目录
1.HashMap
1.1Map的常用方法
1.2HashMap的使用案例
1.HashMap
基于哈希表的实现的Map接口。
| Map底层结构 | HashMap |
| 底层结构 | 哈希桶 |
| 插入/删除/查找时间复杂度 | O(1) |
| 是否有序 | 无序 |
| 线程安全 | 不安全 |
| 插入/删除/查找区别 | 通过哈希函数计算哈希地址 |
| 比较与覆写 | 自定义类型需要覆写equals和 hashCode方法 |
1.1Map的常用方法
| 方法 | 解释 |
| V get(Object key) | 返回 key 对应的 value |
| V getOrDefault(Object key, V defaultValue) | 返回 key 对应的 value,key 不存在,返回默认值 |
| V put(K key, V value) | 设置 key 对应的 value |
| V remove(Object key) | 删除 key 对应的映射关系 |
| Set<K> keySet() | 返回所有 key 的不重复集合 |
| Collection<V> values() | 返回所有 value 的可重复集合 |
| Set<Map.Entry<K, V>> entrySet() | 返回所有的 key-value 映射关系 |
| boolean containsKey(Object key) | 判断是否包含 key |
| boolean containsValue(Object value) | 判断是否包含 value |
注意:Map.Entry<>是Map内部实现的用来存放key-value相应键值对的内部类
其内部有getKey(),getValue与setValue()方法
1.2HashMap的使用案例
创建一个HashMap,及put的使用
import java.util.*;
public class Test {
public static void Map(){
Map<String,Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
//创建一个HashMap key的类型为"String" value的类型为"Integer"
map.put("a",1);
map.put("b",2);
map.put("c",3);
map.put("d",100);
map.put(null,null);
map.put("d",4);//当key存在时,则会更新value
//向map中put入五个键值对
//注意噢,在HashMap中的key和value都可以为null
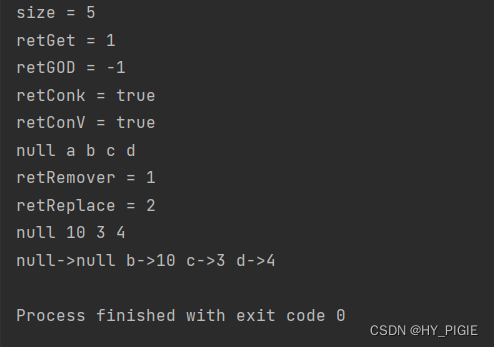
int size = map.size();
System.out.println("size = " + size);
//通过size()方法,得到map中键值对的数量.此时size == 5
int retGet = map.get("a");
System.out.println("retGet = " + retGet);
//通过get()方法,得到对应key的value值.此时retGet为1
//retGet = map.get("z");//map中的key没有"z",此条程序会报错
//注意!!! 当使用get方法时,map中没有对应的key值时,程序会报错
int retGOD = map.getOrDefault("z",-1);
System.out.println("retGOD = " + retGOD);
//此处retGOD为-1
//通过getOrDefault()方法,得到对应的key的value值,如果key值不存在
//则返回我们设置的默认值"-1".
//与get()不同的是,查找的key如果不存在于map中,也不会进行报错
boolean retConK = map.containsKey("a");
boolean retConV = map.containsValue(4);
System.out.println("retConk = " + retConK);
System.out.println("retConV = " + retConV);
//通过containsKey()方法查找map中是否存在对应的key值
//containsValue()方法查找map中是否存在对应的value,可以是一个或多个
Set<String> set = map.keySet();
for (String s:set) {
System.out.print(s + " ");
}
System.out.println();
//通过keySet()方法,返回map中所有的key值,并以set的形式返回
int retRemove = map.remove("a");
System.out.println("retRemover = " + retRemove);
//通过remove()方法,根据key值删除相应的键值对,并返回删除的value值
int retReplace = map.replace("b",10);
System.out.println("retReplace = " + retReplace);
//通过replace()方法,更新key的value--好像直接put也一样?
Collection<Integer> collection = map.values();
// for (int i:collection) { 此方法因为value中有一个null,直接遍历会有一个空指针的报错,int类型也不能与null比较
// System.out.println(i + " "); 于是乎,有了以下使用迭代器的方式来遍历
// }
// System.out.println();
Iterator<Integer> iterator = collection.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()){
System.out.print(iterator.next() + " ");
}
System.out.println();
//通过keySet()方法,返回map中所有的value值,以collection的形式返回
Set<Map.Entry<String,Integer>> entrySet = map.entrySet();
for (Map.Entry<String, Integer> s : map.entrySet()) {
System.out.print(s.getKey() + "->" + s.getValue() + " ");
}
System.out.println();
//通过entrySet()方法,得到key与value的对应关系,并使用其getKey与getValue得到相应的值
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map();
}
}




![[HDCTF2019]MFC](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/869172a2ffde42f588521815fa822c3f.png)