目录
一、Ansible概述
二、Ansible特点
三、Ansible应用
1、使用者
2、Ansible工具集合
3、作用对象
四、Ansible的搭建
1、实验环境
2、环境准备
Ansible:
3、创建ssh免密交互登录
client端环境准备
五、Ansible配置
六、Ansible命令
1、ansible
实验案例:
1.检查所有主机是否存活
2.列出Rich组中所有主机列表
3.批量显示Rich组中的磁盘使用情况
2、Ansible-doc
1.列出支持的模块
2.查询ping模块的说明信息
3、ansible-playbook
4、ansible-console
七、Ansible模块
1.command模块
实验案例
2.shell模块
实验案例
1、重定向
2、测试管道符
3.raw模块
4.copy模块
5.hostname模块
6.yum模块
实验案例
1. client端yum安装bind
7.service模块
实验案例
1.启动httpd服务并设置为开启自启动
8.User模块
实验案例
1. 创建用户
2. 删除用户及家目录
9.script模块
一、Ansible概述
Ansible是最近非常火的一款开源运维自动化工具,通过Ansible可以实现运维自动化,提高运维工程师的工作效率,减少人为失误,Ansible可以通过本身集成的非常丰富的模块实现各种管理任务,其自带模块数量已超过上千个,更为重要的是,它的操作非常简单,即使新手也比较容易上手,Ansible提供的功能却非常丰富,在运维领域,几乎可以实现任何事情。目前属于RedHat公司产品,官方地址:Ansible is Simple IT Automation。
二、Ansible特点
Ansible自2012年发布以来,很快在全球流行,其特点表现如下:
- Ansible基于python开发,运维工程师对其二次开发相对容易
- Ansible拥有丰富的内置模块,基本可以满足一切要求
- 管理模式非常简单,一条命令可以影响上千台机器
- 无客户端模式设计,底层基于SSH通信
- Ansible发布后也陆续被AWS,Google,Cloud Platfrom,Microsoft Azure,Cisco,HP,VMware,Twitter等大公司接纳并投入使用
三、Ansible应用
Ansible没有客户端,也不需要在被管理主机添加任何代理程序,通过SSH完成底层通信,而SSH在Linux的发型版本中默认已经安装并启用,而在Windows系统下则依赖于PowerShell,Ansible要求管理端必须是Linux系统,在管理节点通过应用模块将指令发送到被管理主机上,并在执行完毕后自动删除产生的临时文件,根据Ansible使用过程中不同角色,可将其分为三个部分。
- 使用者如何使用Ansible实现自动化运维?
- Ansible的工具集,Ansible可以实现的功能?
- 作用对象,Ansible可以影响哪些主机?
1、使用者
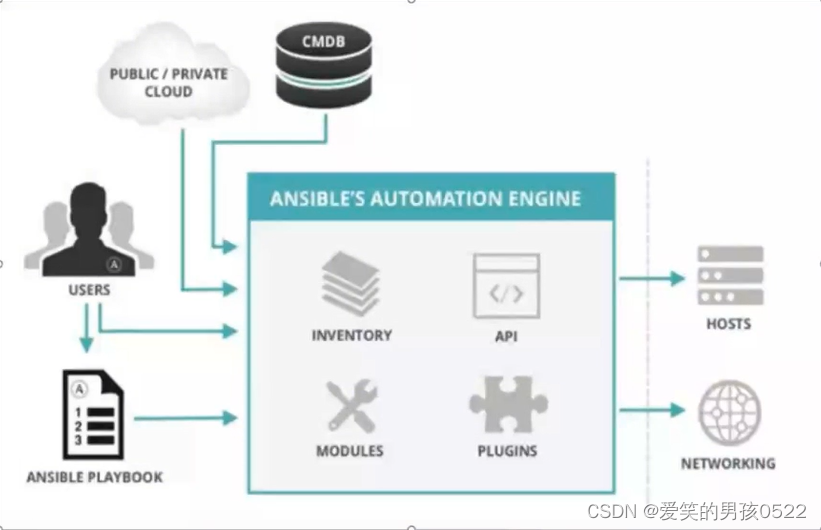
如图所示:Ansible使用者可以采用多种方式和Ansible交互,图中我们展示了四种方式
- CMDB:CMDB系统存储和管理着企业IT架构中的各种配置信息,是构建ITL项目核心工具,运维人员可以组合CMDB和Ansible,通过CMDB直接下发指令调用Ansible工具完成操作者所希望达到的目标。
- PUBLIC/PRIVATE方式,Ansible除了丰富的内置模块外,同时提供丰富的API语言接口,如PHP,Pythone,PERL等多种流行语言,基于PUBLIC/PRIVATE,Ansible以API调用的方式运行。
- Ad-Hoc命令集,Users直接通过Ad-Hoc命令集调用Ansible工具来完成工作。
- Playbooks:Users预先编写好Ansible Playbooks,通过执行Playbooks中预先编排好的任务集按序执行命令。
2、Ansible工具集合
Ansible工具集合了inventory,Moudles,Plugins和API。其中,inventory用来管理设备列表,可以通过分组(不同的业务)实现,对组的调用直接影响组内所有的主机;Moudles是各种执行模块,几乎所有的管理任务都是通过模块来执行的;Plugins提供了各种附加功能;API为编程人员提供了一个调用接口,可以做Ansible的二次开发具体表现如下:
- Ansible Playbook:任务脚本,编排定义Ansible任务集的配置文件,由Ansible按序依次执行,通常是JSON格式的YML/YAML文件;
- inventory:Ansible管理主机清单
- Moudle:Ansible执行命令功能模块,多数为内置的核心模块也可以用户自定义;
- Plugins:模块功能的补充,如连接类型插件,循环插件,变量插件,过滤插件等,该功能不常用。
- API:提供第三方程序调用的应用程序编程接口;
Ansible:该部分图中表示的,组合inventory,API,Moudles,Plugins可以理解为Ansible
命令工具其核心执行工具。
3、作用对象
Ansible的作用对象不仅仅是Linux和非Linux操作系统的主机,也可以作用于各类PUBLIC/PRIVATE,商业和非商业设备的网络设施。
使用者使用Ansible或Ansible-playbooks时,在服务器终端输入Ansible的Ad-Hoc命令集或playbooks后,Ansible会遵循预先定义安排的规则将Playbooks逐步拆解为Play,再将Play组织成Ansible可以识别的任务,随后调用任务涉及的所有模板和插件,根据inventory中自定义的主机列表通过SSH将任务集以临时文件或命令的形式传输给远程客户端执行并返回执行结果,如果是临时文件则执行完毕后自动删除。
四、Ansible的搭建
接下来我们来学习Ansible的安装和部署。Ansible的安装部署非常简单,以RPM安装为例,配置好阿里云的yum源直接安装就可以了,Ansible的管理端只能是Linux,如Redhat,Debian,CentOS。下面介绍在CentOS7.x上安装部署Ansible。
1、实验环境
| 操作系统 | IP地址 | 角色 | 主机名 | CPU核心 |
| CentOS7.5 | 192.168.200.111 | Ansible | ansible | 1 |
| CentOS7.5 | 192.168.200.112 | Client | client1 | 1 |
| CentOS7.5 | 192.168.200.113 | Client | client2 | 2 |
2、环境准备
Ansible:
[root@localhost ~]# iptables -F
[root@localhost ~]# setenforce 0
setenforce: SELinux is disabled
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl stop firewalld
[root@localhost ~]# hostname ansible
[root@localhost ~]# bash
YUM方式安装asible
[root@ansible ~]# rpm -ivh epel-release-latest-7.noarch.rpm
[root@ansible ~]# cd /etc/yum.repos.d/
[root@ansible yum.repos.d]# ls
backup CentOS-aliyun.repo CentOS-Media.repo epel.repo epel-testing.repo
[root@ansible yum.repos.d]# mv CentOS-aliyun.repo backup/
[root@ansible yum.repos.d]# mv backup/CentOS-Base.repo ./
[root@ansible yum.repos.d]# ls
backup CentOS-Base.repo CentOS-Media.repo epel.repo epel-testing.repo
[root@ansible yum.repos.d]# yum -y install ansible
[root@ansible yum.repos.d]# ansible --version #测试可以显示信息表示安装成功
ansible 2.9.10
config file = /etc/ansible/ansible.cfg
configured module search path = [u'/root/.ansible/plugins/modules', u'/usr/share/ansible/plugins/modules']
ansible python module location = /usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages/ansible
executable location = /usr/bin/ansible
python version = 2.7.5 (default, Oct 30 2018, 23:45:53) [GCC 4.8.5 20150623 (Red Hat 4.8.5-36)]3、创建ssh免密交互登录
Ansible是通过SSH协议对设备进行管理,而SSH服务包含两种认证方式,一种是通过密码认证,另一种是通过密钥对认证,密码方式必须和系统进行交互,而密钥对是免交互登录,如果希望通过Ansible自动管理设备应该配置为免交互登录被管理设备。
[root@ansible ~]# ssh-keygen -t rsa #生成SSH密钥对
Generating public/private rsa key pair.
Enter file in which to save the key (/root/.ssh/id_rsa):
#设置密钥对存放位置默认即可
Created directory '/root/.ssh'.
Enter passphrase (empty for no passphrase): #设置密钥对的保护密码 回车表示设置为空
Enter same passphrase again: #再次输入密码确认,上面没有下面也不用
Your identification has been saved in /root/.ssh/id_rsa.
Your public key has been saved in /root/.ssh/id_rsa.pub.
The key fingerprint is:
SHA256:hUqzTeV/+I7jdbIsQBL9IIyQ+Wt/FCTJoHQ4qGZnHkk root@ansible
The key's randomart image is:
+---[RSA 2048]----+
| .o=o= o. |
| .E=o. B++ |
| .. ooo o=oo |
|.o = ..*..o... |
|o + . o.So .o . |
| . o o o |
| . . . . + .|
| . . o= + |
| . .oo+ |
+----[SHA256]-----+client端环境准备
client1
[root@localhost ~]# hostname client1
[root@localhost ~]# bash
[root@client1 ~]# iptables -F
[root@client1 ~]# setenforce 0
[root@client1 ~]# systemctl stop firewalldclient2
[root@localhost ~]# hostname client2
[root@localhost ~]# bash
[root@client2 ~]# iptables -F
[root@client2 ~]# setenforce 0
[root@client2 ~]# systemctl stop firewalldansible端发送公钥给client
[root@ansible ~]# ssh-copy-id root@192.168.2.222
[root@ansible ~]# ssh-copy-id root@192.168.2.223
[root@ansible ~]# vim /etc/hosts #三台机子都操作
127.0.0.1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost4 localhost4.localdomain4
::1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost6 localhost6.localdomain6
192.168.2.222 client1
192.168.2.223 client2
192.168.2.221 ansible
五、Ansible配置
inventory是Ansible管理主机信息的配置文件,相当于系统的Hosts文件功能,默认存放在/etc/ansible/hosts。在hosts文件中通过分组来组织设备,Ansible通过inventory来定义主机和分组,通过ansible命令中是用选项-i或者--inventory-file指定inventory。
[root@ansible ~]# cp /etc/ansible/hosts{,.bak} #备份配置文件
[root@ansible ~]# vim /etc/ansible/hosts
[Rich]
192.168.2.222
192.168.2.223
[root@ansible ~]# ansible -i /etc/ansible/hosts Rich -m ping
192.168.2.223 | SUCCESS => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}
192.168.2.222 | SUCCESS => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}配置完成后可以针对hosts定义服务组件进行远程操作,也可以针对组中的指定的某一个或多个主机操作,下面接收如何针对特定的服务器操作
1.针对Rich组中的192.168.2.222主机操作,通--limit参数限定主机的变更
[root@ansible ~]# ansible Rich -m command -a "head -5 /etc/passwd" --limit 192.168.2.222
192.168.2.222 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
bin:x:1:1:bin:/bin:/sbin/nologin
daemon:x:2:2:daemon:/sbin:/sbin/nologin
adm:x:3:4:adm:/var/adm:/sbin/nologin
lp:x:4:7:lp:/var/spool/lpd:/sbin/nologin2.只对192.168.2.0网段主机进行操作。通过通配符限定主机变更
[root@ansible ~]# ansible 192.168.2.* -m command -a "head -5 /etc/passwd"
192.168.2.223 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
bin:x:1:1:bin:/bin:/sbin/nologin
daemon:x:2:2:daemon:/sbin:/sbin/nologin
adm:x:3:4:adm:/var/adm:/sbin/nologin
lp:x:4:7:lp:/var/spool/lpd:/sbin/nologin
192.168.2.222 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
bin:x:1:1:bin:/bin:/sbin/nologin
daemon:x:2:2:daemon:/sbin:/sbin/nologin
adm:x:3:4:adm:/var/adm:/sbin/nologin
lp:x:4:7:lp:/var/spool/lpd:/sbin/nologin六、Ansible命令
Ansible的维护命令大多以ansible开头,在终端输入ansible后连续按两次tab键,会补全所有以ansible字母开头的命令,下面介绍Ansible的一些常用命令。
[root@ansible ~]# ansible #连续按两次tab键
ansible ansible-console ansible-doc-2.7 ansible-playbook ansible-pull-2.7
ansible-2 ansible-console-2 ansible-galaxy ansible-playbook-2 ansible-test
ansible-2.7 ansible-console-2.7 ansible-galaxy-2 ansible-playbook-2.7 ansible-vault
ansible-config ansible-doc ansible-galaxy-2.7 ansible-pull ansible-vault-2
ansible-connection ansible-doc-2 ansible-inventory ansible-pull-2 ansible-vault-2.71、ansible
Ansible是生产环境中使用非常频繁的命令之一,主要在以下场景应用
- 非固化需求
- 临时一次性操作
- 二次开发接口调用
非固化需求是指临时性的维护,如查看Rich服务器组的磁盘使用情况,复制一个文件
到其他机器等,类似这些没有规律的,临时需要做的任务,我们称为非固化需求,临时一次性操作
语法:ansible <host-pattern> [options]
可用选项如下
- -v(--verbose):输出详细的执行过程信息,可以得到执行过程所有信息
- -i PATH(inventory=PATH):指定inventory信息,默认为/etc/ansible/hosts
- -f NUM(--forks=NUM):并发线程数,默认为5个线程
- --private-key=PRIVATE_KEY_FILE:指定密钥文件
- -m NAME,--moudle-name=NAME:指定执行时使用的模块
- -M DIRECTORY(--module-path=DIRECTORY):指定模块存放路径,默认为/usr/share/ansible,也可以通过ANSIBLE_LIBRARY设定默认目录
- -a ARGUMENTS(--args=ARGUMENTS):指定模块参数
- -u USERNAME(--user=USERNAME):指定远程主机USERNAME运行命令
- -l subset(--limit=SUBSET):限定运行主机
- --list-hosts:列出符合条件的主机列表,不执行任何命令
实验案例:
1.检查所有主机是否存活
[root@ansible ~]# ansible all -f 5 -m ping
192.168.2.222 | SUCCESS => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}
192.168.2.223 | SUCCESS => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}2.列出Rich组中所有主机列表
[root@ansible ~]# ansible Rich --list-host
hosts (2):
192.168.2.222
192.168.2.223
[root@ansible ~]# ansible Rich --list
hosts (2):
192.168.2.222
192.168.2.223 3.批量显示Rich组中的磁盘使用情况
[root@ansible ~]# ansible Rich -m command -a "df -Th"
192.168.200.112 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
文件系统 类型 容量 已用 可用 已用% 挂载点
/dev/mapper/centos-root xfs 50G 4.5G 46G 9% /
devtmpfs devtmpfs 2.0G 0 2.0G 0% /dev
tmpfs tmpfs 2.0G 0 2.0G 0% /dev/shm
tmpfs tmpfs 2.0G 12M 2.0G 1% /run
tmpfs tmpfs 2.0G 0 2.0G 0% /sys/fs/cgroup
/dev/sr0 iso9660 4.3G 4.3G 0 100% /media/cdrom
/dev/sda1 xfs 1014M 166M 849M 17% /boot
/dev/mapper/centos-home xfs 146G 37M 146G 1% /home
tmpfs tmpfs 394M 0 394M 0% /run/user/0
192.168.200.113 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
文件系统 类型 容量 已用 可用 已用% 挂载点
dev/mapper/centos-root xfs 50G 4.5G 46G 9% /
devtmpfs devtmpfs 2.0G 0 2.0G 0% /dev
tmpfs tmpfs 2.0G 0 2.0G 0% /dev/shm
tmpfs tmpfs 2.0G 12M 2.0G 1% /run
tmpfs tmpfs 2.0G 0 2.0G 0% /sys/fs/cgroup
/dev/sr0 iso9660 4.3G 4.3G 0 100% /media/cdrom
/dev/sda1 xfs 1014M 166M 849M 17% /boot
/dev/mapper/centos-home xfs 146G 37M 146G 1% /home
tmpfs tmpfs 394M 0 394M 0% /run- Rich需要提前在/etc/ansible/hosts文件中定义组
- Ansible的返回结果非常友好,一般会用三种颜色执行结果:红色,绿色和橘黄色,其中红色表示执行过程中有异常,橘黄色表示命令执行后目标有状态变化,绿色表示执行成功且没有对目标机器做修改
2、Ansible-doc
ansible-doc用来查询ansible模块文档的说明,类似于man命令,针对每个模块都有详细的用法说明及应用案例介绍
[root@ansible ~]# ansible-doc -l #查看总帮助
[root@ansible ~]# ansible-doc -s shell #查看shell模块的帮助
[root@ansible ~]# ansible-doc -s raw
语法:ansible-doc [options] [module……]
实验案例
1.列出支持的模块
[root@ansible ~]# ansible-doc -l #敲完会卡一会
fortios_router_community_list Configure community lists in Fortinet's FortiOS ...
azure_rm_devtestlab_info Get Azure DevTest Lab facts
ecs_taskdefinition register a task definition in ecs
avi_alertscriptconfig Module for setup of AlertScriptConfig Avi RESTfu...
tower_receive Receive assets from Ansible Tower
…… #省略部分内容2.查询ping模块的说明信息
[root@ansible ~]# ansible-doc ping #=ansible-doc -s ping
> PING (/usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages/ansible/modules/system/ping.py)
A trivial test module, this module always returns `pong' on successful contact. It
does not make sense in playbooks, but it is useful from `/usr/bin/ansible' to verify
the ability to login and that a usable Python is configured. This is NOT ICMP ping,
this is just a trivial test module that requires Python on the remote-node. For
Windows targets, use the [win_ping] module instead. For Network targets, use the
[net_ping] module instead.
* This module is maintained by The Ansible Core Team
OPTIONS (= is mandatory):
- data
Data to return for the `ping' return value.
If this parameter is set to `crash', the module will cause an exception.
[Default: pong]
type: str3、ansible-playbook
Ansible-playbook是日常应用中使用频率最高的命令,类似于Linux系统中的sh或source命令,用来执行系列任务,其工作机制是,通过读取编写好的playbook文件实现集中处理任务,ansible-playbook命令后跟yml或者yaml格式的playbook文件,playbook文件存放了要执行的任务代码,命令使用方式如下
语法:ansible-playbook playbook.yml
ansible-playbook需要之前编译好、建议写playbook.yml文件的绝对路径
4、ansible-console
ansible-console是ansible为用户提供的一款交互式工具,类似于Windows中的cmd以及Linux中的shell,用户可以在ansible-console虚拟出来的终端上做像shell一样使用ansible内置的各种命令,这为习惯于使用shell交互方式的用户提供了良好的体验,在终端输入ansible-console命令后显示如下
[root@ansible ~]# ansible-console
Welcome to the ansible console.
Type help or ? to list commands.
root@all (2)[f:5]$ cd Rich
root@Rich (2)[f:5]$ list
192.168.2.222
192.168.2.223
root@Rich (2)[f:5]$ exit所有操作与shell类似,而且支持Tab键补全,按快捷键Ctrl+D或Ctrl+C即可退出当前的虚拟终端
七、Ansible模块
1.command模块
command模块在远程主机执行命令,但是不支持管道,重定向等shell的特征,常用参数如下(不支持管道,不建议使用)。
- chdir:在远程主机上运行命令前要提前进入的目录
- creates:在命令运行时创建一个文件,如果文件已经存在,则不会创建任务
- removes:在命令运行时移除一个文件,如果文件不存在,则不会执行移除任务
- executable:指明运行命令的shell程序
实验案例
1.在所有主机上运行“ls./”命令,运行前切换到/home目录。操作如下。
准备一下环境:在两台主机上分别创建Rich用户否则/home下是空的查看不到效果
[root@ansible ~]# ansible Rich -m command -a "useradd Rich"
192.168.2.223 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
192.168.2.222 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
[root@ansible ~]# ansible Rich -m command -a "chdir=/home ls -l"
192.168.2.223 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
总用量 4
drwx------ 3 Rich Rich 78 8月 13 18:57 Rich
drwx------. 15 test test 4096 6月 22 18:37 test
192.168.2.2222 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
总用量 4
drwx------ 3 Rich Rich 78 8月 13 18:57 Rich
drwx------. 15 test test 4096 6月 22 18:37 test
[root@ansible ~]# ansible Rich -m command -a "uptime"
192.168.2.223 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
18:58:34 up 3:15, 3 users, load average: 0.00, 0.01, 0.05
192.168.2.222 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
18:58:34 up 3:15, 3 users, load average: 0.00, 0.01, 0.052.shell模块
shell模块在远程主机执行命令,相当于调用远程主机的shell进程,然后在该shell下打开一个子shell运行命令,和command模块的区别是它支持shell特征,如管道,重定向等。
实验案例
1、重定向
[root@ansible ~]# ansible Rich -m shell -a "echo 1111 > 1.txt"
192.168.2.223 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
192.168.2.222 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
[root@client1 ~]# ls
1.txt anaconda-ks.cfg initial-setup-ks.cfg 公共 模板 视频 图片 文档 下载 音乐 桌面
[root@client1 ~]# cat 1.txt
11112、测试管道符
过滤client端mac地址严格遵守文档格式 要不会报错
[root@ansible ~]# ansible Rich -m shell -a 'ifconfig ens32 | awk "/ether/{print $2}"'
192.168.200.113 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
ether 00:0c:29:5d:59:b8 txqueuelen 1000 (Ethernet)
92.168.200.112 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
ether 00:0c:29:46:d7:f2 txqueuelen 1000 (Ethernet)3.raw模块
最原始的方式运行命令(不依赖python,仅通过ssh实现)
清除yum缓存
[root@ansible ~]# ansible Rich -m raw -a "yum clean all"
192.168.2.223 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
已加载插件:fastestmirror, langpacks
Repodata is over 2 weeks old. Install yum-cron? Or run: yum makecache fast
正在清理软件源: c7-media
Cleaning up list of fastest mirrors
Other repos take up 116 M of disk space (use --verbose for details)
Shared connection to 192.168.200.113 closed.
192.168.2.222 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
已加载插件:fastestmirror, langpacks
Repodata is over 2 weeks old. Install yum-cron? Or run: yum makecache fast
正在清理软件源: c7-media
Cleaning up list of fastest mirrors
Other repos take up 116 M of disk space (use --verbose for details)
Shared connection to 192.168.200.112 closed.4.copy模块
copy模块用于复制指定主机文件到远程主机的指定位置,常见参数如下
- dest:指出复制文件的目标目录位置,使用绝对路径。如果源是目录,指目标也要是目录,如果目标文件已经存在会覆盖原有内容。
- src:指出源文件的路径,可以使用相对路径或绝对路径,支持直接指定目录,如果源是目录则目标也要是目录
- mode:指出复制时,目标文件的权限 可选
- owner:指出复制时,目标文件的属主 可选
- group:指出复制时,目标文件的属组 可选
- content:指出复制到目标主机上的内容,不能与src一起使用,相当于复制content指明的数据到目标文件中
特别提示:
参数:backup=yes===>意思是,如果目标路径下,有与我同名但不同内容的文件时,在覆盖前,对目标文件先进行备份。
所有被管理端节点必须安装libselinux-python包
[root@client1 ~]# rpm -q libselinux-python
libselinux-python-2.5-15.el7.x86_64
实验案例
将Rich组中主机的/etc/hosts文件拷贝到/tmp下 指定权限为777 更改属主为Rich更改属组为root
[root@ansible ~]# ansible Rich -m copy -a "src=/etc/hosts dest=/tmp mode=777 owner=Rich group=root"
192.168.2.222 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": true,
"checksum": "7335999eb54c15c67566186bdfc46f64e0d5a1aa",
"dest": "/tmp/hosts",
"gid": 0,
"group": "root",
"md5sum": "54fb6627dbaa37721048e4549db3224d",
"mode": "0777",
"owner": "Rich",
"size": 158,
"src": "/root/.ansible/tmp/ansible-tmp-1597371126.82-11091-132452980530176/source",
"state": "file",
"uid": 1001
}
192.168.2.223 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": true,
"checksum": "7335999eb54c15c67566186bdfc46f64e0d5a1aa",
"dest": "/tmp/hosts",
"gid": 0,
"group": "root",
"md5sum": "54fb6627dbaa37721048e4549db3224d",
"mode": "0777",
"owner": "Rich",
"size": 158,
"src": "/root/.ansible/tmp/ansible-tmp-1597371126.84-11093-220512889812301/source",
"state": "file",
"uid": 1001
}
[root@client1 ~]# ls -l /tmp/hosts
-rwxrwxrwx 1 Rich root 158 8月 14 10:12 /tmp/hosts
[root@client2 ~]# ls -l /tmp/hosts
-rwxrwxrwx 1 Rich root 158 8月 14 10:12 /tmp/hosts5.hostname模块
hostname模块用于管理远程主机上的主机名,常用参数如下
1. name:指明主机名
实验案例
更改client1(192.168.200.112)的主机名为Rich
[root@ansible ~]# ansible 192.168.2.222 -m hostname -a "name=Rich"
192.168.2.222 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"ansible_domain": "",
"ansible_fqdn": "Rich",
"ansible_hostname": "Rich",
"ansible_nodename": "Rich",
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": true,
"name": "Rich"
}client1上查看
[root@client1 ~]# hostname
Rich
注意:更改回来,否则后面如果在测试主机名会报错
[root@ansible ~]# ansible 192.168.2.222 -m hostname -a "name=client1"
192.168.2.222 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"ansible_domain": "",
"ansible_fqdn": "client1",
"ansible_hostname": "client1",
"ansible_nodename": "client1",
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": true,
"name": "client1"
}6.yum模块
Yum模块基于yum机制,对远程主机管理程序包,常用参数如下。
- name:程序包的名称,可以带上版本号,如不指定版本号默认安装为最新版本
- state=present | latest | absent:指明对程序包执行的操作,present表示安装程序包,latest表示安装最新版本的程序包,absent表示卸载程序包
- disablerepo:在用yum安装时禁用某个仓库的ID
- enablerepo:在用yum安装时启用某个参考的ID
- conf_file:yum运行时的配置文件而不是使用默认的配置文件
- diable_gpg_check=yes | no:是否启用完整性校验功能
实验案例
注意实验前要在client端配置yum仓库
管理员只是发送yum命令道被管理端,被管理端要存在可用的yum仓库才可以成功安装
1. client端yum安装bind
[root@ansible ~]# ansible Rich -m yum -a "name=bind state=present"
192.168.2.223 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": true,
"changes": {
"installed": [
"bind"
]
},
"msg": "Non-fatal POSTTRANS scriptlet failure in rpm package 32:bind-9.9.4-72.el7.x86_64\n",
"rc": 0,
"results": [
"Loaded plugins: fastestmirror, langpacks\nLoading mirror speeds from cached hostfile\n * c7-media: \nResol
ving Dependencies\n--> Running transaction check\n---> Package bind.x86_64 32:9.9.4-72.el7 will be installed\n--> Finished Dependency Resolution\n\nDependencies Resolved\n\n================================================================================\n Package Arch Version Repository Size\n================================================================================\nInstalling:\n bind x86_64 32:9.9.4-72.el7 c7-media 1.8 M\n\nTransaction Summary\n================================================================================\nInstall 1 Package\n\nTotal download size: 1.8 M\nInstalled size: 4.5 M\nDownloading packages:\nRunning transaction check\nRunning transaction test\nTransaction test succeeded\nRunning transaction\n Installing : 32:bind-9.9.4-72.el7.x86_64 1/1 \nOSError: No such file or directory\nValueError: SELinux policy is not managed or store cannot be accessed.\nwarning: %posttrans(bind-32:9.9.4-72.el7.x86_64) scriptlet failed, exit status 1\n Verifying : 32:bind-9.9.4-72.el7.x86_64 1/1 \n\nInstalled:\n bind.x86_64 32:9.9.4-72.el7 \n\nComplete!\n" ]
}
192.168.2.222 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": true,
"changes": {
"installed": [
"bind"
]
},
"msg": "Non-fatal POSTTRANS scriptlet failure in rpm package 32:bind-9.9.4-72.el7.x86_64\n",
"rc": 0,
"results": [
"Loaded plugins: fastestmirror, langpacks\nLoading mirror speeds from cached hostfile\n * c7-media: \nResol
ving Dependencies\n--> Running transaction check\n---> Package bind.x86_64 32:9.9.4-72.el7 will be installed\n--> Finished Dependency Resolution\n\nDependencies Resolved\n\n================================================================================\n Package Arch Version Repository Size\n================================================================================\nInstalling:\n bind x86_64 32:9.9.4-72.el7 c7-media 1.8 M\n\nTransaction Summary\n================================================================================\nInstall 1 Package\n\nTotal download size: 1.8 M\nInstalled size: 4.5 M\nDownloading packages:\nRunning transaction check\nRunning transaction test\nTransaction test succeeded\nRunning transaction\n Installing : 32:bind-9.9.4-72.el7.x86_64 1/1 \nOSError: No such file or directory\nValueError: SELinux policy is not managed or store cannot be accessed.\nwarning: %posttrans(bind-32:9.9.4-72.el7.x86_64) scriptlet failed, exit status 1\n Verifying : 32:bind-9.9.4-72.el7.x86_64 1/1 \n\nInstalled:\n bind.x86_64 32:9.9.4-72.el7 \n\nComplete!\n" ]
}
[root@client1 ~]# rpm -q bind
bind-9.9.4-72.el7.x86_647.service模块
Service模块为用来管理远程主机上的服务的模块,常见参数如下:
- name:被管理的服务名称
- state=started | stopped | restarted:动作包含启动关机或重启
- enabled=yes | no:表示是否设置该服务开机自启动
- runlevel:如果设定了enabled开机自启动,则要定义在哪些运行目标下自启动
实验案例
1.启动httpd服务并设置为开启自启动
client准备操作 #如果没有需要进行安装
[root@client1 ~]# rpm -q httpd
httpd-2.4.6-93.el7.centos.x86_64
[root@client2 ~]# rpm -q httpd
httpd-2.4.6-93.el7.centos.x86_64
[root@ansible ~]# ansible Rich -m service -a "name=httpd state=started enabled=yes"
192.168.200.112 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": true,
"enabled": true,
"name": "httpd",
"state": "started",
"status": {
"ActiveEnterTimestampMonotonic": "0",
"ActiveExitTimestampMonotonic": "0",
"ActiveState": "inactive",
"After": "nss-lookup.target -.mount remote-fs.target systemd-journald.socket tmp.mount network.target basic
.target system.slice",
…………………………………… #省略部分内容8.User模块
User模块用于管理远程主机上的用户账户,常见参数如下:
- name:必选参数 账号名称
- state=present | absent:创建账号或者删除账号,present表示创建,absent表示删除
- system=yes | no:是否为系统账号
- uid:用户UID
- group:用户的基本组
- groups:用户的附加组
- shell:默认使用的shell
- home:用户的家目录
- move_home=yes | no:如果设置的家目录已经存在,是否将已经存在的家目录进行移动
- password:用户的密码,建议使用加密后的字符串
- comment:用户的注释信息
- remove=yes | no:当state=absent时,是否删除用户的家目录
实验案例
1. 创建用户
[root@ansible ~]# ansible Rich -m user -a 'name=user1 system=yes uid=502 group=root groups=sshd shell=/sbin/nologin home=/home/user1 password=user1 comment="test user"' #ansible 命令字 对Rich组进行操作 -m 指定模块为user -a 信息 ‘用户名为user1 是系统账号 uid是502 用户的基本组是root 附加组是sshd shell是/sbin/nologin 家目录是/home/user1 注释信息是测试用户’
[WARNING]: The input password appears not to have been hashed. The 'password' argument must be encrypted for this
module to work properly.
192.168.2.223 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": true,
"comment": "test user",
"create_home": true,
"group": 0,
"groups": "sshd",
"home": "/home/********",
"name": "VALUE_SPECIFIED_IN_NO_LOG_PARAMETER",
"password": "NOT_LOGGING_PASSWORD",
"shell": "/sbin/nologin",
"state": "present",
"system": true,
"uid": 502
}
192.168.2.222 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": true,
"comment": "test user",
"create_home": true,
"group": 0,
"groups": "sshd",
"home": "/home/********",
"name": "VALUE_SPECIFIED_IN_NO_LOG_PARAMETER",
"password": "NOT_LOGGING_PASSWORD",
"shell": "/sbin/nologin",
"state": "present",
"system": true,
"uid": 502
}
[root@client1 ~]# tail -1 /etc/passwd
user1:x:502:0:test user:/home/user1:/sbin/nologin
[root@client2 ~]# tail -1 /etc/passwd
user1:x:502:0:test user:/home/user1:/sbin/nologin2. 删除用户及家目录
[root@ansible ~]# ansible Rich -m user -a 'name=user1 state=absent remove=yes'
192.168.2.223 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": true,
"force": false,
"name": "user1",
"remove": true,
"state": "absent",
"stderr": "userdel: user1 邮件池 (/var/spool/mail/user1) 未找到\n",
"stderr_lines": [
"userdel: user1 邮件池 (/var/spool/mail/user1) 未找到"
]
}
192.168.2.222 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": true,
"force": false,
"name": "user1",
"remove": true,
"state": "absent",
"stderr": "userdel: user1 邮件池 (/var/spool/mail/user1) 未找到\n",
"stderr_lines": [
"userdel: user1 邮件池 (/var/spool/mail/user1) 未找到"
]
}
[root@client1 ~]# tail -1 /etc/passwd
named:x:25:25:Named:/var/named:/bin/false9.script模块
script模块能够实现远程服务器批量运行本地的shell脚本
所有被管理端需要挂载光盘,并创建本地yum仓库文件
[root@ansible ~]# vim /opt/file20.sh
#!/bin/bash
touch /tmp/file{1..20}.txt
[root@ansible ~]# ansible Rich -m script -a "/opt/file20.sh"
192.168.200.112 | CHANGED => {
"changed": true,
"rc": 0,
"stderr": "Shared connection to 192.168.200.112 closed.\r\n",
"stderr_lines": [
"Shared connection to 192.168.200.112 closed."
],
"stdout": "",
"stdout_lines": []
}
192.168.200.113 | CHANGED => {
"changed": true,
"rc": 0,
"stderr": "Shared connection to 192.168.200.113 closed.\r\n",
"stderr_lines": [
"Shared connection to 192.168.200.113 closed."
],
"stdout": "",
"stdout_lines": []
}
[root@client1 ~]# ls /tmp/
file10.txt file17.txt file4.txt systemd-private-9e4d0685272b4012a7bf002b6e2de6e7-chronyd.service-iv8Fn6
file11.txt file18.txt file5.txt systemd-private-9e4d0685272b4012a7bf002b6e2de6e7-cups.service-btJJf2
file12.txt file19.txt file6.txt systemd-private-9e4d0685272b4012a7bf002b6e2de6e7-httpd.service-w14lQM
file13.txt file1.txt file7.txt vmware-root_8657-1722094600
file14.txt file20.txt file8.txt
file15.txt file2.txt file9.txt
file16.txt file3.txt hosts