,
.sync_mode = WB_SYNC_ALL,
.nr_pages = LONG_MAX,
.range_cyclic = 0,
.done = &done,
.reason = WB_REASON_SYNC,
.for_sync = 1,
};
...
wait_sb_inodes(sb);
}6. for_reclaim 字段
主要来自mm模块,比如回收page将dirty page回写时设置:
static pageout_t pageout(struct page *page, struct address_space *mapping,
struct scan_control *sc)
{
...
if (clear_page_dirty_for_io(page)) {
int res;
struct writeback_control wbc = {
.sync_mode = WB_SYNC_NONE,
.nr_to_write = SWAP_CLUSTER_MAX,
.range_start = 0,
.range_end = LLONG_MAX,
.for_reclaim = 1,
};
...
}7. nr_to_write 字段
回写的页面数量,注意单位是page。
问题:for_background阈值触发回写时候,wbc中的nr_to_write要回写多少page?
fs/fs-writeback.c中计算而得
static long writeback_chunk_size(struct bdi_writeback *wb,
struct wb_writeback_work *work)
{
long pages;
/*
* WB_SYNC_ALL mode does livelock avoidance by syncing dirty
* inodes/pages in one big loop. Setting wbc.nr_to_write=LONG_MAX
* here avoids calling into writeback_inodes_wb() more than once.
*
* The intended call sequence for WB_SYNC_ALL writeback is:
*
* wb_writeback()
* writeback_sb_inodes() <== called only once
* write_cache_pages() <== called once for each inode
* (quickly) tag currently dirty pages
* (maybe slowly) sync all tagged pages
*/
if (work->sync_mode == WB_SYNC_ALL || work->tagged_writepages)
pages = LONG_MAX;
else {
pages = min(wb->avg_write_bandwidth / 2,
global_wb_domain.dirty_limit / DIRTY_SCOPE);
pages = min(pages, work->nr_pages);
pages = round_down(pages + MIN_WRITEBACK_PAGES,
MIN_WRITEBACK_PAGES);
}
return pages;
}8. tagged_writepages
回写标记为PAGECACHE_TAG_TOWRITE的页。
mpage_da_data
/*
* Delayed allocation stuff
*/
struct mpage_da_data {
struct inode *inode;
struct writeback_control *wbc;
pgoff_t first_page; /* The first page to write */
pgoff_t next_page; /* Current page to examine */
pgoff_t last_page; /* Last page to examine */
/*
* Extent to map - this can be after first_page because that can be
* fully mapped. We somewhat abuse m_flags to store whether the extent
* is delalloc or unwritten.
*/
struct ext4_map_blocks map;
struct ext4_io_submit io_submit; /* IO submission data */
unsigned int do_map:1;
unsigned int scanned_until_end:1;
};- inode : address_space->host对应的文件inode
- wbc:即上文提到的writeback_control,记录writeback的信息
- first_page : 回写的第一个页面
- next_page : 正在操作回写(examine)的page。
- last_page :最后一个操作回写的page
- map : 存储文件逻辑块号和磁盘物理块号的映射
- scanned_until_end:是否达到文件末尾
ext4_map_blocks数据结构
struct ext4_map_blocks {
ext4_fsblk_t m_pblk; // 物理块号,相对于文件系统而言的
ext4_lblk_t m_lblk; // 逻辑块号,相对于文件的
unsigned int m_len; // 长度,单位为文件块
unsigned int m_flags; // 映射关系的各种标记,参考EXT4_MAP_NEW附近的宏定义
};物理块号:ext4文件系统默认将磁盘划分为4K的块,每一个4K的block有一个物理块号,物理块号从0开始,由于文件系统系统的磁盘空间可能是个分区,因此通用块层根据下发的物理块号计算真正的磁盘的sector(512B一般)时要加上分区的sector偏移。
逻辑块号:逻辑块号是相对于文件而言的,对于上层应用来说文件的内容是连续的,而实际的物理存储块号可能不连续,也可以把文件以4K为一个单位分割,比0-4K-1范围的文件的逻辑块号为0,依次类推增加。
extent status tree
ext4在内存中为每个文件维护一颗extent status tree,起初这树的名字是delay extent tree,是为了区分delay extent。ext4的delay allocation特性,真正分配physical block是推迟到page cache writeback时候进行,这里面临一个问题,根据ext4理论篇文章我们知道,extent tree是存储在磁盘上的,启用delay allocation特性的时候没有为写入的数据分配physical block,那么自然文件磁盘的extent tree没有更新。此时如果要区分文件的一个extent,到底是delay allocation的,还是hole,就只能去看文件的address space中有没有该extent对应的page cache,这种实现会有很多问题,所以在内存维护了extent status tree,dealloc的时候,write routine不会为写入数据分配physical block,但是会往extent status tree中插入一个delay extent status.
除了维护delay extent status之外,将磁盘的extent status缓存到内存中,也能加快extent status的查询速度,因而文件的extent status tree除了维护delay extent status之外,实际上还是磁盘中的extent tree的映像。
每个ext4 inode都维护一颗extent status tree,实际上是一个rbtree,其中所有extent status按照logical block number排序。
struct ext4_inode_info {
/* extents status tree */
struct ext4_es_tree i_es_tree;
...
}
struct ext4_es_tree {
struct rb_root root;
struct extent_status *cache_es; /* recently accessed extent */
};extent status
extent status tree中的每个节点就是一个extent status,每个extent status实际上就是磁盘上一个extent的缓存。
struct extent_status {
struct rb_node rb_node;
ext4_lblk_t es_lblk; /* first logical block extent covers */
ext4_lblk_t es_len; /* length of extent in block */
ext4_fsblk_t es_pblk; /* first physical block */
};extent status分为几种类型,分别是written/unwritten/delay/hole/referenced,@es_pblk高位存储extent status 类型:
enum {
ES_WRITTEN_B,
ES_UNWRITTEN_B,
ES_DELAYED_B,
ES_HOLE_B,
ES_REFERENCED_B,
ES_FLAGS
};delay
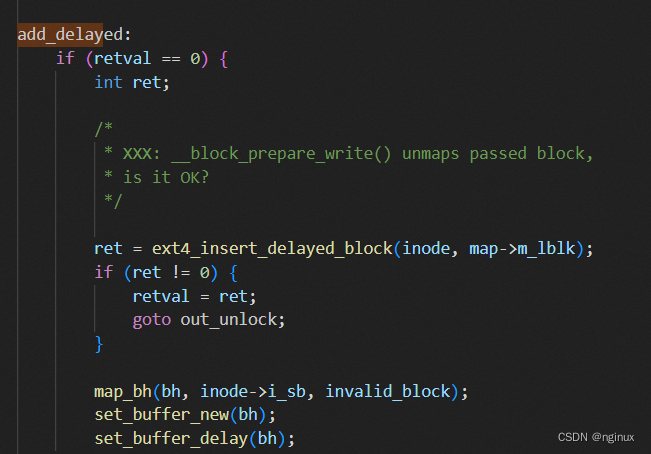
delay extent status描述delay allocation对应的extent,此时es_lblk/es_len有效,而es_pblk无效,如果上文提到delay allocation开启时,write routine写入page cache时不会分配physical block,而是往extent status tree中添加一个delay extent status中:
fs/ext4/inode.c : ext4_da_map_blocks
hole
hole extent status描述文件的一个hole,此时es_lblk/es_len有效,而es_pblk字段无效。在extent lookup过程中,读取磁盘的extent tree后,如果发现传入的logical block number没有对应的extent,就会往extent status tree中插入一个hole extent status。
written
written extent status就是平常所说的磁盘中存储的extent tree在内存中缓存,此时es_lblk/es_len/es_pblk均有效。
unwritten
unwritten extent status也是磁盘中存储的extent tree的内存中的缓存,但是和written extent status的区别在于,unwritten extent status主要用户描述fallocate syscall分配的extent。
为了满足对于fallocate预分配的磁盘空间执行读操作英翻返回0的定义,一种实现时对预分配的physical block做填0处理,但是这种操作很低效,ext4中的实现是在extent tree中区分written/unwritten extent,written extent就是映射通过正常的写操作分配的physical tree,而unwritten extent则是映射通过fallocate预分配的physical block,这样read遇到unwritten extent可以返回0.
ext4中使用ee_len的最高bit来区分written/unwritten
struct ext4_extent {
__le16 ee_len; /* number of blocks covered by extent */
...
};
@ee_len 是一个 16 bit 的数据,其最高 bit 来用于区分 written/unwritten extent
- @ee_len 的值小于等于 0x8000 表示 written extent,也就是说最高 bit 为 0、或者最高 bit 为 1 但是其余 bit 都为 0 的情况下,表示 written extent,也就是说 written extent 最大为 0x8000 个 block 大小,即 block size 为 4KB 时,written extent 最大为 128MB 大小
- @ee_len 的值大于 0x8000 表示 unwritten extent
因而 unwritten extent status 实际上也是磁盘中存储的 unwritten extent 在内存中的缓存,此时 @es_lblk/es_len/es_pblk 都是有效的
ext4_ext_path
/*
* Array of ext4_ext_path contains path to some extent.
* Creation/lookup routines use it for traversal/splitting/etc.
* Truncate uses it to simulate recursive walking.
*/
struct ext4_ext_path {
ext4_fsblk_t p_block;
__u16 p_depth;
__u16 p_maxdepth;
struct ext4_extent *p_ext;
struct ext4_extent_idx *p_idx;
struct ext4_extent_header *p_hdr;
struct buffer_head *p_bh;
};
/*
* This is the extent on-disk structure.
* It's used at the bottom of the tree.
*/
struct ext4_extent {
__le32 ee_block; /* first logical block extent covers */
__le16 ee_len; /* number of blocks covered by extent */
__le16 ee_start_hi; /* high 16 bits of physical block */
__le32 ee_start_lo; /* low 32 bits of physical block */
};
/*
* This is index on-disk structure.
* It's used at all the levels except the bottom.
*/
struct ext4_extent_idx {
__le32 ei_block; /* index covers logical blocks from 'block' */
__le32 ei_leaf_lo; /* pointer to the physical block of the next *
* level. leaf or next index could be there */
__le16 ei_leaf_hi; /* high 16 bits of physical block */
__u16 ei_unused;
};
/*
* Each block (leaves and indexes), even inode-stored has header.
*/
struct ext4_extent_header {
__le16 eh_magic; /* probably will support different formats */
__le16 eh_entries; /* number of valid entries */
__le16 eh_max; /* capacity of store in entries */
__le16 eh_depth; /* has tree real underlying blocks? */
__le32 eh_generation; /* generation of the tree */
};
上述数据结构用来表示磁盘extent b+数据结构,比如:
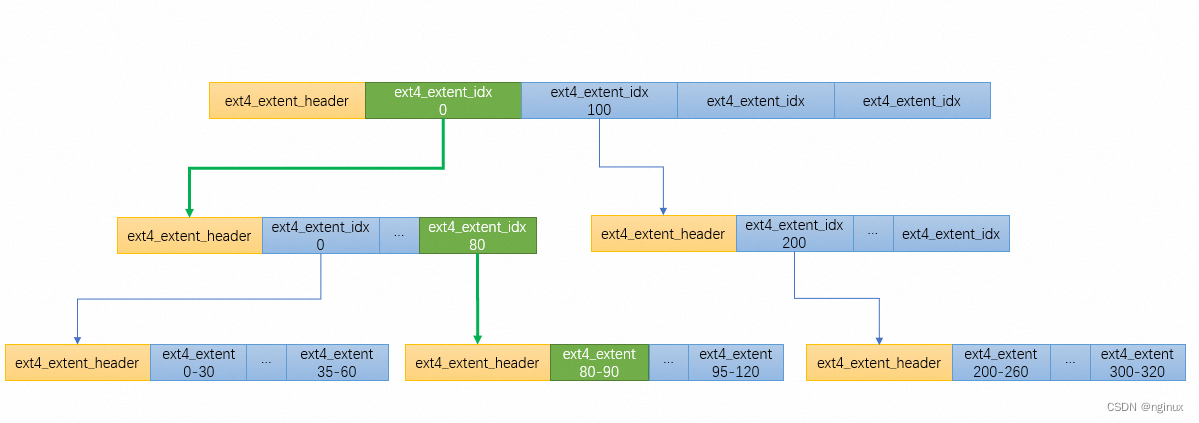
图中数字范围是logical block number
参考文章:
Ext4 - extent status tree - LostJeffle