STL算法篇之拷贝修改类算法
- 拷贝类算法
- copy与copy_backward
- remove与remove_copy
- remove_if与remove_copy_if
- 修改类算法
- replace与replace_copy
- replace_if与replace_copy_if
- iter_swap与swap与swap_range、
- unique与unique_copy
拷贝类算法
1.copy 区间拷贝
2.copy_backward 逆向拷贝
3.remove 删除
4.remove_copy 删除另存
5.remove_if 条件删除
6.remove_copy_if 条件删除结果另存
copy与copy_backward
这两个函数的前两个参数,表示被拷贝迭代器的范围,
第三个参数有所区别,
copy的第三个参数是迭代器的初始位置(正向拷贝),
copy_backward的第三个参数是迭代器的末位置(反向拷贝)注意:这里的反向拷贝指的是拷贝的位置反向,不是说将拷贝的数据反向
#include<iostream>
#include<functional>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
#include<array>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
array<int, 4> v1 = { 1, 2, 3,4 };
vector<int> v2(v1.size()); //copy
vector<int> v3(v1.size()); //copy_backward
copy(v1.begin(), v1.end(), v2.begin());
/*for (auto& v: v2)
{
cout << v;
}*/
for_each(v2.begin(), v2.end(), [](int& date) {cout << " " << date; });
cout << endl;
copy_backward(v1.begin(), v1.end(), v3.end());
copy(v3.begin(), v3.end(), ostream_iterator<int>(cout, " "));
//copy函数与流型迭代器的结合打印数据
return 0;
}
容器数据的打印方法有很多
1.可以用auto关键字的范围for循环
2.可以用for_each()算法
3.可以用copy()函数与流型迭代器相结合
4.可以采用迭代器的方式去打印
remove与remove_copy
注意:这remove删除,并不是真正意义上的删除**(如果想真正意义上的删除,再用一个尾删就行**),他只是把删除的数据覆盖,但是容器元素的个数是没有改变的。
remove_copy 将删除的结果另存,倒是可以做到真正意义上的删除
#include<iostream>
#include<functional>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
#include<array>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
vector<int> v1 = { 1, 2, 3 ,4, 5, 6 };
vector<int> v2(v1.size());
vector<int> ::iterator it = remove(v1.begin(), v1.end(), 2);
for_each(v1.begin(), v1.end(), [](int& date) {cout << date << " "; });
return 0;
}
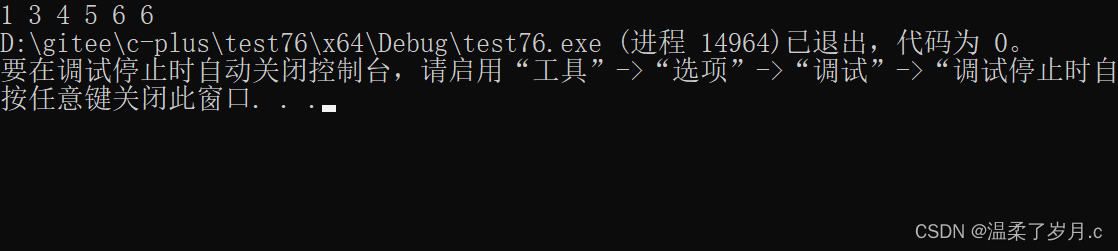
#include<iostream>
#include<functional>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
#include<array>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
vector<int> v1 = { 1, 2, 3 ,4, 5, 6 };
vector<int> v2(v1.size() - 1);
vector<int> ::iterator it = remove(v1.begin(), v1.end(), 2);
for_each(v1.begin(), v1.end(), [](int& date) {cout << date << " "; });
cout << endl;
auto it1 = remove_copy(v1.begin(), v1.end(), v2.begin(), 3);
for_each(v2.begin(), v2.end(), [](int& date) {cout << date << " "; });
return 0;
}
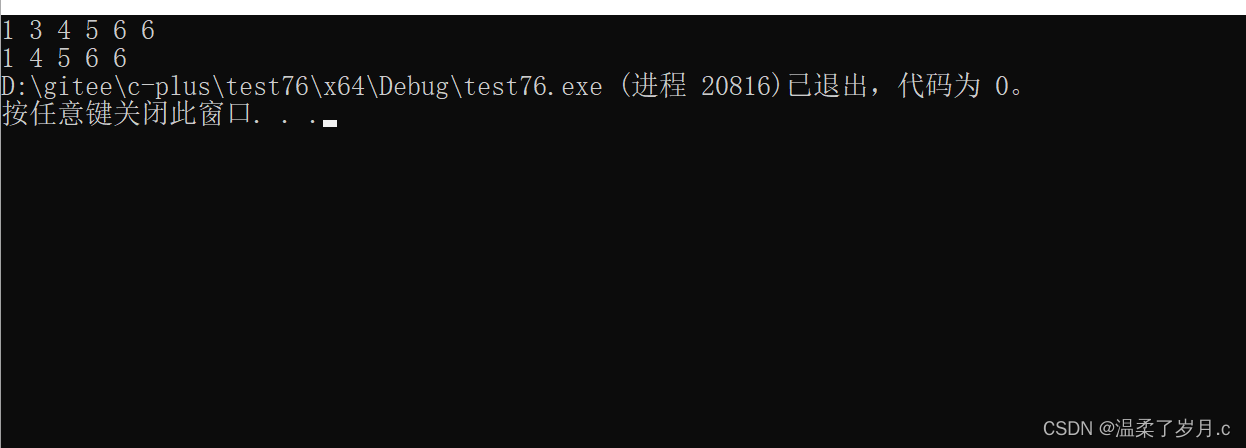
remove_if与remove_copy_if
#include<iostream>
#include<functional>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
#include<array>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
vector<int> v1 = { 1, 2, 3 ,4, 5, 6 };
vector<int> v2(v1.size() - 2);
vector<int> ::iterator it = remove_if(v1.begin(), v1.end(), [](int& date) {return date % 2 == 0; });
//将所有的偶数覆盖,当然也不是真正意义上的删除,只是单纯的数据覆盖,容器的元素个数不变
for_each(v1.begin(), v1.end(), [](int& date) {cout << date << " ";});
cout << endl;
//真正意义上的删除
auto it1 = remove_copy_if(v1.begin(), v1.end(), v2.begin(), [](int& date) {return date % 2 == 0; });
for_each(v2.begin(), v2.end(), [](int& date) {cout << date << " "; });
return 0;
}
修改类算法
1.replace 修改
2. replace_copy 修改结果另存
3.replace_if 条件替换
4.replace_copy_if 条件替换,结果另存
5.iter_swap 迭代器交换
6.swap 容器交换
7.swap_range 区间交换
8.unique: 去重操作
unique_copy: 去重结果另存
replace与replace_copy
replace 前两个参数是迭代器范围,第三个参数是容器中要被替换的数据,第四个参数是数据
replace_copy 结果另存,就加了个另存容器的初位置
#include<iostream>
#include<functional>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
#include<array>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
vector<int> v1 = { 1, 2, 3,4, 5, 6 };
vector<int> v2(v1.size());
replace(v1.begin(), v1.end(), 1, 99);
copy(v1.begin(), v1.end(), ostream_iterator<int>(cout, " "));
cout << endl;
replace_copy(v1.begin(), v1.end(), v2.begin(), 2, 888);
copy(v2.begin(), v2.end(), ostream_iterator<int>(cout, " "));
return 0;
}
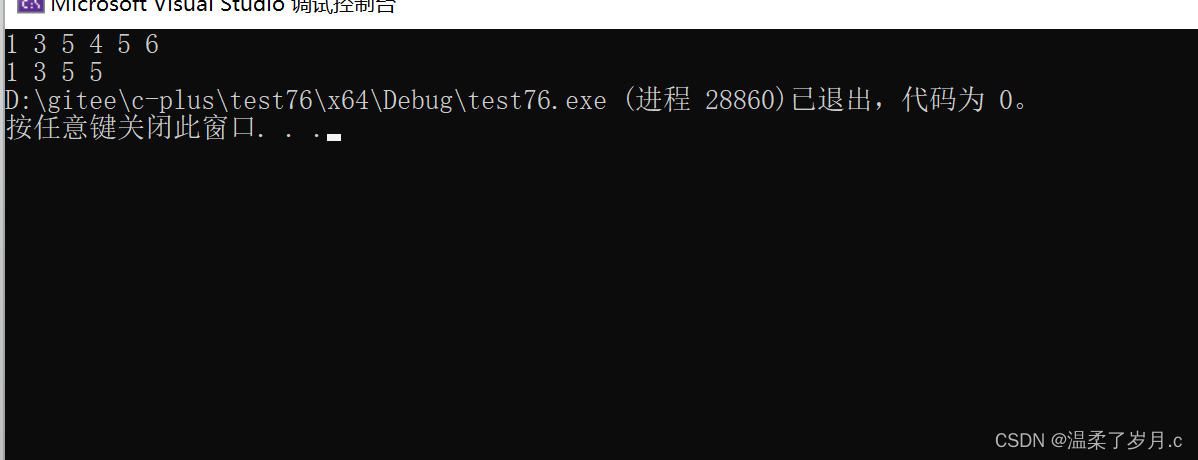
replace_if与replace_copy_if
也就是一个条件替换,条件和一个条件替换另存
#include<iostream>
#include<functional>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
#include<array>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
vector<int> v1 = { 1, 2, 3,4, 5, 6 };
vector<int> v2(v1.size());
replace_if(v1.begin(), v1.end(), [](int& date) {return date % 2 == 0; }, 99);
copy(v1.begin(), v1.end(), ostream_iterator<int>(cout, " "));
cout << endl;
replace_copy_if(v1.begin(), v1.end(), v2.begin(), [](int& date) {return date % 2 == 0; }, 888);
copy(v2.begin(), v2.end(), ostream_iterator<int>(cout, " "));
return 0;
iter_swap与swap与swap_range、
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<functional>
#include<algorithm>
#include<list>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
//iter_swap 迭代器的交换 就是将迭代器中元素的位置进行交换
//注意;在list容器中,如果用 end() -1 会报错
//这个时候,为了解决这一个问题,可以采用 advance()函数,将元素移动 -1个距离
//advance的第一个参数是迭代器类型的位置,第二个参数是移动的距离,可以为负数
list<int> list1 = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
list<int> ::iterator it = list1.end();
advance(it, -1);
iter_swap(list1.begin(), it);
copy(list1.begin(), list1.end(), ostream_iterator<int>(cout, " "));
cout << endl;
// swap 迭代器交换
//参数为2个容器的对象
list<int> list2 = { 99, 99, 2 };
cout << "交换前 :";
copy(list1.begin(), list1.end(), ostream_iterator<int>(cout, " "));
cout << endl;
copy(list2.begin(), list2.end(), ostream_iterator<int>(cout, " "));
cout << endl;
swap(list1, list2);
cout << "交换后 :";
copy(list1.begin(), list1.end(), ostream_iterator<int>(cout, " "));
cout << endl;
copy(list2.begin(), list2.end(), ostream_iterator<int>(cout, " "));
//swap_ranges 区间交换
cout << endl;
vector<int> v1 = { 1,23, 4, 5 };
vector<int> v2 = { 9, 8 , 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1 };
swap_ranges(v1.begin(), v1.begin() + 2, v2.begin());
for (auto& v : v1)
{
cout << v << " ";
}
cout << endl;
for (auto& v : v2)
{
cout << v << " ";
}
return 0;
}
unique与unique_copy
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<functional>
#include<algorithm>
#include<list>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
// unique 去重
// 注意:这个函数去重,感觉其实挺鸡肋的,因为它不能够将所有元素去重,只能够实现部分去重
vector<int> v1 = { 1, 1, 3,4 ,4, 4, 4, 4, 4,5 ,5 ,6 ,6 ,7, 8, 8 };
unique(v1.begin(), v1.end());
for (auto& v : v1)
{
cout << v << " ";
}
//unique_copy
//unique_copy倒是可以实现所有元素去重
//不过去重的元素必须是要有序的,不然就会报错
vector<int> v2 = { 1, 1, 3,4 ,4, 4, 4, 4, 4,5 ,5 ,6 ,6 ,7, 8, 8 };
vector<int> v3(v2.size());
cout << endl;
unique_copy(v2.begin(), v2.end(), v3.begin());
for (auto& v : v3)
{
cout << v << " ";
}
return -0;
}