文章目录
- 一、RestClient
- 1、什么是RestClient
- 2、导入demo工程
- 3、数据结构分析与索引库创建
- 4、初始化JavaRestClient
- 二、RestClient操作索引库
- 1、创建索引库
- 2、删除索引库
- 3、判断索引库是否存在
- 三、RestClient操作文档
- 1、新增文档
- 2、查询文档
- 3、删除文档
- 4、修改文档
- 5、批量导入文档
一、RestClient
1、什么是RestClient
ES官方提供了各种不同语言的客户端,用来操作ES,即RestClient。这些客户端的本质就是组装DSL语句,通过http请求发送给ES。
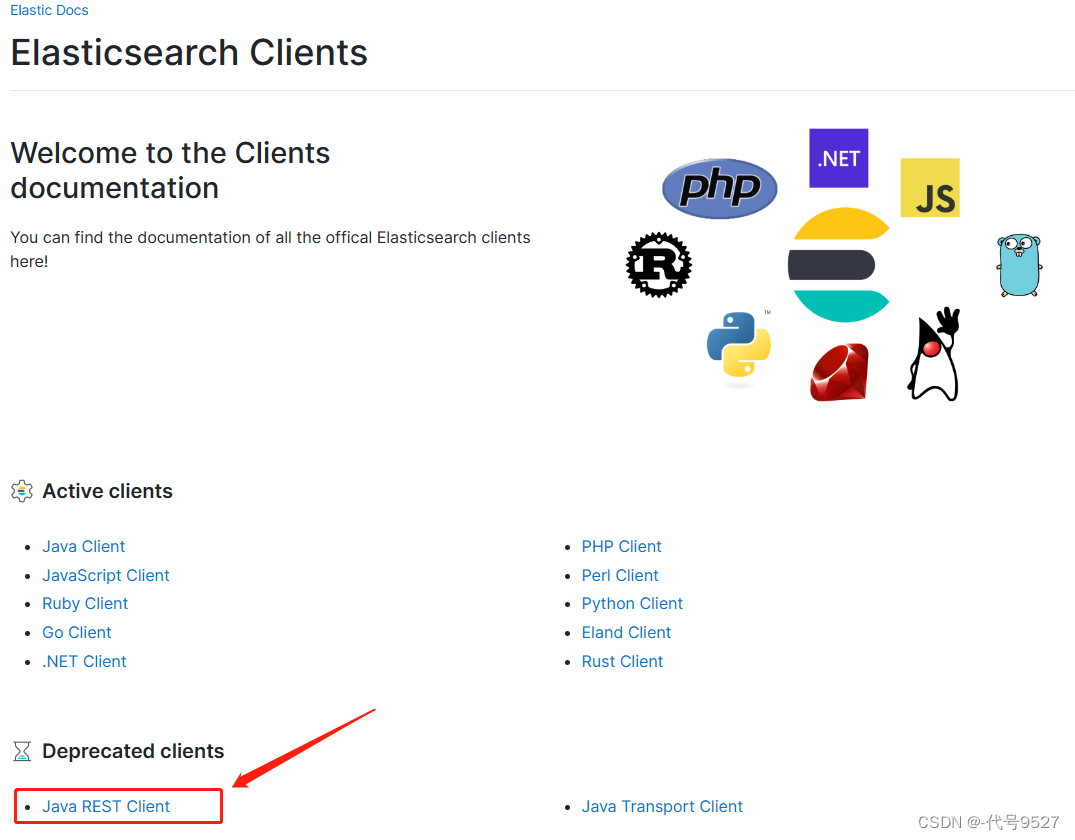
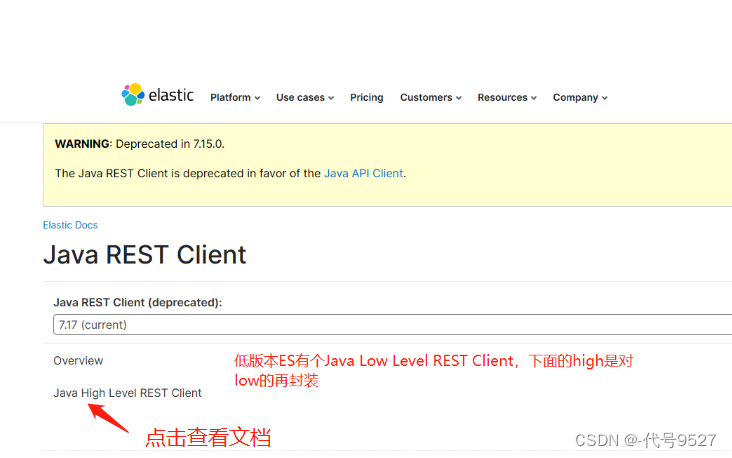
官方文档地址:
https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/client/index.html
2、导入demo工程
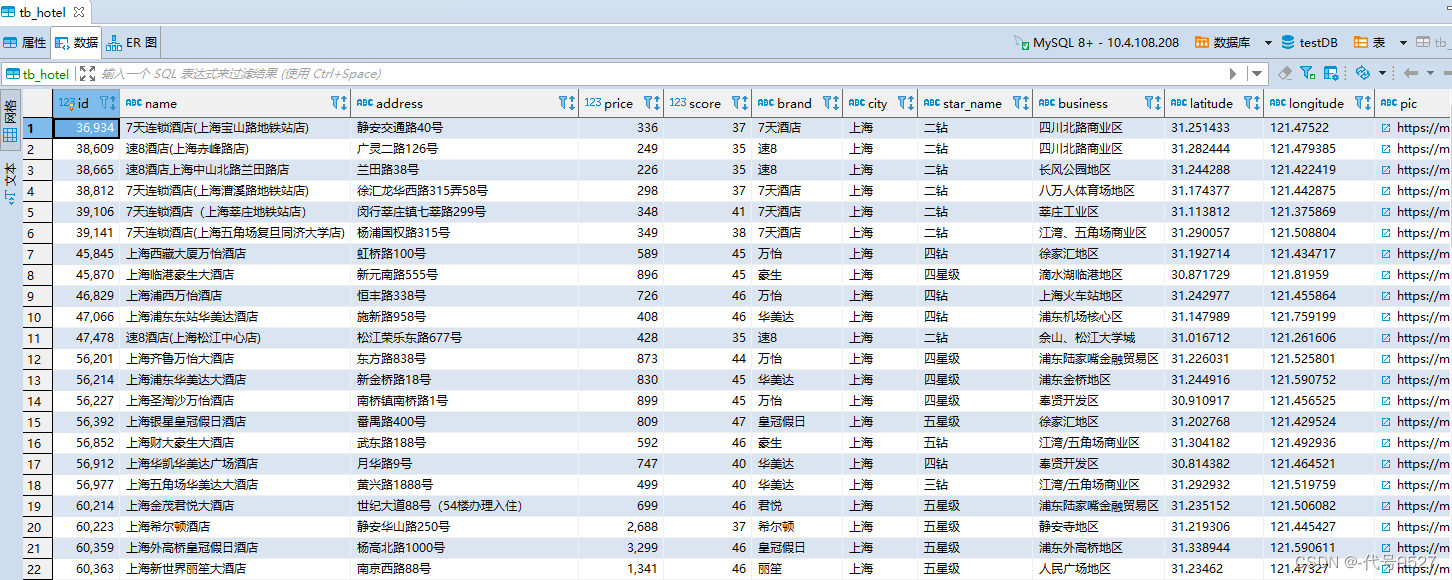
数据库信息如下:
mysql -h localhost -P3306 -uroot -padmian123 testDB < tb_hotel.sql
导入demo工程,基本结构如下:
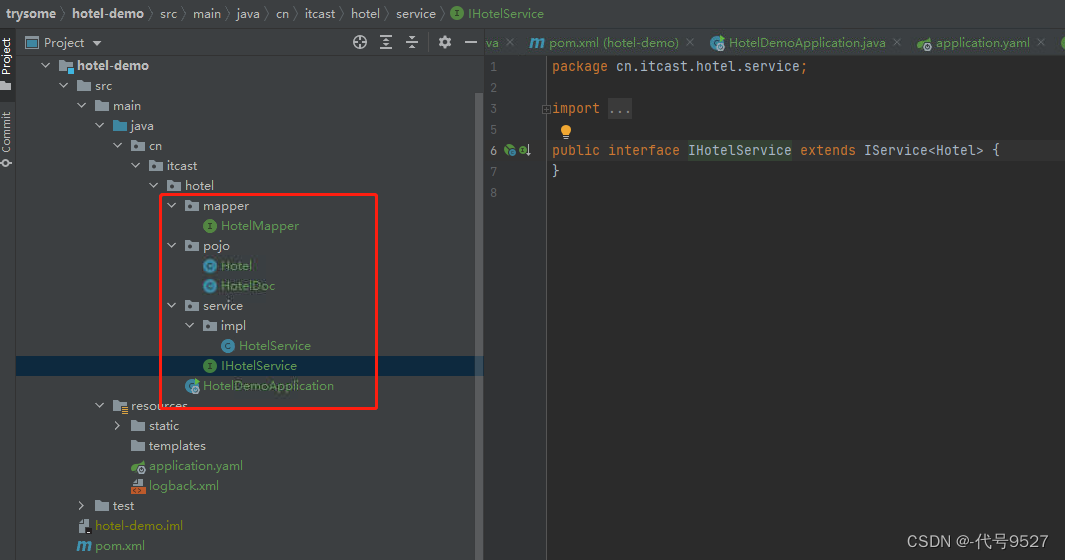
3、数据结构分析与索引库创建
ES的mapping要考虑的点主要有:
- 字段名(name)
- 字段类型(type)
- 是否参与搜索(index)
- 是否分词(type/keyword)
- 分词时,分词器用哪种(analyzer)
接下来,照着表结构,创建ES索引库:
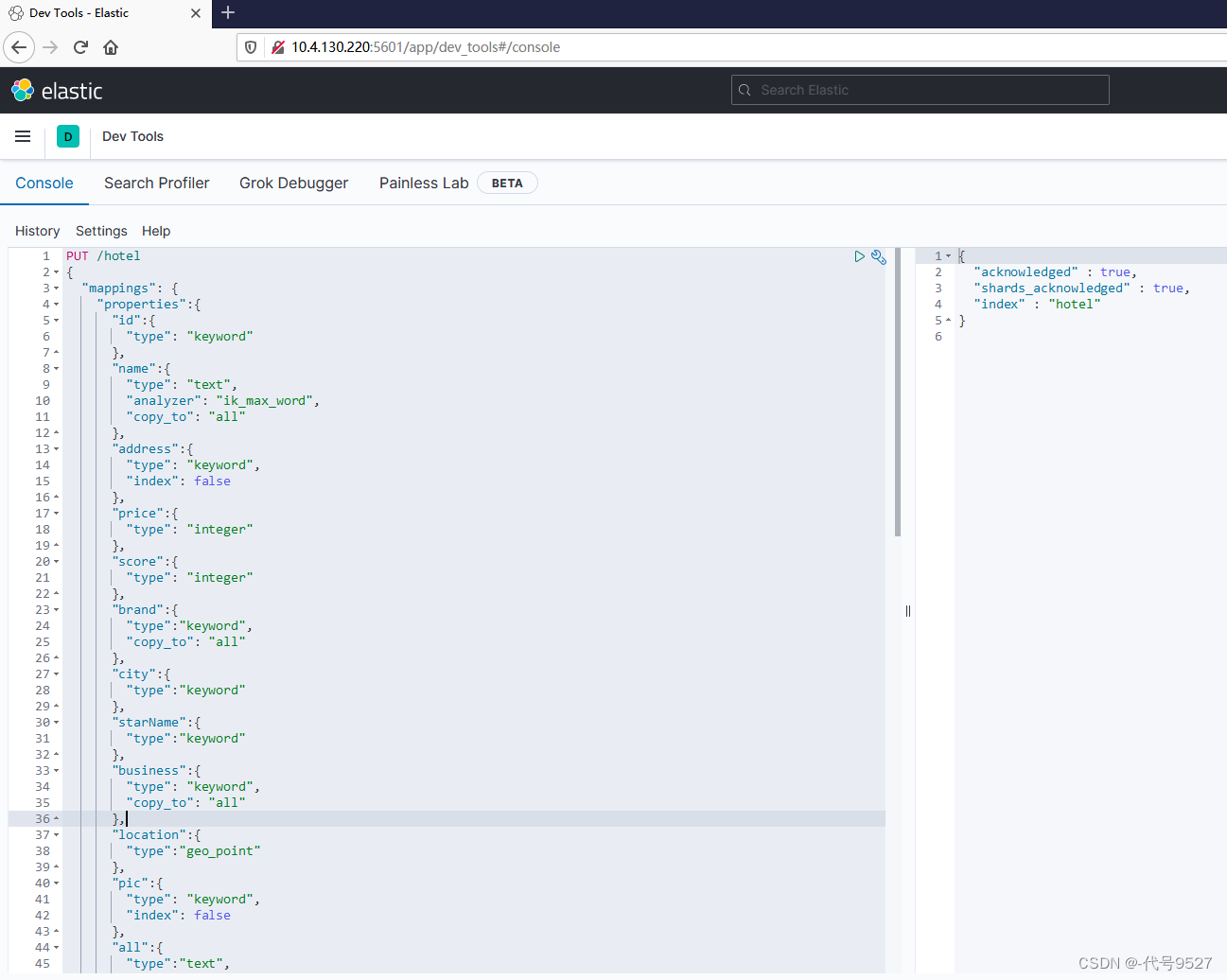
PUT /hotel
{
"mappings": {
"properties":{
"id":{
"type": "keyword" //注意这个类型
},
"name":{
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "ik_max_word",
"copy_to": "all"
},
"address":{
"type": "keyword",
"index": false //根据业务场景,用户刚来,不会去搜地址address,不参与搜索,index改为false,不再默认,类型选用keyword
},
"price":{
"type": "integer"
},
"score":{ //price、score等将来要参与过滤和排序,需要index,用默认的true
"type": "integer"
},
"brand":{ //city、brand品牌参与搜索,且不分词
"type":"keyword",
"copy_to": "all"
},
"city":{
"type":"keyword"
},
"starName":{ //不用下划线
"type":"keyword"
},
"business":{
"type": "keyword",
"copy_to": "all"
},
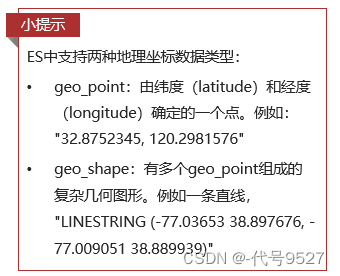
"location":{
"type":"geo_point" //经纬度两个字段合并为location,用ES的特定类型geo_point
},
"pic":{
"type": "keyword",
"index": false //pic既不分词,也不搜索
},
"all":{ //copy_to用的
"type":"text",
"analyzer": "ik_max_word"
}
}
}
}
用户就输入一个虹桥,我既想返回地址带虹桥的,也想返回商圈在虹桥的,还想返回酒店名称带虹桥的,如何实现?
加all字段,给需要的字段里加上从copy_to,这样all字段就可以代表这些加了copy_to的字段。
实现了在一个字段里搜到多个字段的内容。

4、初始化JavaRestClient
- 引入es的RestHighLevelClient依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.elasticsearch.client</groupId>
<artifactId>elasticsearch-rest-high-level-client</artifactId>
</dependency>
- 因为SpringBoot下默认的ES版本是7.6.2,所以我们需要定义properties覆盖默认的ES版本
<properties>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
<elasticsearch.version>7.12.1</elasticsearch.version>
</properties>
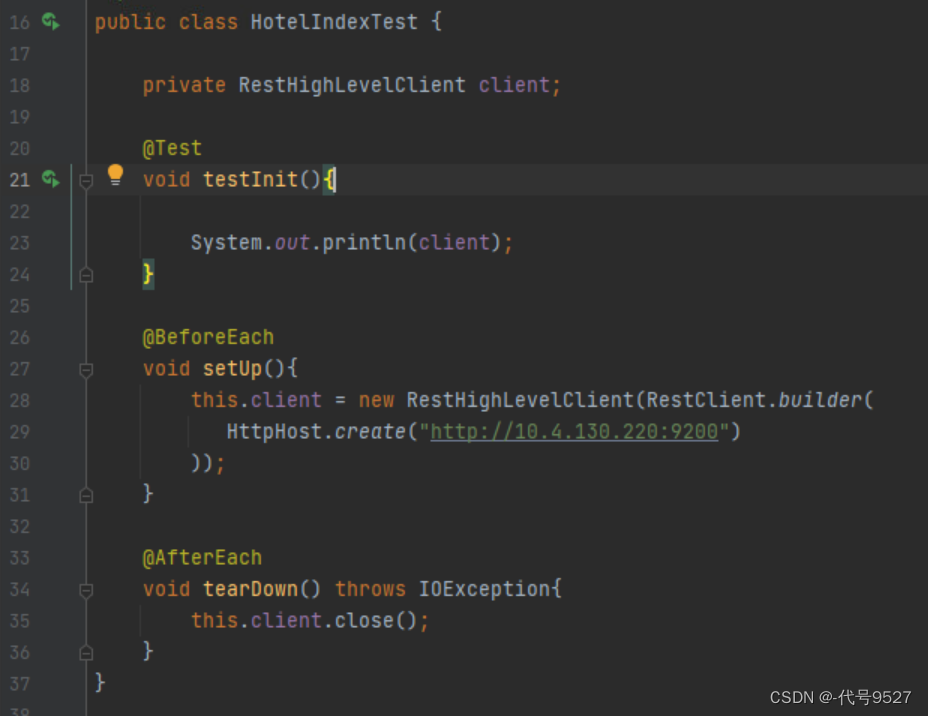
- 初始化RestHighLevelClient
RestHighLevelClient client = new RestHighLevelClient(RestClient.builder(
HttpHost.create("http://10.4.130.110:9200"),
HttpHost.create("http://10.4.130.111:9200"),
HttpHost.create("http://10.4.130.112:9200") //集群模式写多个
));
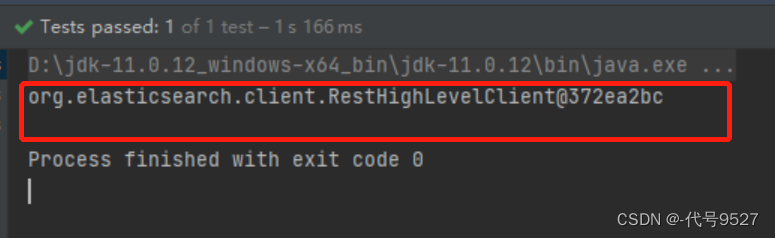
在单元测试里看下效果,打印restHighLevelClient对象:
二、RestClient操作索引库
1、创建索引库
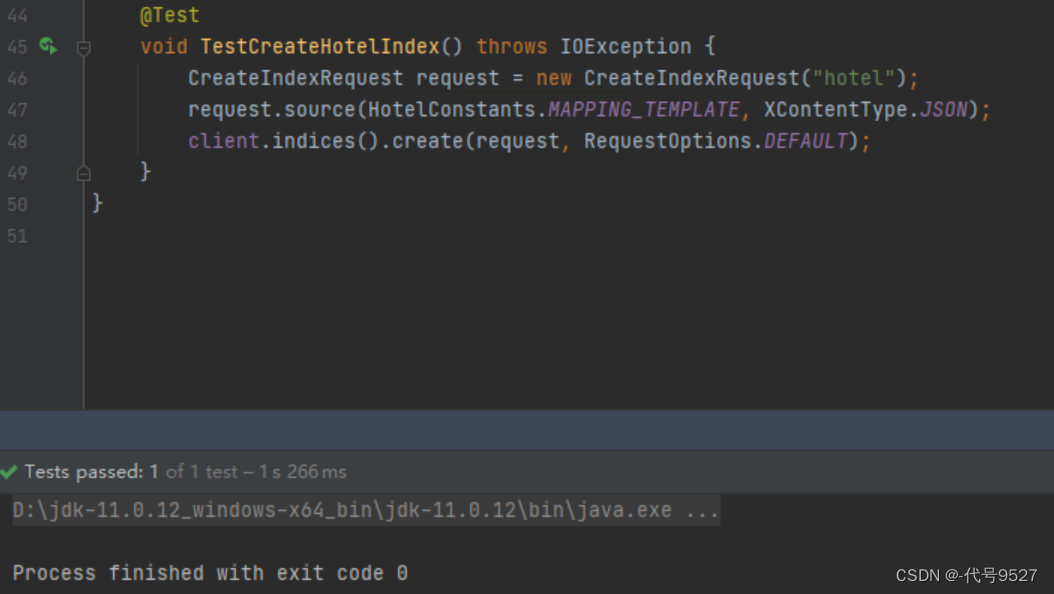
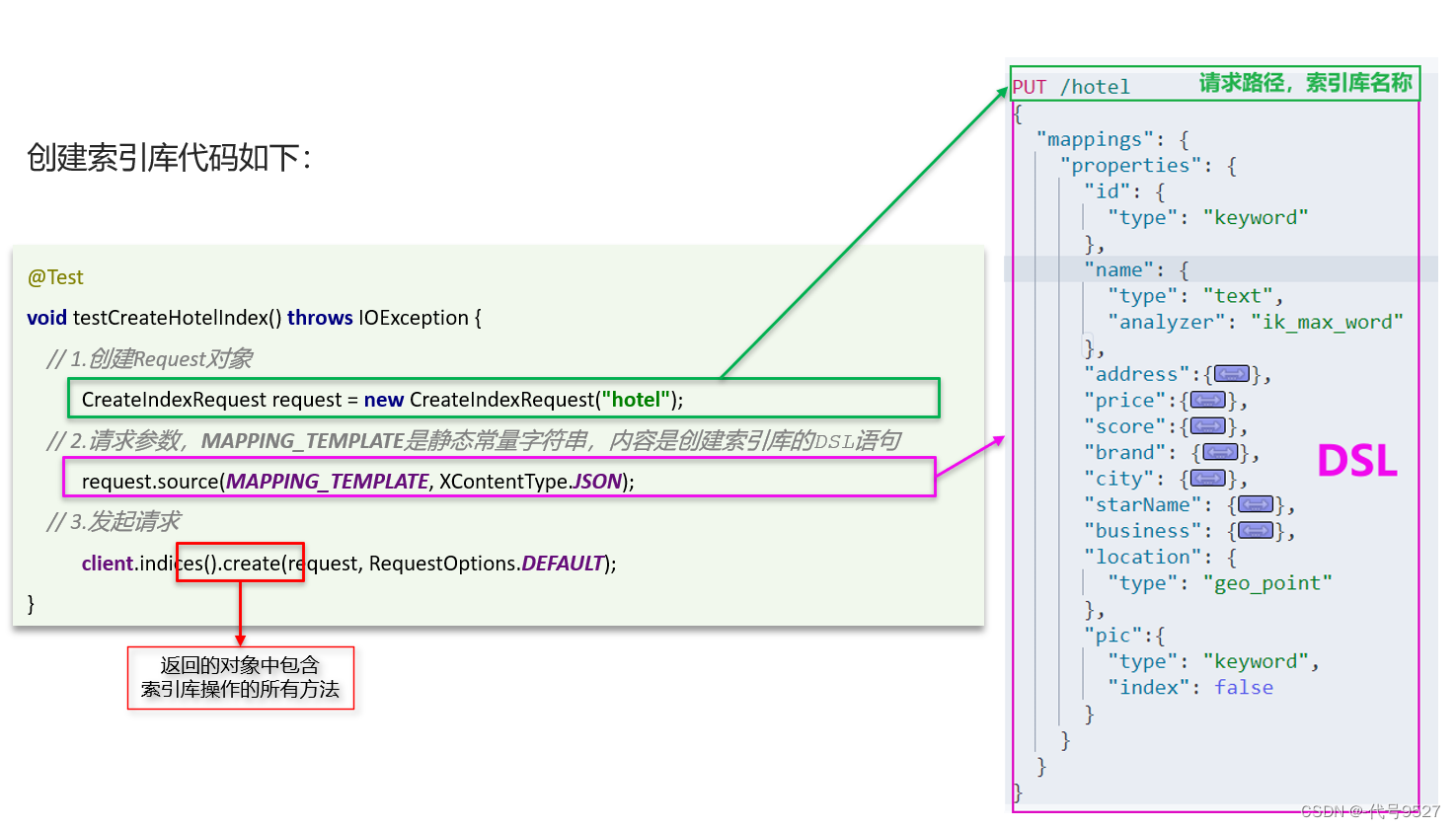
示例代码:
@Test
void testCreateHotelIndex() throws IOException {
// 1.创建Request对象
CreateIndexRequest request = new CreateIndexRequest("hotel");
// 2.请求参数,MAPPING_TEMPLATE是静态常量字符串,内容是创建索引库的DSL语句
request.source(MAPPING_TEMPLATE, XContentType.JSON);
// 3.发起请求
client.indices().create(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
}
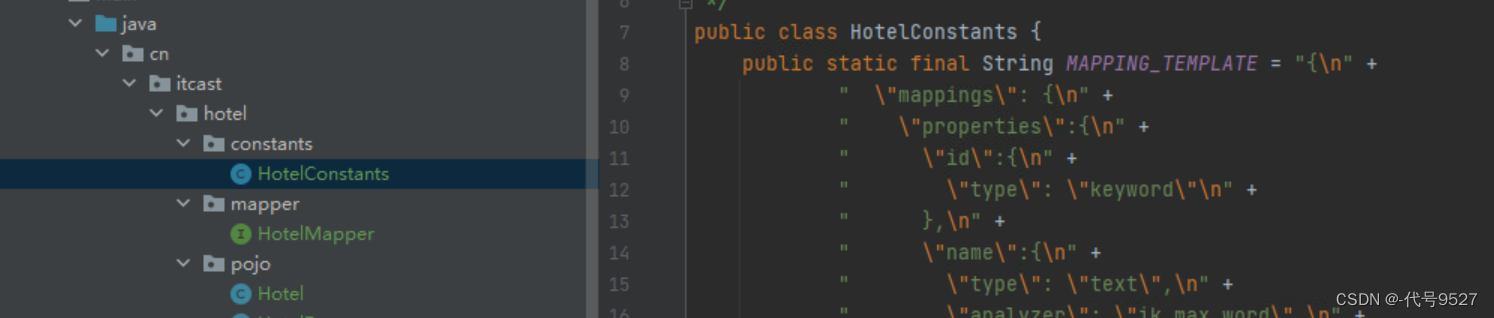
将创建索引库的DSL语句以静态字符串常量的形式统一写在常量类里:
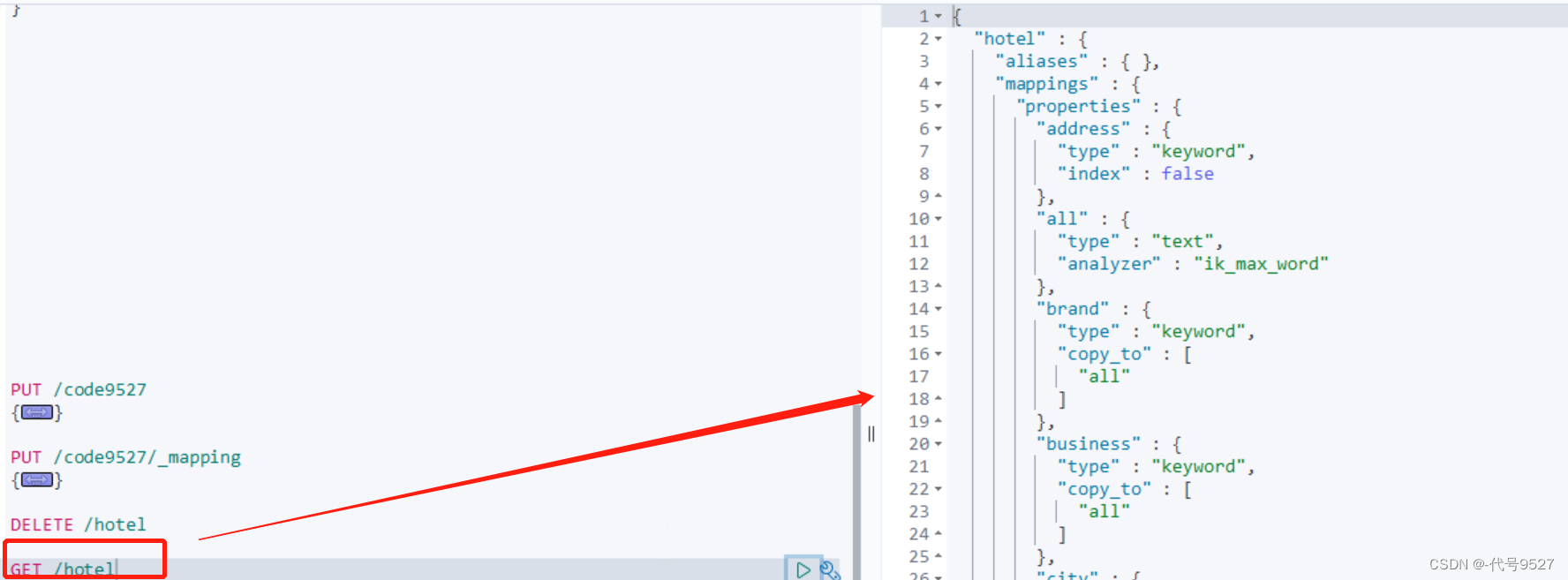
运行完成后,查看ES索引库:
GET /hotel
整个过程,和我们去Kiana手动执行DSL对比:
2、删除索引库
示例代码:
@Test
void testDeleteHotelIndex() throws IOException {
// 1.创建Request对象
DeleteIndexRequest request = new DeleteIndexRequest("hotel");
// 2.发起请求
client.indices().delete(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
}
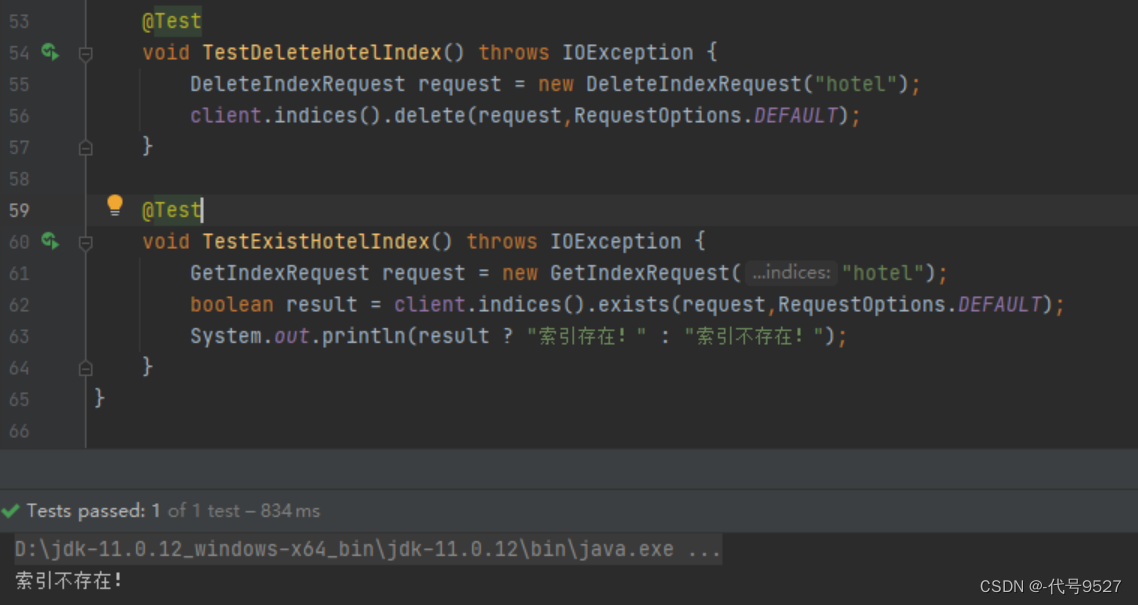
3、判断索引库是否存在
示例代码:
@Test
void testExistsHotelIndex() throws IOException {
// 1.创建Request对象
GetIndexRequest request = new GetIndexRequest("hotel");
// 2.发起请求
boolean exists = client.indices().exists(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
// 3.输出
System.out.println(exists);
}
小结:

三、RestClient操作文档
接下来利用JavaRestClient实现文档的CRUD,去数据库查询酒店数据,导入到hotel索引库,实现酒店数据的CRUD。
和操作索引库一样,还是要先完成JavaRestClient的初始化:
public class ElasticsearchDocumentTest {
// 客户端
private RestHighLevelClient client;
@BeforeEach
void setUp() {
client = new RestHighLevelClient(RestClient.builder(
HttpHost.create("http://192.168.150.101:9200")
));
}
@AfterEach
void tearDown() throws IOException {
client.close();
}
}
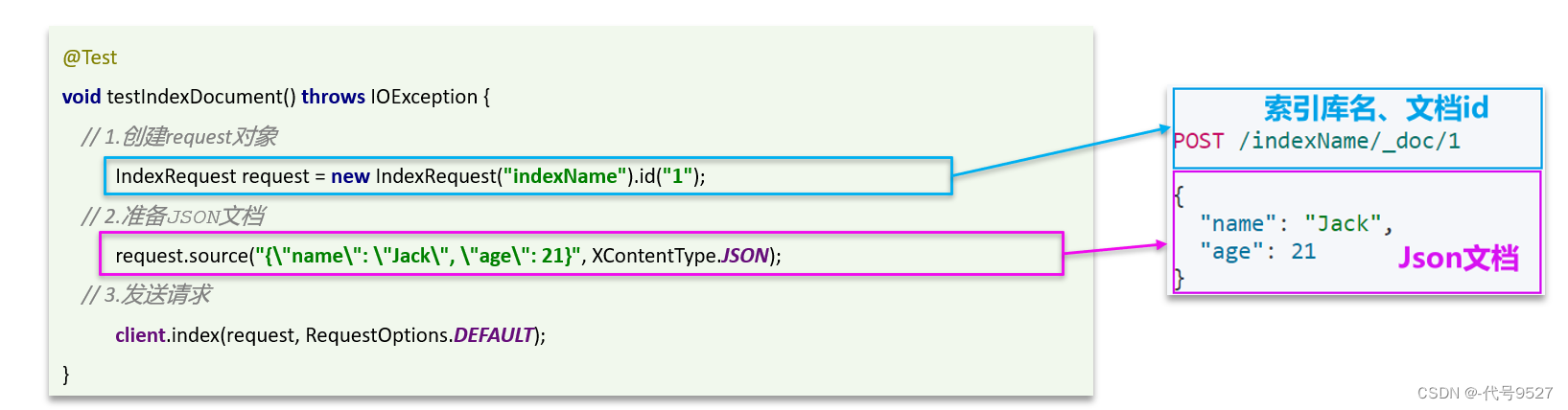
1、新增文档
先看下DSL语法和使用JavaRestClient操作代码来实现的对比:

![ruoyi若依 组织架构设计--[ 菜单管理 ]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/3fffdef07a60461fafab48745137f543.png)