VOC(Visual Object Classes)数据集是一个广泛使用的计算机视觉数据集,主要用于目标检测、图像分割和图像分类等任务。VOC数据集最初由英国牛津大学的计算机视觉小组创建,并在PASCAL VOC挑战赛中使用。
VOC数据集包含各种不同类别的标记图像,每个图像都有与之相关联的边界框(bounding box)和对象类别的标签。数据集中包括了20个常见的目标类别,例如人、汽车、猫、狗等。此外,VOC数据集还提供了用于图像分割任务的像素级标注。
VOC数据集涵盖了多个年度的发布,每个年度的数据集包含训练集、验证集和测试集。训练集用于模型的训练和参数优化,验证集用于模型的调参和性能评估,而测试集则用于最终模型的性能评估和比较。
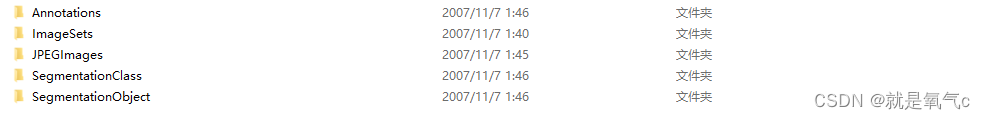
VOC数据集下载的目录如下
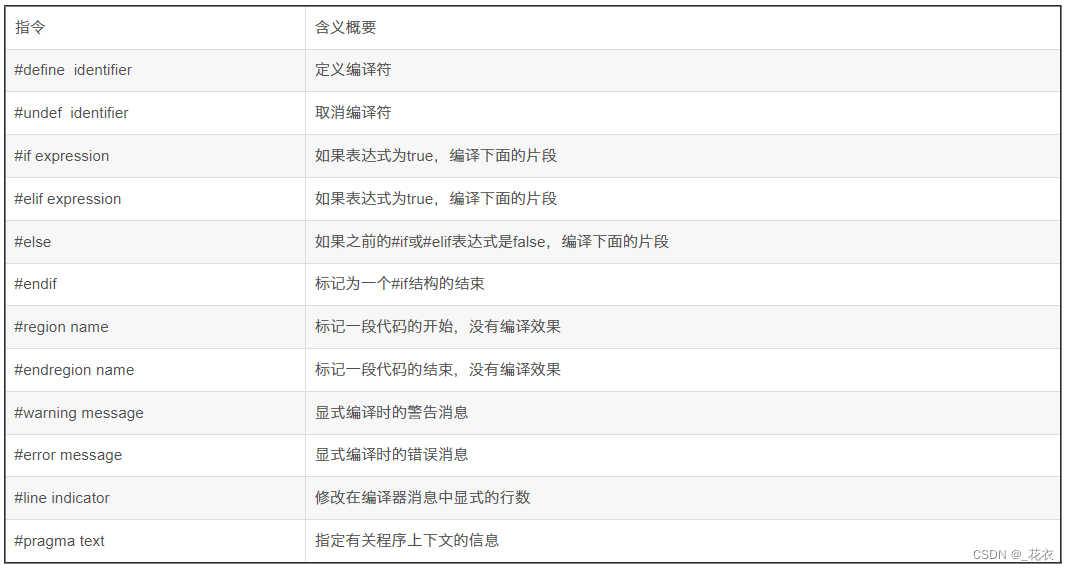
- Annotations是用于目标检测的xml标注文件
- ImageSets是提前分好的train val test的txt文件,如果不提交比赛,可以自己写一个
- JPEGImages是原本的jpg图像
- 剩余两个均用于图像分割中
读取VOC数据集的一般流程(目标检测)
Annotations中的xml标注文件样式如下:
<annotation>
<folder>VOC2007</folder>
<filename>000001.jpg</filename>
<source>
<database>The VOC2007 Database</database>
<annotation>PASCAL VOC2007</annotation>
<image>flickr</image>
<flickrid>341012865</flickrid>
</source>
<owner>
<flickrid>Fried Camels</flickrid>
<name>Jinky the Fruit Bat</name>
</owner>
<size>
<width>353</width>
<height>500</height>
<depth>3</depth>
</size>
<segmented>0</segmented>
<object>
<name>dog</name>
<pose>Left</pose>
<truncated>1</truncated>
<difficult>0</difficult>
<bndbox>
<xmin>48</xmin>
<ymin>240</ymin>
<xmax>195</xmax>
<ymax>371</ymax>
</bndbox>
</object>
<object>
<name>person</name>
<pose>Left</pose>
<truncated>1</truncated>
<difficult>0</difficult>
<bndbox>
<xmin>8</xmin>
<ymin>12</ymin>
<xmax>352</xmax>
<ymax>498</ymax>
</bndbox>
</object>
</annotation>
xml中object标签下是关于检测框的坐标信息,(xmin,ymin)表示左上角,(xmax,ymax)表示右下角
其对应的图像如下:

通常采取的方式是
- 将xml文件转换为txt文本文件,每一行代表了一张图片的坐标信息和类别信息
- 读取txt文本文件放入dataset中
以下是xml转换为文本的python code
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
import os
def parse_rec(filename):
print(filename)
tree = ET.parse(filename)
objects = []
for obj in tree.findall('object'):
obj_struct = {}
difficult = int(obj.find('difficult').text)
if difficult == 1:
continue
obj_struct['name'] = obj.find('name').text
bbox = obj.find('bndbox')
obj_struct['bbox'] = [int(float(bbox.find('xmin').text)),
int(float(bbox.find('ymin').text)),
int(float(bbox.find('xmax').text)),
int(float(bbox.find('ymax').text))]
objects.append(obj_struct)
"""
obj_struct:{'name': 'dog', 'bbox': [48, 240, 195, 371]}
"""
"""
objects: [{'name': 'dog', 'bbox': [48, 240, 195, 371]}, {'name': 'person', 'bbox': [8, 12, 352, 498]}]
"""
return objects
VOC_CLASSES = ( # always index 0
'aeroplane', 'bicycle', 'bird', 'boat',
'bottle', 'bus', 'car', 'cat', 'chair',
'cow', 'diningtable', 'dog', 'horse',
'motorbike', 'person', 'pottedplant',
'sheep', 'sofa', 'train', 'tvmonitor')
train_val_dataset = open('VOC_train_val.txt', 'r')
test_dataset = open('VOC_test.txt', 'r')
train_val_file = open('myDataset_train_val', 'w')
test_file = open('myDataset_test', 'w')
# 读取训练验证图像的名称
train_val_lines = train_val_dataset.readlines()
train_val_lines = [x[:-1].split(' ')[0] for x in train_val_lines]
# 读取测试图像的名称
test_lines = test_dataset.readlines()
test_lines = [x[:-1] for x in test_lines]
Annotations = r'D:/Detection/VOC2007/VOCdevkit/VOC2007/Annotations/'
xml_files = os.listdir(Annotations)
count = 0
for xml_file in xml_files:
count += 1
image_path = xml_file.split('.')[0] + '.jpg'
results = parse_rec(Annotations + xml_file)
# 理论不存在
if len(results) == 0:
continue
write_line = image_path
for result in results:
class_name = result['name']
name = VOC_CLASSES.index(class_name)
bbox = result['bbox']
write_line += ' '+str(bbox[0])+' '+str(bbox[1])+' '+str(bbox[2])+' '+str(bbox[3])+' '+str(name)
write_line += '\n'
if xml_file.split('.')[0] in train_val_lines:
train_val_file.write(write_line)
elif xml_file.split('.')[0] in test_lines:
test_file.write(write_line)
train_val_file.close()
test_file.close()
转后的txt文件如下:
000001.jpg 48 240 195 371 11 8 12 352 498 14
000002.jpg 139 200 207 301 18
000003.jpg 123 155 215 195 17 239 156 307 205 8
000004.jpg 13 311 84 362 6 362 330 500 389 6 235 328 334 375 6 175 327 252 364 6 139 320 189 359 6 108 325 150 353 6 84 323 121 350 6
000006.jpg 187 135 282 242 15 154 209 369 375 10 255 207 366 375 8 138 211 249 375 8
000008.jpg 192 16 364 249 8
000010.jpg 87 97 258 427 12 133 72 245 284 14
000011.jpg 126 51 330 308 7
000013.jpg 299 160 446 252 9
...
第一个表示图片的名称,接下来没5个数字看成一组,前四个分别为xmin,ymin,xmax,ymax,第五个为类别编号。