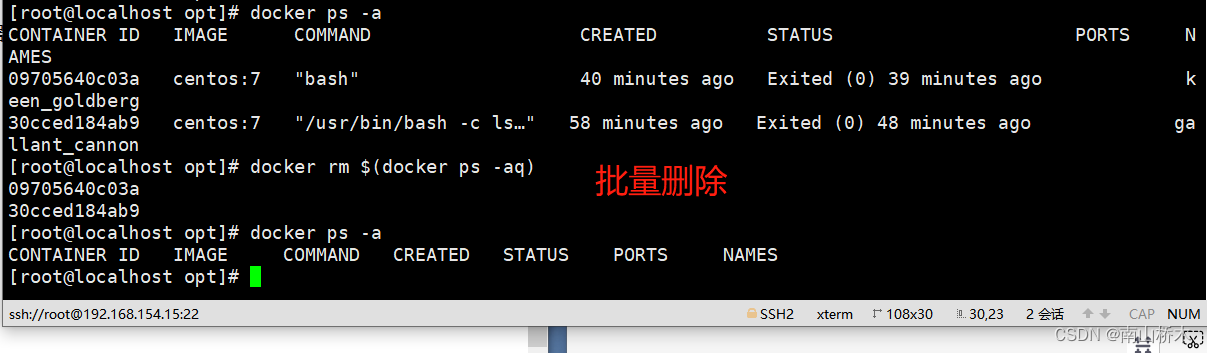
对ArrayList中的元素进行排序的几种方式
一、使用Collections工具类
1、对基本类型排序
通过Collections.sort()对基本类型排序默认是以升序排序
// 1.Collections.sort()默认按照升序排序
List<Integer> integerList = new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(integerList,1,2,6,5,5,4,55,4,5,5,4,5,2,4,6,2,45);
Collections.sort(integerList);
System.out.println(integerList);
2、对字符串类型排序
对字符串类型排序默认按照首字母a-z排序
// 2.对字符串类型排序
List<String> strings = new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(strings,"d","gsf","trh","fsd","an");
Collections.sort(strings);
System.out.println(strings);
3、对对象排序
如何使用Collections对对象排序呢?
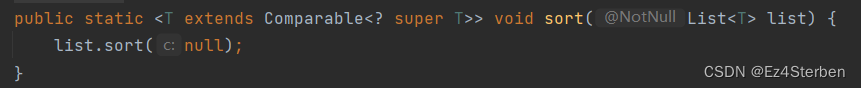
其实只需要让我们的数据类型实现Comparable接口即可,下面定义一个实现Comparable接口的学生类,并且实现compareTo方法,让学生类只比较年龄。
/**
* 学生
*
* @author ez4sterben
* @date 2023/07/18
*/
public class Student implements Comparable<Student> {
private String id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
private String sex;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"age=" + age +
'}';
}
public Student(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getSex() {
return sex;
}
public void setSex(String sex) {
this.sex = sex;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Student o) {
// 这种是升序
return this.getAge() - o.getAge();
// 这种是降序
// return o.getAge() - this.getAge();
}
}
排序方法和正常使用一样,直接把整个list传入即可
// 3.对对象排序
List<Student> students = new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(students,
new Student(18),
new Student(26),
new Student(20),
new Student(16),
new Student(12));
System.out.println(students);
Collections.sort(students);
System.out.println(students);

二、使用stream流
// 2.lambda表达式
Stream<Integer> sorted = integerList.stream().sorted();
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(sorted.toArray()));

三、使用排序算法(以冒泡排序为例)
// 3.直接使用排序算法(以冒泡排序为例)
for(int i = 0; i < integerList.size() - 1; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < integerList.size() - i - 1; j++){
if(integerList.get(j) > integerList.get(j + 1)){
Integer temp = integerList.get(j);
integerList.set(j, integerList.get(j + 1));
integerList.set(j + 1, temp);
}
}
}
System.out.println(integerList);

四、测试类整体代码
import java.util.*;
import java.util.stream.Stream;
/**
* 数组列表排序
*
* @author ez4sterben
* @date 2023/07/19
*/
public class ArrayListSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Integer> integerList = new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(integerList,1,2,6,5,5,4,55,4,5,5,4,5,2,4,6,2,45);
// 1.Collections.sort()默认按照升序排序
Collections.sort(integerList);
System.out.println(integerList);
// 2.对字符串类型排序
List<String> strings = new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(strings,"d","gsf","trh","fsd","an");
Collections.sort(strings);
System.out.println(strings);
// 3.对对象排序
List<Student> students = new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(students,
new Student(18),
new Student(26),
new Student(20),
new Student(16),
new Student(12));
System.out.println(students);
Collections.sort(students);
System.out.println(students);
// 2.lambda表达式
Stream<Integer> sorted = integerList.stream().sorted();
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(sorted.toArray()));
// 3.直接使用排序算法(以冒泡排序为例)
for(int i = 0; i < integerList.size() - 1; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < integerList.size() - i - 1; j++){
if(integerList.get(j) > integerList.get(j + 1)){
Integer temp = integerList.get(j);
integerList.set(j, integerList.get(j + 1));
integerList.set(j + 1, temp);
}
}
}
System.out.println(integerList);
}
}