In general, as temperature increases, the delay of standard cells increases because of mobility degradation at higher temperatures.
But in lower technology nodes the impact of temperature on the delay of the cell is inverse. In lower nodes, the delay of the cell decreases with an increase in temperature. So in the lower technology node, the effect of temperature on the delay of the cell is inverted and this effect is called the temperature inversion. The main reason behind this inversion is in the lower technology node, the effect of the threshold voltage is dominating over the mobility.

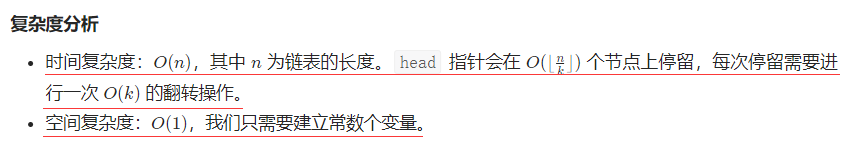
The saturation current of MOSFET
The delay of a cell is simply the time required to charge/discharge the load capacitance. The charging and discharging time of the load capacitor depends on the drain current. If the drain current is high, it will take a lesser time to charge/discharge the load capacitor and so delay will be lesser and vice-versa.
Now let’s see the dependency of drain current Id.
载流子迁移率u
- 对于老旧工艺,与温度相关的载流子迁移率对于驱动电流的变化起主导作用(温度升高,delay增大)
- The drain current Id is directly proportional(正比) to the mobility of charge carriers. So as the temperature increases, the
lattice scattering(晶格散射)increases, and ultimately the mobility of the charge carrier decreases which leads to the decrease in drain current Id and so it increases in the delay of the cell.
- The drain current Id is directly proportional(正比) to the mobility of charge carriers. So as the temperature increases, the
过 驱动/阈值 电压(Vgs – Vt)
Now let’s come to the second important factor, the term (Vgs – Vt) in the above equation is called overdrive voltage. There is a variation in threshold voltage with temperature as per the following equation

-
As temperature increases, the threshold voltage decrease, and overdrive voltage increases.
(升温--->阈值电压降低--->过阈值电压增大--->Id增大--->delay减小)--- Temperature Inversion -
This overdrive voltage is more dominating in the lower technology node
- because in the lower technology node the Vgs and Vt are more closers and so a slight change in Vt will have more impact on overdrive voltage. (先进工艺节点过阈值电压较小,Vgs和Vth量级接近,Vth细微变化都会影响过阈值电压。先进工艺温度delay关系,过阈值电压占主导)
- gain the Id is proportional to the squire of overdrive voltage. So changes in overdrive voltage are further amplified and it is dominating over the mobility in lower technology node.
-
But in a higher technology node since Vgs is much larger than Vt so a slight change in Vt not causes much change in overdrive voltage. A(老旧工艺节点,Vgs和Vth量级相差较大,所以Vth对过阈值电压影响没有很大,老旧(长沟道)工艺,载流子迁移速率u占据主导)
- 随着工艺的先进,过阈值电压越来越低,Vgs 和 Vth量级逐渐接近(Vth对Vgs 影响变大)

- 老工艺25度和125度的过阈值电压相差5%(由于量级有差距,温度升高,阈值电压变小,Vth对过阈值电压影响不大)—载流子迁移率u占主导
- 随着工艺的先进25度和125度的过阈值电压相差21%,Vgs和Vth量级差距缩小,Vth对过阈值电压的影响变大,温度delay关系中,过阈值电压占据主导(因此升温,Vth减小,过阈值电压增大,Id增大,delay减小)