目录
前言: 上文传送
4.六大模式实际操作(续)
4.4 路由模式:
---> 4.4.1 消费者配置类
---> 4.4.2 消费者代码
--->4.4.3 生产者代码
4.5 主题模式: (路由升级版)
---> 4.5.1 消费者配置类
---> 4.5.2 消费者代码
---> 4.5.3 生产者代码
---> 4.5.4 测试效果
4.6 RPC异步调用模式(用的少)
---> 4.6.1 消费者配置类
---> 4.6.2 消费者代码
---> 4.6.3 生产者代码
---> 4.6.4 实现效果
文章总结:
前言: 上文传送
微服务 02-rabbitmq在springboot中如何使用(上篇)
4.六大模式实际操作(续)
4.4 路由模式:
---> 4.4.1 消费者配置类
package cn.pingzhuyan.rabbitmq.config;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.DirectExchange;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.FanoutExchange;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Queue;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
/**
* rabbitmq的默认手动确认模式
* @author pzy
* @version 0.1.0
* @description: TODO
*/
@Configuration
public class RabbitConfig {
/**
* 创建(声明)一个简单队列
* @return
*/
@Bean
public Queue helloQueue(){
// return new Queue("PZY",true,false,false);
return new Queue("PZY");
}
/**
* 创建radioFanout交换机
* 消费者需要绑定此交换机
* @return
*/
@Bean
public FanoutExchange radioFanout(){
return new FanoutExchange("PZY_RADIO",false,false);
}
/**
* 路由模式 指定路由交换机
* 指定接收路由键
* @return
*/
@Bean
public DirectExchange directExchange(){
return new DirectExchange("PZY_DIRECT",false,false);
}
}
---> 4.4.2 消费者代码
package cn.pingzhuyan.rabbitmq.directM4;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.Exchange;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.Queue;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.QueueBinding;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* 路由交换机消费者
*
* @author pzy
* @version 0.1.0
* @description: TODO
*/
@Component
public class DirectM4Consumer {
@RabbitListener(bindings = @QueueBinding(
value = @Queue, //不写就是随机队列, false true true
exchange = @Exchange(name = "PZY_DIRECT", declare = "false"),//交换机(PZY_RADIO, 不创建并使用已经存在的交换机)
key = {"pzy1", "pzy2"}
))
public void radioFanoutMessage1(String msg) {
System.out.printf("消费者1接收到<1/2>: %s\n", msg);
}
@RabbitListener(bindings = @QueueBinding(
value = @Queue, //不写就是随机队列, false true true
exchange = @Exchange(name = "PZY_DIRECT", declare = "false"),//交换机(PZY_RADIO, 不创建并使用已经存在的交换机)
key = {"pzy3", "pzy4"}
))
public void radioFanoutMessage2(String msg) {
System.out.printf("消费者2接收到<3/4>: %s\n", msg);
}
}
--->4.4.3 生产者代码
package cn.pingzhuyan.rabbitmq.directM4;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.AmqpTemplate;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.Async;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.Scheduled;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.Random;
/**
* 路由交换机生产者
*
* @author pzy
* @version 0.1.0
* @description: TODO
*/
@Component
public class DirectM4Provider {
@Autowired
private AmqpTemplate amqpTemplate;
@Async
@Scheduled(cron = "*/1 * * * * ?")
public void directSend01() {
int num = new Random().nextInt(4) + 1;//生成1-4的随机数
System.out.println("生产者1: <发布和订阅模式>定时(1次/s)发送 -> " + "我是消息,编号是: " + num);
amqpTemplate.convertAndSend("PZY_DIRECT", "pzy" + num, "我是消息,编号是: " + num);
}
}
4.5 主题模式: (路由升级版)
---> 4.5.1 消费者配置类
/**
* 主题模式(升级版路由) 指定路由交换机
* 指定接收路由键表达式
* @return
*/
@Bean
public TopicExchange topicExchange(){
return new TopicExchange("PZY_TOPIC",false,false);
}
---> 4.5.2 消费者代码
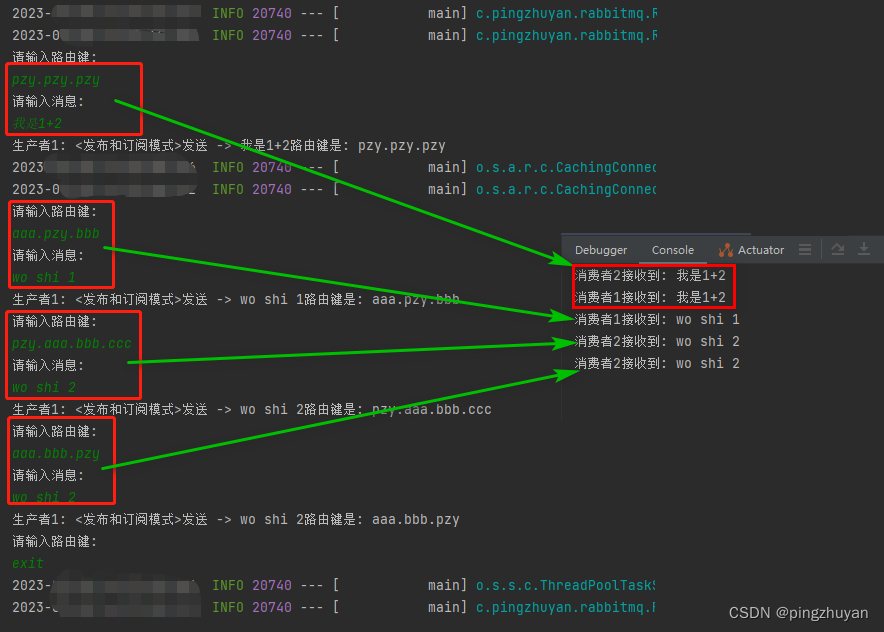
//测试四种
//1. pzy.pzy.pzy 1和2 都能收到
//2. aaa.pzy.bbb 1能收到
//3. pzy.aaa.bbb.ccc 2能收到
//4. aaa.bbb.pzy 2能收到
package cn.pingzhuyan.rabbitmq.topicM5;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.Exchange;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.Queue;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.QueueBinding;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* 路由交换机消费者
* 测试四种
* 1. pzy.pzy.pzy 1和2 都能收到
* 2. aaa.pzy.bbb 1能收到
* 3. pzy.aaa.bbb.ccc 2能收到
* 4. aaa.bbb.pzy 2能收到
*
* @author pzy
* @version 0.1.0
* @description: TODO
*/
@Component
public class TopicM5Consumer {
/**
* 消费者1
*
* @param msg
*/
@RabbitListener(bindings = @QueueBinding(
value = @Queue, //不写就是随机队列, false true true
exchange = @Exchange(name = "PZY_TOPIC", declare = "false"),//交换机(PZY_RADIO, 不创建并使用已经存在的交换机)
key = {"*.pzy.*"}
))
public void radioFanoutMessage1(String msg) {
System.out.printf("消费者1接收到: %s\n", msg);
}
/**
* 消费者2
*
* @param msg
*/
@RabbitListener(bindings = @QueueBinding(
value = @Queue, //不写就是随机队列, false true true
exchange = @Exchange(name = "PZY_TOPIC", declare = "false"),//交换机(PZY_RADIO, 不创建并使用已经存在的交换机)
key = {"pzy.#", "*.*.pzy"}
))
public void radioFanoutMessage2(String msg) {
System.out.printf("消费者2接收到: %s\n", msg);
}
}
---> 4.5.3 生产者代码
@PostConstruct解释传送门===> : 启动类加载时方法执行的几种实现方式
package cn.pingzhuyan.rabbitmq.topicM5;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.AmqpTemplate;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import javax.annotation.PostConstruct;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* 主题模式生产者
*
* @author pzy
* @version 0.1.0
* @description: TODO
*/
@Component
public class TopicM5Provider {
@Autowired
private AmqpTemplate amqpTemplate;
@PostConstruct
public void topicSend01() {
for (; ; ) {
System.out.println("请输入路由键: ");
String routingKey = new Scanner(System.in).nextLine();
/*中断测试,启动程序完成*/
if ("exit".equalsIgnoreCase(routingKey)) break;
System.out.println("请输入消息: ");
String message = new Scanner(System.in).nextLine();
System.out.println("生产者1: <发布和订阅模式>发送 -> " + message + "路由键是: " + routingKey);
amqpTemplate.convertAndSend("PZY_TOPIC", routingKey, message);
}
}
}
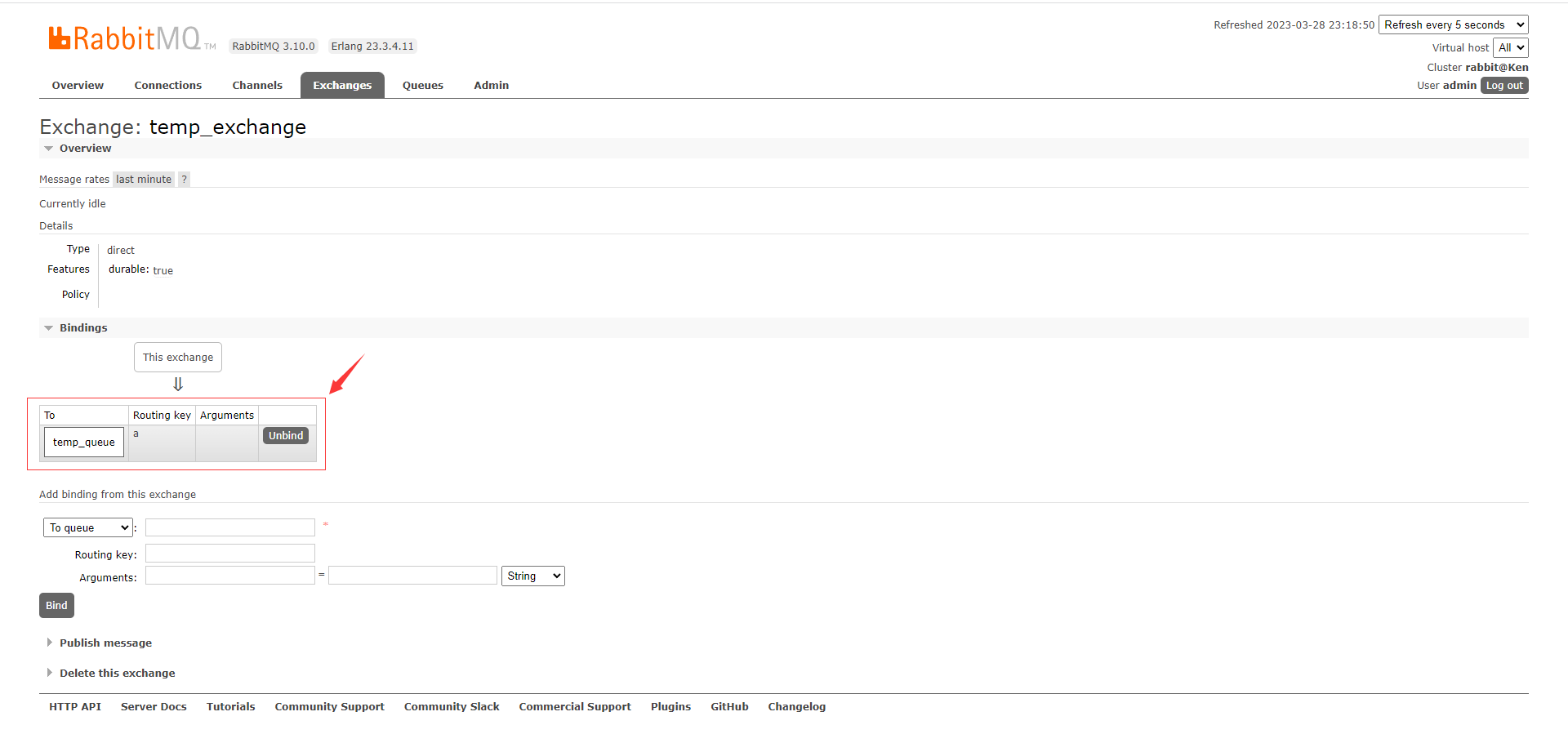
---> 4.5.4 测试效果
4.6 RPC异步调用模式(用的少)
---> 4.6.1 消费者配置类
---> 4.6.2 消费者代码
---> 4.6.3 生产者代码
---> 4.6.4 实现效果
文章总结:
到此 springboot整合rabbitmq的基础demo结束了 代码一行行敲得 结果都是实际测试成功的
还有其他写法 后续可能会补充进去 , 欢迎评论