这里写目录标题
本文章会对Java线性表的相关知识进行讲解,也会以Java代码示例来进行解释 对线性表的讲解分析 定义 可以表示为 线性表可以用多种方式来表示和实现,常见的实现方式包括顺序表和链表两种。
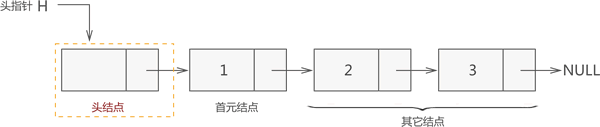
注意 代码实现 在Java中,我们可以使用数组或链表来实现线性表。 使用数组实现线性表: 在Java语言中,我们可以使用数组来实现线性表的增删改查操作线性表的例子: 使用链表实现线性表: 在Java语言中,我们用链表来实现线性表的增删改查操作线性表的例子:
线性表是一种数据结构,它是由一系列具有相同类型的元素组成的有序集合。线性表中的元素按照线性的顺序
排列,每个元素只有一个前驱元素和一个后继元素,除了第一个元素没有前驱元素,最后一个元素没有后继
元素。
表中的元素序列{x1,x2,...,xn},其中xi是表中的元素,它们具有相同的数据类型,n表示表中元素的个数。
线性表满足以下特性:
元素的有序性:线性表中的元素按照线性的顺序排列,每个元素都有一个确定的位置。
有限性:线性表中的元素个数是有限的。
相同数据类型:线性表中的元素具有相同的数据类型,即它们具有相同的属性和操作。
是一种基于数组的实现方式,元素在内存中连续存储,通过下标访问元素,插入和删除操作需要移动其他元素。
是一种通过节点之间的指针来连接的实现方式,节点包含元素和指向下一个节点的指针,可以实现高效的插入
和删除操作,但访问元素的效率相对较低。
线性表作为数据结构中的基本概念,广泛应用于各个领域的算法和程序设计中。掌握线性表的定义和实现方式,
能够帮助我们更好地理解和应用其他数据结构和算法。
线性表是一种常见的数据结构,它由一系列元素组成,这些元素之间存在着一对一的前后关系。线性表中的元
素可以是任何类型的数据,如整数、字符或对象等。
线性表中的元素排列有序,每个元素都有一个直接前驱元素和一个直接后继元素,除了第一个元素没有前驱元
素,最后一个元素没有后继元素。
线性表的访问方式可以根据元素在表中的位置进行操作,如按索引访问、插入、删除等。其中,按索引访问是
通过元素在表中的位置(索引)来获取对应的元素值。插入和删除可以在指定的位置上插入新的元素或者移除
现有的元素。
线性表有很多种实现方式,常见的包括数组和链表。数组作为一种静态数据结构,需要提前声明一个固定大小
的空间来存储元素,操作灵活性较差。链表则以节点的形式存储元素,每个节点包含了数据及指向下一个节点
的指针,操作相对灵活,但涉及到频繁的内存分配和释放。
线性表常用的算法包括遍历、查找和排序等。遍历操作用于依次访问线性表中的所有元素。查找操作可以根据
某个条件查找满足要求的元素,常见的方法有线性查找和二分查找。排序操作可以将线性表中的元素按照一定
的规则进行排列,常见的排序算法有冒泡排序、插入排序和快速排序等。
总之,线性表是一种简单、常用的数据结构,能够有效地组织和处理大量的数据,广泛应用于各个领域的算法
与程序设计中。
public class ArrayList {
private int size;
private Object[ ] array;
public ArrayList ( ) {
this . size = 0 ;
this . array = new Object [ 10 ] ;
}
public void add ( Object item ) {
if ( size == array. length) {
Object[ ] newArray = new Object [ array. length * 2 ] ;
System. arraycopy ( array, 0 , newArray, 0 , size) ;
array = newArray;
}
array[ size++ ] = item;
}
public Object get ( int index) {
if ( index >= 0 && index < size) {
return array[ index] ;
} else {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException ( ) ;
}
}
public int size ( ) {
return size;
}
}
public class MyArrayList {
private Object [ ] array;
private int size;
private int capacity;
public MyArrayList ( ) {
capacity = 10 ;
array = new Object [ capacity] ;
size = 0 ;
}
public int getSize ( ) {
return size;
}
public boolean isEmpty ( ) {
return size == 0 ;
}
public void add ( Object element) {
if ( size == capacity) {
increaseCapacity ( ) ;
}
array[ size] = element;
size++ ;
}
public void remove ( int index) {
if ( index < 0 || index >= size) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException ( "Index out of range" ) ;
}
for ( int i = index; i < size - 1 ; i++ ) {
array[ i] = array[ i + 1 ] ;
}
array[ size - 1 ] = null ;
size-- ;
}
public void set ( int index, Object element) {
if ( index < 0 || index >= size) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException ( "Index out of range" ) ;
}
array[ index] = element;
}
public Object get ( int index) {
if ( index < 0 || index >= size) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException ( "Index out of range" ) ;
}
return array[ index] ;
}
public boolean contains ( Object element) {
for ( int i = 0 ; i < size; i++ ) {
if ( array[ i] . equals ( element) ) {
return true ;
}
}
return false ;
}
private void increaseCapacity ( ) {
capacity *= 2 ;
Object [ ] newArray = new Object [ capacity] ;
for ( int i = 0 ; i < size; i++ ) {
newArray[ i] = array[ i] ;
}
array = newArray;
}
}
使用示例:
public class Main {
public static void main ( String [ ] args) {
MyArrayList list = new MyArrayList ( ) ;
list. add ( "A" ) ;
list. add ( "B" ) ;
list. add ( "C" ) ;
System . out. println ( "Size: " + list. getSize ( ) ) ;
list. remove ( 1 ) ;
System . out. println ( "Size: " + list. getSize ( ) ) ;
list. set ( 0 , "D" ) ;
System . out. println ( list. get ( 0 ) ) ;
System . out. println ( list. contains ( "C" ) ) ;
}
}
public class LinkedList {
private Node head;
private int size;
private class Node {
Object data;
Node next;
public Node ( Object data) {
this . data = data;
this . next = null ;
}
}
public LinkedList ( ) {
this . head = null ;
this . size = 0 ;
}
public void add ( Object item) {
Node newNode = new Node ( item) ;
if ( head == null ) {
head = newNode;
} else {
Node current = head;
while ( current. next != null ) {
current = current. next;
}
current. next = newNode;
}
size++ ;
}
public Object get ( int index) {
if ( index >= 0 && index < size) {
Node current = head;
for ( int i = 0 ; i < index; i++ ) {
current = current. next;
}
return current. data;
} else {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException ( ) ;
}
}
public int size ( ) {
return size;
}
}
代码演示了使用链表实现线性表的增加、删除、修改和查询操作,并使用
MyLinkedList类来实现这些功能。你可以根据需要进一步扩展和优化这个实现。
public class ListNode {
Object data;
ListNode next;
public ListNode ( Object data) {
this . data = data;
this . next = null ;
}
}
public class MyLinkedList {
private ListNode head;
private int size;
public MyLinkedList ( ) {
head = null ;
size = 0 ;
}
public int getSize ( ) {
return size;
}
public boolean isEmpty ( ) {
return size == 0 ;
}
public void add ( Object element) {
ListNode newNode = new ListNode ( element) ;
if ( head == null ) {
head = newNode;
} else {
ListNode current = head;
while ( current. next != null ) {
current = current. next;
}
current. next = newNode;
}
size++ ;
}
public void remove ( int index) {
if ( index < 0 || index >= size) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException ( "Index out of range" ) ;
}
if ( index == 0 ) {
head = head. next;
} else {
ListNode previous = getNode ( index - 1 ) ;
ListNode current = previous. next;
previous. next = current. next;
}
size-- ;
}
public void set ( int index, Object element) {
if ( index < 0 || index >= size) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException ( "Index out of range" ) ;
}
ListNode node = getNode ( index) ;
node. data = element;
}
public Object get ( int index) {
if ( index < 0 || index >= size) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException ( "Index out of range" ) ;
}
ListNode node = getNode ( index) ;
return node. data;
}
public boolean contains ( Object element) {
ListNode current = head;
while ( current != null ) {
if ( current. data. equals ( element) ) {
return true ;
}
current = current. next;
}
return false ;
}
private ListNode getNode ( int index) {
ListNode current = head;
for ( int i = 0 ; i < index; i++ ) {
current = current. next;
}
return current;
}
}
使用示例:
public static void main ( String [ ] args) {
MyLinkedList list = new MyLinkedList ( ) ;
list. add ( "A" ) ;
list. add ( "B" ) ;
list. add ( "C" ) ;
System . out. println ( "Size: " + list. getSize ( ) ) ;
list. remove ( 1 ) ;
System . out. println ( "Size: " + list. getSize ( ) ) ;
list. set ( 0 , "D" ) ;
System . out. println ( list. get ( 0 ) ) ;
System . out. println ( list. contains ( "C" ) ) ;
}