文章目录
- 系列文章
- 0x0. 前言
- 0x1. 🐕 Supervised finetuning (SFT) 教程翻译
- 🏃 如何训练模型
- 🏃 如何对SFT checkpoint进行评测?
- 💁 模型和数据
- ☀️来自OPT-1.3B及其SFT变体(使用不同微调数据)的提示示例
- ☀️ 一些参数解释和可训练的最大模型
- 👀 其它
- 0x2. 评测脚本解读
- 0x3. 训练脚本解读
- 0x3.1 头文件相关解析
- create_prompt_dataset解析
- 工具函数解析
- print_rank_0
- to_device
- save_hf_format
- set_random_seed
- get_all_reduce_mean
- get_optimizer_grouped_parameters
- save_zero_three_model
- load_hf_tokenizer
- convert_linear_layer_to_lora
- convert_lora_to_linear_layer
- only_optimize_lora_parameters
- create_hf_model
- 0x3.2 main.py主体解析
- parse_args解析
- main函数解析
- 0x4. hybrid_engine的细节 & log
- 0x5. 总结
系列文章
- DeepSpeed-Chat 打造类ChatGPT全流程 笔记一
- 【DeepSpeed 教程翻译】三,在 DeepSpeed中使用 PyTorch Profiler和Flops Profiler
- DeepSpeed结合Megatron-LM训练GPT2模型笔记(上)
- 【DeepSpeed 教程翻译】二,Megatron-LM GPT2,Zero 和 ZeRO-Offload
- 【DeepSpeed 教程翻译】开始,安装细节和CIFAR-10 Tutorial
0x0. 前言
在 DeepSpeed-Chat 打造类ChatGPT全流程 笔记一 中跑通了DeepSpeed Chat的训练和推理流程,DeepSpeed Chat的训练流程包含监督指令微调(SFT),Reward模型微调,基于人类反馈的强化学习(RLHF)三个步骤。接着上面文章的todo,这篇文章主要是解析一下监督指令微调(SFT)阶段的代码实现。
0x1. 🐕 Supervised finetuning (SFT) 教程翻译
监督微调(SFT)与在自然语言任务(例如,WikiText-103)上的标准语言模型微调非常相似。主要的区别来自于数据集资源,SFT将收集高质量的查询-回答对来微调模型以达到人类更倾向的生成结果。
🏃 如何训练模型
我们提供了多个脚本用于在单个GPU(例如,单个A6000-48G,V100-32G,A100-40G等),单节点(例如,8/16x V100-32G,8 A100-40G/80G)和多节点设置(例如,64x A100-80G)上进行训练,这些可以在 training_scripts 目录中找到。例如,如果你有一个单独的A6000-48G,你可以简单地运行对应的脚本
training_scripts/single_gpu/run_1.3b.sh
来训练一个OPT-1.3b模型。我们的单节点脚本很容易扩展到多节点系统。
🏃 如何对SFT checkpoint进行评测?
一旦你使用上述代码完成训练,你可以简单地执行 bash evaluation_scripts/run_prompt.sh
它会要求用户提供两个模型的路径:(a) 原始预训练模型(即 --model_name_or_path_baseline facebook/opt-1.3b)和 (b) 微调后的模型(即 --model_name_or_path_finetune output/check_base)。“prompt_eval.py” 包含了几个可以根据你的喜好进行更新的提示。
💁 模型和数据
由于GPT3没有开源的checkpoint,我们使用了Meta OPT家族的预训练模型(即facebook/opt-1.3b)。你也可以使用其他预训练模型(如GPT-Neo,Bloom等)。至于数据集,我们也使用了来自Huggingface数据集的开源数据集,具体如下:
Dahoas/rm-static
Dahoas/full-hh-rlhf
Dahoas/synthetic-instruct-gptj-pairwise
yitingxie/rlhf-reward-datasets
openai/webgpt_comparisons
stanfordnlp/SHP
感谢DeepSpeed RLHF的数据抽象和融合技术,我们现在可以将多个数据源合并用于训练。然而,重要的是要注意,不同的数据集可能使用不同的提示词(例如,Dohas/rm-static使用"Human:"表示查询,"Assistant:"表示回答)。因此,用户必须自行对齐这些提示。在我们的例子中,我们一致使用了Dohas/rm-static的格式。通过我们的评估,我们发现整合多样化的数据集可以提高模型的质量。请参考下一节以获取不同查询-答案对的示例。
☀️来自OPT-1.3B及其SFT变体(使用不同微调数据)的提示示例

☀️ 一些参数解释和可训练的最大模型
main.py文件中使用的大多数参数都有清晰的解释,如果你有解码器模型微调的经验,通常很容易理解。然而,如果你对其中任何一个不清楚,请不要犹豫在GitHub问题上向我们求助。在这一部分,我们提供了一些具体的参数解释和它们的使用方法。
| 参数 | 解释 | 注意事项 |
|---|---|---|
| –data_path | 用于微调模型的数据 | 你可以指定多个数据资源来训练模型,例如:Dahoas/rm-static Dahoas/full-hh-rlhf |
| –data_split | 为三步训练切分数据 | 根据InstructGPT,我们提供了切分数据集的能力,使得每个分区只在一个步骤中使用。设置为"2,4,4"意味着我们分别使用20%,40%,40%的数据在每个步骤中。如果你只做SFT,或者你发现在不同步骤中使用重叠数据是可以的/有帮助的,你可以将它改为"10,0,0"。 |
| –sft_only_data_path | 用于微调模型的单响应数据 | 对于只在步骤1中使用的单响应数据,你应该将它们作为这个参数的一部分,而不是上面的data_path参数。这个参数中的数据集将不会被切分,而只在步骤1中全面使用。 |
| –gradient_checkpoint | 为模型启用梯度检查点(也称为激活检查点) | 这可以显著降低训练内存成本 |
| –offload | DeepSpeed特定功能。将模型卸载到CPT/NVME以节省内存 | 这可以在内存消耗较少的情况下训练更大的模型。但是它会减慢训练的速度。 |
| –zero_stage | DeepSpeed特定功能,适用于多GPU系统 | 这可以帮助将模型/优化器分布在多个GPU上。请参见https://www.deepspeed.ai/tutorials/zero/ |
| –lora_dim | 当它大于0时,将启用LoRA | 通常,LoRA需要更大的学习率才能更好地收敛 |
| –lora_module_name | 启用LoRA模块的范围。 | |
| –only_optimize_lora | 冻结所有其他参数,只优化LoRA相关参数 | |
| –gradient_checkpoint, --lora_dim, only_optimize_lora | 当启用LoRA和梯度检查点时,不能启用只优化LoRA | 如果全部启用,将影响梯度流(也就是由PyTorch支持的auto-grad系统后端) |
对于用户来说,一个重要的考虑是确定他们可以使用当前系统训练的最大模型大小。在这里,我们提供了一个估计这个限制的方法。假设你不使用卸载功能,并启用(i)零阶段3(如果使用多个GPU),(ii)梯度检查点,以及(iii)LoRA,那么你可以训练的大致最大模型大小(以十亿参数为单位)可以估计为"总GPU内存(GB)除以3"。例如,如果你有一台单一的A6000-48G GPU,你可能可以训练最多16十亿参数的模型。需要注意的是,这只是一个粗略的估计,你应该自己验证。
👀 其它
从InstructGPT的工作中,我们建议为了得到更好的人类偏好的答案,让模型过度拟合(即更长的训练周期)。通过我们的探索,我们发现这对于较小模型的微调,如OPT-1.3B,特别有帮助。值得注意的是,我们在脚本中提供的超参数并没有经过大量的调整。因此,我们鼓励用户和实践者自己找到最优的配置。此外,我们的系统可以很容易地扩展到其他语言,如中文和日语。为了证明这一点,我们在"training_scripts/other_language"目录下包含了两个例子。
0x2. 评测脚本解读
DeepSpeedExamples/applications/DeepSpeed-Chat/training/step1_supervised_finetuning/evaluation_scripts/run_prompt.sh这个脚本是对输入的模型进行评测,我们看一下内容:
# You can provide two models to compare the performance of the baseline and the finetuned model
export CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0
python prompt_eval.py \
--model_name_or_path_baseline XXX \
--model_name_or_path_finetune XXX
这表示我们可以调用prompt_eval.py来对baseline模型和finetune模型进行对比评测。所以评测的实现就是这里的prompt_eval.py,接下来对prompt_eval.py做一个解读。
- 首先是头文件导入部分,除了一些常规的需要用到的包还从DeepSpeed Chat的utils下面导入了2个函数。
# DeepSpeed Team
import argparse
import logging
import torch
import sys
import os
from transformers import (
AutoModelForCausalLM, )
sys.path.append(
os.path.abspath(os.path.join(os.path.dirname(__file__), os.path.pardir)))
from utils.model.model_utils import create_hf_model # 从utils下面导入自定义函数
from utils.utils import load_hf_tokenizer
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
接下来解析一下create_hf_model和load_hf_tokenizer两个函数的实现。首先是create_hf_model函数:
# 这段代码定义了一个名为create_hf_model的函数,该函数的作用是创建或加载一个预训练模型。该函数的主要参数包括:
# model_class:模型的类别,例如GPT-2、BERT等。
# tokenizer:用于模型的分词器。
# ds_config: DeepSpeed的配置参数。
# rlhf_training:一个标志,用来表示是否正在进行RLHF(Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback)训练。
# disable_dropout:一个标志,用来表示是否禁用dropout。Dropout是一种防止过拟合的技术。
def create_hf_model(model_class,
model_name_or_path,
tokenizer,
ds_config=None,
rlhf_training=False,
disable_dropout=False):
# 根据model_name_or_path从预训练模型获取模型配置model_config。
model_config = AutoConfig.from_pretrained(model_name_or_path)
# 如果disable_dropout为真,则将模型配置中的dropout设为0.0。
if disable_dropout:
model_config.dropout = 0.0
# Note: dschf is defined in function scope to avoid global effects
# https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main_classes/deepspeed#nontrainer-deepspeed-integration
# 根据ds_config中的设置,创建DeepSpeed的配置对象dschf,以便进行DeepSpeed优化。
if ds_config is not None and ds_config["zero_optimization"]["stage"] == 3:
dschf = HfDeepSpeedConfig(ds_config)
else:
dschf = None
# 根据rlhf_training的值,确定是从配置中创建模型还是从预训练模型中加载模型。如果rlhf_training为真,则根据模型配置创建模型;否则,从预训练模型加载模型。
if rlhf_training:
# the weight loading is handled by create critic model
model = model_class.from_config(model_config)
else:
model = model_class.from_pretrained(
model_name_or_path,
from_tf=bool(".ckpt" in model_name_or_path),
config=model_config)
# 将模型的结束标记和填充标记设为分词器的结束标记id。
model.config.end_token_id = tokenizer.eos_token_id
model.config.pad_token_id = model.config.eos_token_id
# 调整模型的词汇表大小,使其为8的倍数。这样做的目的是为了在某些硬件(如GPU)上提高效率。
model.resize_token_embeddings(int(
8 *
math.ceil(len(tokenizer) / 8.0))) # make the vocab size multiple of 8
return model
然后是load_hf_tokenizer函数:
# 这段代码定义了一个名为load_hf_tokenizer的函数,该函数的作用是加载一个指定的分词器。这个函数的参数有:
# model_name_or_path:模型的名称或者预训练模型的路径。
# fast_tokenizer:是否使用Fast Tokenizer,这是一种更快的分词器实现。
def load_hf_tokenizer(model_name_or_path, fast_tokenizer=True):
# 检查model_name_or_path是否存在。如果存在,可能意味着这是一个本地的模型路径。
if os.path.exists(model_name_or_path):
# Locally tokenizer loading has some issue, so we need to force download
# 如果是本地模型,再检查在该路径下的"config.json"文件是否存在。如果存在,打开该文件,并从文件中读取"_name_or_path"字段,将其赋值给model_name,然后通过AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained函数,使用该模型名称和fast_tokenizer参数,从HuggingFace模型库下载并加载分词器。
model_json = os.path.join(model_name_or_path, "config.json")
if os.path.exists(model_json):
model_json_file = json.load(open(model_json))
model_name = model_json_file["_name_or_path"]
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name,
fast_tokenizer=True)
else:
# 如果model_name_or_path不存在,直接使用AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained函数,使用model_name_or_path和fast_tokenizer参数,从HuggingFace模型库下载并加载分词器。
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name_or_path,
fast_tokenizer=True)
return tokenizer
- 接下来是参数解析部分,解析如下:
# 这段代码定义了一个名为parse_args的函数,该函数的作用是解析命令行参数。它使用Python的argparse库来完成这个工作。下面是每个参数的详解:
def parse_args():
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description="Eval the finetued SFT model")
# model_name_or_path_baseline:基线模型的路径,这是一个必须提供的参数(required=True)。
parser.add_argument(
"--model_name_or_path_baseline",
type=str,
help="Path to baseline model",
required=True,
)
# model_name_or_path_finetune:微调后模型的路径,这也是一个必须提供的参数。
parser.add_argument(
"--model_name_or_path_finetune",
type=str,
help="Path to pretrained model",
required=True,
)
# num_beams:用于指定集束搜索的集束宽度,其默认值为1。
parser.add_argument(
"--num_beams",
type=int,
default=1,
help='Specify num of beams',
)
# num_beam_groups:用于指定集束搜索的组数,其默认值为1。
parser.add_argument(
"--num_beam_groups",
type=int,
default=1,
help='Specify num of beams',
)
# top_k:用于指定在Top-K采样中考虑的最高可能性词汇的数量,其默认值为4。
parser.add_argument(
"--top_k",
type=int,
default=4,
help='Specify num of beams',
)
# penalty_alpha:惩罚因子,其默认值为0.6。
parser.add_argument(
"--penalty_alpha",
type=float,
default=0.6,
help='Specify num of beams',
)
# num_return_sequences:生成序列的数量,其默认值为1。
parser.add_argument(
"--num_return_sequences",
type=int,
default=1,
help='Specify num of return sequences',
)
# max_new_tokens:生成的最大新token数,其默认值为100。
parser.add_argument(
"--max_new_tokens",
type=int,
default=100,
help='Specify num of return sequences',
)
# language:语言类型,可以是"English"、"Chinese"或"Japanese",默认为"English"。
parser.add_argument("--language",
type=str,
default="English",
choices=["English", "Chinese", "Japanese"])
# parser.parse_args()这个函数将解析命令行参数,并将结果保存在一个Namespace对象中。这个对象被返回,可以在其他地方使用这些参数。
args = parser.parse_args()
return args
- 接下来是
generate函数的解析:
# 这个函数是用来利用训练好的模型生成文本的,它接受以下参数
# model:已经训练好的模型。
# tokenizer:用于将文本转换为模型可理解的输入的工具。
# inputs:模型的输入数据。
# num_beams:在使用束搜索算法时的束宽,其默认值为1。
# num_beam_groups:在使用分组束搜索时的组数,默认为1。
# do_sample:是否进行随机采样。如果设为True,则在生成过程中会随机选择下一个单词,而不是仅选择最可能的单词。默认为False。
# num_return_sequences:模型返回的序列数,默认为1。
# max_new_tokens:模型生成的最大新token数,即最大生成文本的长度,默认为100。
def generate(model,
tokenizer,
inputs,
num_beams=1,
num_beam_groups=1,
do_sample=False,
num_return_sequences=1,
max_new_tokens=100):
# 函数首先使用模型的generate方法,根据提供的参数生成文本。
generate_ids = model.generate(inputs.input_ids,
num_beams=num_beams,
num_beam_groups=num_beam_groups,
do_sample=do_sample,
num_return_sequences=num_return_sequences,
max_new_tokens=max_new_tokens)
# 使用tokenizer的batch_decode方法将生成的令牌ID解码为可读的文本。注意,这里跳过了特殊的令牌(如填充和开始/结束令牌),并且不会清理tokenize产生的额外空格。
result = tokenizer.batch_decode(generate_ids,
skip_special_tokens=True,
clean_up_tokenization_spaces=False)
return result
- 接下来是
generate_constrastive_search函数的解析:
# 这个函数叫做 generate_constrastive_search,它是用于利用训练好的模型进行对比搜索生成文本的。这个函数接受以下参数:
# model:已经训练好的模型。
# tokenizer:用于将文本转换为模型可理解的输入的工具。
# inputs:模型的输入数据。
# top_k:在每一步生成时,只考虑概率最高的top_k个候选项,然后进行随机抽样。默认为4。
# penalty_alpha:用于惩罚新生成的token与原始输入之间的差异,默认为0.6。
# num_return_sequences:模型返回的序列数,默认为1。
# max_new_tokens:模型生成的最大新token数,即最大生成文本的长度,默认为100。
def generate_constrastive_search(model,
tokenizer,
inputs,
top_k=4,
penalty_alpha=0.6,
num_return_sequences=1,
max_new_tokens=100):
# 函数首先使用模型的generate方法,根据提供的参数生成文本。注意这里使用了模型的一个特殊的生成方式,这种方式在每一步生成时,只考虑概率最高的top_k个候选项,然后进行随机抽样,同时使用了一个惩罚因子penalty_alpha来惩罚新生成的token与原始输入之间的差异。
generate_ids = model.generate(inputs.input_ids,
top_k=top_k,
penalty_alpha=penalty_alpha,
num_return_sequences=num_return_sequences,
max_new_tokens=max_new_tokens)
# 然后,使用tokenizer的batch_decode方法将生成的token ID解码为可读的文本。注意,这里跳过了特殊的token(如填充和开始/结束token),并且不会清理token化产生的额外空格。
result = tokenizer.batch_decode(generate_ids,
skip_special_tokens=True,
clean_up_tokenization_spaces=False)
return result
- 接下来是一个简单的打印工具函数:
# gen_output:这是一个列表,其中包含了我们希望打印的内容,每一项都是一段文本。
def print_utils(gen_output):
# 函数会遍历gen_output列表中的每一项,然后将每一项都打印出来。为了在不同项之间增加一些可视化的分隔,函数在每一项前后都额外打印了一个空行。
for i in range(len(gen_output)):
print()
print(gen_output[i])
print()
- 然后是
prompt_eval这个函数,这个函数prompt_eval的目的是评估和比较基线模型(model_baseline)和微调过的模型(model_fintuned)对于一组提示(prompts)的生成性能。让我们逐行进行解析:
# 输入参数包括:args(命令行参数)、model_baseline(基线模型)、model_fintuned(微调模型)、tokenizer(用于编码和解码的分词器)、device(指定运行模型的设备)、prompts(一组要评估的提示)。
def prompt_eval(args, model_baseline, model_fintuned, tokenizer, device,
prompts):
# 对于prompts中的每一个提示,我们都做以下操作:
for prompt in prompts:
# 使用分词器将提示转换为模型所需的输入格式,并将其移至指定的设备上。
inputs = tokenizer(prompt, return_tensors="pt").to(device)
# 打印一条消息表示我们现在正在进行基线模型的生成。
print("==========Baseline: Greedy=========")
# 然后,我们调用之前定义的generate函数使用贪婪搜索方法生成文本,并使用print_utils函数打印生成的结果。
r_base = generate(model_baseline,
tokenizer,
inputs,
num_beams=1,
num_return_sequences=args.num_return_sequences,
max_new_tokens=args.max_new_tokens)
print_utils(r_base)
# 打印一条消息表示我们现在正在进行微调模型的生成。
print("==========finetune: Greedy=========")
# 同样地,我们调用generate函数使用贪婪搜索方法生成文本,并使用print_utils函数打印生成的结果。
r_finetune_g = generate(model_fintuned,
tokenizer,
inputs,
num_beams=1,
num_return_sequences=args.num_return_sequences,
max_new_tokens=args.max_new_tokens)
print_utils(r_finetune_g)
# 注意:在此函数中,贪婪搜索被用作基线方法。然而,该函数还提供了其他几种搜索策略的例子,包括多项式采样、束搜索、束搜索多项式采样、多样性束搜索和对比搜索。这些策略在此函数中都被注释掉了,但你可以根据需要去掉注释,使用这些策略。
# print("==========finetune: Multinomial sampling=========")
# r_finetune_m = generate(model_fintuned, tokenizer, inputs,
# num_beams=1,
# do_sample=True,
# num_return_sequences=args.num_return_sequences,
# max_new_tokens=args.max_new_tokens)
# print_utils(r_finetune_m)
# print("==========finetune: Beam Search=========")
# r_finetune_b = generate(model_fintuned, tokenizer, inputs,
# num_beams=args.num_beams,
# num_return_sequences=args.num_return_sequences,
# max_new_tokens=args.max_new_tokens)
# print_utils(r_finetune_b)
# print("==========finetune: Beam-search multinomial sampling=========")
# r_finetune_s = generate(model_fintuned, tokenizer, inputs,
# num_beams=args.num_beams,
# do_sample=True,
# num_return_sequences=args.num_return_sequences,
# max_new_tokens=args.max_new_tokens)
# print_utils(r_finetune_s)
# print("==========finetune: Diverse Beam Search=========")
# r_finetune_d = generate(model_fintuned, tokenizer, inputs,
# num_beams=args.num_beams,
# num_beam_groups=args.num_beam_groups,
# num_return_sequences=args.num_return_sequences,
# max_new_tokens=args.max_new_tokens)
# print_utils(r_finetune_d)
# print("==========finetune: Constrastive Search=========")
# r_finetune_c = generate_constrastive_search(model_fintuned, tokenizer, inputs,
# top_k=args.top_k,
# penalty_alpha=args.penalty_alpha,
# num_return_sequences=args.num_return_sequences,
# max_new_tokens=args.max_new_tokens)
# print_utils(r_finetune_c)
# 最后,打印一条消息表示这个提示的处理已经结束。然后打印两个空行作为分隔。
print("====================prompt end=============================")
print()
print()
- 解析main函数:
# main函数负责解析命令行参数、准备模型和分词器、定义提示,然后使用这些来评估和比较基线模型和微调模型。
def main():
# 这个main函数是整个脚本的入口点。它首先通过parse_args函数解析命令行参数。然后它设置了运行模型的设备为第一个GPU。
args = parse_args()
device = torch.device("cuda:0")
# 接着,它使用load_hf_tokenizer函数加载分词器,然后使用create_hf_model函数创建基线模型(model_baseline)和微调模型(model_fintuned)
tokenizer = load_hf_tokenizer(args.model_name_or_path_baseline,
fast_tokenizer=True)
model_baseline = create_hf_model(AutoModelForCausalLM,
args.model_name_or_path_baseline,
tokenizer, None)
model_fintuned = create_hf_model(AutoModelForCausalLM,
args.model_name_or_path_finetune,
tokenizer, None)
# 然后,这些模型被移动到指定的设备上。
model_baseline.to(device)
model_fintuned.to(device)
# 在接下来的部分,函数定义了一组用于评估的提示。注意,这里特别指出,如果提示以空格结束,那么没有经过微调的原始模型有可能会陷入停滞并无法产生响应。微调过的模型在这方面表现得更好。因此,这里所有的提示都以冒号":"结束,以使得比较更有意义。
# 这个脚本支持英文、中文和日文的评估,它通过args.language参数判断用户选择的语言,并根据此选择加载对应的提示。
if args.language == "English":
prompts = [
"Human: Please tell me about Microsoft in a few sentence? Assistant:",
"Human: Explain the moon landing to a 6 year old in a few sentences. Assistant:",
"Human: Write a short poem about a wise frog. Assistant:",
"Human: Who was president of the United States in 1955? Assistant:",
"Human: How does a telescope work? Assistant:",
"Human: Why do birds migrate south for the winter? Assistant:"
]
elif args.language == "Chinese":
prompts = [
"Human: 请用几句话介绍一下微软? Assistant:",
"Human: 用几句话向6岁的孩子解释登月。 Assistant:",
"Human: 写一首关于一只聪明的青蛙的短诗。 Assistant:",
"Human: 谁是1955年的美国总统? Assistant:", "Human: 望远镜是如何工作的? Assistant:",
"Human: 鸟类为什么要南迁过冬? Assistant:"
]
elif args.language == "Japanese":
prompts = [
"Human: マイクロソフトについて簡単に教えてください。 Assistant:",
"Human: 6歳児に月面着陸を短い文で説明する。 Assistant:",
"Human: 賢いカエルについて短い詩を書いてください。 Assistant:",
"Human: 1955年のアメリカ合衆国大統領は誰? Assistant:",
"Human: 望遠鏡はどのように機能しますか? Assistant:",
"Human: 鳥が冬に南に移動するのはなぜですか? Assistant:"
]
# 最后,它调用prompt_eval函数,将所有的参数和提示传递给它,以进行模型评估。
prompt_eval(args, model_baseline, model_fintuned, tokenizer, device,
prompts)
0x3. 训练脚本解读
训练过程都集中在DeepSpeedExamples/applications/DeepSpeed-Chat/training/step1_supervised_finetuning/main.py这个脚本,我们逐行解析一下这个脚本。
0x3.1 头文件相关解析
# DeepSpeed Team
# 首先,它导入了Python的标准库,如argparse(用于解析命令行参数),os和math。
# 然后,它导入了PyTorch库,这是一个用于深度学习的开源库,同时也导入了一些PyTorch的辅助模块,如DataLoader(用于加载数据)、
# RandomSampler和SequentialSampler(用于数据抽样)以及DistributedSampler(用于在分布式设置中进行数据抽样)。
import argparse
import os
import math
import sys
import torch
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader, RandomSampler, SequentialSampler
from torch.utils.data.distributed import DistributedSampler
# 接下来,它导入了Hugging Face的transformers库的一些模块,包括用于因果语言建模的模型(AutoModelForCausalLM),优化器调度类型(SchedulerType),默认的数据整理函数(default_data_collator)和获取优化器调度器的函数(get_scheduler)。
from transformers import (
AutoModelForCausalLM,
SchedulerType,
default_data_collator,
get_scheduler,
)
# 然后,它导入了deepspeed库,这是一个为大规模模型训练优化的库。它也导入了deepspeed库中的一些模块,包括优化器类(DeepSpeedCPUAdam和FusedAdam)
import deepspeed
from deepspeed.ops.adam import DeepSpeedCPUAdam, FusedAdam
# 之后,它将当前脚本的父目录添加到系统路径中,以便可以从该目录下的utils目录导入一些自定义函数和模块。
sys.path.append(
os.path.abspath(os.path.join(os.path.dirname(__file__), os.path.pardir)))
# 最后,它从utils目录中导入了一些自定义模块和函数,包括数据处理函数(create_prompt_dataset),打印和设备转换函数(print_rank_0和to_device),
# 模型保存函数(save_hf_format),随机种子设置函数(set_random_seed),求平均函数(get_all_reduce_mean),
# 获取优化器参数组的函数(get_optimizer_grouped_parameters),保存和加载模型的函数(save_zero_three_model和load_hf_tokenizer),
# 以及创建模型和处理模型的函数(create_hf_model)。这些函数在脚本中的后续部分都将被使用。
from utils.data.data_utils import create_prompt_dataset
from utils.utils import print_rank_0, to_device, save_hf_format, set_random_seed, get_all_reduce_mean, get_optimizer_grouped_parameters, save_zero_three_model, load_hf_tokenizer
from utils.ds_utils import get_train_ds_config
from utils.module.lora import convert_linear_layer_to_lora, convert_lora_to_linear_layer, only_optimize_lora_parameters
from utils.model.model_utils import create_hf_model
create_prompt_dataset解析
create_prompt_dataset这个函数实际上直接或者间接的用到了utils/data中raw_dataset.py和data_utils.py,为了搞清楚这个函数,我们需要对这两个文件做一个解析。
首先解析一下raw_dataset.py。这里先定义了一个PromptRawDataset类:
# DeepSpeed Team
from datasets import load_dataset
from torch.utils.data import Subset
import re
# 这段代码定义了一个名为PromptRawDataset的类,这个类是一个模板类,用于处理和组织模型输入数据的格式。
# 如果有新的数据集需要进行处理,可以继承这个类并实现相应的方法来确保数据的统一格式和接口。
class PromptRawDataset(object):
# 首先,这个类的构造函数__init__接收四个参数:output_path(输出路径),seed(随机种子),
# local_rank(本地等级)和dataset_name(数据集名称)。
# 在构造函数中,如果数据集名称不是'local/jsonfile',
# 那么会使用Hugging Face的datasets库的load_dataset函数来加载数据集。
def __init__(self, output_path, seed, local_rank, dataset_name):
self.output_path = output_path
self.seed = seed
self.local_rank = local_rank
if not dataset_name == 'local/jsonfile':
self.raw_datasets = load_dataset(dataset_name)
# 然后,这个类定义了一些方法,这些方法在默认情况下并没有实现(只是返回None或者空操作),
# 这是因为这个类只是一个模板类,这些方法需要在实际使用时在子类中具体实现。
def get_train_data(self): # 获取训练数据
return
def get_eval_data(self): # 获取评估数据
return
# The prompt should be in the format of: " Human: " + actual_prompt_sentence + " Assistant:"
# get_prompt方法用于获取样本中的prompt(提示,这是模型的输入)。
def get_prompt(self, sample):
return
# The chosen response should be in the format of: " " + actual_response_sentence
# get_chosen方法用于获取样本中的chosen(已选的回应,这是模型需要生成的目标输出)。
def get_chosen(self, sample):
return
# The rejected response should be in the format of: " " + actual_response_sentence
# If the dataset does not have rejected response, return None
# get_rejected方法用于获取样本中的rejected(被拒绝的回应,这可能用于一些特定的训练场景,比如在对抗训练中,但如果数据集中没有这样的数据,可以返回None)。
def get_rejected(self, sample):
return
# 获取样本中的prompt和chosen
def get_prompt_and_chosen(self, sample):
return
# 获取样本中的prompt和rejected
def get_prompt_and_rejected(self, sample):
return
接下来就是每个具体数据集的定义,我这里以 OpenaiWebgptcomparisonsDataset 为例解析一下,剩下的读者又需要可以自行理解:
# English dataset
# 这个类OpenaiWebgptcomparisonsDataset继承自PromptRawDataset类,
# 针对"openai/webgpt_comparisons"这个具体的数据集进行了特化。
class OpenaiWebgptcomparisonsDataset(PromptRawDataset):
# 在构造函数__init__中,调用了父类的构造函数,并设定了dataset_name和dataset_name_clean两个属性,
# 分别为"openai/webgpt_comparisons"和"openai_webgpt_comparisons"。
def __init__(self, output_path, seed, local_rank, dataset_name):
super().__init__(output_path, seed, local_rank, dataset_name)
self.dataset_name = "openai/webgpt_comparisons"
self.dataset_name_clean = "openai_webgpt_comparisons"
# get_train_data和get_eval_data方法分别从raw_datasets中获取训练数据和测试数据。
# 它们与之前的DahoasRmstaticDataset类不同之处在于,它们使用get_raw_dataset_split_index
# 方法对训练数据进行了划分,将其划分为训练集和验证集,并返回对应的数据子集。
def get_train_data(self):
from .data_utils import get_raw_dataset_split_index
dataset = self.raw_datasets["train"]
index = get_raw_dataset_split_index(self.local_rank, self.output_path,
self.dataset_name_clean,
self.seed, "train_eval", "9,1", 0,
len(dataset))
dataset = Subset(dataset, index)
return dataset
def get_eval_data(self):
from .data_utils import get_raw_dataset_split_index
dataset = self.raw_datasets["train"]
index = get_raw_dataset_split_index(self.local_rank, self.output_path,
self.dataset_name_clean,
self.seed, "train_eval", "9,1", 1,
len(dataset))
dataset = Subset(dataset, index)
return dataset
# get_prompt,get_chosen和get_rejected方法分别从样本中获取提示,已选回应和被拒绝的回应。
# 这里假定样本是一个字典,其中包含了名为'question','score_0','score_1','answer_0'和'answer_1'的字段。
# 其中,'question'字段是一个字典,包含了'full_text'字段。这个字段包含了人类提出的问题。
# 'score_0'和'score_1'字段是字符串,表示对'answer_0'和'answer_1'的评分。
# 如果'score_0'大于等于'score_1',那么'answer_0'就是已选回应,'answer_1'就是被拒绝的回应,反之亦然。
# 在获取已选回应和被拒绝的回应时,还对回应进行了处理,
# 去除了所有形如"[...]"或"(...)"的文本,然后在回应前添加了一个空格。
def get_prompt(self, sample):
return " Human: " + sample['question']['full_text'] + " Assistant:"
def get_chosen(self, sample):
if float(sample['score_0']) >= float(sample['score_1']):
response = sample['answer_0']
else:
response = sample['answer_1']
# This data has citation square brackets and numbers (e.g., "[1]").
# Right now we are not doing browser-assisted finetuning, thus we
# remove these citations to avoid confusing the model.
response = re.sub(r" [\(\[].*?[\)\]]", "", response)
response = re.sub(r"[\(\[].*?[\)\]]", "", response)
return " " + response
def get_rejected(self, sample):
if float(sample['score_0']) < float(sample['score_1']):
response = sample['answer_0']
else:
response = sample['answer_1']
response = re.sub(r" [\(\[].*?[\)\]]", "", response)
response = re.sub(r"[\(\[].*?[\)\]]", "", response)
return " " + response
# get_prompt_and_chosen和get_prompt_and_rejected方法则分别返回样本中的'prompt'和'chosen',
# 以及'prompt'和'rejected'的组合。这两个方法的返回值可以直接作为模型的输入和目标输出。
# 在返回这两个组合时,也进行了类似的处理,去除了所有形如"[...]"或"(...)"的文本。
def get_prompt_and_chosen(self, sample):
if float(sample['score_0']) >= float(sample['score_1']):
response = sample['answer_0']
else:
response = sample['answer_1']
response = re.sub(r" [\(\[].*?[\)\]]", "", response)
response = re.sub(r"[\(\[].*?[\)\]]", "", response)
return " Human: " + sample['question'][
'full_text'] + " Assistant: " + response
def get_prompt_and_rejected(self, sample):
if float(sample['score_0']) < float(sample['score_1']):
response = sample['answer_0']
else:
response = sample['answer_1']
response = re.sub(r" [\(\[].*?[\)\]]", "", response)
response = re.sub(r"[\(\[].*?[\)\]]", "", response)
return " Human: " + sample['question'][
'full_text'] + " Assistant: " + response
接着解析 data_utils.py:
# DeepSpeed Team
"""
Part of the code was adopted from https://github.com/microsoft/Megatron-DeepSpeed/blob/main/megatron/data/dataset_utils.py
"""
import torch
from torch.utils.data import Dataset, Subset, ConcatDataset
from torch.nn.utils.rnn import pad_sequence
import torch.nn.functional as F
from datasets import load_dataset
import numpy as np
import os
import hashlib # Python的内置库,提供了一系列散列函数,如MD5、SHA1等。
from itertools import chain # Python的内置库,提供了一系列用于操作迭代器的函数。
from . import raw_datasets
# 这段代码定义了一个名为get_raw_dataset的函数,其主要作用是根据传入的数据集名称dataset_name
# 返回一个适当的PromptRawDataset子类的实例。
# 这个函数有四个参数:dataset_name,output_path,seed和local_rank。
def get_raw_dataset(dataset_name, output_path, seed, local_rank):
# 在函数中,根据dataset_name的具体值来创建不同的PromptRawDataset子类的实例。
# 例如,如果dataset_name为"Dahoas/rm-static",那么就创建一个DahoasRmstaticDataset的实例;
# 如果dataset_name为"Dahoas/full-hh-rlhf",那么就创建一个DahoasFullhhrlhfDataset的实例,以此类推。
if "Dahoas/rm-static" in dataset_name:
return raw_datasets.DahoasRmstaticDataset(output_path, seed,
local_rank, dataset_name)
elif "Dahoas/full-hh-rlhf" in dataset_name:
return raw_datasets.DahoasFullhhrlhfDataset(output_path, seed,
local_rank, dataset_name)
elif "Dahoas/synthetic-instruct-gptj-pairwise" in dataset_name:
return raw_datasets.DahoasSyntheticinstructgptjpairwiseDataset(
output_path, seed, local_rank, dataset_name)
elif "yitingxie/rlhf-reward-datasets" in dataset_name:
return raw_datasets.YitingxieRlhfrewarddatasetsDataset(
output_path, seed, local_rank, dataset_name)
elif "openai/webgpt_comparisons" in dataset_name:
return raw_datasets.OpenaiWebgptcomparisonsDataset(
output_path, seed, local_rank, dataset_name)
elif "stanfordnlp/SHP" in dataset_name:
return raw_datasets.StanfordnlpSHPDataset(output_path, seed,
local_rank, dataset_name)
elif "pvduy/sharegpt_alpaca_oa_vicuna_format" in dataset_name:
return raw_datasets.PvduySharegptalpacaoavicunaformatDataset(
output_path, seed, local_rank, dataset_name)
elif "wangrui6/Zhihu-KOL" in dataset_name:
return raw_datasets.Wangrui6ZhihuKOLDataset(output_path, seed,
local_rank, dataset_name)
elif "Cohere/miracl-zh-queries-22-12" in dataset_name:
return raw_datasets.CohereMiraclzhqueries2212Dataset(
output_path, seed, local_rank, dataset_name)
elif "Hello-SimpleAI/HC3-Chinese" in dataset_name:
return raw_datasets.HelloSimpleAIHC3ChineseDataset(
output_path, seed, local_rank, dataset_name)
elif "mkqa-Chinese" in dataset_name:
return raw_datasets.MkqaChineseDataset(output_path, seed, local_rank,
"mkqa")
elif "mkqa-Japanese" in dataset_name:
return raw_datasets.MkqaJapaneseDataset(output_path, seed, local_rank,
"mkqa")
elif "Cohere/miracl-ja-queries-22-12" in dataset_name:
return raw_datasets.CohereMiracljaqueries2212Dataset(
output_path, seed, local_rank, dataset_name)
elif "lmqg/qg_jaquad" in dataset_name:
return raw_datasets.LmqgQgjaquadDataset(output_path, seed, local_rank,
dataset_name)
elif "lmqg/qag_jaquad" in dataset_name:
return raw_datasets.LmqgQagjaquadDataset(output_path, seed, local_rank,
dataset_name)
# 如果dataset_name是"local/jsonfile",则会检查在路径chat_path + '/data/train.json'
# 和chat_path + '/data/eval.json'下是否存在文件。如果存在,则创建一个LocalJsonFileDataset的实例;
# 如果不存在,则抛出一个RuntimeError异常。
elif "local/jsonfile" in dataset_name:
chat_path = os.path.abspath(
os.path.join(os.path.dirname(__file__), os.path.pardir,
os.path.pardir, os.path.pardir))
if not (os.path.isfile(chat_path + '/data/train.json')
and os.path.isfile(chat_path + '/data/eval.json')):
raise RuntimeError(
f"Please check both the train.json and eval.json files in your applications/DeepSpeed-Chat/data directory."
)
return raw_datasets.LocalJsonFileDataset(output_path, seed, local_rank,
dataset_name, chat_path)
else:
# 如果dataset_name没有在以上的所有条件中匹配到,那么函数也会抛出一个RuntimeError异常,表示没有为这个数据集的配置。
raise RuntimeError(
f"We do not have configs for dataset {dataset_name}, but you can add it by yourself in raw_datasets.py."
)
再看下 get_shuffle_idx函数:
# 这个函数的作用是生成一个大小为size的乱序索引数组,它接受两个参数:seed和size。
def get_shuffle_idx(seed, size):
np_rng = np.random.RandomState(seed=seed) # 创建一个NumPy的随机状态生成器对象np_rng,seed是随机种子,确定了随机数的生成序列。
dtype_ = np.uint32 # 设置其为NumPy的uint32类型,这是一个无符号32位整数类型。
if size >= (np.iinfo(np.uint32).max - 1): # 如果size大于或等于uint32的最大值减一,这里减一是为了防止可能的溢出。
dtype_ = np.int64 # 则将dtype_改为int64,这是一个64位的有符号整数类型。
shuffle_idx = np.arange(start=0, stop=size, step=1, dtype=dtype_) # 创建一个由0开始,步长为1,到size结束(不包含size),并且数据类型为dtype_的等差数列,将其赋值给shuffle_idx。
np_rng.shuffle(shuffle_idx) # 使用np_rng随机状态生成器对shuffle_idx进行随机排列,这样就打乱了shuffle_idx的顺序。
return shuffle_idx # 返回乱序后的shuffle_idx。
接着解析get_raw_dataset_split_index函数:
# 这个函数主要是根据提供的参数分割数据集,并生成一个分割索引。
# 它首先检查索引文件是否存在,如果不存在,则生成分割索引,并保存到文件。
# 然后,它从文件中加载索引,并返回索引列表。
# 它接受8个参数:local_rank、输出路径、数据集名称、种子、split_name、data_split、split_index和数据大小。
def get_raw_dataset_split_index(local_rank, output_path, dataset_name, seed,
split_name, data_split, split_index,
data_size):
# 根据给定参数生成索引文件名。
index_file_name = f"{output_path}/{dataset_name}_seed{seed}_{split_name}_{data_split}_{split_index}.npy"
# reindex each time when using local jsonfile since it's more likely to get modified
# 如果索引文件不存在,或者数据集名为'jsonfile',则执行下面的操作。
if (not os.path.isfile(index_file_name)) or (dataset_name == 'jsonfile'):
splits = [float(s) for s in data_split.split(',')] # 将data_split(以逗号分隔的字符串)分割为浮点数列表。
splits_sum = sum(splits) # 计算所有分割的总和。
splits = [split / splits_sum for split in splits] # 将每个分割值归一化,使其和为1。
splits_index = [0] # 初始化分割索引列表,起始值为0
for index, split in enumerate(splits): # 遍历分割列表。
# 将新的索引(当前索引加上归一化的分割值与数据大小的乘积)添加到索引列表。
splits_index.append(splits_index[index] +
int(round(split * float(data_size))))
# 计算最后一个索引与数据大小的差值。
diff = splits_index[-1] - data_size
# 遍历除第一个外的所有索引。
for index in range(1, len(splits_index)):
# 将差值从每个索引中减去,以确保最后一个索引等于数据大小。
splits_index[index] -= diff
# 断言最后一个索引等于数据大小
assert splits_index[-1] == data_size
# 生成一个乱序的索引。
shuffle_idx = get_shuffle_idx(seed, data_size)
for split_i in range(len(splits)): # 遍历每个分割。
# 根据给定参数生成乱序索引分割文件名。
shuffle_idx_split_file_name = f"{output_path}/{dataset_name}_seed{seed}_{split_name}_{data_split}_{split_i}.npy"
# 提取乱序索引的一个分割。
shuffle_idx_split = shuffle_idx[
splits_index[split_i]:splits_index[split_i + 1]]
# 将乱序索引分割保存到文件。
np.save(shuffle_idx_split_file_name,
shuffle_idx_split,
allow_pickle=True)
# 加载索引文件。
index = np.load(index_file_name, allow_pickle=True)
# 将索引数组转换为列表并返回。
return index.tolist()
接下来解析一下继承自Dataset的PromptDataset类:
# 这是一个自定义的PromptDataset类,它继承自torch.utils.data.Dataset。
# 这是一个数据集类,通常被用于PyTorch中数据的加载和预处理。
class PromptDataset(Dataset):
# 类的构造函数,它接受五个参数:prompt_dataset、chosen_dataset、reject_dataset、pad_token_id和train_phase。
def __init__(self, prompt_dataset, chosen_dataset, reject_dataset,
pad_token_id, train_phase) -> None:
super().__init__() # 调用父类torch.utils.data.Dataset的构造函数。
self.prompt_dataset = prompt_dataset # 将传入的参数赋值给类的成员变量。
self.chosen_dataset = chosen_dataset
self.reject_dataset = reject_dataset
self.pad_token_id = pad_token_id
self.train_phase = train_phase
def __len__(self): # 定义类的__len__方法,它返回数据集的长度。这是PyTorch数据集的必要方法。
length = len(self.chosen_dataset) # 初始设定数据集长度为chosen_dataset的长度。
if self.train_phase == 3:
length = len(self.prompt_dataset) # 如果训练阶段为3,则数据集长度设定为prompt_dataset的长度。
return length # 返回计算得出的数据集长度。
# 定义类的__getitem__方法,它接受一个参数idx,返回索引idx处的数据。这是PyTorch数据集的必要方法。
def __getitem__(self, idx):
# 如果训练阶段为1,则返回一个字典,包含input_ids、attention_mask和labels,它们都来自chosen_dataset的索引idx处。
if self.train_phase == 1:
return {
"input_ids": self.chosen_dataset[idx]["input_ids"],
"attention_mask": self.chosen_dataset[idx]["attention_mask"],
"labels": self.chosen_dataset[idx]["input_ids"]
}
# 如果训练阶段为2,则返回来自chosen_dataset和reject_dataset的input_ids和attention_mask。
elif self.train_phase == 2:
return self.chosen_dataset[idx]["input_ids"], self.chosen_dataset[idx]["attention_mask"], \
self.reject_dataset[idx]["input_ids"], self.reject_dataset[idx]["attention_mask"]
# 如果训练阶段为3,则返回来自prompt_dataset的input_ids、attention_mask和pad_token_id
elif self.train_phase == 3:
return self.prompt_dataset[idx]["input_ids"],self.prompt_dataset[idx]["attention_mask"], \
self.pad_token_id
接着再解析一下create_dataset_split函数:
# 这是一个名为create_dataset_split的函数,它的功能是根据给定的训练阶段(train_phase),创建并返回相应的数据集分割。
# 具体来说,它为每个训练阶段生成不同的数据集列表,并将它们放入PromptDataset对象中。
# 函数接受6个参数:当前数据集(current_dataset)、原始数据集(raw_dataset)、训练阶段(train_phase)、
# 分词器(tokenizer)、会话结束标记(end_of_conversation_token)和最大序列长度(max_seq_len)。
def create_dataset_split(current_dataset, raw_dataset, train_phase, tokenizer,
end_of_conversation_token, max_seq_len):
# 创建三个空的列表,用于存储对话提示(prompt_dataset)、选定的对话(chosen_dataset)和被拒绝的对话(reject_dataset)。
prompt_dataset = []
chosen_dataset = []
reject_dataset = []
# 如果训练阶段为1,则将接受的对话进行分词并添加到chosen_dataset中。
if train_phase == 1:
# 遍历当前数据集。
for i, tmp_data in enumerate(current_dataset):
# tokenize the text
# 从原始数据集中获取对话提示和接受的对话。
chosen_sentence = raw_dataset.get_prompt_and_chosen(
tmp_data) # the accept response
# 如果接受的对话不为空,则将其分词并添加到chosen_dataset中。
if chosen_sentence is not None:
chosen_sentence += end_of_conversation_token
chosen_token = tokenizer(chosen_sentence,
max_length=max_seq_len,
padding="max_length",
truncation=True,
return_tensors="pt")
chosen_token["input_ids"] = chosen_token["input_ids"].squeeze(
0)
chosen_token["attention_mask"] = chosen_token[
"attention_mask"].squeeze(0)
chosen_dataset.append(chosen_token)
# 如果训练阶段为2,则将接受和被拒绝的对话都进行分词并分别添加到chosen_dataset和reject_dataset中。
elif train_phase == 2:
for i, tmp_data in enumerate(current_dataset):
# tokenize the text
chosen_sentence = raw_dataset.get_prompt_and_chosen(
tmp_data) # the accept response
reject_sentence = raw_dataset.get_prompt_and_rejected(
tmp_data) # the accept response
if chosen_sentence is not None and reject_sentence is not None:
chosen_sentence += end_of_conversation_token # the accept response
reject_sentence += end_of_conversation_token
chosen_token = tokenizer(chosen_sentence,
max_length=max_seq_len,
padding="max_length",
truncation=True,
return_tensors="pt")
reject_token = tokenizer(reject_sentence,
max_length=max_seq_len,
padding="max_length",
truncation=True,
return_tensors="pt")
chosen_token["input_ids"] = chosen_token["input_ids"]
chosen_token["attention_mask"] = chosen_token["attention_mask"]
chosen_dataset.append(chosen_token)
reject_token["input_ids"] = reject_token["input_ids"]
reject_token["attention_mask"] = reject_token["attention_mask"]
reject_dataset.append(reject_token)
# 如果训练阶段为3,则将对话提示进行分词并添加到prompt_dataset中。
elif train_phase == 3:
for i, tmp_data in enumerate(current_dataset):
# tokenize the text
prompt = raw_dataset.get_prompt(tmp_data)
if prompt is not None:
prompt_token = tokenizer(prompt, return_tensors="pt")
prompt_token["input_ids"] = prompt_token["input_ids"]
prompt_token["attention_mask"] = prompt_token["attention_mask"]
for key_word in ["input_ids", "attention_mask"]:
length = prompt_token[key_word].size()[-1]
if length > max_seq_len:
y = prompt_token[key_word].squeeze(0)[length -
(max_seq_len -
1):].flip(0)
else:
y = prompt_token[key_word].squeeze(0).flip(0)
prompt_token[key_word] = y
prompt_dataset.append(prompt_token)
# 创建一个新的PromptDataset对象,并返回。这个对象包含了对话提示、接受的对话和被拒绝的对话的数据集,以及分词器的填充标记ID和训练阶段。
return PromptDataset(prompt_dataset, chosen_dataset, reject_dataset,
tokenizer.pad_token_id, train_phase)
接下来再解析一下create_dataset这个函数:
这段代码定义了一个函数 create_dataset,主要负责创建训练数据集和评估数据集,具体的功能细节如下:
def create_dataset(local_rank, dataset_name, data_split, output_path,
train_phase, seed, tokenizer, end_of_conversation_token,
max_seq_len):
# 调用 get_raw_dataset 函数,该函数根据提供的数据集名称、输出路径、随机种子和local_rank等参数,从各种预定义的数据集中获取所需的原始数据集。
raw_dataset = get_raw_dataset(dataset_name, output_path, seed, local_rank)
train_dataset = raw_dataset.get_train_data() # 从原始数据集中获取训练数据。
# 获取训练数据集的索引,涉及数据的分割。
train_index = get_raw_dataset_split_index(local_rank, output_path,
raw_dataset.dataset_name_clean,
seed, "train", data_split,
train_phase - 1,
len(train_dataset))
# 根据上一步获取的索引,创建训练数据的子集。
train_dataset = Subset(train_dataset, train_index)
# 调用 create_dataset_split 函数对上一步获得的数据子集进行进一步处理,
# 这可能包括对文本的标记化(tokenization),并且创建一个PromptDataset 对象。
train_dataset = create_dataset_split(train_dataset, raw_dataset,
train_phase, tokenizer,
end_of_conversation_token,
max_seq_len)
# 是用于创建评估数据集的,步骤与训练数据集的创建基本相同。
eval_dataset = raw_dataset.get_eval_data()
eval_index = get_raw_dataset_split_index(local_rank, output_path,
raw_dataset.dataset_name_clean,
seed, "eval",
data_split, train_phase - 1,
len(eval_dataset))
eval_dataset = Subset(eval_dataset, eval_index)
eval_dataset = create_dataset_split(eval_dataset, raw_dataset, train_phase,
tokenizer, end_of_conversation_token,
max_seq_len)
return train_dataset, eval_dataset
这里需要额外注意一点,create_dataset_split 这个函数传入的参数是 train_phase,而不是像 get_raw_dataset_split_index 函数那样传入 train_phase-1,这是为什么?这是因为train_phase用来标识在模型训练过程中的哪个阶段,是一个直接的指示符,与数据分割或索引无关。它用来在create_dataset_split函数中确定当前处于哪个训练阶段,并根据不同的训练阶段对数据进行不同的处理。而在调用get_raw_dataset_split_index函数时,传入的是train_phase - 1,这是因为在这个函数中,我们需要根据当前训练阶段的前一个阶段(由train_phase - 1表示)的数据分割或索引情况,来决定如何对当前阶段的数据进行分割或索引。create_dataset_split主要关注如何根据训练阶段对数据进行处理,而get_raw_dataset_split_index主要关注如何根据前一个训练阶段的数据分割或索引情况,对当前阶段的数据进行分割或索引。
回收本节的开头,我们解析create_prompt_dataset函数:
# 这个函数的主要目的是创建一个包含训练和评估数据集的“提示”数据集,并将这两个数据集保存在指定的文件中。具体来说:
def create_prompt_dataset(local_rank,
data_path,
data_split,
output_path,
train_phase,
seed,
tokenizer,
max_seq_len,
end_of_conversation_token="<|endoftext|>",
sft_only_data_path=[],
reload=False):
"""
Creates the prompt dataset
"""
# os.makedirs(output_path, exist_ok=True): 创建输出目录,如果目录已经存在则不会引发异常。
os.makedirs(output_path, exist_ok=True)
# 构造文件名,这个文件名包含了很多有关数据集和模型的信息,如数据路径、数据分割、训练阶段、
# 随机种子、tokenizer的名称、最大序列长度等。然后将这个文件名哈希化,以避免文件名过长。
fname = "_".join(data_path)
sft_cache_key = "_".join(sft_only_data_path)
tokenizer_name = tokenizer.init_kwargs["name_or_path"].replace("/", "_")
fname = f"{fname}_split{data_split}_phase{train_phase}_seed{seed}_tokenizer{tokenizer_name}_seqlen{max_seq_len}_sft{sft_cache_key}"
fname = "_".join(fname.split("/"))
fname = hashlib.sha256(fname.encode()).hexdigest(
) # hash the file name to avoid too long file name
# 构造训练数据集和评估数据集的文件路径。
train_fname = f"{output_path}/traindata_{fname}.pt"
eval_fname = f"{output_path}/evaldata_{fname}.pt"
# 检查训练数据集和评估数据集的文件是否都已经存在,如果存在,则表示缓存已经找到,否则表示需要创建缓存。
cache_found = os.path.isfile(train_fname) and os.path.isfile(eval_fname)
buf_create_cache = torch.ByteTensor([not cache_found]).cuda()
torch.distributed.all_reduce(buf_create_cache)
# 如果当前进程是主进程(local_rank <= 0)并且需要创建缓存,就执行以下操作。
if local_rank <= 0 and (buf_create_cache.item() != 0 or reload):
# 如果只有一个数据集,直接调用create_dataset函数创建训练数据集和评估数据集。
if len(data_path) == 1: # Single dataset.
train_dataset, eval_dataset = create_dataset(
local_rank, data_path[0], data_split, output_path, train_phase,
seed, tokenizer, end_of_conversation_token, max_seq_len)
else: # Blending datasets.
# 如果有多个数据集,对每个数据集都调用create_dataset函数,并把得到的训练数据集和评估数据集添加到对应的列表中,
train_datasets = []
eval_datasets = []
train_size = 0
eval_size = 0
for d_path in data_path:
train_dataset, eval_dataset = create_dataset(
local_rank, d_path, data_split, output_path, train_phase,
seed, tokenizer, end_of_conversation_token, max_seq_len)
train_datasets.append(train_dataset)
eval_datasets.append(eval_dataset)
train_size += len(train_dataset)
eval_size += len(eval_dataset)
# 然后使用ConcatDataset和Subset函数合并数据集。
train_dataset = ConcatDataset(train_datasets)
shuffle_idx = get_shuffle_idx(seed, train_size)
train_dataset = Subset(train_dataset, shuffle_idx.tolist())
eval_dataset = ConcatDataset(eval_datasets)
shuffle_idx = get_shuffle_idx(seed, eval_size)
eval_dataset = Subset(eval_dataset, shuffle_idx.tolist())
# Append the SFT-only dataset if it exists, and current phase is 1(SFT).
# 如果当前是第一阶段的训练(SFT)并且指定了仅用于SFT的数据集,那么对这些数据集执行类似的操作,
# 然后把得到的训练数据集和评估数据集添加到原有的数据集中。
if train_phase == 1 and sft_only_data_path:
sft_train_datasets = []
sft_eval_datasets = []
sft_train_size = 0
sft_eval_size = 0
for sft_path in sft_only_data_path:
sft_train_dataset, sft_eval_dataset = create_dataset(
local_rank,
sft_path,
"10,0,0",
output_path,
train_phase,
seed,
tokenizer,
end_of_conversation_token,
max_seq_len,
)
sft_train_datasets.append(sft_train_dataset)
sft_eval_datasets.append(sft_eval_dataset)
sft_train_size += len(sft_train_dataset)
sft_eval_size += len(sft_eval_dataset)
if sft_train_datasets: # Check if sft_train_datasets is not empty
sft_train_dataset = ConcatDataset(sft_train_datasets)
train_dataset = ConcatDataset(
[train_dataset, sft_train_dataset])
shuffle_idx = get_shuffle_idx(seed, len(train_dataset))
train_dataset = Subset(train_dataset, shuffle_idx.tolist())
if sft_eval_datasets: # Check if sft_eval_datasets is not empty
sft_eval_dataset = ConcatDataset(sft_eval_datasets)
eval_dataset = ConcatDataset([eval_dataset, sft_eval_dataset])
shuffle_idx = get_shuffle_idx(seed, len(eval_dataset))
eval_dataset = Subset(eval_dataset, shuffle_idx.tolist())
# 把训练数据集和评估数据集保存到对应的文件中。
torch.save(train_dataset, train_fname)
torch.save(eval_dataset, eval_fname)
# 在多进程环境中,确保所有进程都完成了数据集的保存操作。
torch.distributed.barrier()
return torch.load(train_fname), torch.load(eval_fname)
工具函数解析
这里解析一下下面导入的代码,在DeepSpeedExamples/applications/DeepSpeed-Chat/training/utils/utils.py这个路径下:
from utils.utils import print_rank_0, to_device, save_hf_format, set_random_seed, get_all_reduce_mean, get_optimizer_grouped_parameters, save_zero_three_model, load_hf_tokenizer
print_rank_0
# 在rank0也就是master rank打印信息,防止每个机器或GPU都打印消息造成大量重复信息
def print_rank_0(msg, rank=0):
if rank <= 0:
print(msg)
to_device
# 这个函数的作用是把一个数据批次移动到指定的设备上。在PyTorch中,数据默认是在CPU上的,
# 如果要在GPU上进行运算,就需要先把数据移到GPU上。这个函数通过遍历批次中的所有元素并
# 调用to(device)方法来实现这一点。如果某个元素不能被移到指定的设备上
#(例如,这个元素是一个字符串或者其他不能在GPU上使用的类型),那么就直接保留这个元素,不进行任何操作。
def to_device(batch, device):
output = {}
for k, v in batch.items():
try:
output[k] = v.to(device)
except:
output[k] = v
return output
save_hf_format
# 这段代码的功能是将训练好的模型以Hugging Face格式保存,这样之后就可以使用Hugging Face库的from_pretrained方法加载了。
def save_hf_format(model, tokenizer, args, sub_folder=""):
# used to save huggingface format, so we can use it for hf.from_pretrained
# 首先,这行代码检查模型是否有'module'这个属性。这在PyTorch中是一个常见的模式,
# 当模型被封装在torch.nn.DataParallel或torch.nn.parallel.DistributedDataParallel时,
# 模型的所有属性都会被存储在'module'属性中。所以这行代码的目的是确保我们总是在原始模型上进行操作,而不是并行化的包装器。
model_to_save = model.module if hasattr(model, 'module') else model
# 定义模型的配置和权重的文件名。
CONFIG_NAME = "config.json"
WEIGHTS_NAME = "pytorch_model.bin"
# 定义模型保存的目录路径。
output_dir = os.path.join(args.output_dir, sub_folder)
# 如果模型保存的目录不存在,那么创建这个目录。
os.makedirs(output_dir, exist_ok=True)
# 定义模型权重和配置的保存路径。
output_model_file = os.path.join(output_dir, WEIGHTS_NAME)
output_config_file = os.path.join(output_dir, CONFIG_NAME)
# 获取模型的状态字典,这个字典包含了模型的所有权重。
save_dict = model_to_save.state_dict()
# 遍历状态字典中的所有键。这里使用list(save_dict.keys())而不是直接使用
# save_dict.keys()是因为我们在遍历过程中会修改字典,直接遍历字典的键在Python中会导致错误。
for key in list(save_dict.keys()):
# if "lora" in key::如果键中包含"lora",那么删除这个键值对。
# "lora"可能是某种特定的模型组件或参数,这里将其排除在保存的模型权重之外。
if "lora" in key:
del save_dict[key]
# 将处理过的状态字典保存到文件中。
torch.save(save_dict, output_model_file)
# 将模型的配置保存为JSON文件。
model_to_save.config.to_json_file(output_config_file)
# 将分词器的词汇表保存到指定的目录。
tokenizer.save_vocabulary(output_dir)
set_random_seed
# 这段代码的目的是为所有可能用到的随机数生成器设定种子,以确保实验结果的可复现性。
# 随机数生成器的种子是生成随机数序列的初始值,当我们用同一个种子初始化随机数生成器时,它会生成完全一样的随机数序列。
def set_random_seed(seed):
# 首先检查种子是否是None。如果是None,那么就跳过这段代码,随机数生成器将会用一个随机的种子。
if seed is not None:
set_seed(seed)# 这一行调用transformers库的set_seed的函数,将种子设定为指定的值。
random.seed(seed) # 将Python内置的随机数生成器的种子设定为指定的值。
np.random.seed(seed) # 将NumPy的随机数生成器的种子设定为指定的值。
torch.manual_seed(seed) # 将PyTorch的随机数生成器的种子设定为指定的值。
torch.cuda.manual_seed_all(seed) # 将PyTorch的所有GPU随机数生成器的种子设定为指定的值。
get_all_reduce_mean
# 这段代码是在分布式训练环境中进行平均值计算的函数,通过这段代码,
# 所有的处理器(或者叫节点)上的同一个tensor都会被加和起来,然后除以总的处理器数,得到平均值。
def get_all_reduce_mean(tensor):
# 这行代码执行一个分布式的reduce操作。reduce操作是指所有处理器中的同一个tensor都被某种方式结合起来。
# 在这个例子中,torch.distributed.ReduceOp.SUM表示所有处理器上的tensor将被加和起来。
# 加和的结果会在所有处理器上都可用。
torch.distributed.all_reduce(tensor, op=torch.distributed.ReduceOp.SUM)
# 这行代码将前一步得到的加和结果除以处理器的数量(也叫作 world size)。
# 这样,tensor就变成了所有处理器上原始tensor的平均值。
tensor = tensor / torch.distributed.get_world_size()
# 最后,这个平均值tensor被返回。在所有处理器上,这个函数返回的tensor都是相同的,
# 等于所有处理器上原始tensor的平均值。
return tensor
get_optimizer_grouped_parameters
# 这段代码的作用是将模型中的参数分组以便于在优化器中使用。它将模型参数分为两组:
# 一组需要进行权重衰减(L2正则化)的参数,另一组不需要进行权重衰减的参数。
def get_optimizer_grouped_parameters(model,
weight_decay,
no_decay_name_list=[
"bias", "LayerNorm.weight"
]):
# 它定义了一个列表 optimizer_grouped_parameters,其中包含两个字典。每个字典都对应一个参数组,包含 "params" 和 "weight_decay" 这两个关键字。
optimizer_grouped_parameters = [
# 在第一个字典中,它从模型参数中选出那些名称不包含 "bias" 或 "LayerNorm.weight"
# 且需要求梯度的参数。这些参数在优化过程中会应用 weight_decay 作为权重衰减项。
{
"params": [
p for n, p in model.named_parameters()
if (not any(nd in n
for nd in no_decay_name_list) and p.requires_grad)
],
"weight_decay":
weight_decay,
},
# 在第二个字典中,它选出那些名称包含 "bias" 或 "LayerNorm.weight" 且需要求梯度的参数。
# 这些参数在优化过程中不会应用权重衰减,即其 "weight_decay" 值为0。
{
"params": [
p for n, p in model.named_parameters()
if (any(nd in n
for nd in no_decay_name_list) and p.requires_grad)
],
"weight_decay":
0.0,
},
]
return optimizer_grouped_parameters
这种参数的分组策略是很常见的。比如在训练Transformer模型时,通常会为权重和偏置项设定不同的学习策略。这是因为权重衰减对于防止过拟合很有帮助,但对于某些参数(如偏置项或者层归一化的权重)可能会导致性能下降,因此常常会排除这些参数不进行权重衰减。
save_zero_three_model
# 这个函数的主要功能是筛选出那些在DeepSpeed Zero 3优化中被离线存储,但在当前还未获取的参数。
# 在DeepSpeed Zero 3优化中,一些模型参数在使用过后会被离线存储,以此释放GPU显存。
# 当这些参数需要再次被使用时,需要先获取到本地。
def _z3_params_to_fetch(param_list):
# 这个条件语句判断一个参数是否是被DeepSpeed Zero 3优化过的,且其状态为"未获取"(NOT_AVAILABLE)。
# 对于被DeepSpeed Zero 3优化过的参数,它们有一个ds_id属性和一个ds_status属性,其中ds_status表示参数的当前状态。
return [
p for p in param_list
if hasattr(p, 'ds_id') and p.ds_status == ZeroParamStatus.NOT_AVAILABLE
]
# 这个函数的主要作用是保存一个使用了DeepSpeed Zero优化(可能为stage 3)的模型。
# DeepSpeed的Zero优化技术是为了解决模型参数、优化器状态和梯度等内存占用问题,
# 通过这种方式,可以训练比当前GPU内存更大的模型。
def save_zero_three_model(model_ema, global_rank, save_dir, zero_stage=0):
# 首先,检查输入的zero_stage是否为3,确定是否使用了DeepSpeed Zero阶段3优化。
zero_stage_3 = (zero_stage == 3)
# 然后,确保保存模型的目录存在。
os.makedirs(save_dir, exist_ok=True)
# 定义模型权重保存的完整路径。
WEIGHTS_NAME = "pytorch_model.bin"
output_model_file = os.path.join(save_dir, WEIGHTS_NAME)
# 如果模型是被包裹在其它结构(如DataParallel或DistributedDataParallel)中的,我们需要取出真实的模型实例。
model_to_save = model_ema.module if hasattr(model_ema,
'module') else model_ema
if not zero_stage_3:
# 如果没有使用Zero阶段3优化,直接使用PyTorch的torch.save函数保存模型状态。
if global_rank == 0:
torch.save(model_to_save.state_dict(), output_model_file)
else:
# 如果使用了Zero阶段3优化,因为模型的部分参数和优化器状态在不同的设备上,所以需要先将它们收集起来。
output_state_dict = {}
for k, v in model_to_save.named_parameters():
if hasattr(v, 'ds_id'):
# deepspeed.zero.GatheredParameters是DeepSpeed提供的一个上下文管理器,
# 它可以将分布在多个设备上的参数收集到一起。这部分参数保存在CPU上。
with deepspeed.zero.GatheredParameters(_z3_params_to_fetch([v
]),
enabled=zero_stage_3):
v_p = v.data.cpu()
else:
v_p = v.cpu()
# 然后,将收集好的参数(并且不包含“lora”关键字的参数)添加到输出状态字典中。
if global_rank == 0 and "lora" not in k:
output_state_dict[k] = v_p
# 最后,再使用torch.save函数保存模型状态。
if global_rank == 0:
torch.save(output_state_dict, output_model_file)
# 同时为了节省内存,使用del关键字删除了存储参数的字典。
del output_state_dict
load_hf_tokenizer
# 这个函数的目标是加载一个Hugging Face tokenizer,这个tokenizer是用来将文本数据转化为模型可以接受的形式的。
# model_name_or_path: 这个参数可以是一个模型名字或者一个本地路径,指示从哪里获取tokenizer。
# fast_tokenizer=True: 这个参数指示是否使用Hugging Face的"fast" tokenizer。"fast" tokenizer是用Rust编写的,运行速度更快。
def load_hf_tokenizer(model_name_or_path, fast_tokenizer=True):
# 这行代码检查model_name_or_path是否是一个存在的路径。如果是,那么就尝试从本地文件系统中加载tokenizer。
if os.path.exists(model_name_or_path):
# Locally tokenizer loading has some issue, so we need to force download
# 这行代码拼接路径,尝试找到模型的config文件。
model_json = os.path.join(model_name_or_path, "config.json")
# 这行代码检查config文件是否存在。如果存在,那么就尝试从config文件中获取模型名字。
if os.path.exists(model_json):
model_json_file = json.load(open(model_json)) # 这行代码加载config文件。
model_name = model_json_file["_name_or_path"] # 这行代码从config文件中获取模型名字。
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name,
fast_tokenizer=True) # 这行代码使用模型名字从Hugging Face的模型库中下载并加载tokenizer。
else: # 如果model_name_or_path不是一个存在的路径,那么就认为它是一个模型名字。
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name_or_path,
fast_tokenizer=True) # 这行代码使用模型名字从Hugging Face的模型库中下载并加载tokenizer。
return tokenizer
再解析一下DeepSpeedExamples/applications/DeepSpeed-Chat/training/utils/ds_utils.py导入的get_train_ds_config函数:
# DeepSpeed Team
GLOBAL_BATCH_SIZE = 32
MICRO_BATCH_SIZE = 4
# 这个函数的主要目标是生成一个字典,用来配置DeepSpeed训练模型的各种参数。
# DeepSpeed是一个用于加速大规模模型训练的库,其中包括一种叫做ZeRO(Zero Redundancy Optimizer)的优化技术,
# 可以大大减少模型训练过程中的显存和内存占用。
def get_train_ds_config(offload,
stage=2,
enable_hybrid_engine=False,
inference_tp_size=1,
release_inference_cache=False,
pin_parameters=True,
tp_gather_partition_size=8,
max_out_tokens=512):
# 这行代码首先定义了一个变量device。如果参数offload为True,那么就将device设置为"cpu",
# 表示模型的参数和优化器状态将被"offload"到CPU内存中,以减少GPU显存的占用。
# 如果offload为False,那么device就被设置为"none",表示不进行offload。
device = "cpu" if offload else "none"
# 这行代码定义了一个字典zero_opt_dict,包含了ZeRO优化器的各种配置参数。
zero_opt_dict = {
"stage": stage, # ZeRO的阶段,可以为0、1、2、3,阶段越高,显存优化效果越好,但计算复杂度也越高。
"offload_param": { # offload_param和offload_optimizer这两个字段控制是否将模型的参数和优化器状态offload到CPU内存。
"device": device
},
"offload_optimizer": {
"device": device
},
# 这三个字段只有在ZeRO stage 3时有效,用于控制参数offloading的细节。
"stage3_param_persistence_threshold": 1e4,
"stage3_max_live_parameters": 3e7,
"stage3_prefetch_bucket_size": 3e7,
# 这个字段控制是否使用显存更高效的线性层实现。由于当前的显存高效实现可能会导致数值不稳定,所以这里默认设为False。
"memory_efficient_linear": False
}
# 返回一个配置字典,这个字典包含了训练模型的各种参数。
return {
"train_batch_size": GLOBAL_BATCH_SIZE, # 全局的批次大小
"train_micro_batch_size_per_gpu": MICRO_BATCH_SIZE, # 每个GPU的微批次大小。
"steps_per_print": 10, # 每隔10步打印一次训练信息。
"zero_optimization": zero_opt_dict, # 之前定义的ZeRO配置字典。
"fp16": { # 控制是否使用混合精度训练,以及loss scaling的窗口大小。
"enabled": True,
"loss_scale_window": 100
},
"gradient_clipping": 1.0, # 梯度裁剪的阈值。
"prescale_gradients": False, # 是否在梯度累计之前就进行梯度缩放,通常用于防止梯度下溢。
"wall_clock_breakdown": False, # 是否进行每步训练时间的详细分析。
"hybrid_engine": {
"enabled": enable_hybrid_engine,
"max_out_tokens": max_out_tokens,
"inference_tp_size": inference_tp_size,
"release_inference_cache": release_inference_cache,
"pin_parameters": pin_parameters,
"tp_gather_partition_size": tp_gather_partition_size,
}
}
再解析一下DeepSpeedExamples/applications/DeepSpeed-Chat/training/utils/module/lora.py导入的convert_linear_layer_to_lora, convert_lora_to_linear_layer, only_optimize_lora_parameters 这几个函数。
在解析这几个函数之前需要先解析一下 LinearLayer_LoRA 这个类:
# LinearLayer_LoRA 是一个实现了 LoRA(Low-Rank Adaptation)策略的 PyTorch 模块。
# LoRA 是一种在大型预训练模型(如 GPT-3 或者 BERT)微调中使用的策略,可以提高微调的效果。
# 这个类是一个简单的 LoRA 实现,只支持线性层。
class LinearLayer_LoRA(nn.Module):
# an simple implementation of LoRA
# for now only support Linear Layer
# 初始化函数,定义了一些参数,如权重(weight)、LoRA 维度(lora_dim)、
# LoRA 缩放因子(lora_scaling)、LoRA dropout (lora_droppout)以及偏置(bias)。
def __init__(self,
weight,
lora_dim=0,
lora_scaling=1,
lora_droppout=0,
bias=None):
super(LinearLayer_LoRA, self).__init__()
self.weight = weight
self.bias = bias
# 在初始化过程中,首先检查 lora_dim 是否大于0,如果不是,就抛出异常。
if lora_dim <= 0:
raise ValueError(
"You are training to use LoRA, whose reduced dim should be larger than 1"
)
# 然后尝试获取权重的形状,如果权重是在 ZeRO 阶段3中的参数,那么通过 ds_shape 属性获取形状;
# 否则直接使用 shape 属性。
try:
# for zero stage 3
rows, columns = weight.ds_shape
except:
rows, columns = weight.shape
# 然后初始化 LoRA 的左右两个权重矩阵,并设置它们为可学习的参数。
self.lora_right_weight = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(
columns,
lora_dim)) # apply transpose so in forward we do not need to
self.lora_left_weight = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(lora_dim, rows))
self.lora_scaling = lora_scaling / lora_dim
# 如果 lora_droppout 大于0,则创建一个 Dropout 层;否则创建一个 Identity 层。
if lora_droppout > 0:
self.lora_dropout = nn.Dropout(lora_droppout)
else:
self.lora_dropout = nn.Identity()
# 然后调用 reset_parameters 方法对 LoRA 权重进行初始化。
self.reset_parameters()
# disable the original weight gradient
# 最后,关闭原始权重的梯度,设置 LoRA 融合标志位为 False。
self.weight.requires_grad = False
# fuse LoRA to the original weight
self.fuse_lora = False
def eval(self):
self.lora_dropout.eval() # 将模型设置为评估模式,这时候 Dropout 层会停止工作。
# self.fuse_lora_weight()
def train(self, mode=True):
self.lora_dropout.train(mode) # 将模型设置为训练模式,这时候 Dropout 层会开始工作。
# self.unfuse_lora_weight()
def reset_parameters(self): # 初始化 LoRA 权重的方法。右权重使用 kaiming 均匀分布进行初始化,左权重初始化为全0。
nn.init.kaiming_uniform_(self.lora_right_weight, a=math.sqrt(5))
nn.init.zeros_(self.lora_left_weight)
# fuse_lora_weight(self) 和 unfuse_lora_weight(self):
# 这两个方法用于将 LoRA 权重融合到原始权重中,或者从原始权重中解融合。
# 融合操作实质上是将原始权重与 LoRA 权重的乘积(缩放后)相加。
def fuse_lora_weight(self):
if not self.fuse_lora:
self.weight.data += self.lora_scaling * torch.matmul(
self.lora_left_weight.t(), self.lora_right_weight.t())
self.fuse_lora = True
def unfuse_lora_weight(self):
if self.fuse_lora:
self.weight.data -= self.lora_scaling * torch.matmul(
self.lora_left_weight.t(), self.lora_right_weight.t())
self.fuse_lora = False
# 前向传播函数。如果 LoRA 权重已融合,则直接对输入进行线性变换;
# 否则,会额外计算一个 LoRA 项,该项是输入通过 Dropout 层,然后与 LoRA 权重相乘得到的。
def forward(self, input):
if self.fuse_lora:
return F.linear(input, self.weight, self.bias)
else:
return F.linear(
input, self.weight,
self.bias) + (self.lora_dropout(input) @ self.lora_right_weight
@ self.lora_left_weight) * self.lora_scaling
convert_linear_layer_to_lora
# 这个函数 convert_linear_layer_to_lora 是用来将模型中的线性层转换为 LoRA 层的。
# 在训练深度学习模型时,这种方法能够在保持预训练模型参数不变的同时,通过添加额外的参数来微调模型。
# convert the linear layer to LoRA
def convert_linear_layer_to_lora(model,
part_module_name,
lora_dim=0,
lora_scaling=1,
lora_droppout=0):
repalce_name = []
# 函数首先遍历模型中的所有模块(model.named_modules()),找出名称中包含 part_module_name 的线性层(nn.Linear),
# 并将这些层的名称添加到 repalce_name 列表中。
for name, module in model.named_modules():
if isinstance(module, nn.Linear) and part_module_name in name:
repalce_name.append(name)
# 然后,函数遍历 repalce_name 列表,使用 recursive_getattr 函数获取模型中对应名称的模块。
# 这些模块是需要被替换成 LoRA 层的线性层。
for name in repalce_name:
module = recursive_getattr(model, name)
# 对于每一个需要被替换的模块,函数创建一个 LinearLayer_LoRA 实例 tmp,
# 并将其传输到与原始模块相同的设备和数据类型上。创建 LinearLayer_LoRA 实例时,
# 需要传入原始模块的权重、偏置以及 LoRA 层的一些参数,如 lora_dim、lora_scaling 和 lora_droppout。
tmp = LinearLayer_LoRA(
module.weight, lora_dim, lora_scaling, lora_droppout,
module.bias).to(module.weight.device).to(module.weight.dtype)
# 创建完 LinearLayer_LoRA 实例后,函数使用 recursive_setattr 函数将原始模块替换为 LinearLayer_LoRA 实例。
recursive_setattr(model, name, tmp)
return model
convert_lora_to_linear_layer
# 这个函数的主要功能是筛选出那些在DeepSpeed Zero 3优化中被离线存储,但在当前还未获取的参数。
# 在DeepSpeed Zero 3优化中,一些模型参数在使用过后会被离线存储,以此释放GPU显存。
# 当这些参数需要再次被使用时,需要先获取到本地。
def _z3_params_to_fetch(param_list):
# 这个条件语句判断一个参数是否是被DeepSpeed Zero 3优化过的,且其状态为"未获取"(NOT_AVAILABLE)。
# 对于被DeepSpeed Zero 3优化过的参数,它们有一个ds_id属性和一个ds_status属性,其中ds_status表示参数的当前状态。
return [
p for p in param_list
if hasattr(p, 'ds_id') and p.ds_status == ZeroParamStatus.NOT_AVAILABLE
]
# 这个函数 convert_lora_to_linear_layer 是用来将模型中的 LoRA 层转换回线性层的。
# 在训练深度学习模型时,这个操作可以用于在训练完 LoRA 层后,将模型恢复到原始的状态,
# 以便进行下一步的操作,如模型的保存、加载等。
# convert the LoRA layer to linear layer
def convert_lora_to_linear_layer(model):
repalce_name = []
# 函数首先遍历模型中的所有模块(model.named_modules()),找出所有的 LoRA 层(LinearLayer_LoRA),
# 并将这些层的名称添加到 repalce_name 列表中。
for name, module in model.named_modules():
if isinstance(module, LinearLayer_LoRA):
repalce_name.append(name)
# 然后,函数遍历 repalce_name 列表,使用 recursive_getattr 函数获取模型中对应名称的 LoRA 层。
for name in repalce_name:
module = recursive_getattr(model, name)
# 对于每一个 LoRA 层,函数首先检查是否处于 zero stage 3(DeepSpeed 的一个特性,用于在多GPU训练中减少内存占用)。
# 如果是,则设置 zero_stage_3 为 True。
zero_stage_3 = hasattr(module.weight, 'ds_id')
with deepspeed.zero.GatheredParameters(_z3_params_to_fetch([
module.weight, module.bias, module.lora_left_weight,
module.lora_right_weight
]),
modifier_rank=0,
enabled=zero_stage_3):
module.fuse_lora_weight()
return model
only_optimize_lora_parameters
# 这个函数的作用是关闭模型中除LoRA参数之外的所有参数的梯度。这意味着在训练过程中,只有LoRA参数会被优化,其他参数保持不变。
def only_optimize_lora_parameters(model):
# turn off the gradient of all the parameters except the LoRA parameters
# 遍历模型的所有参数。每个参数都有一个唯一的名称name和对应的参数值param。
for name, param in model.named_parameters():
# 查当前参数的名称是否包含lora_right_weight或lora_left_weight。
# 这是因为在LoRA(Low-Rank Adaptation)中,只有这两种参数是需要优化的。
if "lora_right_weight" in name or "lora_left_weight" in name:
# param.requires_grad = True 如果参数名包含lora_right_weight或lora_left_weight,
# 则设置参数的requires_grad属性为True,表示需要对此参数进行梯度下降优化。
param.requires_grad = True
else:
param.requires_grad = False
return model
create_hf_model
# 这段代码定义了一个名为create_hf_model的函数,该函数的作用是创建或加载一个预训练模型。该函数的主要参数包括:
# model_class:模型的类别,例如GPT-2、BERT等。
# tokenizer:用于模型的分词器。
# ds_config: DeepSpeed的配置参数。
# rlhf_training:一个标志,用来表示是否正在进行RLHF(Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback)训练。
# disable_dropout:一个标志,用来表示是否禁用dropout。Dropout是一种防止过拟合的技术。
def create_hf_model(model_class,
model_name_or_path,
tokenizer,
ds_config=None,
rlhf_training=False,
disable_dropout=False):
# 根据model_name_or_path从预训练模型获取模型配置model_config。
model_config = AutoConfig.from_pretrained(model_name_or_path)
# 如果disable_dropout为真,则将模型配置中的dropout设为0.0。
if disable_dropout:
model_config.dropout = 0.0
# Note: dschf is defined in function scope to avoid global effects
# https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main_classes/deepspeed#nontrainer-deepspeed-integration
# 根据ds_config中的设置,创建DeepSpeed的配置对象dschf,以便进行DeepSpeed优化。
if ds_config is not None and ds_config["zero_optimization"]["stage"] == 3:
dschf = HfDeepSpeedConfig(ds_config)
else:
dschf = None
# 根据rlhf_training的值,确定是从配置中创建模型还是从预训练模型中加载模型。如果rlhf_training为真,则根据模型配置创建模型;否则,从预训练模型加载模型。
if rlhf_training:
# the weight loading is handled by create critic model
model = model_class.from_config(model_config)
else:
model = model_class.from_pretrained(
model_name_or_path,
from_tf=bool(".ckpt" in model_name_or_path),
config=model_config)
# 将模型的结束标记和填充标记设为分词器的结束标记id。
model.config.end_token_id = tokenizer.eos_token_id
model.config.pad_token_id = model.config.eos_token_id
# 调整模型的词汇表大小,使其为8的倍数。这样做的目的是为了在某些硬件(如GPU)上提高效率。
model.resize_token_embeddings(int(
8 *
math.ceil(len(tokenizer) / 8.0))) # make the vocab size multiple of 8
return model
0x3.2 main.py主体解析
parse_args解析
def parse_args():
# 创建一个argparse的解析器对象,这个对象可以添加命令行参数和处理它们。description参数提供了一个对程序的简单描述。
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(
description=
"Finetune a transformers model on a causal language modeling task")
parser.add_argument('--data_path',
nargs='*',
default=['Dahoas/rm-static'],
help='Path to the training dataset. Accepted format:'
'1) a single data path, 2) multiple datasets in the'
'form: dataset1-path dataset2-path ...')
parser.add_argument('--data_split',
type=str,
default='2,4,4',
help='Comma-separated list of proportions for training'
'phase 1, 2, and 3 data. For example the split `6,2,2`'
'will use 60% of data for phase 1, 20% for phase 2'
'and 20% for phase 3.')
parser.add_argument(
'--sft_only_data_path',
nargs='*',
default=[],
help='Path to the dataset for only using in SFT phase.')
parser.add_argument(
'--data_output_path',
type=str,
default='/data_turbo/home/zhangxiaoyu/data_files/',
help=
'Where to store the data-related files such as shuffle index. This needs to be on a local storage of a node (not on a shared storage)'
)
parser.add_argument(
"--model_name_or_path",
type=str,
help=
"Path to pretrained model or model identifier from huggingface.co/models.",
required=True,
)
parser.add_argument(
"--per_device_train_batch_size",
type=int,
default=16,
help="Batch size (per device) for the training dataloader.",
)
parser.add_argument(
"--per_device_eval_batch_size",
type=int,
default=16,
help="Batch size (per device) for the evaluation dataloader.",
)
parser.add_argument(
"--max_seq_len",
type=int,
default=512,
help="The maximum sequence length.",
)
parser.add_argument(
"--learning_rate",
type=float,
default=1e-3,
help=
"Initial learning rate (after the potential warmup period) to use.",
)
parser.add_argument("--weight_decay",
type=float,
default=0.,
help="Weight decay to use.")
parser.add_argument("--num_train_epochs",
type=int,
default=1,
help="Total number of training epochs to perform.")
parser.add_argument(
"--gradient_accumulation_steps",
type=int,
default=1,
help=
"Number of updates steps to accumulate before performing a backward/update pass.",
)
parser.add_argument(
"--lr_scheduler_type",
type=SchedulerType,
default="cosine",
help="The scheduler type to use.",
choices=[
"linear", "cosine", "cosine_with_restarts", "polynomial",
"constant", "constant_with_warmup"
],
)
parser.add_argument(
"--num_warmup_steps",
type=int,
default=0,
help="Number of steps for the warmup in the lr scheduler.")
parser.add_argument("--output_dir",
type=str,
default=None,
help="Where to store the model.")
parser.add_argument("--seed",
type=int,
default=1234,
help="A seed for reproducible training.")
parser.add_argument("--local_rank",
type=int,
default=-1,
help="local_rank for distributed training on gpus")
parser.add_argument('--gradient_checkpointing',
action='store_true',
help='Enable HF gradient checkpointing for model.')
parser.add_argument('--disable_dropout',
action='store_true',
help='Disable the dropout of the model.')
# deepspeed features
parser.add_argument('--offload',
action='store_true',
help='Enable ZeRO Offload techniques.')
parser.add_argument(
'--zero_stage',
type=int,
default=0,
help='ZeRO optimization stage for Actor model (and clones).')
## LoRA for efficient training setting
parser.add_argument("--lora_dim",
type=int,
default=0,
help="If > 0, use LoRA for efficient training.")
parser.add_argument("--lora_module_name",
type=str,
default="decoder.layers.",
help="The scope of LoRA.")
parser.add_argument('--only_optimize_lora',
action='store_true',
help='Only optimize the LoRA parameters.')
# 这一行将DeepSpeed的配置参数添加到解析器中。
parser = deepspeed.add_config_arguments(parser)
# 这一行解析命令行参数并将它们存储在args对象中
args = parser.parse_args()
# Validate settings
# 在这个代码块中,验证一些特定的参数设置是否合法。
# 例如,如果同时启用了gradient_checkpointing和仅优化LoRA参数,那么将会抛出一个错误。
if args.gradient_checkpointing and args.lora_dim > 0:
assert (
not args.only_optimize_lora
), "--gradient_checkpointing and --only_optimize_lora cannot be enabled at the same time."
return args
main函数解析
接下来是训练部分的核心函数,也是全文最后一个函数main的解析。
# 这个函数是主函数,是训练语言模型的主流程,主要步骤包括解析命令行参数、
# 设置设备、准备数据、定义模型、配置优化器和学习率调度器、进行训练和评估等。
def main():
# 解析命令行参数。
args = parse_args()
# 如果本地排名为-1,说明不在分布式训练环境下,设备设置为"cuda";
# 否则根据args.local_rank设置对应的cuda设备,并初始化分布式训练。
if args.local_rank == -1:
device = torch.device("cuda")
else:
torch.cuda.set_device(args.local_rank)
device = torch.device("cuda", args.local_rank)
# Initializes the distributed backend which will take care of sychronizing nodes/GPUs
# torch.distributed.init_process_group(backend='nccl')
deepspeed.init_distributed()
# 获取全局rank。
args.global_rank = torch.distributed.get_rank()
# 获取deepspeed的训练配置。
ds_config = get_train_ds_config(offload=args.offload,
stage=args.zero_stage)
# 在配置中设置训练时每个GPU的微批次大小和总的批次大小。
ds_config[
'train_micro_batch_size_per_gpu'] = args.per_device_train_batch_size
ds_config[
'train_batch_size'] = args.per_device_train_batch_size * torch.distributed.get_world_size(
) * args.gradient_accumulation_steps
# If passed along, set the training seed now.
# 设置随机种子以保证结果的可复现性。
set_random_seed(args.seed)
# 在此处添加一个barrier操作,确保所有进程都执行到这一点后再继续执行后续操作。
torch.distributed.barrier()
# 加载预训练模型对应的分词器。
tokenizer = load_hf_tokenizer(args.model_name_or_path, fast_tokenizer=True)
tokenizer.pad_token = tokenizer.eos_token
# make sure tokenizer is right pad in our logic
tokenizer.padding_side = 'right'
# 创建预训练模型。
model = create_hf_model(AutoModelForCausalLM,
args.model_name_or_path,
tokenizer,
ds_config,
disable_dropout=args.disable_dropout)
# 如果参数lora_dim大于0,将模型的线性层转换为LoRa层;如果只优化LoRa参数,关闭其他参数的梯度。
if args.lora_dim > 0:
model = convert_linear_layer_to_lora(model, args.lora_module_name,
args.lora_dim)
if args.only_optimize_lora:
model = only_optimize_lora_parameters(model)
# Prepare the data
# 创建数据集和数据加载器:包括训练集和验证集,以及对应的采样器和数据加载器。
train_phase = 1
train_dataset, eval_dataset = create_prompt_dataset(
args.local_rank,
args.data_path,
args.data_split,
args.data_output_path,
train_phase,
args.seed,
tokenizer,
args.max_seq_len,
sft_only_data_path=args.sft_only_data_path)
# DataLoaders creation:
if args.local_rank == -1:
train_sampler = RandomSampler(train_dataset)
eval_sampler = SequentialSampler(eval_dataset)
else:
train_sampler = DistributedSampler(train_dataset)
eval_sampler = DistributedSampler(eval_dataset)
train_dataloader = DataLoader(train_dataset,
collate_fn=default_data_collator,
sampler=train_sampler,
batch_size=args.per_device_train_batch_size)
eval_dataloader = DataLoader(eval_dataset,
collate_fn=default_data_collator,
sampler=eval_sampler,
batch_size=args.per_device_eval_batch_size)
# 定义模型评估函数,用于计算模型在验证集上的困惑度。
def evaluation(model, eval_dataloader):
model.eval() # 将模型切换为评估模式。
losses = 0 # 初始化loss。
for step, batch in enumerate(eval_dataloader): # 对于评估数据集中的每一个batch。
batch = to_device(batch, device) # 将batch数据移到对应的设备上。
with torch.no_grad(): # 在此上下文管理器中,不计算梯度,这样可以节省存储和计算资源。
# 将batch数据输入模型,进行前向计算。
outputs = model(**batch)
loss = outputs.loss # 取出模型的输出中的loss。
losses += loss.float() # 将当前的loss累加到总的losses中。
losses = losses / (step + 1) # 计算平均的loss。
try:
perplexity = torch.exp(losses) # 尝试计算模型的困惑度,如果捕捉到溢出错误,将困惑度设置为无穷大。
except OverflowError:
perplexity = float("inf")
# 尝试在所有设备上计算困惑度的平均值,如果发生任何错误,就忽略。
try:
perplexity = get_all_reduce_mean(perplexity).item()
except:
pass
return perplexity
# 根据是否使用权重衰减将模型参数分为两组。
# Split weights in two groups, one with weight decay and the other not.
optimizer_grouped_parameters = get_optimizer_grouped_parameters(
model, args.weight_decay)
# 选择优化器类型,如果启用了梯度Offload,使用DeepSpeedCPUAdam,否则使用FusedAdam。
AdamOptimizer = DeepSpeedCPUAdam if args.offload else FusedAdam
# 创建优化器。
optimizer = AdamOptimizer(optimizer_grouped_parameters,
lr=args.learning_rate,
betas=(0.9, 0.95))
# 计算每个epoch的更新步数。
num_update_steps_per_epoch = math.ceil(
len(train_dataloader) / args.gradient_accumulation_steps)
# 创建学习率调度器。
lr_scheduler = get_scheduler(
name=args.lr_scheduler_type,
optimizer=optimizer,
num_warmup_steps=args.num_warmup_steps,
num_training_steps=args.num_train_epochs * num_update_steps_per_epoch,
)
# 使用deepspeed初始化模型、优化器和学习率调度器。
model, optimizer, _, lr_scheduler = deepspeed.initialize(
model=model,
optimizer=optimizer,
args=args,
config=ds_config,
lr_scheduler=lr_scheduler,
dist_init_required=True)
# 如果启用了梯度检查点,那么在模型中也启用梯度检查点。
if args.gradient_checkpointing:
model.gradient_checkpointing_enable()
# Train!
# 使用 print_rank_0 函数在主节点(global_rank为0的节点)打印开始训练的信息。
print_rank_0("***** Running training *****", args.global_rank)
# 在主节点打印在第0个epoch(训练开始前)进行模型评估的信息。
print_rank_0(
f"***** Evaluating perplexity, Epoch {0}/{args.num_train_epochs} *****",
args.global_rank)
# 调用 evaluation 函数对模型进行评估,得到模型的困惑度。
perplexity = evaluation(model, eval_dataloader)
# 在主节点打印模型的困惑度。
print_rank_0(f"ppl: {perplexity}", args.global_rank)
# 循环 args.num_train_epochs 轮进行训练。
for epoch in range(args.num_train_epochs):
print_rank_0(
f"Beginning of Epoch {epoch+1}/{args.num_train_epochs}, Total Micro Batches {len(train_dataloader)}",
args.global_rank) # 在每个epoch开始时,在主节点打印开始新的训练周期的信息。
model.train() # 将模型设置为训练模式。
for step, batch in enumerate(train_dataloader): # 对于训练数据集中的每一个batch。
batch = to_device(batch, device) # 将batch数据移到对应的设备上。
outputs = model(**batch, use_cache=False) # 将batch数据输入模型,进行前向计算。
loss = outputs.loss # 取出模型的输出中的loss。
model.backward(loss) # 进行反向传播,计算梯度。
model.step() # 更新模型的参数。
# Evaluate perplexity on the validation set.
# 在每个epoch结束后,在主节点打印开始评估的信息。
print_rank_0(
f"***** Evaluating perplexity, Epoch {epoch+1}/{args.num_train_epochs} *****",
args.global_rank)
# 对模型进行评估,得到模型的困惑度。
perplexity = evaluation(model, eval_dataloader)
# 在主节点打印模型的困惑度。
print_rank_0(f"ppl: {perplexity}", args.global_rank)
# 更新模型中的epoch计数。
model.tput_timer.update_epoch_count()
# 如果设置了输出目录,进行以下操作。
if args.output_dir is not None:
# 在主节点打印开始保存模型的信息。
print_rank_0('saving the final model ...', args.global_rank)
# 将模型中的LoRA层转换为线性层。
model = convert_lora_to_linear_layer(model)
# 如果是主节点,进行以下操作。
if args.global_rank == 0:
# 以Hugging Face的模型格式保存模型。
save_hf_format(model, tokenizer, args)
# 如果使用了Zero Redundancy Optimizer(Zero)的第三阶段,进行以下操作。
if args.zero_stage == 3:
# For zero stage 3, each gpu only has a part of the model, so we need a special save function
# 使用特殊的保存函数保存模型。在Zero的第三阶段,每个GPU只有模型的一部分,所以需要特殊的保存函数。
save_zero_three_model(model,
args.global_rank,
args.output_dir,
zero_stage=args.zero_stage)
0x4. hybrid_engine的细节 & log
从训练过程的输出日志来看hybrid_engine是默认关闭的,DeepSpeed-Chat 打造类ChatGPT全流程 笔记一 里面提到DeepSpeed Hybrid Engine是用在加速 RLHF 流程中最耗时的部分也就是第三步,而本文介绍的监督指令微调是第一步,所以即使开启hybrid_engine加速效果应该也比较有限,所以这里默认关闭。
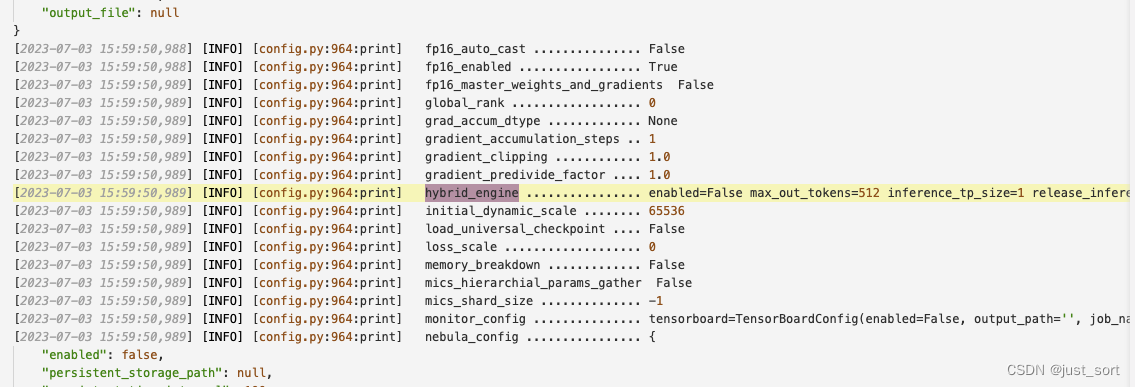
hybrid_engine的优化方法和原理在后续文章中继续探索。
这里分享一下我复现官方sample训练的第一阶段的log:https://paste.ubuntu.com/p/vcG49hQmCW/
0x5. 总结
这篇文章解析了DeepSpeed Chat中监督指令微调这个过程的源码,这个过程和一般的PyTorch DDP分布式训练区别不是特别大,主要是自定义prompt数据集以及将普通的训练流程中的组件如模型,优化器,学习率调度器等等,使用DeepSpeed来warp一下,来用上DeepSpeed提供的Zero,Gradient Checkpoint(注意这个其实就是activation checkpoint)等特性。本文是完全按照训练流程顺序阅读代码,并补全了训练过程中所有涉及到的工具函数或者新的特性如LoRA微调的代码解析。DeepSpeed Chat这部分代码写得比较清晰易懂,因为是在接口层面来使用DeepSpeed,相当于基于DeepSpeed做应用所以代码中不会涉及到DeepSpeed的底层代码,只需要关注算法流程。但这个代码在LoRA微调这部分感觉设计的耦合性有一点高,如果要新增新的微调方式比如QLoRA可能写法就不太优雅了。