目录
5.Clear()
6.Contains(T)
7.ConvertAll(Converter) ,toutput>
8.CopyTo(Int32, T[], Int32, Int32)
9.CopyTo(T[])
10.CopyTo(T[], Int32)
C# List 详解一
1.Add(T),2.AddRange(IEnumerable),3.AsReadOnly(),4.BinarySearch(T),
C# List 详解二
5.Clear(),6.Contains(T),7.ConvertAll(Converter),8.CopyTo(Int32, T[], Int32, Int32),9.CopyTo(T[]),10.CopyTo(T[], Int32)
C# List 详解三
11.Equals(Object),12.Exists(Predicate),13.Find(Predicate),14.FindAll(Predicate),15.FindIndex(Int32, Int32, Predicate),16.FindIndex(Int32, Predicate),17.FindIndex(Predicate)
C# List 详解四
18.FindLast(Predicate),19.FindLastIndex(Int32, Int32, Predicate),20.FindLastIndex(Int32, Predicate),21.FindLastIndex(Predicate),22.ForEach(Action),23.GetEnumerator(),24.GetHashCode(),25.GetRange(Int32, Int32)
C# List 详解五
26.GetType(),27.IndexOf(T),28.IndexOf(T, Int32),29.IndexOf(T, Int32, Int32),30.Insert(Int32, T),31.InsertRange(Int32, IEnumerable),32.LastIndexOf(T),33.LastIndexOf(T, Int32),34.LastIndexOf(T, Int32, Int32)
C# List 详解六
35.MemberwiseClone(),36.Remove(T),37.RemoveAll(Predicate),38.RemoveAt(Int32),39.RemoveRange(Int32, Int32),40.Reverse(),41.Reverse(Int32, Int32)
C# List 详解七
42.Sort(),43.ToArray(),44.ToString(),45.TrimExcess(),46.TrueForAll(Predicate)
C# List 详解一_熊思宇的博客-CSDN博客
C# List 详解三_熊思宇的博客-CSDN博客
C# List 详解四_熊思宇的博客-CSDN博客
C# List 详解五_熊思宇的博客-CSDN博客
C# List 详解六_熊思宇的博客-CSDN博客
C# List 详解七_熊思宇的博客-CSDN博客
5.Clear()
从 List<T> 中移除所有元素。List 中比较常用的方法,用来清空 List 的所有元素。
public void Clear ();案例:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
namespace ListTest
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
List<string> dinosaurs = new List<string>();
dinosaurs.Add("Pachycephalosaurus");
dinosaurs.Add("Parasauralophus");
dinosaurs.Add("Amargasaurus");
Console.WriteLine(dinosaurs.Count);
dinosaurs.Clear();
Console.WriteLine(dinosaurs.Count);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
运行:

6.Contains(T)
确定某元素是否在 List<T> 中。
public bool Contains (T item);参数
item
T
要在 List<T> 中定位的对象。 对于引用类型,该值可以为 null。
返回
Boolean
如果在 true 中找到 item,则为 List<T>;否则为 false。
案例:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
namespace ListTest
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
List<string> dinosaurs = new List<string>();
dinosaurs.Add("Pachycephalosaurus");
dinosaurs.Add("Parasauralophus");
dinosaurs.Add("Amargasaurus");
if (dinosaurs.Contains("Amargasaurus"))
{
Console.WriteLine("包含");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("不包含");
}
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
运行:

7.ConvertAll<TOutput>(Converter<T,TOutput>)
将当前 List<T> 中的元素转换为另一种类型,并返回包含已转换元素的列表。
public System.Collections.Generic.List<TOutput> ConvertAll<TOutput> (Converter<T,TOutput> converter);类型参数
TOutput
目标数组元素的类型。
参数
converter
Converter<T,TOutput>
一个 Converter<TInput,TOutput> 委托,可将每个元素从一种类型转换为另一种类型。
返回
List<TOutput>
目标类型的 List<T>,包含当前 List<T> 中转换后的元素。
案例:
就是将 List 中的每一个元素转换为另一种格式,并返回一个新的 List
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
namespace ListTest
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
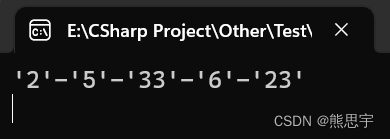
List<int> intList = new List<int>() { 2, 5, 33, 6, 23 };
List<string> stringList = intList.ConvertAll(new Converter<int, string>(convertall));
Console.WriteLine(string.Join("-", stringList));
Console.ReadKey();
}
static string convertall(int val)
{
return string.Format("'{0}'", val);
}
}
}上面代码也可以用 Lambda 表达式去写:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
namespace ListTest
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
List<int> intList = new List<int>() { 2, 5, 33, 6, 23 };
List<string> stringList = intList.ConvertAll(new Converter<int, string>((val) => { return string.Format("'{0}'", val); }));
Console.WriteLine(string.Join("-", stringList));
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}运行:
8.CopyTo(Int32, T[], Int32, Int32)
从目标数组的指定索引处开始,将元素的范围从 List<T> 复制到兼容的一维数组。
public void CopyTo (int index, T[] array, int arrayIndex, int count);参数
index
Int32
复制即从源 List<T> 中从零开始的索引开始。
array
T[]
一维 Array,它是从 List<T> 复制的元素的目标。 Array 必须具有从零开始的索引。
arrayIndex
Int32
array 中从零开始的索引,从此处开始复制。
count
Int32
要复制的元素数。
由于引用类型在改变值后,其他的数组中的值也会改变,所以有时候,数组不得不用拷贝的方式,下面用两个案例来演示 CopyTo 的用法。
案例1:完整的拷贝
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
namespace ListTest
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
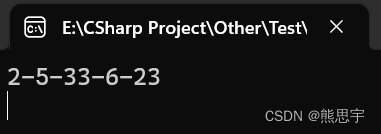
List<int> intList = new List<int>() { 2, 5, 33, 6, 23 };
int[] list = new int[intList.Count];
intList.CopyTo(0, list, 0, intList.Count);
Console.WriteLine(string.Join("-", list));
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}运行:
案例2:拷贝一部分
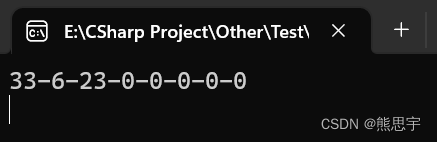
在下面这几个参数中,第一个参数 2 表示从 intList 中的下标 2 开始,即 33 开始,第三个参数 0 表示 list 数组中,从 0 这个下标开始赋值,往后赋值2个参数
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
namespace ListTest
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
List<int> intList = new List<int>() { 2, 5, 33, 6, 23, 45,36,38 };
int[] list = new int[intList.Count];
intList.CopyTo(2, list, 0, 3);
Console.WriteLine(string.Join("-", list));
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
运行:
9.CopyTo(T[])
从目标数组的开头开始,将整个 List<T> 复制到兼容的一维数组。
public void CopyTo (T[] array);参数
array
T[]
一维 Array,它是从 List<T> 复制的元素的目标。 Array 必须具有从零开始的索引。
案例:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
namespace ListTest
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
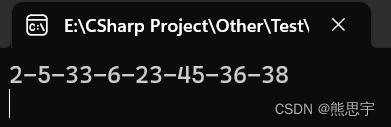
List<int> intList = new List<int>() { 2, 5, 33, 6, 23, 45,36,38 };
int[] list = new int[intList.Count];
intList.CopyTo(list);
Console.WriteLine(string.Join("-", list));
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}运行:
10.CopyTo(T[], Int32)
从目标数组的指定索引处开始,将整个 List<T> 复制到兼容的一维数组。
public void CopyTo (T[] array, int arrayIndex);参数
array
T[]
一维 Array,它是从 List<T> 复制的元素的目标。 Array 必须具有从零开始的索引。
arrayIndex
Int32
array 中从零开始的索引,从此处开始复制。
案例:
这里和上一节的用法差不多,只是多了一个 arrayIndex
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
namespace ListTest
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
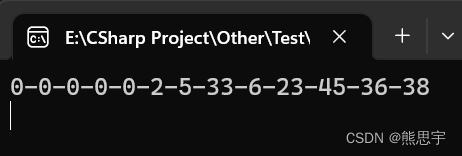
List<int> intList = new List<int>() { 2, 5, 33, 6, 23, 45,36,38 };
int[] list = new int[intList.Count + 5];
intList.CopyTo(list, 5);
Console.WriteLine(string.Join("-", list));
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}运行:
第 2 / 7 篇 End