文章目录
- 前言
- 1. pyc 介绍
- 2. py 代码编译
- 2.1 使用命令行编译
- 2.2 使用代码编译
- 3. 避免名为密钥案例
- 3.1 创建密钥存储代码文件
- 3.2 编译密钥代码
- 3.3 调用密钥代码
前言
写代码过程中,可能遇到一些敏感信息不想明文暴露在代码中的情况,本篇文章介绍使用 pyc 解决明文密钥问题。
1. pyc 介绍
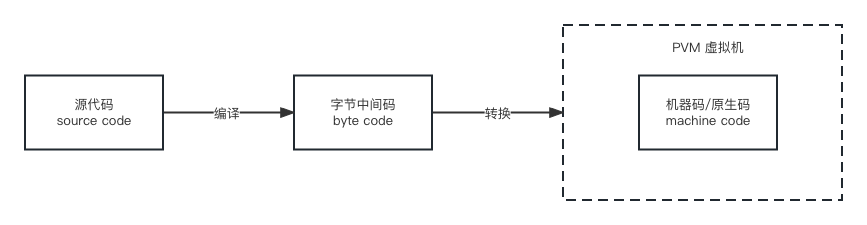
pyc 是 Python 经过 compile 后的文件类型,一段 Python 代码执行前会先将 .py 文件编译成 .pyc 文件它是一种字节码 byte code,然后由 Python 虚拟机执行。
相对于 .py 来讲,.pyc 对源代码有一定保护作用,提高了模块加载速度和跨平台性,但代码执行速度未得到提高。
2. py 代码编译
2.1 使用命令行编译
此时目录下有一个 hello.py 文件,代码内容是打印圆周率:
>>>># ls
pi.py
执行下 pi.py
[root@db4 test]# python3 pi.py
3.14159265359
编译:
python3 -m py_compile pi.py
[root@db4 test]# ls
pi.py __pycache__
编译完成后会在当前目录生成 pycache 目录,里面保存的就是编译后的文件。
2.2 使用代码编译
# 目录下所有 py 文件进行编译
import compileall
compileall.compile_dir('./')
# 单文件编译
import py_compile
py_compile.compile('pi.py')
cat 看的话就是一堆乱码:
�(�d&�@sddlZejZee�dS)�N)ZmathZpi�val�print�rr�pi.py<module>
3. 避免名为密钥案例
3.1 创建密钥存储代码文件
创建 get_token.py 文件,创建 get_token_code 函数 return 密钥:
def get_token_code():
return '727241fa-1ba7-11ee-9601-fab7dbe5cd00'
3.2 编译密钥代码
编译完成后会存储到 pycache 目标中:
python3 -m py_compile get_token.py
进入 pycache 目标,将 get_token.cpython-39.pyc 改名为 get_token.pyc 然后 mv 到代码目录。
mv get_token.cpython-39.pyc ../get_token.pyc
然后删除 get_token.py 文件。
3.3 调用密钥代码
此时密钥存储在 get_token.pyc 文件,创建新代码文件调用它:
from get_token import get_token_code
print(get_token_code())
打印结果:
727241fa-1ba7-11ee-9601-fab7dbe5cd00