博客系统
- 前言
- 一.准备工作
- 1.1 准备好前端文件
- 1.2 设计数据库
- 1.3 编写基本的数据库代码
- 1.4 封装好数据库的连接操作
- 1.5 根据设计的表创建实体类
- 1.6 根据实体类,提供一些简单的增删改查操作
- 二.博客要实现的功能
- 2.1 博客列表页功能
- 2.2 博客详情页
- 2.3 博客登录页
- 2.4 页面强制登录功能
- 2.5 显示用户功能
- 2.6 退出登录功能
- 2.7 发布博客功能
前言
这篇博客相当于是,根据前面的所学的知识,来做一个综合练习
一.准备工作
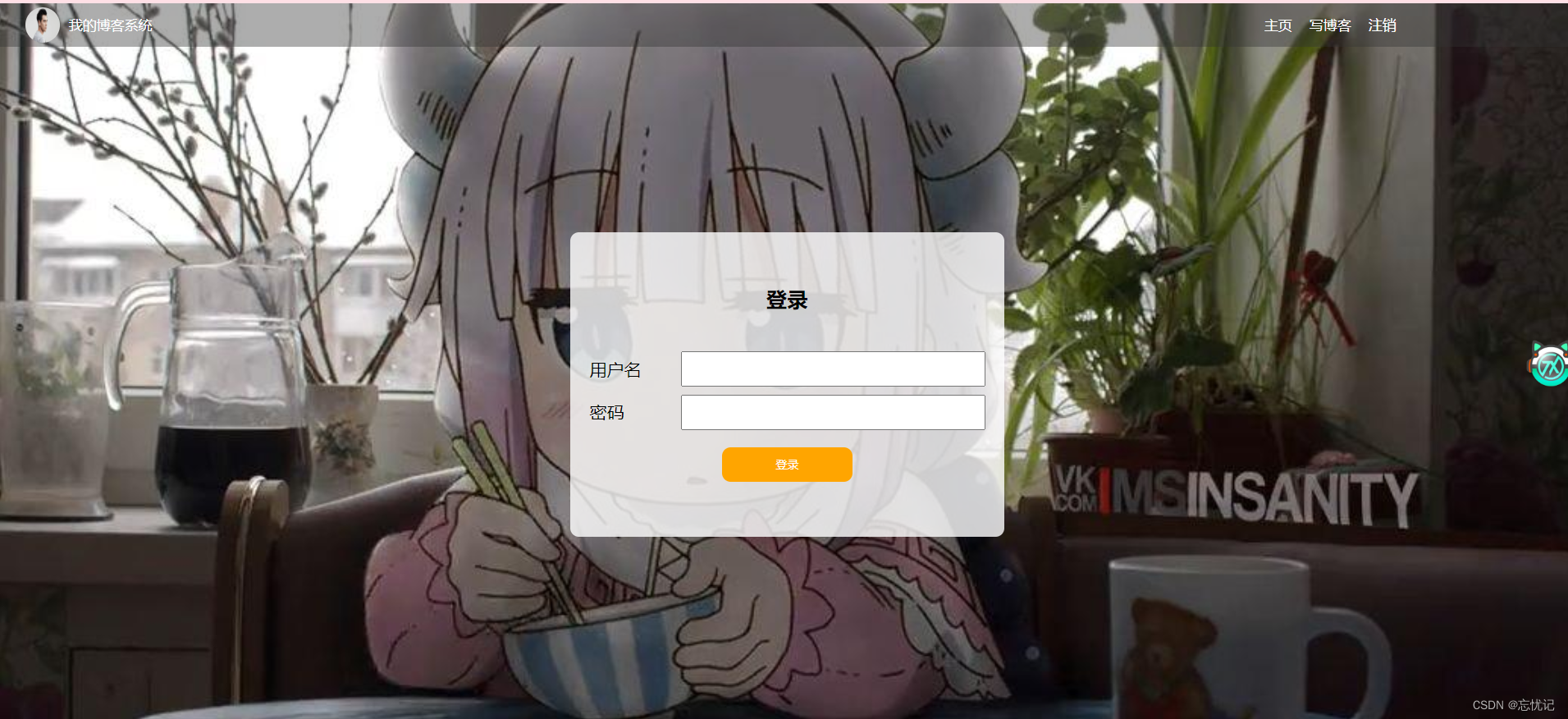
1.1 准备好前端文件
登录页:
列表详情页: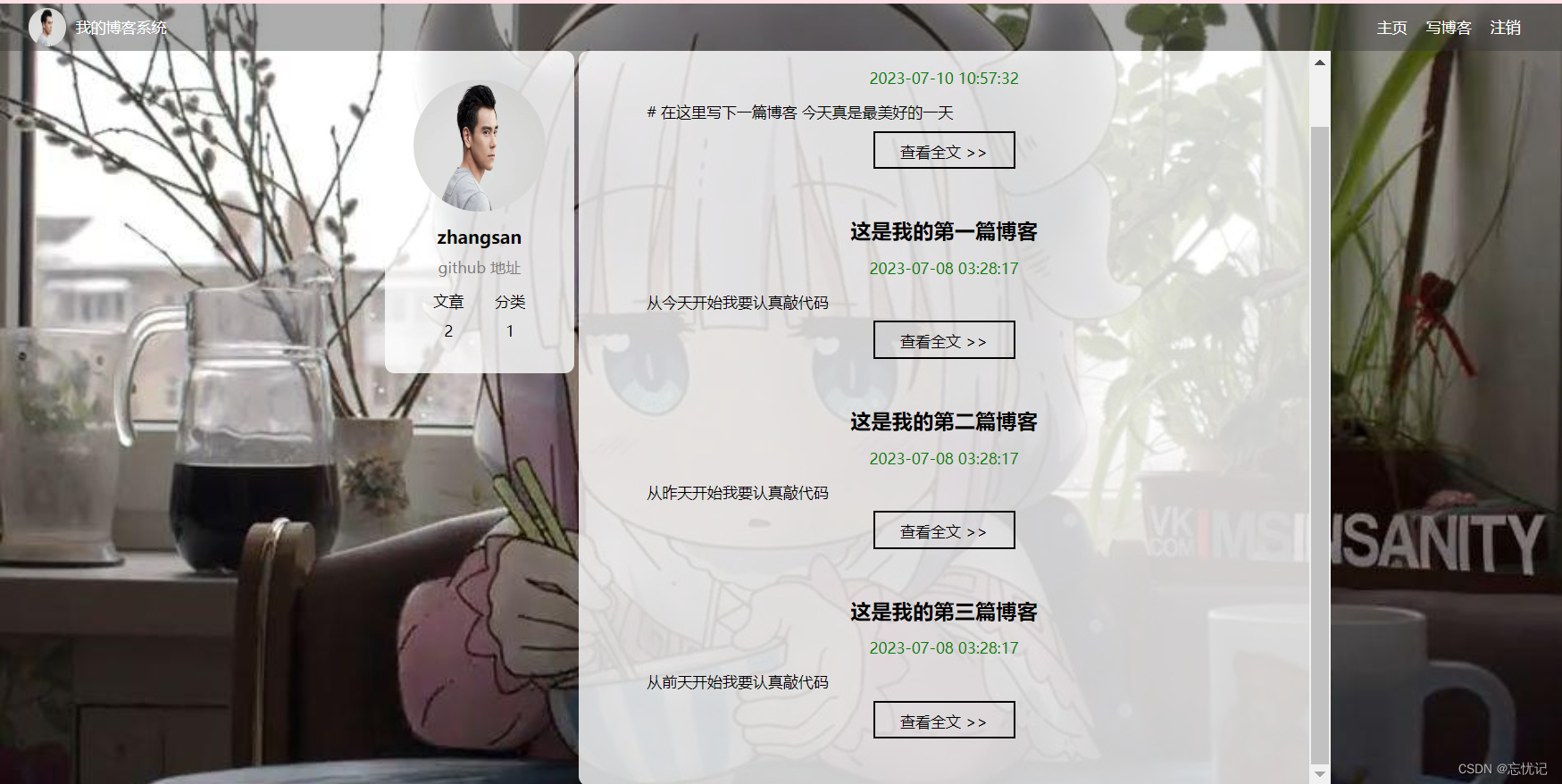
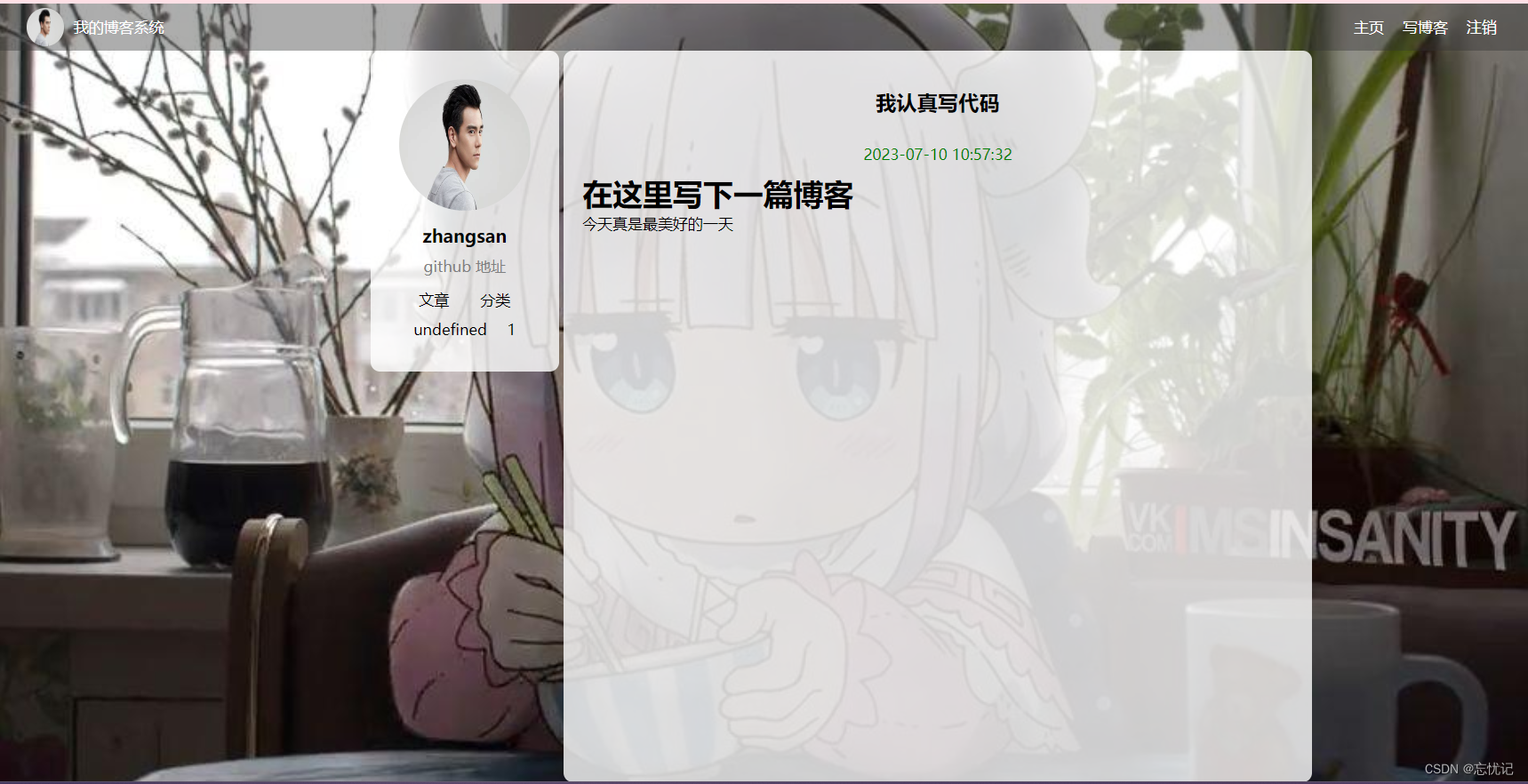
博客详情页
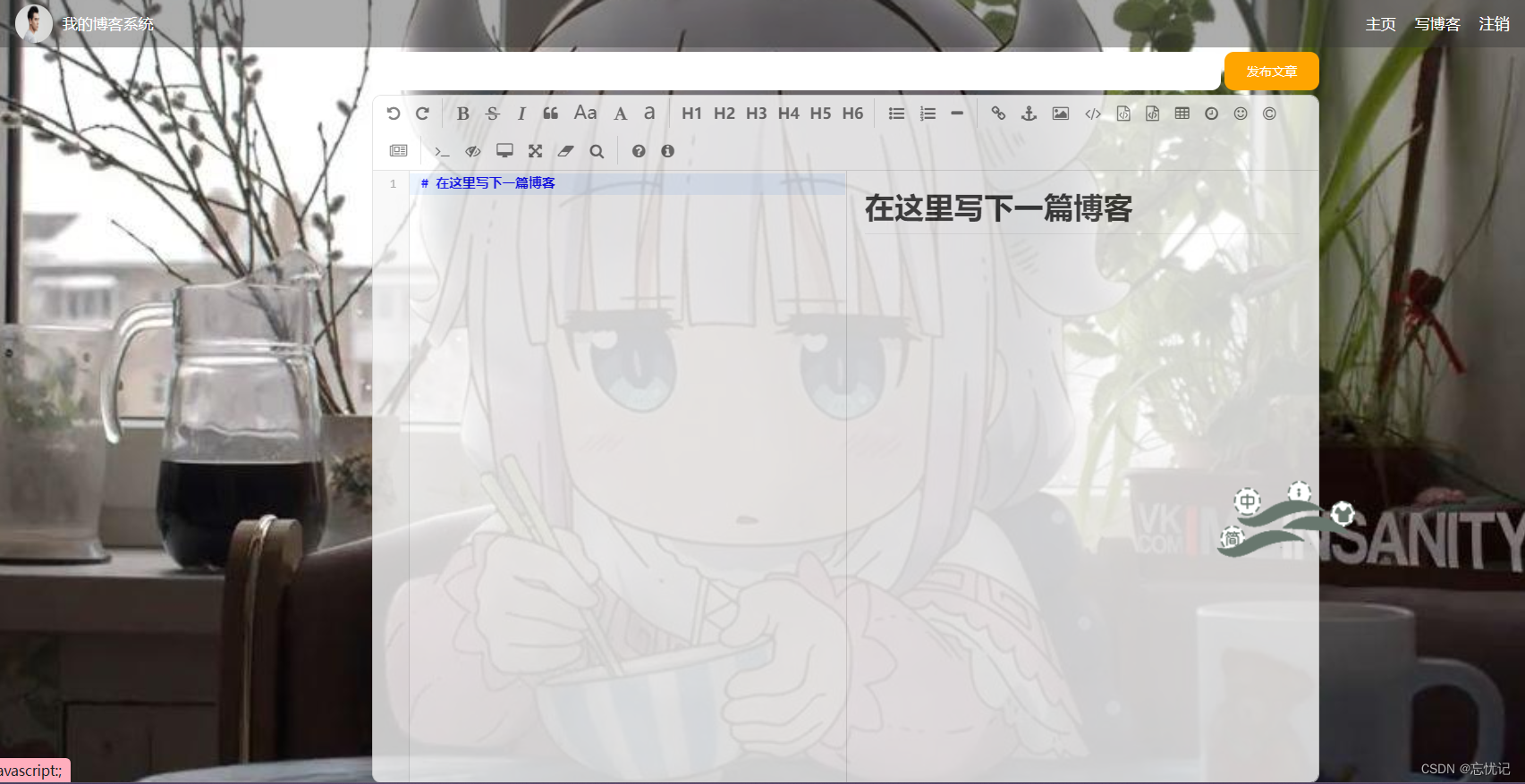
博客编辑页
1.2 设计数据库
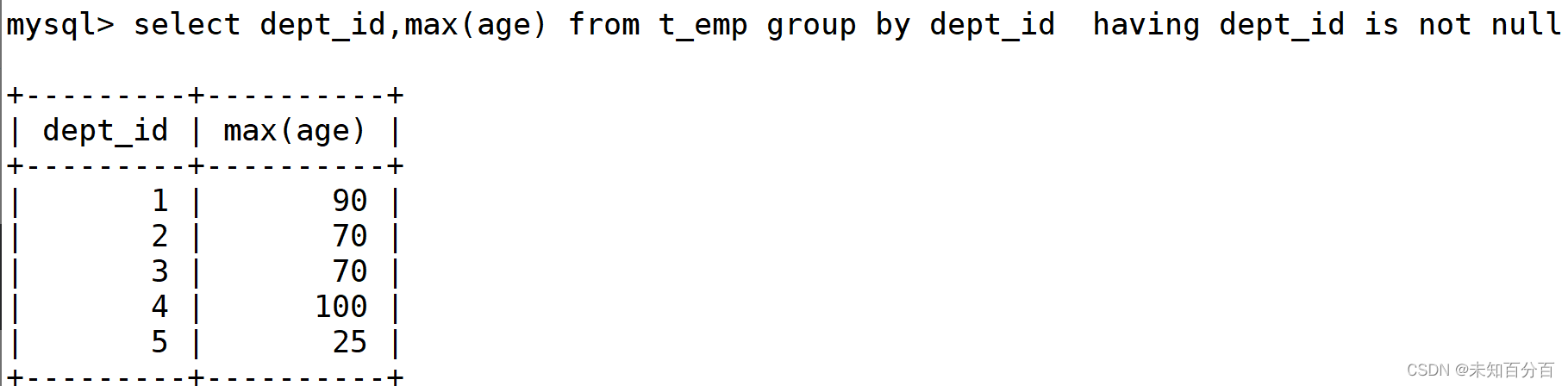
因为是博客管理系统,我们涉及数据库的话,这个两个表的结构如下:
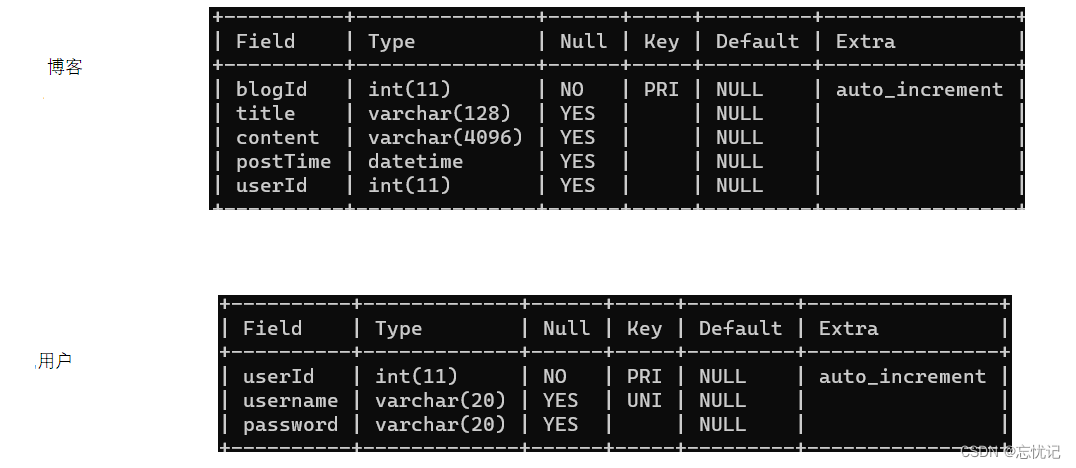
1.3 编写基本的数据库代码
列出数据库的基本代码.
-- 这个文件主要用来写建库建表语句.
-- 一般都建议大家, 在建表的时候把建表 sql 保留下来. 以备后续部署其他机器的时候就方便了.
create database if not exists java_blog_system;
use java_blog_system;
-- 删除旧表, 重新创建新表. 删除旧表是为了防止之前的残留数据对后续的程序有负面影响.
drop table if exists user;
drop table if exists blog;
-- 真正创建表.
create table blog (
blogId int primary key auto_increment,
title varchar(128),
content varchar(4096),
postTime datetime,
userId int
);
create table user (
userId int primary key auto_increment,
username varchar(20) unique, -- 要求用户名和别人不重复~~
password varchar(20)
);
-- 构造测试数据
insert into blog values(1, '这是我的第一篇博客', '从今天开始我要认真敲代码', now(), 1);
insert into blog values(2, '这是我的第二篇博客', '从昨天开始我要认真敲代码', now(), 1);
insert into blog values(3, '这是我的第三篇博客', '从前天开始我要认真敲代码', now(), 1);
-- 构造测试数据
insert into user values(1, 'zhangsan', '123');
insert into user values(2, 'lisi', '123');
1.4 封装好数据库的连接操作
我们会对数据库有基本的操作.
package model;
import com.mysql.jdbc.jdbc2.optional.MysqlDataSource;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
/**
* @author <a href="mailto:1065043594@qq.com">ChenJiaYi</a>
* @CreateDate 2023/7/7
* @ProjectDetails [项目简述]
*/
public class DBUtil {
private static DataSource dataSource = new MysqlDataSource();
static {
((MysqlDataSource) dataSource).setUrl("jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/java_blog_system?characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=false");
((MysqlDataSource) dataSource).setUser("root");
((MysqlDataSource) dataSource).setPassword("123456");
}
public static Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
return dataSource.getConnection();
}
public static void close(Connection connection, PreparedStatement statement, ResultSet resultSet) {
if (resultSet != null) {
try {
resultSet.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (statement != null) {
try {
statement.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (connection != null) {
try {
connection.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
1.5 根据设计的表创建实体类
Blog表 =>Blog类对应的Blog的一个对象,就对应表中的一个记录
User表 => User类对应的User的一个对象,就对应表中的一个记录
实体类有哪些属性都跟表中的东西一一对应的
实体类如下:
Blog类
package model;
/**
* @author <a href="mailto:1065043594@qq.com">ChenJiaYi</a>
* @CreateDate 2023/7/7
* @ProjectDetails [项目简述]
*/
import java.sql.Timestamp;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
public class Blog {
private int blogId;
private String title;
private String content;
private Timestamp postTime;
private int userId;
public int getBlogId() {
return blogId;
}
public void setBlogId(int blogId) {
this.blogId = blogId;
}
public String getTitle() {
return title;
}
public void setTitle(String title) {
this.title = title;
}
public String getContent() {
return content;
}
public void setContent(String content) {
this.content = content;
}
public Timestamp getPostTimestamp() {
return postTime;
}
public String getPostTime() {
// 把时间戳转成 格式化 时间.
// 这个类的用法千万不要背, 一定要去查一下.
SimpleDateFormat simpleDateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss");
return simpleDateFormat.format(postTime);
}
public void setPostTime(Timestamp postTime) {
this.postTime = postTime;
}
public int getUserId() {
return userId;
}
public void setUserId(int userId) {
this.userId = userId;
}
}
User类
package model;
/**
* @author <a href="mailto:1065043594@qq.com">ChenJiaYi</a>
* @CreateDate 2023/7/7
* @ProjectDetails [项目简述]
*/
public class User {
private int userId;
private String username;
private String password;
public int getUserId() {
return userId;
}
public void setUserId(int userId) {
this.userId = userId;
}
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
}
1.6 根据实体类,提供一些简单的增删改查操作
首先我们对blog博客类的操作
- 新增一个博客.
- 根据博客 id 来查询指定博客 (博客详情页中)
- 直接查询出数据库中所有的博客列表 (用于博客列表页)
- 删除指定博客
package model;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
// 通过这个类, 封装针对 博客表 的基本操作
// 此处暂时不涉及到修改博客~~ (修改也可以通过 删除/新增 )
public class BlogDao {
// 1. 新增一个博客.
public void add(Blog blog) {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement statement = null;
try {
// 1. 和数据库建立连接
connection = DBUtil.getConnection();
// 2. 构造 SQL
String sql = "insert into blog values(null, ?, ?, ?, ? )";
statement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
statement.setString(1, blog.getTitle());
statement.setString(2, blog.getContent());
statement.setTimestamp(3, blog.getPostTimestamp());
statement.setInt(4, blog.getUserId());
// 3. 执行 sql
statement.executeUpdate();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
DBUtil.close(connection, statement, null);
}
}
// 2. 根据博客 id 来查询指定博客 (博客详情页中)
public Blog selectById(int blogId) {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement statement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
// 1. 和数据库建立连接
connection = DBUtil.getConnection();
// 2. 构造 SQL
String sql = "select * from blog where blogId = ?";
statement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
statement.setInt(1, blogId);
// 3. 执行 SQL
resultSet = statement.executeQuery();
// 4. 遍历结果集合. 由于 blogId 在 blog 表中是唯一的. (主键)
// 此时的查询结果, 要么是没有查到任何数据, 要么只有一条记录!!
// 此处可以不使用 while, 直接 if 判定即可.
if (resultSet.next()) {
Blog blog = new Blog();
blog.setBlogId(resultSet.getInt("blogId"));
blog.setTitle(resultSet.getString("title"));
blog.setContent(resultSet.getString("content"));
blog.setPostTime(resultSet.getTimestamp("postTime"));
blog.setUserId(resultSet.getInt("userId"));
return blog;
}
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// 5. 释放必要的资源
DBUtil.close(connection, statement, resultSet);
}
return null;
}
// 3. 直接查询出数据库中所有的博客列表 (用于博客列表页)
public List<Blog> selectAll() {
List<Blog> blogs = new ArrayList<>();
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement statement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
// 1. 和服务器建立连接.
connection = DBUtil.getConnection();
// 2. 构造 SQL 语句
String sql = "select * from blog order by postTime desc";
statement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
// 3. 执行 SQL
resultSet = statement.executeQuery();
// 4. 遍历结果集合
while (resultSet.next()) {
Blog blog = new Blog();
blog.setBlogId(resultSet.getInt("blogId"));
blog.setTitle(resultSet.getString("title"));
// 注意这里的正文!!! 在博客列表页中, 不需要把整个正文内容都显示出来!!
String content = resultSet.getString("content");
if (content == null) {
content = "";
}
if (content.length() >= 100) {
content = content.substring(0, 100) + "...";
}
blog.setContent(content);
blog.setPostTime(resultSet.getTimestamp("postTime"));
blog.setUserId(resultSet.getInt("userId"));
blogs.add(blog);
}
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
} finally {
DBUtil.close(connection, statement, resultSet);
}
return blogs;
}
// 4. 删除指定博客
public void delete(int blogId) {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement statement = null;
try {
// 1. 和数据库建立连接.
connection = DBUtil.getConnection();
// 2. 构造 SQL
String sql = "delete from blog where blogId = ?";
statement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
statement.setInt(1, blogId);
// 3. 执行 SQL
statement.executeUpdate();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// 4. 关闭
DBUtil.close(connection, statement, null);
}
}
}
二.博客要实现的功能
这里所实现的功能基本我们思路都是这样
1.实际上就是借助ajax给服务器发送一个请求
2.服务器查找数据库获取到博客列表数据,返回给浏览器
3.浏览器再根据数据构造页面内容
基本步骤如下:
1)约定前后端交互接口
2)编写后端代码
3)编写前端代码
2.1 博客列表页功能
这里列表页的逻辑如下.
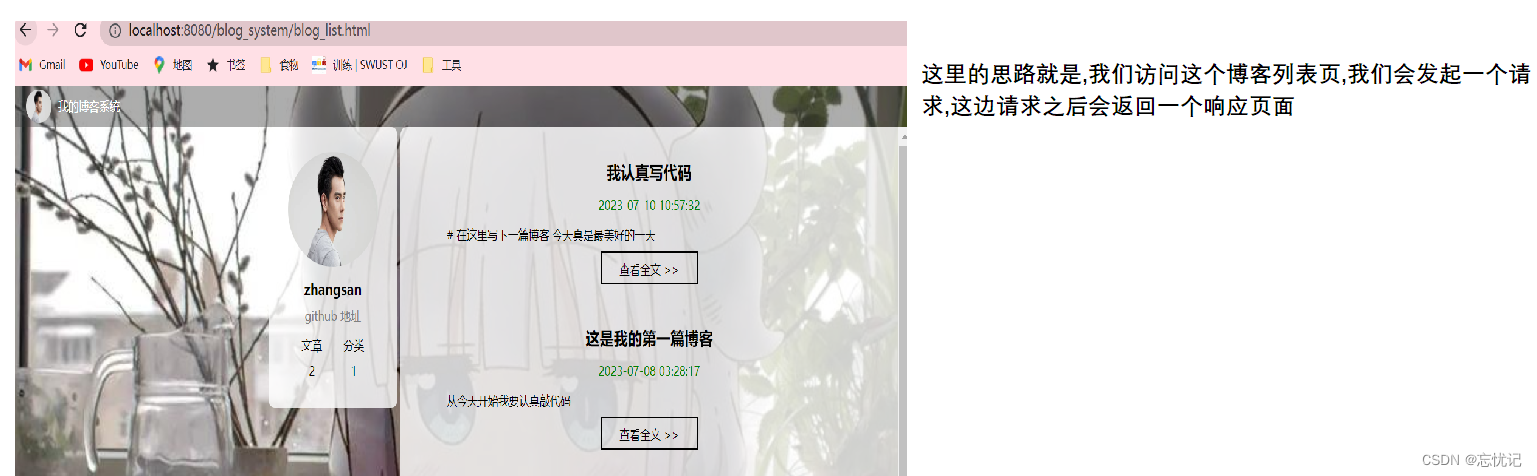
我们具体的步骤如下:
-
约定前后端接口
我们在约定前后端接口之前,我们先回答几个问题?
前端要发什么样子的请求?
后端要返回什么样子的响应?
大概就是如下所示:

-
编写后端代码
后端代码入下:
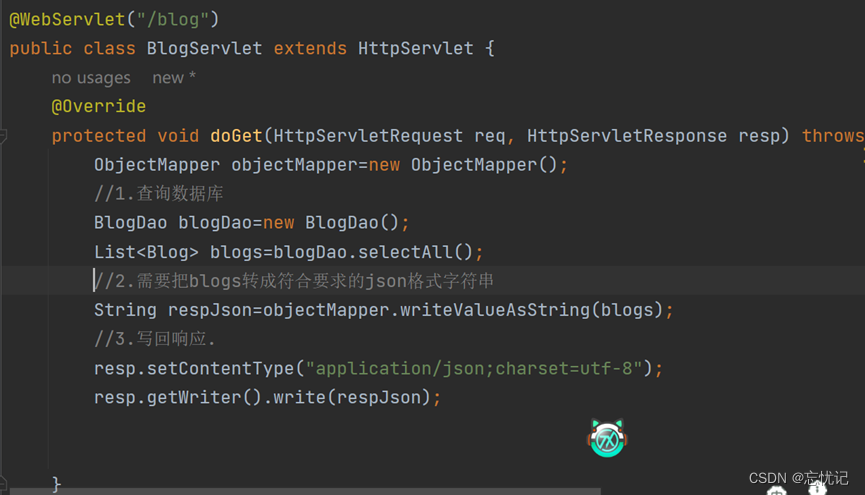
-
编写前端代码
function getBlogs() {
$.ajax({
type: 'get',
url: 'blog',
success: function(body) {
// 响应的正文 是一个 json 字符串, 此处已经被 jquery 自动解析成 js 对象数组了.
// 直接 for 循环遍历即可.
let containerRight = document.querySelector('.container-right');
for (let blog of body) {
// 构造页面内容, 参考之前写好的 html 代码
// 构造整个博客 div
let blogDiv = document.createElement('div');
blogDiv.className = 'blog';
// 构造标题
let titleDiv = document.createElement('div');
titleDiv.className = 'title';
titleDiv.innerHTML = blog.title;
blogDiv.appendChild(titleDiv);
// 构造发布时间
let dateDiv = document.createElement('div');
dateDiv.className = 'date';
dateDiv.innerHTML = blog.postTime;
blogDiv.appendChild(dateDiv);
// 构造 博客 摘要
let descDiv = document.createElement('div');
descDiv.className = 'desc';
descDiv.innerHTML = blog.content;
blogDiv.appendChild(descDiv);
// 构造查看全文按钮
let a = document.createElement('a');
a.innerHTML = '查看全文 >>';
// 期望点击之后能跳转到博客详情页. 为了让博客详情页知道是点了哪个博客, 把 blogId 给传过去
a.href = 'blog_detail.html?blogId=' + blog.blogId;
blogDiv.appendChild(a);
// 把 blogDiv 加到父元素中
containerRight.appendChild(blogDiv);
}
}
});
}
// 要记得调用
getBlogs();
2.2 博客详情页
具体的逻辑如下:
点击”查看全文”按钮,就能够跳转到博客详情页中.
跳转过去之后,在博客详情页中发起一个ajax,从服务器获取当前博客的具体内容.
再显示出来
1)约定前后端接口

2) 编写后端代码
BlogDao blogDao = new BlogDao();
String blogId = req.getParameter("blogId");
private ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
// queryString 存在, 说明本次请求获取的是指定 id 的博客.
Blog blog = blogDao.selectById(Integer.parseInt(blogId));
if (blog == null) {
System.out.println("当前 blogId = " + blogId + " 对应的博客不存在!");
}
String respJson = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(blog);
resp.setContentType("application/json; charset=utf8");
resp.getWriter().write(respJson);
3)编写前端代码
$.ajax({
type: 'get',
url: 'blog' + location.search,
success: function(body) {
// 处理响应结果, 此处的 body 就是表示一个博客的 js 对象.
// 1. 更新标题
let titleDiv = document.querySelector('.container-right .title');
titleDiv.innerHTML = body.title;
// 2. 更新日期
let dateDiv = document.querySelector('.date');
dateDiv.innerHTML = body.postTime;
// 3. 更新博客正文
// 此处不应该直接把博客正文填充到这个标签里~~
// let contentDiv=document.querySelector('#content');
// contentDiv.innerHTML=body.content;
editormd.markdownToHTML('content', { markdown: body.content });
}
})
在 JavaScript 中,location 是用于获取或设置窗口的 URL,并可以用来对 URL 进行解析和操作。
location.search 属性用于获取 URL 的查询字符串部分,也就是问号 (?) 后的内容。
2.3 博客登录页
具体思路:
1.在此处输入用户名和密码
2.点击登录就会触发一个http请求
3.服务器验证结果,判定是否登录成功
4.如果成功就跳转到博客列表页
1) 约定前后端交互接口

2) 编写后端代码
private ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
// 设置请求的编码. 告诉 servlet 按照啥格式来理解请求
req.setCharacterEncoding("utf8");
// 设置响应的编码. 告诉 servlet 按照啥格式来构造响应
// resp.setCharacterEncoding("utf8");
resp.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf8");
// 1. 读取参数中的用户名和密码
// 注意!! 如果用户名密码包含中文, 此处的读取可能会乱码.
String username = req.getParameter("username");
String password = req.getParameter("password");
if (username == null || "".equals(username) || password == null || "".equals(password)) {
// 登录失败!!
String html = "<h3>登录失败! 缺少 username 或者 password 字段</h3>";
resp.getWriter().write(html);
return;
}
// 2. 读数据库, 看看用户名是否存在, 并且密码是否匹配
UserDao userDao = new UserDao();
User user = userDao.selectByUsername(username);
if (user == null) {
// 用户不存在.
String html = "<h3>登录失败! 用户名或密码错误</h3>";
resp.getWriter().write(html);
return;
}
if (!password.equals(user.getPassword())) {
// 密码不对
String html = "<h3>登录失败! 用户名或密码错误</h3>";
resp.getWriter().write(html);
return;
}
// 3. 用户名密码验证通过, 登录成功, 接下来就创建会话. 使用该会话保存用户信息.
//这里就是创建信息
HttpSession session = req.getSession(true);
session.setAttribute("user", user);
// 4. 进行重定向. 跳转到博客列表页
resp.sendRedirect("blog_list.html");
}
3)编写前端代码
这是里是通过from表单构造请求.
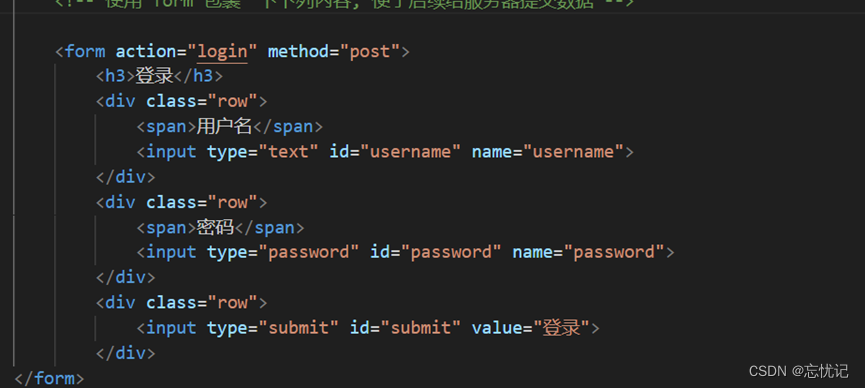
2.4 页面强制登录功能
当用户访问 博客列表页 和 博客详情页 时, 如果用户当前尚未登陆, 就自动跳转到登陆页面.
在页面加载的时候,专门发起一个新的ajax.
举个例子
以博客列表页为例子,会先发送一个请求获取博客列表,再发一个ajax获取用户的登录状态.
如果用户已经登录相安无事,如果未登录,就跳转登录页
具体思路:
首先判断登录状态
- 看是否能查到http Session对象
- 看session 对象里有没有user
然后如果有这种状态就直接可以访问
如果没有就强制登录即可
1)约定前后端交互接口

2)编写后端代码
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
resp.setContentType("application/json; charset=utf8");
// 使用这个方法来获取到用户的登录状态.
// 如果用户未登录, 这里的会话就拿不到!!
HttpSession session = req.getSession(false);
if (session == null) {
// 未登录, 返回一个空的 user 对象
User user = new User();
String respJson = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(user);
resp.getWriter().write(respJson);
return;
}
User user = (User) session.getAttribute("user");
if (user == null) {
user = new User();
String respJson = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(user);
resp.getWriter().write(respJson);
return;
}
// 确实成功取出了 user 对象, 就直接返回即可.
String respJson = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(user);
resp.getWriter().write(respJson);
}
3)编写前端代码
function checkLogin() {
$.ajax({
type: 'get',
url: 'login',
success: function(body) {
if (body.userId && body.userId > 0) {
// 登录成功!!
console.log("当前用户已经登录!!");
} else {
// 当前未登录
// 强制跳转到登录页.
location.assign('login.html');
}
}
});
}
checkLogin();
这里的前端代码,要在每一个页面中都要检查.
2.5 显示用户功能

具体思路:
- 如果是博客列表页,此处显示登录用户的信息
- 如果是博客详情页,此时显示的是该文章的作者.
这里的工作就是根据实际的用户,来生成响应的用户
1)约定前后端交互接口
博客列表页

博客详情页

2)编写后端代码
博客列表的后端代码
这里是利用之前的的强制登录的一个逻辑
@WebServlet("/login")
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
resp.setContentType("application/json; charset=utf8");
// 使用这个方法来获取到用户的登录状态.
// 如果用户未登录, 这里的会话就拿不到!!
HttpSession session = req.getSession(false);
if (session == null) {
// 未登录, 返回一个空的 user 对象
User user = new User();
String respJson = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(user);
resp.getWriter().write(respJson);
return;
}
User user = (User) session.getAttribute("user");
if (user == null) {
user = new User();
String respJson = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(user);
resp.getWriter().write(respJson);
return;
}
// 确实成功取出了 user 对象, 就直接返回即可.
String respJson = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(user);
resp.getWriter().write(respJson);
}
博客详情页的后端代吗
@WebServlet("/author")
public class AuthorServlet extends HttpServlet {
private ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
String blogId = req.getParameter("blogId");
if (blogId == null) {
resp.setContentType("text/html; charset=utf8");
resp.getWriter().write("参数非法, 缺少 blogId");
return;
}
// 根据 blogId 查询 Blog 对象
BlogDao blogDao = new BlogDao();
Blog blog = blogDao.selectById(Integer.parseInt(blogId));
if (blog == null) {
// 博客不存在.
resp.setContentType("text/html; charset=utf8");
resp.getWriter().write("没有找到指定博客: blogId = " + blogId);
return;
}
// 根据 blog 中的 userId 找到对应的用户信息
UserDao userDao = new UserDao();
User author = userDao.selectById(blog.getUserId());
String respJson = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(author);
resp.setContentType("application/json; charset=utf8");
resp.getWriter().write(respJson);
}
}
3)编写前端代码
博客列表页
function checkLogin() {
$.ajax({
type: 'get',
url: 'login',
success: function(body) {
if (body.userId && body.userId > 0) {
// 登录成功!!
console.log("当前用户已经登录!!");
//加上一个功能,把当前用户界面加载到界面上
let h3 = document.querySelector('.container-left .card h3');
h3.innerHTML = body.username;
} else {
// 当前未登录
// 强制跳转到登录页.
location.assign('login.html');
}
}
});
}
checkLogin();
博客详情页
// 函数定义
function getAuthor() {
$.ajax({
type: 'get',
url: 'author' + location.search,
success: function(body) {
// 把 username 设置到界面上
let h3 = document.querySelector('.container-left .card h3');
h3.innerHTML = body.username;
}
});
}
// 函数调用
getAuthor();
2.6 退出登录功能
基本思路:
思路:
首先判断登录状态
- 看是否能查到http Session对象
- 看session 对象里有没有user
- 实现退出登录
要么把HttpSession干掉
要么把user干掉.
这里的请求就是a标签了,就不是ajax了
我们这里选择把user干掉
1) 约定前后端交互接口

2) 编写后端代码
@WebServlet("/logout")
public class LogoutServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
HttpSession httpSession = req.getSession(false);
if (httpSession == null) {
// 未登录状态, 就直接提示出错.
resp.setContentType("text/html; charset=utf8");
resp.getWriter().write("当前未登录!");
return;
}
httpSession.removeAttribute("user");
resp.sendRedirect("login.html");
}
}
3)编写前端代码

2.7 发布博客功能
具体思路

1.点击发布文章就会向服务器发布一个请求
2.服务器做出相关操作
3.浏览器跳转到指定页面
我们这里使用from构造请求.
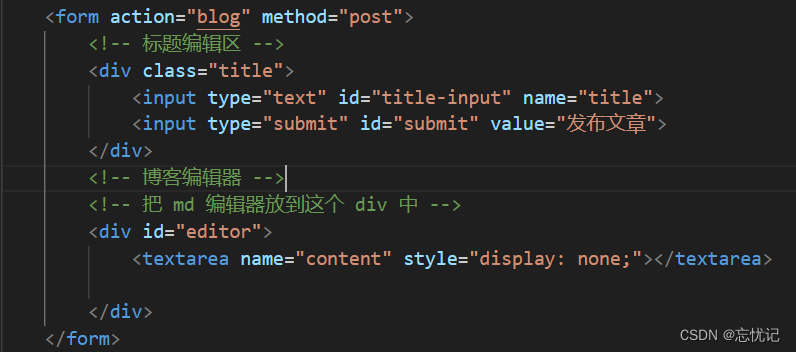
1)约定前后端交互接口

2)编写后端代码
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
// 发布博客
// 读取请求, 构造 Blog 对象, 插入数据库中即可!!
HttpSession httpSession = req.getSession(false);
if (httpSession == null) {
resp.setContentType("text/html; charset=utf8");
resp.getWriter().write("当前未登录, 无法发布博客!");
return;
}
User user = (User) httpSession.getAttribute("user");
if (user == null) {
resp.setContentType("text/html; charset=utf8");
resp.getWriter().write("当前未登录, 无法发布博客!");
return;
}
// 确保登录之后, 就可以把作者给拿到了.
// 获取博客标题和正文
req.setCharacterEncoding("utf8");
String title = req.getParameter("title");
String content = req.getParameter("content");
if (title == null || "".equals(title) || content == null || "".equals(content)) {
resp.setContentType("text/html; charset=utf8");
resp.getWriter().write("当前提交数据有误! 标题或者正文为空!");
return;
}
// 构造 Blog 对象
Blog blog = new Blog();
blog.setTitle(title);
blog.setContent(content);
blog.setUserId(user.getUserId());
// 发布时间, 在 java 中生成 / 数据库中生成 都行
blog.setPostTime(new Timestamp(System.currentTimeMillis()));
// 插入数据库
BlogDao blogDao = new BlogDao();
blogDao.add(blog);
// 跳转到博客列表页
resp.sendRedirect("blog_list.html");
}
3)编写前端代码
<div class="blog-edit-container">
<form action="blog" method="post">
<!-- 标题编辑区 -->
<div class="title">
<input type="text" id="title-input" name="title">
<input type="submit" id="submit" value="发布文章">
</div>
<!-- 博客编辑器 -->
<!-- 把 md 编辑器放到这个 div 中 -->
<div id="editor">
<textarea name="content" style="display: none;"></textarea>
</div>
</form>