Overview
ext4文件系统分割成多个block groups,为了解决碎片化问题,block allocator尽量将一个文件的block放在一个group中。block groups的size通过sb.s_blocks_per_group指定,同样也可以通过8*block_size_in_bytes计算得到。block默认大小是4KB,每个group包含32768个blocks,一个block group所有的block data大小是8*4K*4K=128M。
ext4在磁盘上是little-endian order。然后 jbd2(the journal)是big-endian order.
Layout

如上图,磁盘分割成多个block Group,每个Block Group都有相似的结构(之所以有不同,是因为收到sparse_super/flex_bg等feature影响)。每个block group引用ext4 spec如下:

super block:记录文件系统的整体信息。dumpe2fs命令最开始的输出部分就是superblock的信息
Group Descriptors: 块组描述符,每个block group对一个一个描述信息,由ext4_group_desc数据结构表示,其中描述块block bitmap的block号,inode bitmap的block号,空闲的block数目,空闲的inode数目等信息。dumpe2fs打印如下:
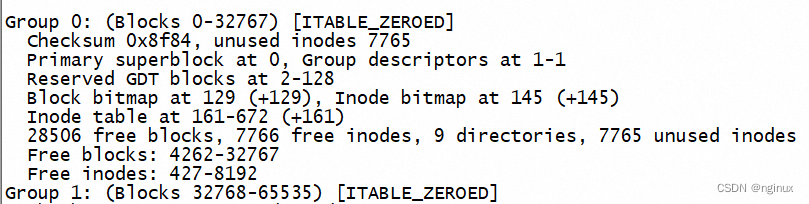
Data Block Bitmap: 数据块位图,记录数据块(data blocks)的使用情况。
Inode bitmap: inode位图,记录inode的使用情况。
Inode Table:inode表,存放inode数据结构的表格。磁盘数据的每个inode通过ext4_inode数据结构表示。
Data Blocks:存放文件数据的部分。
Flexible Block Groups
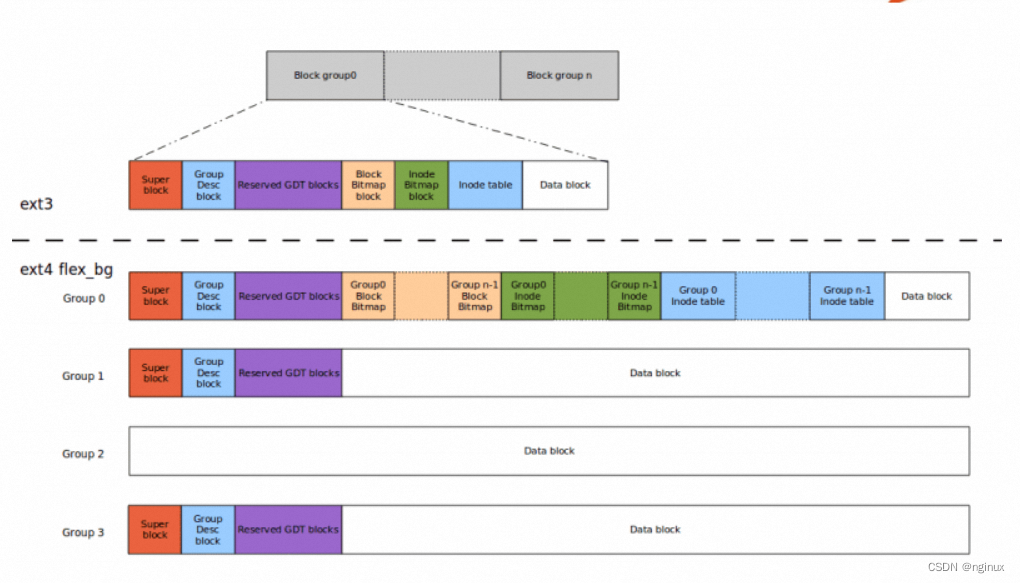

ext4引入了flexible block groups新特性,把相邻的几个block group组成一组(logic block group),称之为flex_bg。如上图,flex_bg中block group会把bitmaps(data block bitmap和inode bitmap)和inode table都放在了第一个group中,除了第一个group,其他group可以可以只包含data block(也有一些block存放了superblock和group desc的冗余数据)。这样将metadata紧凑存放加速了loading读取速度,同时有利于大文件的连续存放,提升访问性能。
Sparse_Super特性
由于文件系统metadata对于安全性非常重要,比如一个硬盘只保留一份superblock信息,如果恰好存放superblock的block损坏,那么将无法访问文件。所以如前文ext4 layout我们知道,每个block group都冗余存放了superblock和group desc,其实大可不必这么冗余,启用sparse_super特性就可以0,1以及3,5,7的整数次方(power of 3, 5 , 7)的block group存放冗余。
Bigalloc特性
block默认的大小是4K,如果一个文件系统大文件很多,那么以多个块(cluster)为单元管理磁盘可以减少碎片化,也可以减少metadata的空间占用,所以ext4引入bigalloc。格式化此片可以设置cluster size,data block bitmap的一位将表示一个cluster状态,当然申请数据块也是以一个cluster为单位。cluster size存储在sb.s_log_cluster_size。
Block and Inode Allocation Policy
数据块分配分配核心要解决碎片化(fragment)问题。ext4如下方法避免:
- multi-block allocator
- delayed allocation
- keep a file's data blocks in the same block group as its inode
- all the inodes in a directory are placed in the same block group
- e4defrag碎片整理工具
Inline Data特性
主要是为了处理tiny file,比如一个文件小于60字节,完全可以嵌入文件的inode里面存储。
Meta Block Groups(META_BG)特性

磁盘数据结构
dumpe2fs之所以能打印磁盘信息,就是因为磁盘上的数据按特定协议或者格式存储,跟ELF是类似的,这种二进制文件都必然有一定的格式,而ext4也定义几种数据结构分别对应这种格式或者协议。
ext4_super_block : 描述磁盘上super block格式的数据结构。
ext4_group_desc : 描述磁盘上group descriptor格式的数据结构。
ext4_inode:描述述磁盘上inode格式的数据结构。block group中的ext4_inode以数组的形式存放在inode table中,即inode table数组中每一项都是ext4_inode。
ext4_super_block数据结构
具体看参考文章ext4 Disk Layout,截取部分如下:

ext4_group_desc 数据结构
具体看参考文章ext4 Disk Layout,截取部分如下:

ext4_inode数据结构

内存数据结构
前面介绍了磁盘数据结构,linux操作按照磁盘数据结构解析了磁盘数据,在内存中同样需要结构体存储这些信息。对应关系如下:
| 磁盘数据结构 | 内存数据结构 |
| ext4_super_block | ext4_sb_info(总是缓存在RAMneicun中) |
| ext4_group_desc | ext4_group_info(总是缓存在RAMneicun中) |
| ext4_inode | ext4_inode_info(动态缓存,如文件删除会从高速缓存中动态删除) |
| data block bitmap | 缓冲区中的位数组 |
| inode bitmap | 缓冲区中的位数组 |
| block(数据块) | VFS缓冲区 |
ext4_sb_info
定义在fs/ext4/ext4.h中,关联了VFS的super_block和ext4_super_block,同时保存了文件系统的通用信息,比如:
- 磁盘超级块中大部分字段
- buffer_head * s_sbh指针:指向包含磁盘超级块所在的缓冲区的缓冲区首部。
- ext4_super_block *s_es:指向磁盘超级块缓冲区
- super_block *s_sb:指向vfs super block。
- 组描述符的个数s_desc_per_block
- s_group_desc指针,指向缓冲区首部。
代码截取部分信息如下(详细字段可以查看fs/ext4/ext4.h内核代码)中ext4_sb_info结构体定义
/*
* fourth extended-fs super-block data in memory
*/
struct ext4_sb_info {
unsigned long s_desc_size; /* Size of a group descriptor in bytes */
unsigned long s_inodes_per_block;/* Number of inodes per block */
unsigned long s_blocks_per_group;/* Number of blocks in a group */
unsigned long s_clusters_per_group; /* Number of clusters in a group */
unsigned long s_inodes_per_group;/* Number of inodes in a group */
unsigned long s_itb_per_group; /* Number of inode table blocks per group */
unsigned long s_gdb_count; /* Number of group descriptor blocks */
unsigned long s_desc_per_block; /* Number of group descriptors per block */
ext4_group_t s_groups_count; /* Number of groups in the fs */
ext4_group_t s_blockfile_groups;/* Groups acceptable for non-extent files */
unsigned long s_overhead; /* # of fs overhead clusters */
unsigned int s_cluster_ratio; /* Number of blocks per cluster */
unsigned int s_cluster_bits; /* log2 of s_cluster_ratio */
loff_t s_bitmap_maxbytes; /* max bytes for bitmap files */
struct buffer_head * s_sbh; /* Buffer containing the super block */
struct ext4_super_block *s_es; /* Pointer to the super block in the buffer */
struct buffer_head * __rcu *s_group_desc;
...
struct super_block *s_sb;
...
};
ext4_sb_info和ext4_super_block中的很多字段相似,但也有区别,ext4_sb_info中的很多字段是根据ext4_super_block的字段计算而得,虽然可以通过 ext4_super_block计算而得到,但是定义在ext4_sb_info定义可以省去重复计算的时间。
super_block的结构提s_fs_info字段指向了ext4_sb_info,EXT4_SB宏就是通过该字段获取ext4_sb_info。内核代码举例:
int ext4_inode_bitmap_csum_verify(struct super_block *sb, ext4_group_t group,
struct ext4_group_desc *gdp,
struct buffer_head *bh, int sz)
{
__u32 hi;
__u32 provided, calculated;
struct ext4_sb_info *sbi = EXT4_SB(sb);
...
}ext4_inode_info
VFS的inode结构体与磁盘数据结构ext4_inode结构体之间也需要一座桥梁,就是ext4_inode_info,截取内核重要的字段如下:
/*
* fourth extended file system inode data in memory
*/
struct ext4_inode_info {
__le32 i_data[15]; /* unconverted */
__u32 i_dtime;
ext4_fsblk_t i_file_acl;
/*
* i_block_group is the number of the block group which contains
* this file's inode. Constant across the lifetime of the inode,
* it is used for making block allocation decisions - we try to
* place a file's data blocks near its inode block, and new inodes
* near to their parent directory's inode.
*/
ext4_group_t i_block_group;
ext4_lblk_t i_dir_start_lookup;
unsigned long i_flags;
/*
* i_disksize keeps track of what the inode size is ON DISK, not
* in memory. During truncate, i_size is set to the new size by
* the VFS prior to calling ext4_truncate(), but the filesystem won't
* set i_disksize to 0 until the truncate is actually under way.
*
* The intent is that i_disksize always represents the blocks which
* are used by this file. This allows recovery to restart truncate
* on orphans if we crash during truncate. We actually write i_disksize
* into the on-disk inode when writing inodes out, instead of i_size.
*
* The only time when i_disksize and i_size may be different is when
* a truncate is in progress. The only things which change i_disksize
* are ext4_get_block (growth) and ext4_truncate (shrinkth).
*/
loff_t i_disksize;
...
struct inode vfs_inode;
struct jbd2_inode *jinode;
...
}ext4_inode_info内嵌了inode,可以通过传递inode对象到EXT4_I宏来获得ext4_inode_info,内核代码:
void ext4_discard_preallocations(struct inode *inode)
{
struct ext4_inode_info *ei = EXT4_I(inode);
...
}但是,ext4_inode_info没有定义指向ext4_inode的字段,只是拷贝了ext4_inode的i_block,i_flags等字段;同时inode结构体也包含了与ext4_inode类似的字段,比如i_atime,i_mtime,i_ctime等,所以三者的关系是:ext4_inode_info内嵌了vfs的inode,这两者一起“瓜分”了ext4_inode的信息。
ext4_group_info
struct ext4_group_info {
unsigned long bb_state;
struct rb_root bb_free_root;
//第一个空闲的block号
ext4_grpblk_t bb_first_free; /* first free block */
//空闲block总数
ext4_grpblk_t bb_free; /* total free blocks */
//碎片的数量
ext4_grpblk_t bb_fragments; /* nr of freespace fragments */
//最大空闲的order(cat /proc/fs/ext4/mb_groups可看到)
ext4_grpblk_t bb_largest_free_order;/* order of largest frag in BG */
struct list_head bb_prealloc_list;
#ifdef DOUBLE_CHECK
void *bb_bitmap;
#endif
struct rw_semaphore alloc_sem;
ext4_grpblk_t bb_counters[]; /* Nr of free power-of-two-block
* regions, index is order.
* bb_counters[3] = 5 means
* 5 free 8-block regions. */
};内核多块分配mballoc中ext4_group_info使用的很频繁,比如bb_largest_free_order的计算逻辑:
/*
* Cache the order of the largest free extent we have available in this block
* group.
*/
static void
mb_set_largest_free_order(struct super_block *sb, struct ext4_group_info *grp)
{
int i;
int bits;
grp->bb_largest_free_order = -1; /* uninit */
bits = sb->s_blocksize_bits + 1;
for (i = bits; i >= 0; i--) {
if (grp->bb_counters[i] > 0) {
grp->bb_largest_free_order = i;
break;
}
}
}mballoc为了解决block分配碎片化问题,使用memory buddy思想,将块按order组织成各种大小的,bb_largest_free_order就是还有剩余空间的最大order。
参考文章
Ext4 Disk Layout - Ext4
.ext4的新特性-bigalloc.pdf