《机器学习公式推导与代码实现》学习笔记,记录一下自己的学习过程,详细的内容请大家购买作者的书籍查阅。
线性判别分析
线性判别分析(linear discriminant analysis, LDA)是一种经典的线性分类方法,其基本思想是将数据投影到低维空间,使得同类数据尽可能接近,异类数据尽可能疏远。
另外线性判别分析能够通过投影来降低样本维度,并且在投影过程中用到了标签信息,线性判别分析是一种监督降维方法。
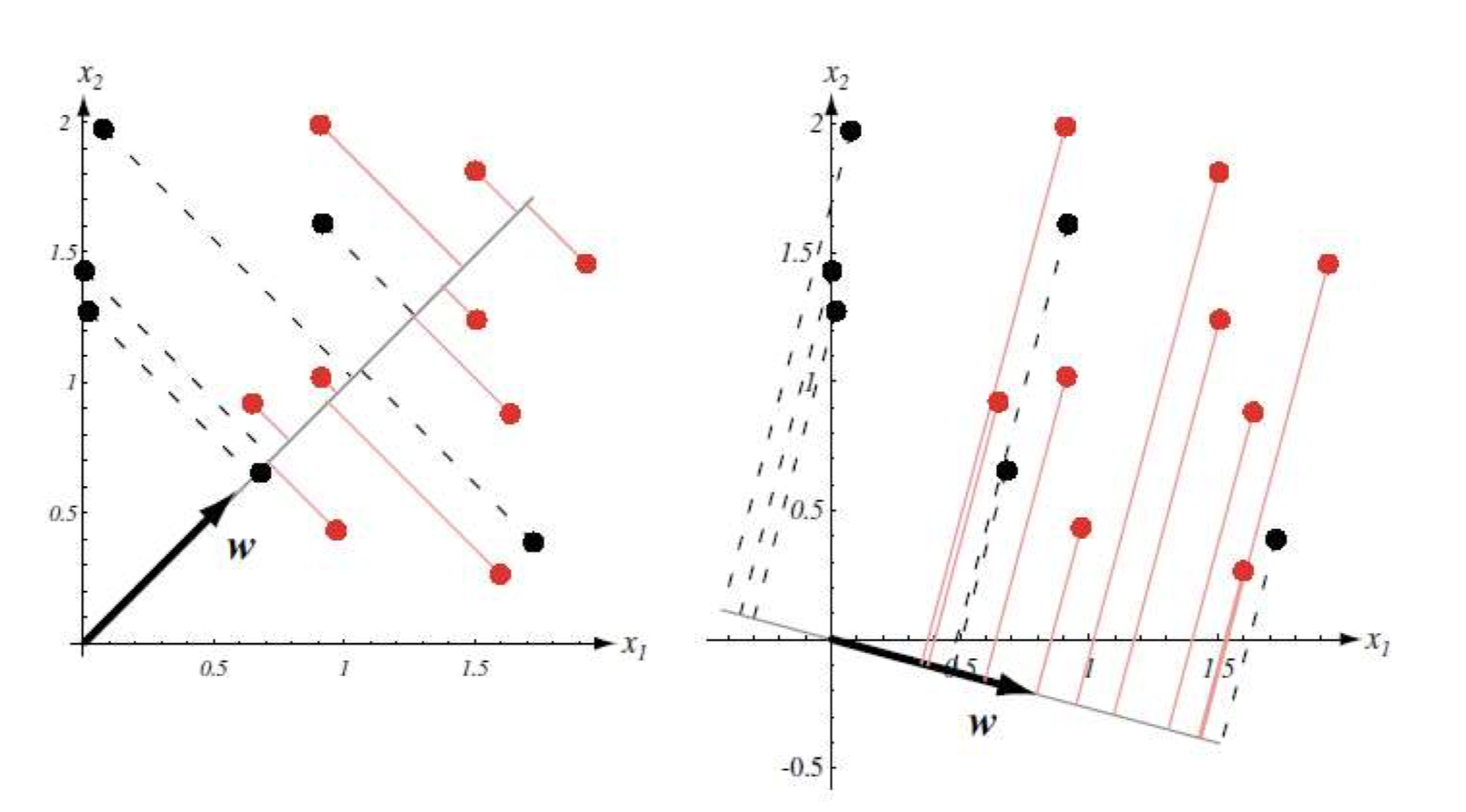
1 LDA数学推导


2 基于numpy的LDA算法实现
完整的LDA算法流程如下:
- (1)对训练集按类别进行分组;
- (2)分别计算每组样本的均值和协方差;
- (3)计算类间散度矩阵 S w S_{w} Sw;
- (4)计算两类样本的均值差 μ 0 − μ 1 \mu _{0} -\mu_{1} μ0−μ1;
- (5)对类间散度矩阵 S w S_{w} Sw进行奇异值分解,并求逆;
- (6)根据$S_{w}^{-1} \left ( \mu _{0} -\mu _{1} \right ) 得到 得到 得到w$;
- (7)计算投影后的数据点 Y = w X Y = wX Y=wX。
模型定义:
import numpy as np
class LDA():
def __init__(self): # 初始化权重矩阵
self.w = None
def calc_cov(self, X, Y=None): # 计算协方差矩阵
m = X.shape[0]
# 将数据缩放到均值为0,标准差为1的标准正态分布
X = (X - np.mean(X, axis=0))/np.std(X, axis=0) # 数据标准化
Y = X if Y == None else (Y - np.mean(Y, axis=0))/np.std(Y, axis=0)
return 1 / m * np.matmul(X.T, Y)
def fit(self, X, y): # LDA拟合过程
# 按类分组
X0 = X[y == 0]
X1 = X[y == 1]
# 分别计算两类数据自变量的协方差矩阵
sigma0 = self.calc_cov(X0)
sigma1 = self.calc_cov(X1)
Sw = sigma0 + sigma1 # 计算类内散度矩阵
# 分别计算两类数据自变量的均值和差
u0, u1 = np.mean(X0, axis=0), np.mean(X1, axis=0)
mean_diff = np.atleast_1d(u0 - u1) # 如果 u0 - u1 是一个标量,则将其转换为长度为1的一维数组。如果 u0 - u1 是一个数组,则保持不变
# 利用 SVD 分解,我们可以通过计算矩阵 U、Σ 和 V 来得到原始矩阵的逆矩阵的近似
U, S, V = np.linalg.svd(Sw) # # 对类内散度矩阵进行奇异值分解
Sw_ = np.dot(np.dot(V.T, np.linalg.pinv(np.diag(S))), U.T) # 计算类内散度矩阵的逆
self.w = Sw_.dot(mean_diff) # 计算w
def predict(self, X): # LDA分类预测
y_pred = []
for sample in X:
h = sample.dot(self.w)
y = 1 * (h < 0) # 如果h小于0,则将y设置为1,否则将y设置为0
y_pred.append(y)
return y_pred
读取数据:
from sklearn import datasets
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
data = datasets.load_iris()
X = data.data
y = data.target
X = X[y != 2]
y = y[y != 2]
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=41)
X_train.shape, X_test.shape, y_train.shape, y_test.shape
((80, 4), (20, 4), (80,), (20,))
数据测试:
lda = LDA()
lda.fit(X_train, y_train)
y_pred = lda.predict(X_test)
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
accuracy = accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred)
print(accuracy)
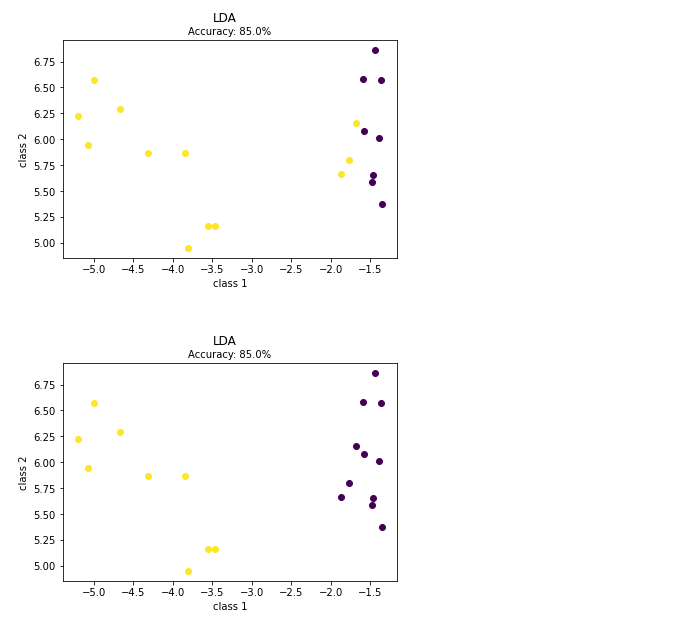
0.85
结果可视化:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
class Plot():
def __init__(self):
self.cmap = plt.get_cmap('viridis')
def _transform(self, X, dim):
covariance = LDA().calc_cov(X)
eigenvalues, eigenvectors = np.linalg.eig(covariance)
# Sort eigenvalues and eigenvector by largest eigenvalues
idx = eigenvalues.argsort()[::-1]
eigenvalues = eigenvalues[idx][:dim]
eigenvectors = np.atleast_1d(eigenvectors[:, idx])[:, :dim]
# Project the data onto principal components
X_transformed = X.dot(eigenvectors)
return X_transformed
# Plot the dataset X and the corresponding labels y in 2D using PCA.
def plot_in_2d(self, X, y=None, title=None, accuracy=None, legend_labels=None):
X_transformed = self._transform(X, dim=2)
x1 = X_transformed[:, 0]
x2 = X_transformed[:, 1]
class_distr = []
y = np.array(y).astype(int)
colors = [self.cmap(i) for i in np.linspace(0, 1, len(np.unique(y)))]
# Plot the different class distributions
for i, l in enumerate(np.unique(y)):
_x1 = x1[y == l]
_x2 = x2[y == l]
_y = y[y == l]
class_distr.append(plt.scatter(_x1, _x2, color=colors[i]))
# Plot legend
if not legend_labels is None:
plt.legend(class_distr, legend_labels, loc=1)
# Plot title
if title:
if accuracy:
perc = 100 * accuracy
plt.suptitle(title)
plt.title("Accuracy: %.1f%%" % perc, fontsize=10)
else:
plt.title(title)
# Axis labels
plt.xlabel('class 1')
plt.ylabel('class 2')
plt.show()
Plot().plot_in_2d(X_test, y_pred, title="LDA", accuracy=accuracy)
Plot().plot_in_2d(X_test, y_test, title="LDA", accuracy=accuracy)
3 基于sklearn的LDA算法实现
from sklearn.discriminant_analysis import LinearDiscriminantAnalysis
clf = LinearDiscriminantAnalysis()
clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
y_pred = clf.predict(X_test)
accuracy = accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred)
print(accuracy)
1.0
笔记本_Github地址