1. 环境说明
Kubernetes源码版本:remotes/origin/release-1.25
Kubernetes编译出来的Kubelet版本:Kubernetes v1.24.0-beta.0.2463+ee7799bab469d7
Kubernetes集群实验环境:使用Kubernetes v1.25.4二进制的方式搭建了一个单节点集群
K8S 单节点单节点搭建可以参考:Kubernetes v1.25 搭建单节点集群用于Debug K8S源码
Golang版本:go1.19.3 linux/amd64
IDEA版本:2022.2.3
Delve版本:1.9.1
[root@k8s-master1 kubernetes]#
[root@k8s-master1 kubernetes]# dlv version
Delve Debugger
Version: 1.9.1
Build: $Id: d81b9fd12bfa603f3cf7a4bc842398bd61c42940 $
[root@k8s-master1 kubernetes]#
[root@k8s-master1 kubernetes]# go version
go version go1.19.3 linux/amd64
[root@k8s-master1 kubernetes]#
[root@k8s-master1 kubernetes]# kubectl version
WARNING: This version information is deprecated and will be replaced with the output from kubectl version --short. Use --output=yaml|json to get the full version.
Client Version: version.Info{Major:"1", Minor:"25", GitVersion:"v1.25.4", GitCommit:"872a965c6c6526caa949f0c6ac028ef7aff3fb78", GitTreeState:"clean", BuildDate:"2022-11-09T13:36:36Z", GoVersion:"go1.19.3", Compiler:"gc", Platform:"linux/amd64"}
Kustomize Version: v4.5.7
Server Version: version.Info{Major:"1", Minor:"25", GitVersion:"v1.25.4", GitCommit:"872a965c6c6526caa949f0c6ac028ef7aff3fb78", GitTreeState:"clean", BuildDate:"2022-11-09T13:29:58Z", GoVersion:"go1.19.3", Compiler:"gc", Platform:"linux/amd64"}
[root@k8s-master1 kubernetes]#
[root@k8s-master1 kubernetes]#
[root@k8s-master1 kubernetes]# kubectl get nodes -owide
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION INTERNAL-IP EXTERNAL-IP OS-IMAGE KERNEL-VERSION CONTAINER-RUNTIME
k8s-master1 Ready <none> 31h v1.25.4 192.168.11.71 <none> CentOS Linux 7 (Core) 3.10.0-1160.80.1.el7.x86_64 containerd://1.6.10
[root@k8s-master1 kubernetes]#
[root@k8s-master1 kubernetes]#
[root@k8s-master1 kubernetes]# kubectl get componentstatus
Warning: v1 ComponentStatus is deprecated in v1.19+
NAME STATUS MESSAGE ERROR
etcd-0 Healthy {"health":"true","reason":""}
controller-manager Healthy ok
scheduler Healthy ok
[root@k8s-master1 kubernetes]#
Kubelet启动参数配置如下:
[root@k8s-master1 kubernetes]# ps -ef|grep "/usr/local/bin/kubelet"
root 7972 1 6 07:06 ? 00:00:06 /usr/local/bin/kubelet --bootstrap-kubeconfig=/etc/kubernetes/bootstrap-kubelet.kubeconfig --kubeconfig=/etc/kubernetes/kubelet.kubeconfig --config=/etc/kubernetes/kubelet-conf.yml --container-runtime-endpoint=unix:///run/containerd/containerd.sock --node-labels=node.kubernetes.io/node= --v=8
root 9549 6424 0 07:07 pts/0 00:00:00 grep --color=auto /usr/local/bin/kubelet
[root@k8s-master1 kubernetes]#
Kubelet参数配置如下:
apiVersion: kubelet.config.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: KubeletConfiguration
address: 0.0.0.0
port: 10250
readOnlyPort: 10255
authentication:
anonymous:
enabled: false
webhook:
cacheTTL: 2m0s
enabled: true
x509:
clientCAFile: /etc/kubernetes/pki/ca.pem
authorization:
mode: Webhook
webhook:
cacheAuthorizedTTL: 5m0s
cacheUnauthorizedTTL: 30s
cgroupDriver: systemd
cgroupsPerQOS: true
clusterDNS:
- 10.96.0.10
clusterDomain: cluster.local
containerLogMaxFiles: 5
containerLogMaxSize: 10Mi
contentType: application/vnd.kubernetes.protobuf
cpuCFSQuota: true
cpuManagerPolicy: none
cpuManagerReconcilePeriod: 10s
enableControllerAttachDetach: true
enableDebuggingHandlers: true
enforceNodeAllocatable:
- pods
eventBurst: 10
eventRecordQPS: 5
evictionHard:
imagefs.available: 15%
memory.available: 100Mi
nodefs.available: 10%
nodefs.inodesFree: 5%
evictionPressureTransitionPeriod: 5m0s
failSwapOn: true
fileCheckFrequency: 20s
hairpinMode: promiscuous-bridge
healthzBindAddress: 127.0.0.1
healthzPort: 10248
httpCheckFrequency: 20s
imageGCHighThresholdPercent: 85
imageGCLowThresholdPercent: 80
imageMinimumGCAge: 2m0s
iptablesDropBit: 15
iptablesMasqueradeBit: 14
kubeAPIBurst: 10
kubeAPIQPS: 5
makeIPTablesUtilChains: true
maxOpenFiles: 1000000
maxPods: 110
nodeStatusUpdateFrequency: 10s
oomScoreAdj: -999
podPidsLimit: -1
registryBurst: 10
registryPullQPS: 5
resolvConf: /etc/resolv.conf
rotateCertificates: true
runtimeRequestTimeout: 2m0s
serializeImagePulls: true
staticPodPath: /etc/kubernetes/manifests
streamingConnectionIdleTimeout: 4h0m0s
syncFrequency: 1m0s
volumeStatsAggPeriod: 1m0s
2. 源码分析
| syncLoop |
syncLoop函数并不长,具体逻辑如下:
- 1、sss
- 2、胜多负少
// pkg/kubelet/kubelet.go
func (kl *Kubelet) syncLoop(updates <-chan kubetypes.PodUpdate, handler SyncHandler) {
klog.InfoS("Starting kubelet main sync loop")
syncTicker := time.NewTicker(time.Second)
defer syncTicker.Stop()
// 这里的housekeeping英文翻译过来是家务管理的意思
housekeepingTicker := time.NewTicker(housekeepingPeriod)
defer housekeepingTicker.Stop()
// 看到这里是不是顿然开悟,PLEG生产的PodLifecycleEvent最终落到了syncLoop这里
plegCh := kl.pleg.Watch()
const (
base = 100 * time.Millisecond
max = 5 * time.Second
factor = 2
)
duration := base
if kl.dnsConfigurer != nil && kl.dnsConfigurer.ResolverConfig != "" {
kl.dnsConfigurer.CheckLimitsForResolvConf()
}
// 下面就是一个死循环了,对得起syncLoop中的Loop
for {
// 如果运行时报错,就跳出Pod同步
if err := kl.runtimeState.runtimeErrors(); err != nil {
klog.ErrorS(err, "Skipping pod synchronization")
// exponential backoff
time.Sleep(duration)
duration = time.Duration(math.Min(float64(max), factor*float64(duration)))
continue
}
// reset backoff if we have a success
duration = base
kl.syncLoopMonitor.Store(kl.clock.Now())
if !kl.syncLoopIteration(updates, handler, syncTicker.C, housekeepingTicker.C, plegCh) {
break
}
kl.syncLoopMonitor.Store(kl.clock.Now())
}
}
| syncLoopIteration |
具体的逻辑在syncLoopIteration函数当中,具体逻辑如下:
- 1、时尚大方
func (kl *Kubelet) syncLoopIteration(configCh <-chan kubetypes.PodUpdate, handler SyncHandler,
syncCh <-chan time.Time, housekeepingCh <-chan time.Time, plegCh <-chan *pleg.PodLifecycleEvent) bool {
select {
case u, open := <-configCh:
// Update from a config source; dispatch it to the right handler
// callback.
if !open {
klog.ErrorS(nil, "Update channel is closed, exiting the sync loop")
return false
}
switch u.Op {
case kubetypes.ADD:
klog.V(2).InfoS("SyncLoop ADD", "source", u.Source, "pods", klog.KObjs(u.Pods))
handler.HandlePodAdditions(u.Pods)
case kubetypes.UPDATE:
klog.V(2).InfoS("SyncLoop UPDATE", "source", u.Source, "pods", klog.KObjs(u.Pods))
handler.HandlePodUpdates(u.Pods)
case kubetypes.REMOVE:
klog.V(2).InfoS("SyncLoop REMOVE", "source", u.Source, "pods", klog.KObjs(u.Pods))
handler.HandlePodRemoves(u.Pods)
case kubetypes.RECONCILE:
klog.V(4).InfoS("SyncLoop RECONCILE", "source", u.Source, "pods", klog.KObjs(u.Pods))
handler.HandlePodReconcile(u.Pods)
case kubetypes.DELETE:
klog.V(2).InfoS("SyncLoop DELETE", "source", u.Source, "pods", klog.KObjs(u.Pods))
// DELETE is treated as a UPDATE because of graceful deletion.
handler.HandlePodUpdates(u.Pods)
case kubetypes.SET:
// TODO: Do we want to support this?
klog.ErrorS(nil, "Kubelet does not support snapshot update")
default:
klog.ErrorS(nil, "Invalid operation type received", "operation", u.Op)
}
kl.sourcesReady.AddSource(u.Source)
case e := <-plegCh:
if e.Type == pleg.ContainerStarted {
kl.lastContainerStartedTime.Add(e.ID, time.Now())
}
if isSyncPodWorthy(e) {
// PLEG event for a pod; sync it.
if pod, ok := kl.podManager.GetPodByUID(e.ID); ok {
klog.V(2).InfoS("SyncLoop (PLEG): event for pod", "pod", klog.KObj(pod), "event", e)
handler.HandlePodSyncs([]*v1.Pod{pod})
} else {
// If the pod no longer exists, ignore the event.
klog.V(4).InfoS("SyncLoop (PLEG): pod does not exist, ignore irrelevant event", "event", e)
}
}
if e.Type == pleg.ContainerDied {
if containerID, ok := e.Data.(string); ok {
kl.cleanUpContainersInPod(e.ID, containerID)
}
}
case <-syncCh:
// Sync pods waiting for sync
podsToSync := kl.getPodsToSync()
if len(podsToSync) == 0 {
break
}
klog.V(4).InfoS("SyncLoop (SYNC) pods", "total", len(podsToSync), "pods", klog.KObjs(podsToSync))
handler.HandlePodSyncs(podsToSync)
case update := <-kl.livenessManager.Updates():
if update.Result == proberesults.Failure {
handleProbeSync(kl, update, handler, "liveness", "unhealthy")
}
case update := <-kl.readinessManager.Updates():
ready := update.Result == proberesults.Success
kl.statusManager.SetContainerReadiness(update.PodUID, update.ContainerID, ready)
status := ""
if ready {
status = "ready"
}
handleProbeSync(kl, update, handler, "readiness", status)
case update := <-kl.startupManager.Updates():
started := update.Result == proberesults.Success
kl.statusManager.SetContainerStartup(update.PodUID, update.ContainerID, started)
status := "unhealthy"
if started {
status = "started"
}
handleProbeSync(kl, update, handler, "startup", status)
case <-housekeepingCh:
if !kl.sourcesReady.AllReady() {
// If the sources aren't ready or volume manager has not yet synced the states,
// skip housekeeping, as we may accidentally delete pods from unready sources.
klog.V(4).InfoS("SyncLoop (housekeeping, skipped): sources aren't ready yet")
} else {
start := time.Now()
klog.V(4).InfoS("SyncLoop (housekeeping)")
if err := handler.HandlePodCleanups(); err != nil {
klog.ErrorS(err, "Failed cleaning pods")
}
duration := time.Since(start)
if duration > housekeepingWarningDuration {
klog.ErrorS(fmt.Errorf("housekeeping took too long"), "Housekeeping took longer than 15s", "seconds", duration.Seconds())
}
klog.V(4).InfoS("SyncLoop (housekeeping) end")
}
}
return true
}
2.1. PodUpdate
| PodUpdate |
这里我们来看看PodUpate,不知道大家有没有注意到,进入到syncLoop函数的时候,首先引入眼帘的就是它的参数,直觉告诉我,这两个参数还是比较重要的。
向上追溯可以发现,PodUpate是通过PodCfg.Updates()传进来的
// cmd/kubelet/app/server.go
func startKubelet(k kubelet.Bootstrap, podCfg *config.PodConfig, kubeCfg *kubeletconfiginternal.KubeletConfiguration, kubeDeps *kubelet.Dependencies, enableServer bool) {
// start the kubelet
go k.Run(podCfg.Updates())
// 此处省略其它逻辑
}
点进去,我们发现PodCfg.Updates()方法就是把自己内部的updates属性传了出来
// pkg/kubelet/config/config.go
func (c *PodConfig) Updates() <-chan kubetypes.PodUpdate {
return c.updates
}
那么,这个属性是在什么地方、什么时候、被谁写入的呢?,我们带着这个问题继续往下追,按住IDEA的ctrl + G,找到所有写入updates这个属性的地方。
搜索结果让人很开心,就一个地方写入,也就是创建PodConfig的时候写入的,但是创建PodConfig也是通过updates := make(chan kubetypes.PodUpdate, 50)创建了一个空的channel啊。
用脚趾头想,这个channel一定在某个地方被使用,我们仔细看一下,storage := newPodStorage(updates, mode, recorder),其实在创建PodStorage的时候也传入了updates,也就是说PodConfig.updates属性一定是通过PodStrorage来改变的,我们继续通过IDEA搜索来看看PodStorage是如何使用这个PodConfig.updates的。
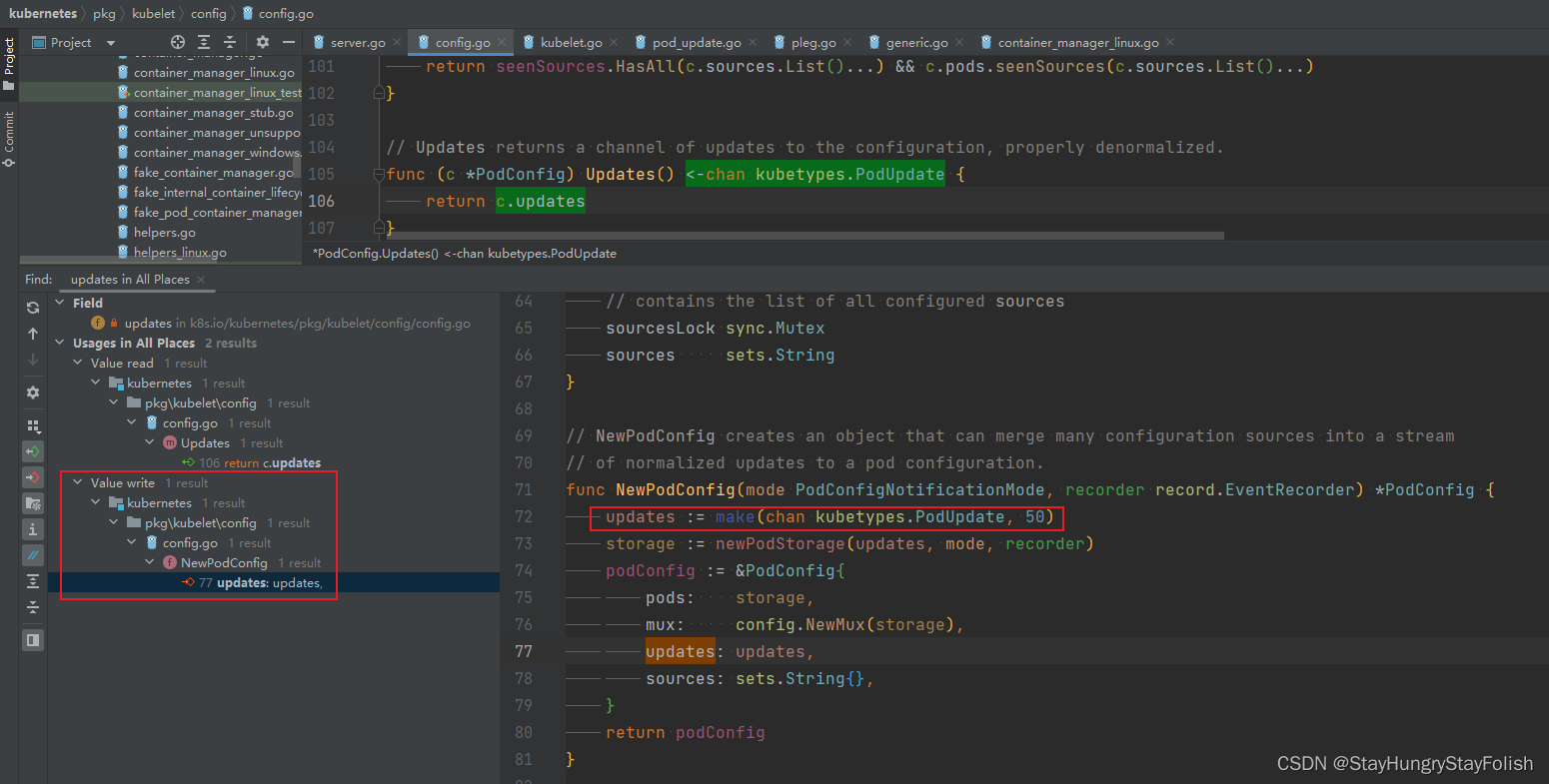
居然有如此之多的地方在修改PodConfig.updates属性,PodStorage主要有两块在修改PodConfig.updates,一块是在Merge,一块是在Sync的时候。看来分析PodStorage是势在必行了,我们一起来看看PodStorage干了啥
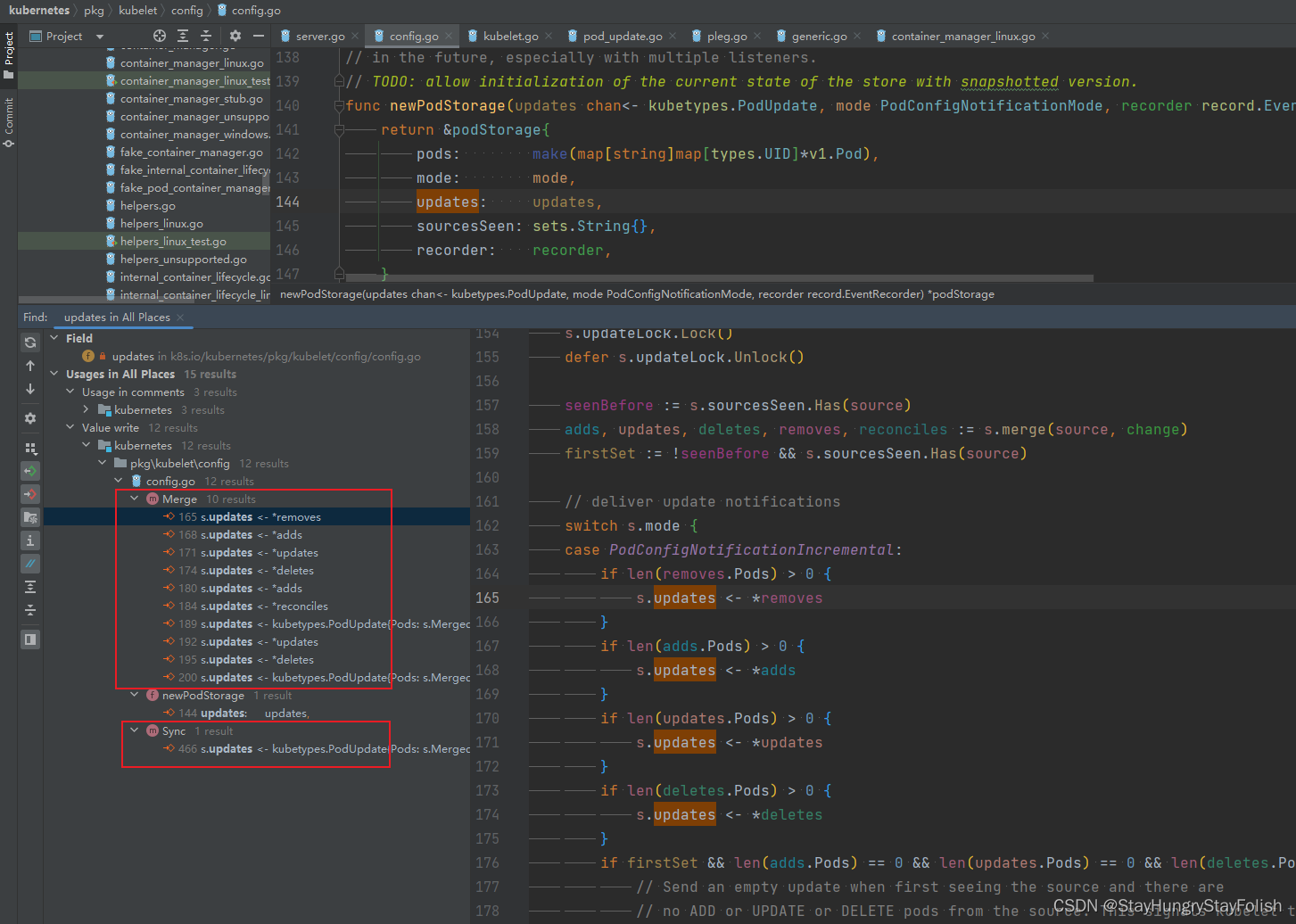
2.1.1. PodStorage
| PodStorage |
顾名思义,PodStorage势必是Pod的缓存,
// pkg/kubelet/config/config.go
type podStorage struct {
podLock sync.RWMutex
// 果然没有让我们失望,对得起Storage, 这里用了一个Map存放Pod, 按照我的猜测本来应该就是一个简单的Map,key为PodId,值为Pod,但是这里多嵌套了一层
pods map[string]map[types.UID]*v1.Pod
mode PodConfigNotificationMode
updateLock sync.Mutex
// 这个udpates属性,实际上就是PodConfig.updates,他们两个持有相同的引用
updates chan<- kubetypes.PodUpdate
sourcesSeenLock sync.RWMutex
sourcesSeen sets.String
recorder record.EventRecorder
}
| PodStorage.Merge |
// pkg/kubelet/config/config.go
func (s *podStorage) Merge(source string, change interface{}) error {
s.updateLock.Lock()
defer s.updateLock.Unlock()
seenBefore := s.sourcesSeen.Has(source)
adds, updates, deletes, removes, reconciles := s.merge(source, change)
firstSet := !seenBefore && s.sourcesSeen.Has(source)
// deliver update notifications
switch s.mode {
case PodConfigNotificationIncremental:
if len(removes.Pods) > 0 {
s.updates <- *removes
}
if len(adds.Pods) > 0 {
s.updates <- *adds
}
if len(updates.Pods) > 0 {
s.updates <- *updates
}
if len(deletes.Pods) > 0 {
s.updates <- *deletes
}
if firstSet && len(adds.Pods) == 0 && len(updates.Pods) == 0 && len(deletes.Pods) == 0 {
// Send an empty update when first seeing the source and there are
// no ADD or UPDATE or DELETE pods from the source. This signals kubelet that
// the source is ready.
s.updates <- *adds
}
// Only add reconcile support here, because kubelet doesn't support Snapshot update now.
if len(reconciles.Pods) > 0 {
s.updates <- *reconciles
}
case PodConfigNotificationSnapshotAndUpdates:
if len(removes.Pods) > 0 || len(adds.Pods) > 0 || firstSet {
s.updates <- kubetypes.PodUpdate{Pods: s.MergedState().([]*v1.Pod), Op: kubetypes.SET, Source: source}
}
if len(updates.Pods) > 0 {
s.updates <- *updates
}
if len(deletes.Pods) > 0 {
s.updates <- *deletes
}
case PodConfigNotificationSnapshot:
if len(updates.Pods) > 0 || len(deletes.Pods) > 0 || len(adds.Pods) > 0 || len(removes.Pods) > 0 || firstSet {
s.updates <- kubetypes.PodUpdate{Pods: s.MergedState().([]*v1.Pod), Op: kubetypes.SET, Source: source}
}
case PodConfigNotificationUnknown:
fallthrough
default:
panic(fmt.Sprintf("unsupported PodConfigNotificationMode: %#v", s.mode))
}
return nil
}
| PodStorage.merge |
// pkg/kubelet/config/config.go
func (s *podStorage) merge(source string, change interface{}) (adds, updates, deletes, removes, reconciles *kubetypes.PodUpdate) {
s.podLock.Lock()
defer s.podLock.Unlock()
addPods := []*v1.Pod{}
updatePods := []*v1.Pod{}
deletePods := []*v1.Pod{}
removePods := []*v1.Pod{}
reconcilePods := []*v1.Pod{}
pods := s.pods[source]
if pods == nil {
pods = make(map[types.UID]*v1.Pod)
}
updatePodsFunc := func(newPods []*v1.Pod, oldPods, pods map[types.UID]*v1.Pod) {
filtered := filterInvalidPods(newPods, source, s.recorder)
for _, ref := range filtered {
// Annotate the pod with the source before any comparison.
if ref.Annotations == nil {
ref.Annotations = make(map[string]string)
}
ref.Annotations[kubetypes.ConfigSourceAnnotationKey] = source
if existing, found := oldPods[ref.UID]; found {
pods[ref.UID] = existing
needUpdate, needReconcile, needGracefulDelete := checkAndUpdatePod(existing, ref)
if needUpdate {
updatePods = append(updatePods, existing)
} else if needReconcile {
reconcilePods = append(reconcilePods, existing)
} else if needGracefulDelete {
deletePods = append(deletePods, existing)
}
continue
}
recordFirstSeenTime(ref)
pods[ref.UID] = ref
addPods = append(addPods, ref)
}
}
update := change.(kubetypes.PodUpdate)
switch update.Op {
case kubetypes.ADD, kubetypes.UPDATE, kubetypes.DELETE:
if update.Op == kubetypes.ADD {
klog.V(4).InfoS("Adding new pods from source", "source", source, "pods", klog.KObjs(update.Pods))
} else if update.Op == kubetypes.DELETE {
klog.V(4).InfoS("Gracefully deleting pods from source", "source", source, "pods", klog.KObjs(update.Pods))
} else {
klog.V(4).InfoS("Updating pods from source", "source", source, "pods", klog.KObjs(update.Pods))
}
updatePodsFunc(update.Pods, pods, pods)
case kubetypes.REMOVE:
klog.V(4).InfoS("Removing pods from source", "source", source, "pods", klog.KObjs(update.Pods))
for _, value := range update.Pods {
if existing, found := pods[value.UID]; found {
// this is a delete
delete(pods, value.UID)
removePods = append(removePods, existing)
continue
}
// this is a no-op
}
case kubetypes.SET:
klog.V(4).InfoS("Setting pods for source", "source", source)
s.markSourceSet(source)
// Clear the old map entries by just creating a new map
oldPods := pods
pods = make(map[types.UID]*v1.Pod)
updatePodsFunc(update.Pods, oldPods, pods)
for uid, existing := range oldPods {
if _, found := pods[uid]; !found {
// this is a delete
removePods = append(removePods, existing)
}
}
default:
klog.InfoS("Received invalid update type", "type", update)
}
s.pods[source] = pods
adds = &kubetypes.PodUpdate{Op: kubetypes.ADD, Pods: copyPods(addPods), Source: source}
updates = &kubetypes.PodUpdate{Op: kubetypes.UPDATE, Pods: copyPods(updatePods), Source: source}
deletes = &kubetypes.PodUpdate{Op: kubetypes.DELETE, Pods: copyPods(deletePods), Source: source}
removes = &kubetypes.PodUpdate{Op: kubetypes.REMOVE, Pods: copyPods(removePods), Source: source}
reconciles = &kubetypes.PodUpdate{Op: kubetypes.RECONCILE, Pods: copyPods(reconcilePods), Source: source}
return adds, updates, deletes, removes, reconciles
}
| PodStorage.Sync |
// pkg/kubelet/config/config.go
// Sync sends a copy of the current state through the update channel.
func (s *podStorage) Sync() {
s.updateLock.Lock()
defer s.updateLock.Unlock()
s.updates <- kubetypes.PodUpdate{Pods: s.MergedState().([]*v1.Pod), Op: kubetypes.SET, Source: kubetypes.AllSource}
}








![[附源码]Python计算机毕业设计Django影评网站系统](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/a63e5a0f555f4e738179ce9b089b3eeb.png)