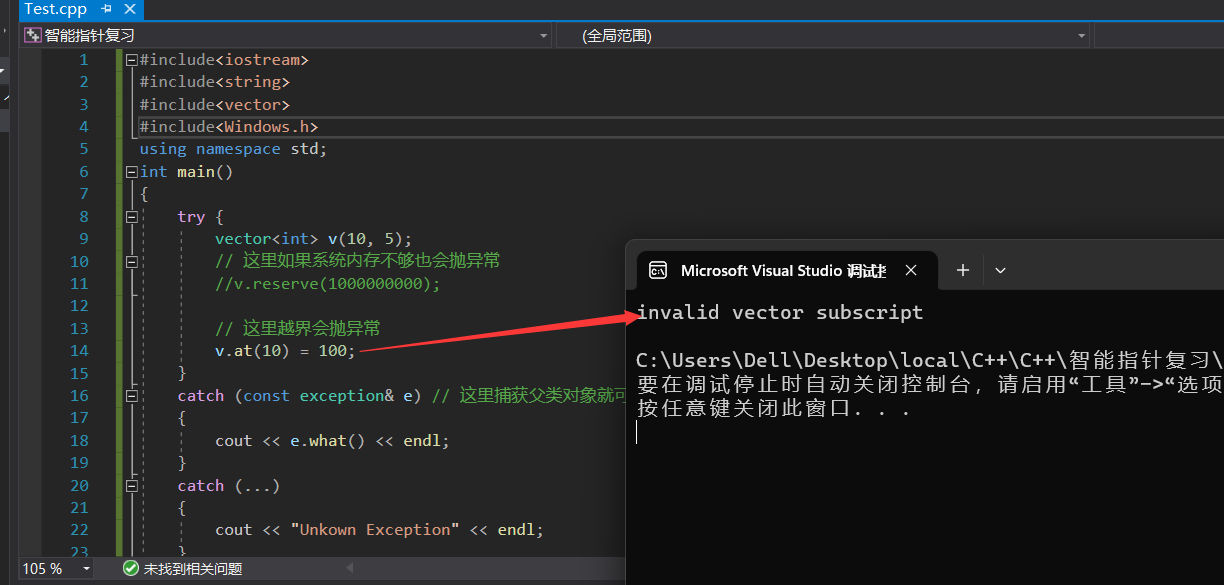
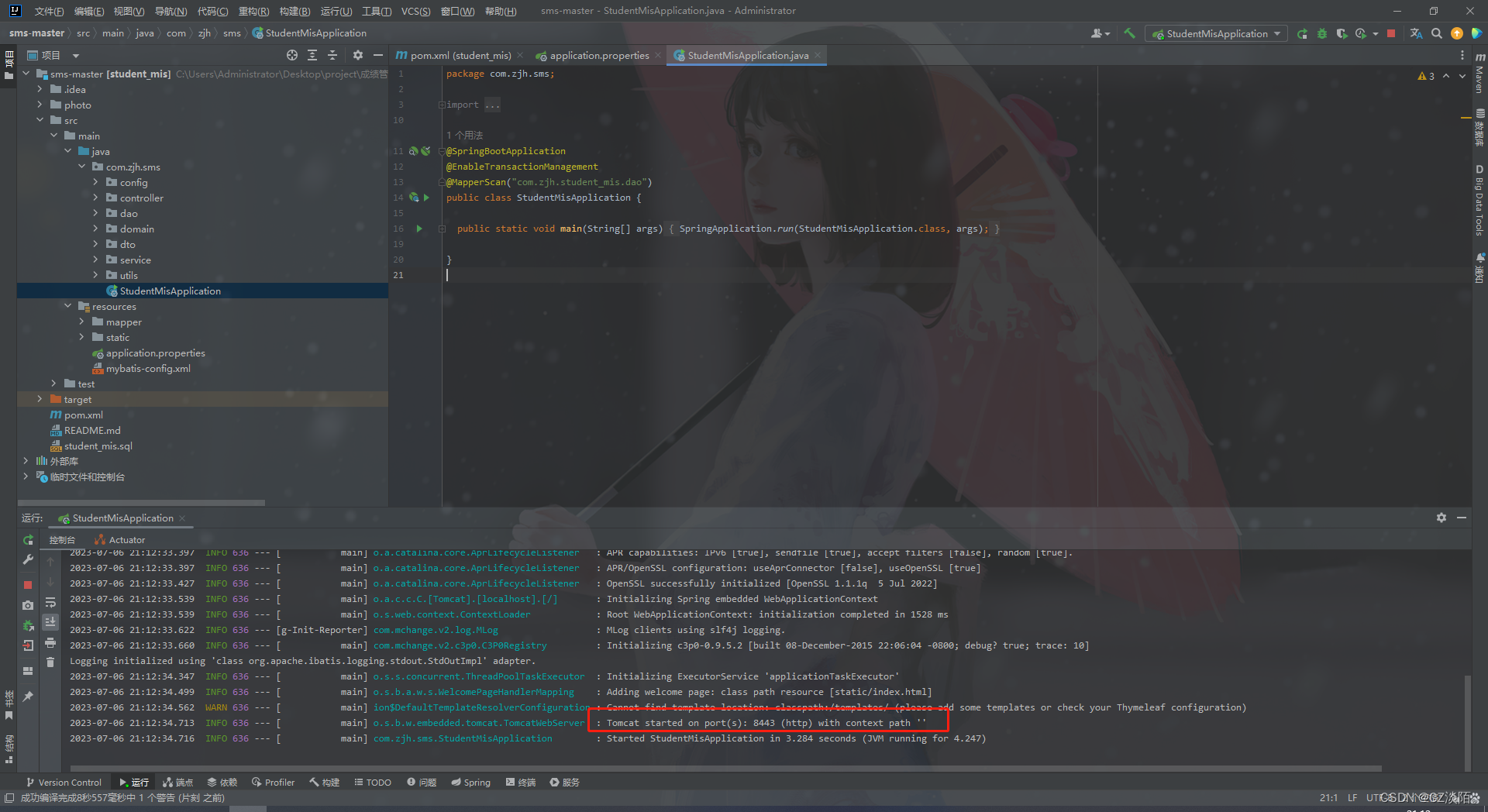
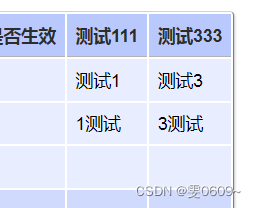
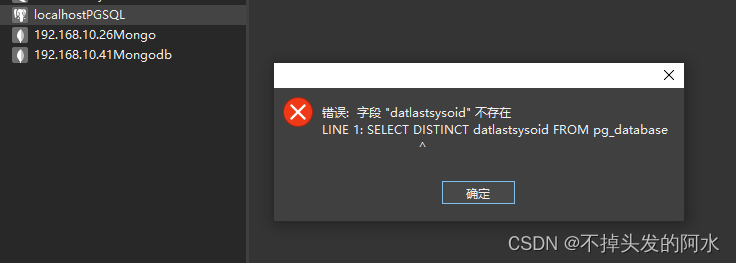
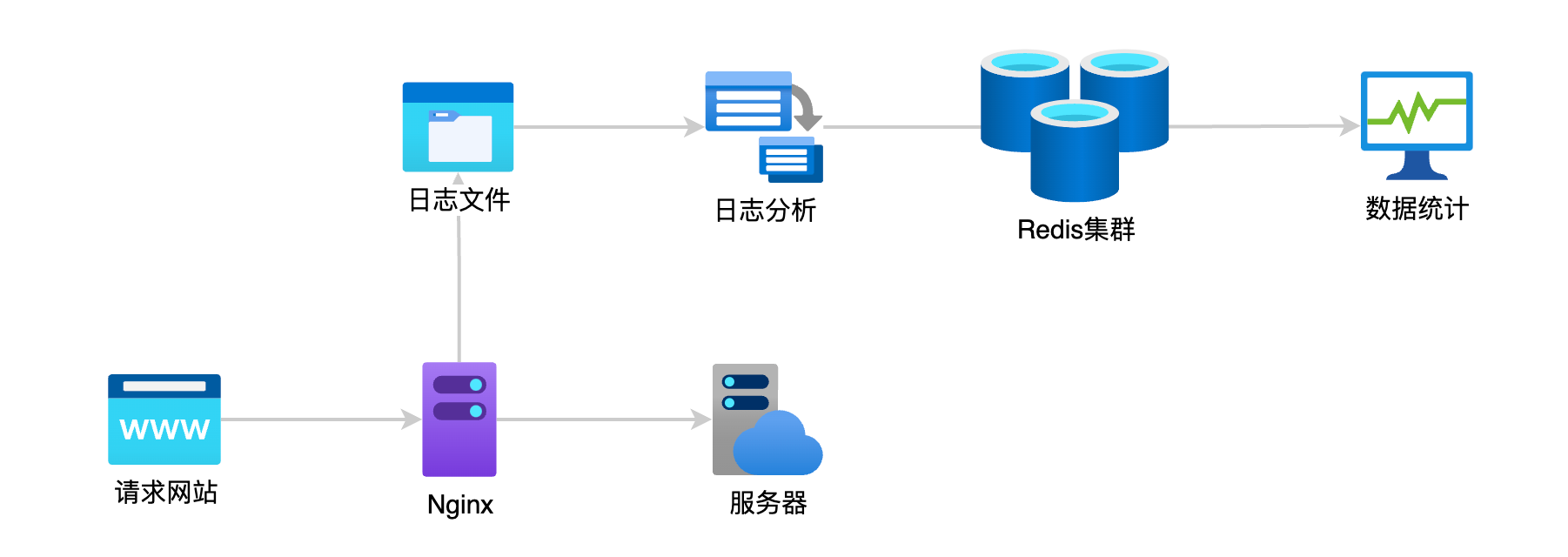
ref属性

src/components/SchoolName.vue
<template>
<div class="school">
<h2>学校名称:{{name}}</h2>
<h2>学校地址:{{address}}</h2>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name:'SchoolName',
data() {
return {
name:'黑马',
address:'广州'
}
},
}
</script>
<style>
.school{
background-color: orange;
}
</style>src/App.vue
<template>
<div>
<h1 v-text="msg" ref="title"></h1>
<button ref="btn" @click="showDOM">点我输出上方的DOM元素</button>
<SchoolName ref="sch"/>
</div>
</template>
<script>
// 引入School组件
import SchoolName from './components/School.vue'
export default {
name: 'App',
data(){
return{
msg:'欢迎学习Vue!'
}
},
components: { SchoolName },
methods:{
showDOM(){
console.log(this);
console.log(this.$refs.title);//真实DOM元素
console.log(this.$refs.btn);//真实DOM元素
console.log(this.$refs.sch);//School组件的实例对象
}
}
}
</script>


props配置项

src/App.vue
<template>
<div>
<StudentName name="李四" sex="女" /><hr/>
<StudentName name="王五" sex="男" :age="18"/><hr/>
</div>
</template>
<script>
// 引入School组件
import StudentName from './components/StudentName'
export default {
name: 'App',
components: { StudentName }
}
</script>
src/components/StudentName.vue
<template>
<div>
<h1>{{ msg }}</h1>
<h2>学生姓名:{{ name }}</h2>
<h2>学生性别:{{ sex }}</h2>
<h2>学生年龄:{{ myAge+1 }}</h2>
<button @click="updateAge">尝试修改到的年龄</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'StudentName',
data() {
return {
msg: '我是一个尚硅谷的学生',
myAge: this.age
}
},
methods:{
updateAge(){
this.myAge++;
}
},
// 1.简单声明接收
// props:[
// 'name','sex','age'
// ]
// 2.接收的同时对数据类型进行限制
// props: {
// name: String,
// sex: String,
// age: Number
// }
// 3.接收的同时:进行类型限制+默认值的指定+必要性的限制
props: {
name: {
type: String,
required: true,
},
sex: {
type: String,
required: true,
},
age: {
type: Number,
default: 99,
}
}
}
</script>

注意:当props中与当前组件配置同名时,props中的配置优先级高于当前组件
mixin混入

1.组件和混入对象含有同名选项时,这些选项将以恰当的方式进行“合并”,在发生冲突时以组件优先
var mixin={
data:function(){
return{
message:'hello',
foo:'abc
}
}
}
new Vue({
mixins:[mixin],
data(){
return{
message:'goodbye',
bar:'def'
}
},
created(){
console.log(this.$data)
// =>{message:"ggodbye",foo:"abc",bar:"def"}
}
})2.同名生命周期函数将合并为一个数组,都会被调用。另外,混入对象的生命周期函数将在自身生命周期函数之前调用
var mixin={
created(){
console.log('混入对象的钩子被调用')
}
}
new Vue({
mixins:[mixin],
created(){
console.log('组件钩子被调用')
}
})
// =>"混入对象的钩子被调用"
// =>"组件钩子被调用"src/mixin.js
export const hunhe={
methods:{
showName(){
alert(this.name);
}
},
mounted(){
console.log('你好啊');
}
}
export const hunhe2={
data(){
return {
x:100,
y:200
}
}
}src/components/School.vue
<template>
<div>
<h2 @click="showName">学校名称:{{ name }}</h2>
<h2>学校地址:{{ address }}</h2>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import {hunhe,hunhe2} from '../mixin'
export default {
name: 'School',
data() {
return {
name:'黑马',
address:'广州',
x:666
}
},
mixins:[hunhe,hunhe2]//局部混入
}
</script>
src/components/Student.vue
<template>
<div>
<h2 @click="showName">学生姓名:{{ name }}</h2>
<h2>学生性别:{{ sex }}</h2>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import {hunhe,hunhe2} from '../mixin'
export default {
name: 'Student',
data() {
return {
name:'张三',
sex:'男'
}
},
mixins:[hunhe,hunhe2]//局部混入
}
</script>
src/App.vue
<template>
<div>
<Student/>
<hr/>
<School/>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Student from './components/Student'
import School from './components/School'
export default {
name: 'App',
components: { Student,School }
}
</script>
src/main.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
import { hunhe } from './mixin'
// import {mixin} from './mixin'
Vue.config.productionTip = false
// Vue.mixin(hunhe) //全局混合引入
// Vue.mixin(hunhe2) //全局混合引入
new Vue({
el: '#app',
render: h => h(App)
})

plugin插件

src/plugins.js
export default {
install(Vue,x,y,z){
console.log(x,y,z)
// 全局过滤器
Vue.filter('mySlice',function(value){
return value.slice(0,4)
})
// 定义全局指令
Vue.directive('fbind',{
// 指令与元素成功绑定时
bind(element,binding){
element.value=binding.value
},
// 指令所在元素被插入页面时
inserted(element,binding){
element.focus()
},
// 指令所在的模板被重新解析时
update(element,binding){
element.value=binding.value
}
})
// 定义混入
Vue.mixin({
data(){
return{
x:100,
y:200
}
}
})
// 给Vue原型上添加一个方法(vm和vc都能用
Vue.prototype.hello=()=>{
alert('你好啊')
}
}
}
src/main.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
import plugins from './plugins.js'
Vue.config.productionTip = false
//应用插件
Vue.use(plugins,1,2,3)
//创建vm
new Vue({
el: '#app',
render: h => h(App)
})src/components/School.vue
<template>
<div>
<h2>学校名称:{{ name|mySlice }}</h2>
<h2>学校地址:{{ address }}</h2>
<button @click="test">点我测试一个hello方法</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'School',
data() {
return {
name:'黑马',
address:'广州'
}
},
methods:{
test(){
this.hello()
}
}
}
</script>
src/components/Student.vue
<template>
<div>
<h2>学生姓名:{{ name }}</h2>
<h2>学生性别:{{ sex }}</h2>
<input type="text" v-bind:value="name"/>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'Student',
data() {
return {
name:'张三',
sex:'男'
}
}
}
</script>
src/App.vue
<template>
<div>
<Student/>
<hr/>
<School/>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Student from './components/Student'
import School from './components/School'
export default {
name: 'App',
components: { Student,School }
}
</script>
scoped样式

查看版本npm view webpack versions
src/components/Student.vue
<template>
<div class="demo">
<h2 class="title">学生姓名:{{ name }}</h2>
<h2 class="atguigu">学生性别:{{ sex }}</h2>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'Student',
data() {
return {
name:'张三',
sex:'男'
}
}
}
</script>
<style lang="less">
.demo{
background-color: pink;
.atguigu{
font-size: 40px;
}
}
</style>
src/components/School.vue
<template>
<div class="demo">
<h2 class="title">学校名称:{{ name}}</h2>
<h2>学校地址:{{ address }}</h2>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'School',
data() {
return {
name:'黑马',
address:'广州'
}
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
.demo{
background-color: skyblue;
}
</style>
src/App.vue
<template>
<div>
<h1 class="title">你好啊</h1>
<Student/>
<School/>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Student from './components/Student'
import School from './components/School'
export default {
name: 'App',
components: { Student,School }
}
</script>
<style scoped>
.title{
background-color: red;
}
</style>