目录:导读
- 前言
- 一、Python编程入门到精通
- 二、接口自动化项目实战
- 三、Web自动化项目实战
- 四、App自动化项目实战
- 五、一线大厂简历
- 六、测试开发DevOps体系
- 七、常用自动化测试工具
- 八、JMeter性能测试
- 九、总结(尾部小惊喜)
前言
fixture说明
fixture可以让我们自定义测试用例的前置条件,fixture可作为共享数据使用
1、fixture可以当做参数传入
import pytest
@pytest.fixture()
def test1():
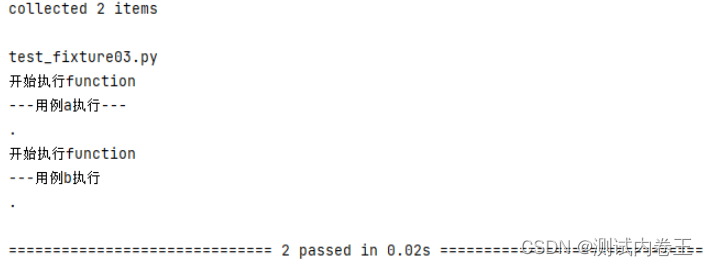
print('\n开始执行function')
def test_a(test1): #传函数名
print('---用例a执行---')
class TestCase:
def test_b(self, test1):
print('---用例b执行')
if __name__ == '__main__':
pytest.main(["-s", "-v", "-q","test_fixture03.py"])
运行结果:
2、使用装饰器@pytest.mark.usefixtures()修饰需要运行的用例
import pytest
@pytest.fixture()
def test1():
print('\n开始执行function')
@pytest.mark.usefixtures('test1') #关键字,可以传多个
def test_a():
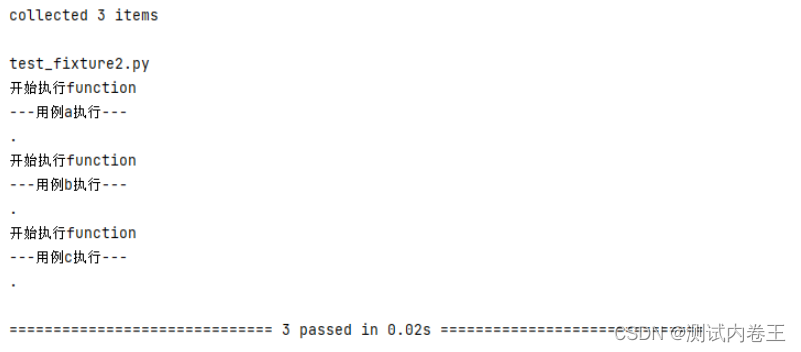
print('---用例a执行---')
@pytest.mark.usefixtures('test1')
class TestCase:
def test_b(self):
print('---用例b执行---')
def test_c(self):
print('---用例c执行---')
if __name__ == '__main__':
pytest.main(["-s", "-v", "-q","test_fixture2.py"])
运行结果:
3、usefixtures与传fixture区别
如果fixture有返回值,那么usefixture就无法获取到返回值,这个是装饰器usefixture与用例直接传fixture参数的区别。
当fixture需要用到return出来的参数时,只能将参数名称直接当参数传入,不需要用到return出来的参数时,两种方式都可以。
fixture的参数使用
示例代码如下:
import pytest
seq=["hello","itesting"]
@pytest.fixture(scope="function",params=seq,autouse=True,ids=['test1','test2'],name='test')
def my_method(request):
# request用来接收param列表数据
print(request.param)
def test_use_fixtures_01():
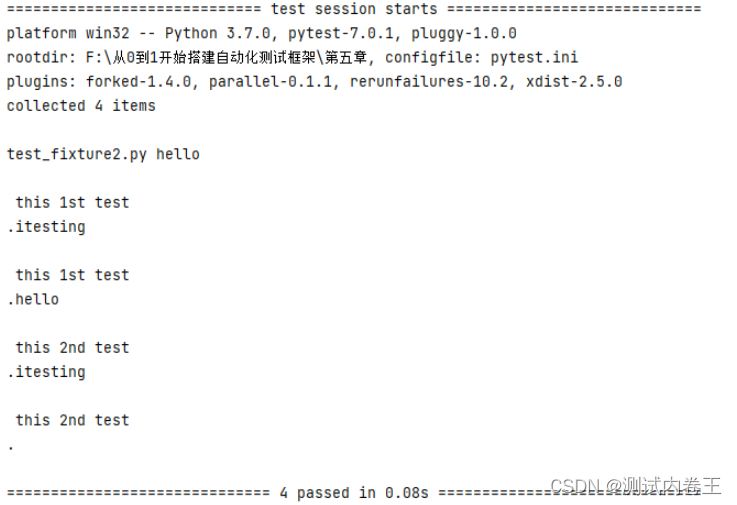
print("\n this 1st test")
def test_use_fixtures_02():
print("\n this 2nd test")
if __name__ == '__main__':
pytest.main(["-s", "-v", "-q","test_fixture2.py"])
运行结果:
参数说明:
scope:即作用域,function"(默认),“class”,“module”,"session"四个,本例中使用function即每一个测试函数都会执行;
params:可选参数列表,它将导致多个参数调用fixture函数和所有测试使用它。params提供了2组参数,所以共有4条测试用例被执行;
autouse:默认:False,需要用例手动调用该fixture;如果是True,所有作用域内的测试用例都会自动调用该fixture;
ids:params测试ID的一部分。如果没有将从params自动生成.
name:默认:装饰器的名称,同一模块的fixture相互调用建议写个不同的name。
session的作用域:是整个测试会话,即开始执行pytest到结束测试
使用conftest.py共享fixture
全局范围内使用同一个测试前置操作,例如,测试开始时先登录,再连接数据库
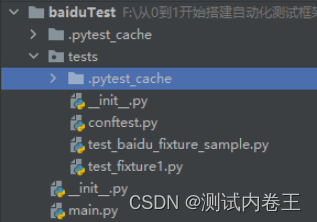
目录结构:
conftest文件内容:
import pytest
from selenium import webdriver
import requests
import time
@pytest.fixture(scope="session")
def login():
driver = webdriver.Chrome()
driver.implicitly_wait(30)
base_url = "http://www.baidu.com/"
s=requests.Session()
#注意关键字yield
yield driver,s,base_url
print('turn off browser driver')
driver.quit()
print('turn off request driver')
time.sleep(2)
s.close()
@pytest.fixture(scope="function",autouse=True)
def connect_db():
print('connecting db')
pass
def pytest_configure(config):
config.addinivalue_line(
"markers", "baidu" # login_success 是标签名
)
test_baidu_fixture_sample.py文件内容:
import pytest
import time
@pytest.mark.baidu
class TestBaidu:
@pytest.mark.parametrize('search_string,expect_string',[('iTesting','iTesting'),('helloqa.com','iTesting')])
def test_baidu_search(self,login,search_string,expect_string):
driver, s, base_url =login
time.sleep(2)
driver.get(base_url + './')
driver.find_element_by_id("kw").send_keys(search_string)
driver.find_element_by_id("su").click()
time.sleep(2)
search_results=driver.find_element_by_xpath('//*[@id="1"]/h3/a').get_attribute('innerHTML')
print(search_results)
assert(expect_string in search_results) is True
if __name__ == '__main__':
pytest.main([])
test_fixture1.py文件内容:
class TestClass:
def test_use_fixtures_01(self,login):
print('\nI am data:{}'.format(login))
在项目根目录下执行命令:
pytest -s -q --tb=no tests
运行成功后,可以看到connecting db 语句打印了3次,原因是conftest.py文件里面,connect_db 的作用范围为function和autouse,login的作用范围是session
在conftest.py文件里有一个关键字yeild,当他作用与pytest的fixture时,yield关键字之前的语句属于前置操作,而yield之后的语句属于后置操作,即可以用一个函数实现测试前的初始化和测试后的初始化
| 下面是我整理的2023年最全的软件测试工程师学习知识架构体系图 |
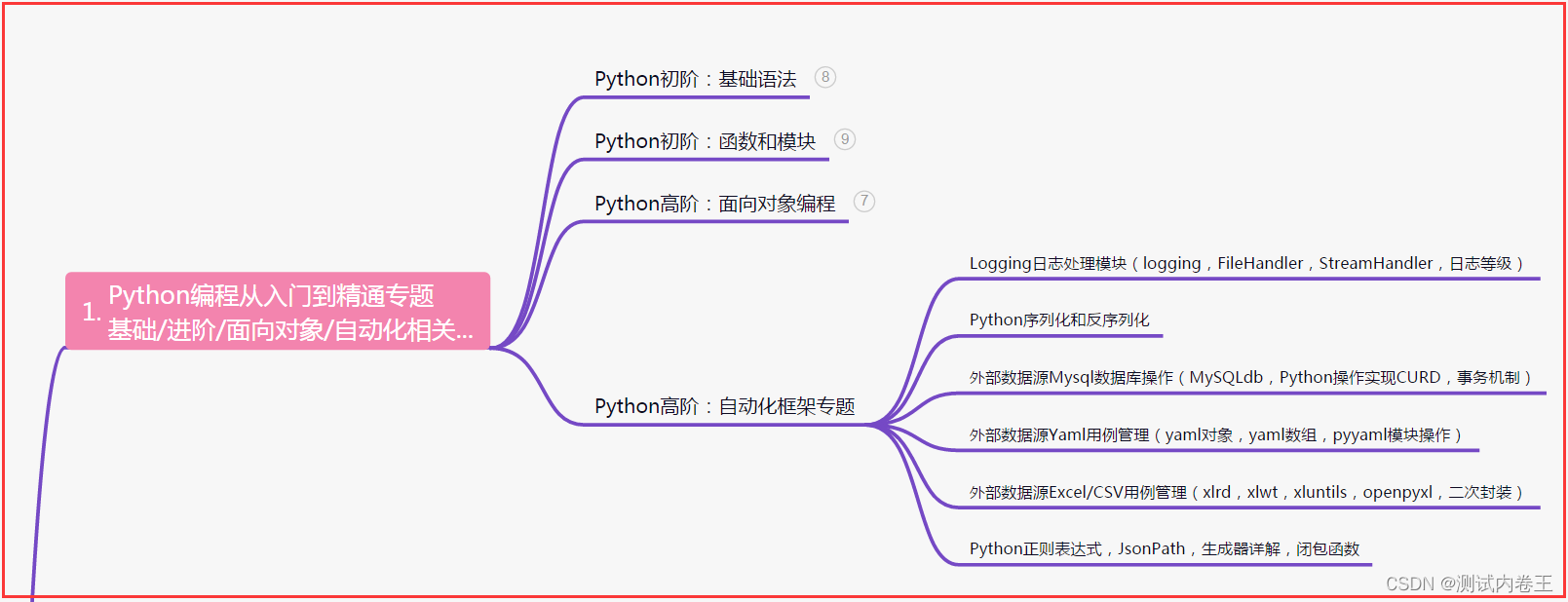
一、Python编程入门到精通
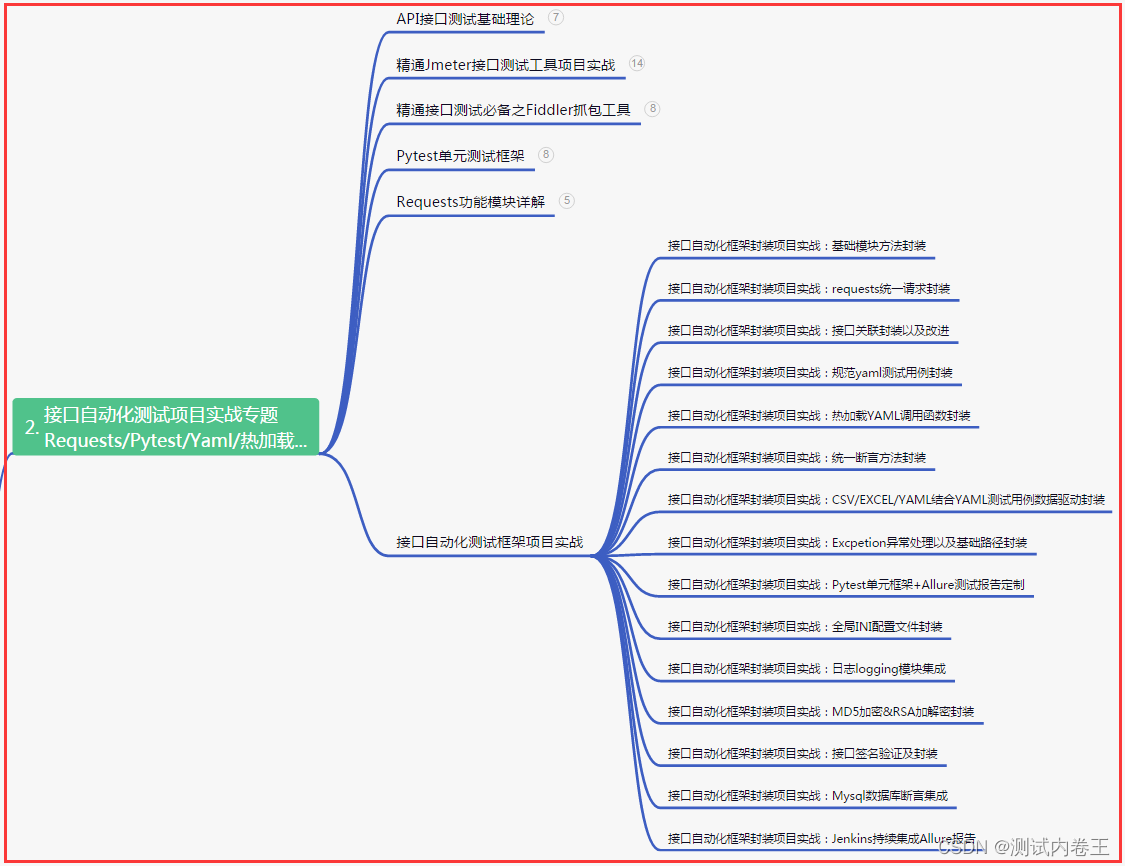
二、接口自动化项目实战
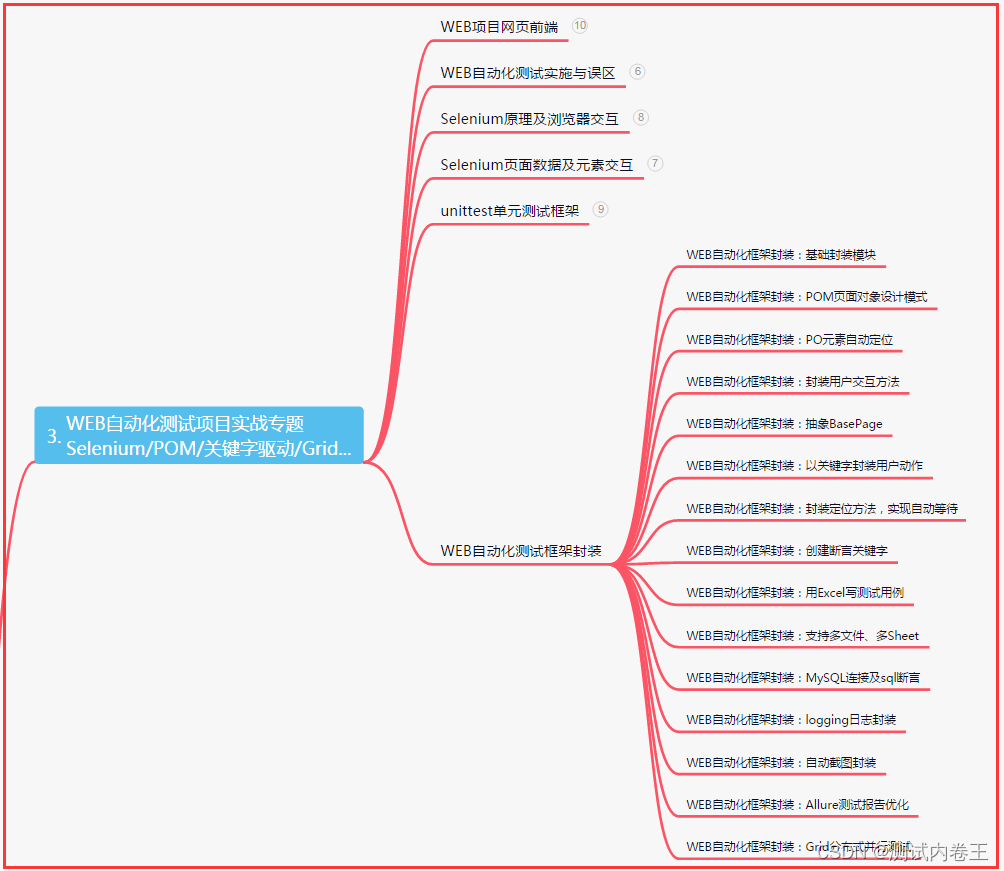
三、Web自动化项目实战
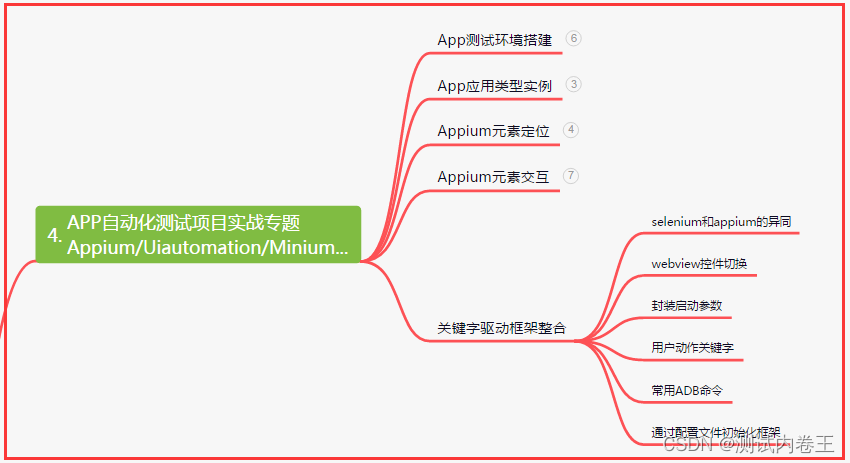
四、App自动化项目实战
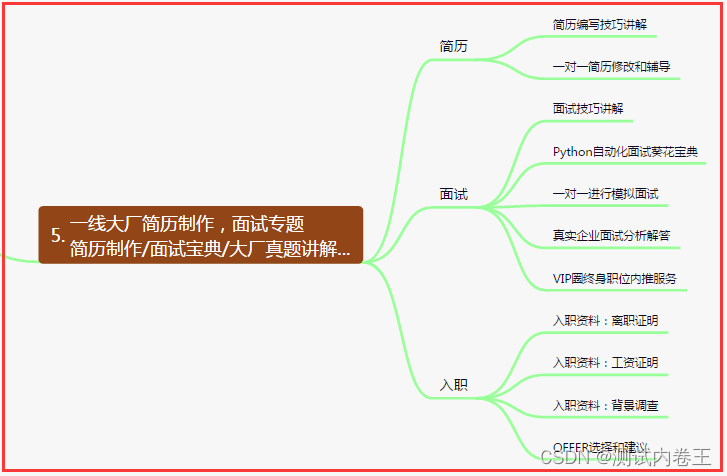
五、一线大厂简历
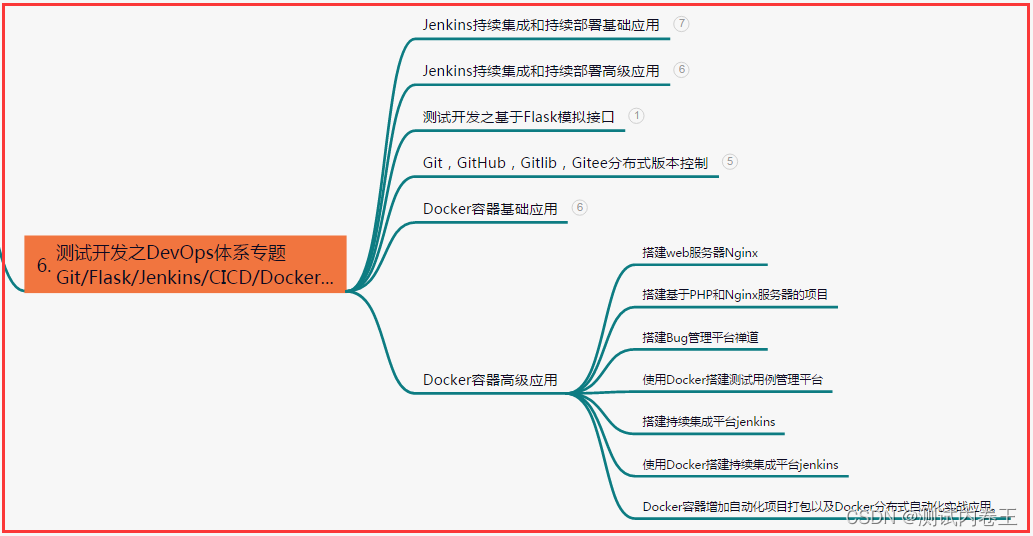
六、测试开发DevOps体系
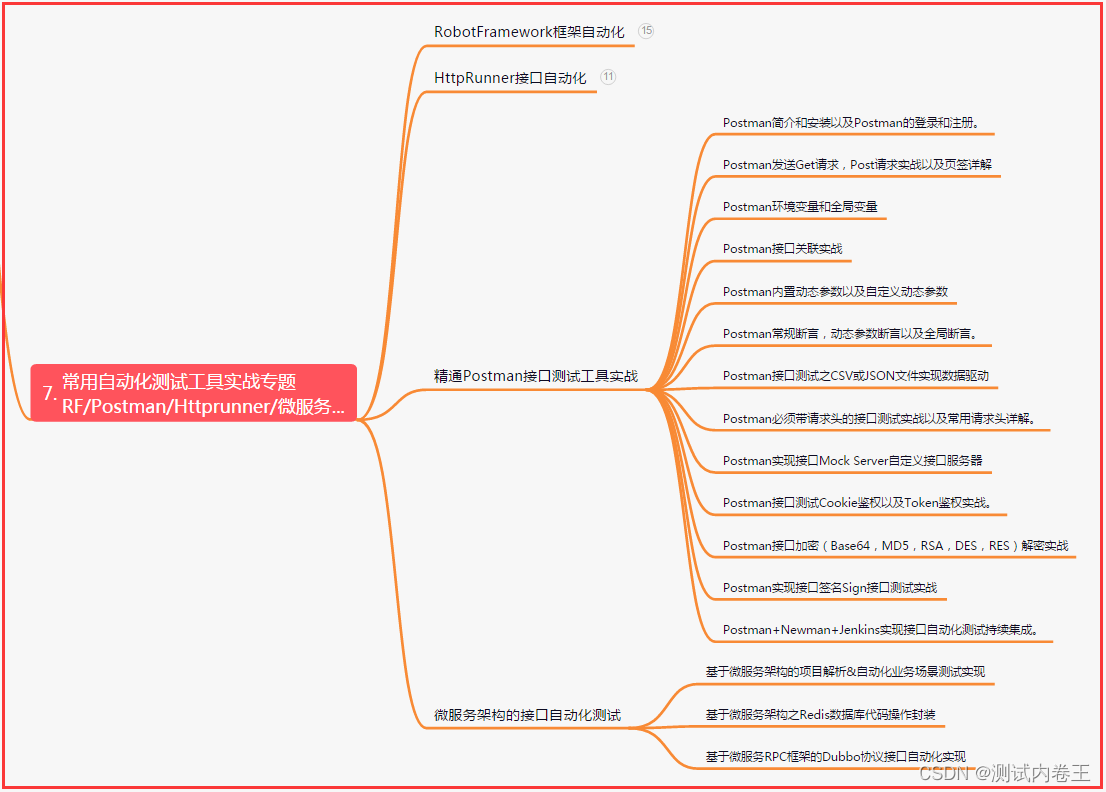
七、常用自动化测试工具
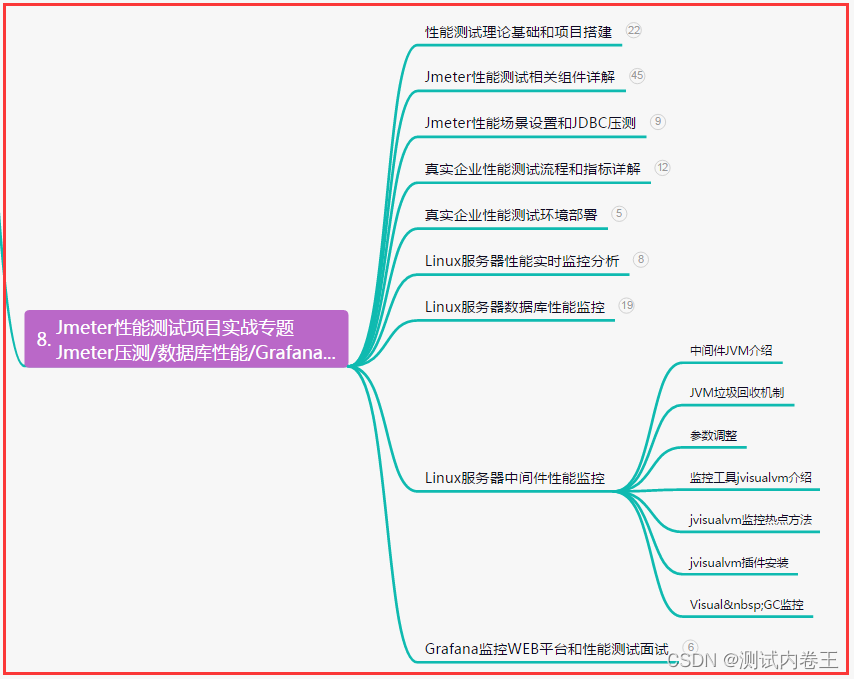
八、JMeter性能测试
九、总结(尾部小惊喜)
只有坚持不懈的努力,才能绽放出属于自己的辉煌。无论前路多么艰难险阻,只要心中燃起希望的火焰,我们定能攀登人生高峰。相信自己,奋斗不止。
时光荏苒,机遇稍纵即逝,只有付出才能收获,只有奋斗才能成功。坚持不懈的努力,将点滴汇聚成壮丽的波涛,让梦想在实现的道路上一路绽放辉煌!
奋斗是实现梦想的舞台,不放弃是成功的密码,坚持是进步的阶梯,努力是超越自我的力量。相信自己,勇往直前,每一份付出都将成就更加辉煌的未来!