了解如何创建索引,添加,删除,更新文档
参考文档 开始使用 Elasticsearch 1
本文用到Elasticsearch和Kibana 可以看之前的两篇先安装好
Elasticsearch 安装
Kibana安装
Elasticsearch 里的接口都是通过 REST 接口来实现的。
GET 读取数据
POST 插入数据
PUT 或 PATCH 更新数据,或如果是一个新的 id,则插入数据
DELETE 删除数据
http://localhost:5601/app/dev_tools
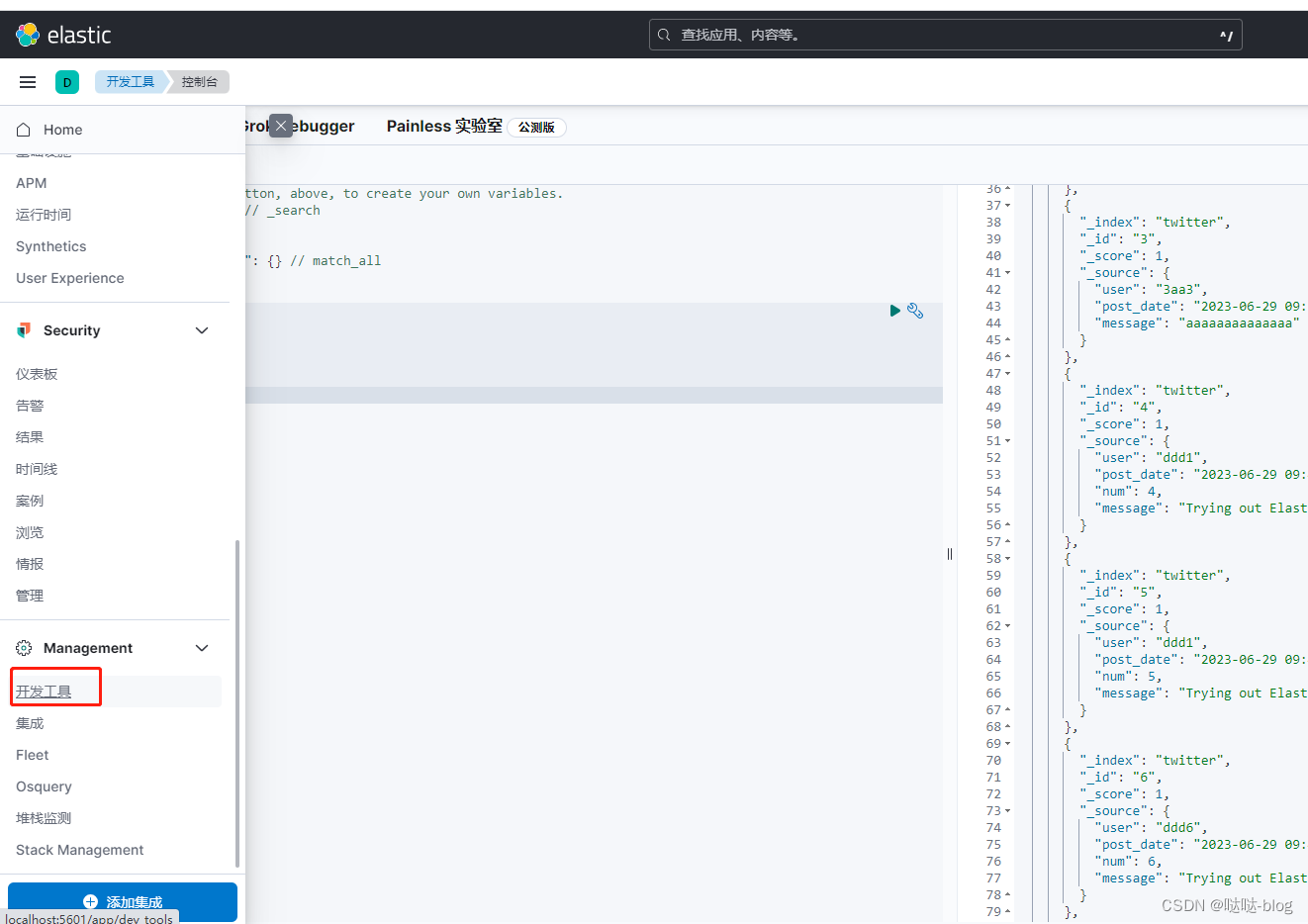

GET /
还可以复制为Curl
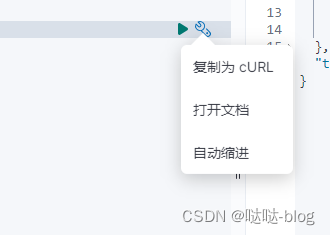
curl -XGET "https://1270.0.1:9200/" -H "kbn-xsrf: reporting"
同样可以 复制curl至页面就会变成 GET /
查看当前索引的 mapping:
GET dada/_mapping
{
"dada": {
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"cc": {
"type": "text",
"fields": {
"keyword": {
"type": "keyword",
"ignore_above": 256
}
}
},
"uid": {
"type": "text",
"fields": {
"keyword": {
"type": "keyword",
"ignore_above": 256
}
}
},
"user": {
"type": "text",
"fields": {
"keyword": {
"type": "keyword",
"ignore_above": 256
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
Elasticsearch 的数据类型:
text: 全文搜索字符串
keyword: 用于精确字符串匹配和聚合
date 及 date_nanos: 格式化为日期或数字日期的字符串
byte, short, integer, long: 整数类型
boolean: 布尔类型
float,double,half_float: 浮点数类型
分级的类型:object 及 nested。
创建一个索引 test,并且含有 id 及 message 字段。id 字段为 keyword 类型,而 message 字段为 text 类型,那么我们可以使用如下的方法来创建:
PUT test
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"id": {
"type": "keyword"
},
"message": {
"type": "text"
}
}
}
}
#--------返回结果--------
{
"acknowledged": true,
"shards_acknowledged": true,
"index": "test"
}
追加一个新的字段 age,并且它的类型为 long 类型:
PUT test/_mapping
{
"properties": {
"age": {
"type": "long"
}
}
}
#--------返回结果--------
{
"acknowledged": true
}
#查看结果
GET test/_mapping
#--------返回结果--------
{
"test": {
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"age": {
"type": "long"
},
"id": {
"type": "keyword"
},
"message": {
"type": "text"
}
}
}
}
}
_refresh用于使新文档在搜索时可见。
反过来,_flush用于在硬盘上持久化内存段。
_flush不会影响Elasticsearch中文档的可见性,因为搜索是在内存段中进行的,而_refresh会影响它们的可见性。
#存在就会修改
PUT dada/_doc/2
{
"user":"222",
"uid":2,
"cc":"222"
}
#存在就会返回报错
PUT dada/_create/2
{
"user":"222",
"uid":2,
"cc":"222"
}
#效果一样
PUT dada/_doc/2?op_type=create
{
"user":"22222",
"uid":2,
"cc":"222"
}
#--------返回报错--------
{
"error": {
"root_cause": [
{
"type": "version_conflict_engine_exception",
"reason": "[2]: version conflict, document already exists (current version [2])",
"index_uuid": "gFA5LQXRQIef2WBv3d_aWw",
"shard": "0",
"index": "dada"
}
],
"type": "version_conflict_engine_exception",
"reason": "[2]: version conflict, document already exists (current version [2])",
"index_uuid": "gFA5LQXRQIef2WBv3d_aWw",
"shard": "0",
"index": "dada"
},
"status": 409
}
查询只看_source部分
GET dada/_doc/2
#正常返回
{
"_index": "dada",
"_id": "2",
"_version": 2,
"_seq_no": 6,
"_primary_term": 1,
"found": true,
"_source": {
"user": "222",
"uid": 2,
"cc": "222"
}
}
#--------_source-------
GET dada/_source/2
#返回
{
"user": "222",
"uid": 2,
"cc": "222"
}
自动 ID 生成
使用 POST
POST dada/_doc/
{
"user":"55",
"uid":5,
"cc":"55"
}
#-----返回的结果:-----
{
"_index": "dada",
"_id": "u_g9C4kB2SZh9y2Iu2Gc",
"_version": 1,
"result": "created",
"_shards": {
"total": 2,
"successful": 1,
"failed": 0
},
"_seq_no": 7,
"_primary_term": 1
}
只读部分数据
GET dada/_doc/2?_source=user,uid
#-----返回的结果------
{
"_index": "dada",
"_id": "2",
"_version": 2,
"_seq_no": 6,
"_primary_term": 1,
"found": true,
"_source": {
"user": "222",
"uid": 2
}
}
GET dada/_source/2?_source=user,uid
#-----返回的结果------
{
"user": "222",
"uid": 2
}
一次请求查找多个文档 _mget
GET _mget
{
"docs":[
{
"_index":"dada",
"_id":2
},
{
"_index":"test",
"_id":"vPhIC4kB2SZh9y2IU2G6"
}
]
}
#-----------返回的结果------------
{
"docs": [
{
"_index": "dada",
"_id": "2",
"_version": 2,
"_seq_no": 6,
"_primary_term": 1,
"found": true,
"_source": {
"user": "222",
"uid": 2,
"cc": "222"
}
},
{
"_index": "test",
"_id": "vPhIC4kB2SZh9y2IU2G6",
"_version": 1,
"_seq_no": 0,
"_primary_term": 1,
"found": true,
"_source": {
"age": 20,
"id": 11,
"message": "lalalalaaaa"
}
}
]
}
也可以只获得部分字段
GET _mget
{
"docs":[
{
"_index":"dada",
"_id":2,
"_source":["user","uid"]
},
{
"_index":"test",
"_id":"vPhIC4kB2SZh9y2IU2G6"
}
]
}
#---------返回的结果---------
{
"docs": [
{
"_index": "dada",
"_id": "2",
"_version": 2,
"_seq_no": 6,
"_primary_term": 1,
"found": true,
"_source": {
"user": "222",
"uid": 2
}
},
{
"_index": "test",
"_id": "vPhIC4kB2SZh9y2IU2G6",
"_version": 1,
"_seq_no": 0,
"_primary_term": 1,
"found": true,
"_source": {
"age": 20,
"id": 11,
"message": "lalalalaaaa"
}
}
]
}
GET _mget
{
"docs":[
{
"_index":"dada",
"_id":2,
"_source":["user","uid"]
},
{
"_index":"dada",
"_id":1
}
]
}
#--------可简写:---------
GET dada/_mget
{
"ids":["1","2"]
}
#------------返回结果------------
{
"docs": [
{
"_index": "dada",
"_id": "1",
"_version": 1,
"_seq_no": 0,
"_primary_term": 1,
"found": true,
"_source": {
"user": "GB",
"uid": "sss",
"cc": "aa"
}
},
{
"_index": "dada",
"_id": "2",
"_version": 2,
"_seq_no": 6,
"_primary_term": 1,
"found": true,
"_source": {
"user": "222",
"uid": 2,
"cc": "222"
}
}
]
}
修改一个文档
在上面我们看到了可以使用 POST 的命令来修改改一个文档。通常我们使用 POST 来创建一个新的文档。在使用 POST 的时候,我们甚至不用去指定特定的 id,系统会帮我们自动生成。但是我们修改一个文档时,我们通常会使用 PUT 来进行操作,并且,我们需要指定一个特定的 id 来进行修改:
PUT修改时,每一项都会改
PUT test/_doc/1
{
"age":110,
"id":1212
}
使用POST 只改需要改的字段,其他字段会保留下来
POST test/_update/1
{
"doc": {
"age":22222,
"id":20
}
}
先查询后修改 script
通过查询的方式来进行查询,让后进行修改。ES 也提供了相应的 REST 接口。
会把所有age为22222的都修改
POST test/_update_by_query
{
"query": {
"match": {
"age": "22222"
}
},
"script": {
"source": "ctx._source.id=params.id;ctx._source.message=params.message",
"lang": "painless",
"params":{
"id":888,
"message":"new哈哈哈",
"oth":"????"
}
}
}
可以通过 update 接口,使用 script 的方法来进行修改。这个方法也是需要知道文档的 id
POST test/_update/vPhIC4kB2SZh9y2IU2G6
{
"script": {
"source": "ctx._source.id=params.id;ctx._source.message=params.message",
"lang": "painless",
"params":{
"id":999,
"message":"new999哈哈哈",
"oth":"??999??"
}
}
}
#------返回结果--------
{
"_index": "test",
"_id": "vPhIC4kB2SZh9y2IU2G6",
"_version": 2,
"result": "updated",
"_shards": {
"total": 2,
"successful": 1,
"failed": 0
},
"_seq_no": 9,
"_primary_term": 1
}
在我们使用上面的方法更新文档时,如果当前的文档 id 不存在,那么我们甚至可以使用 upsert 属性来创建一个文档:
POST test/_update/3
{
"script": {
"source": "ctx._source.id=params.id;ctx._source.message=params.message",
"lang": "painless",
"params":{
"id":999,
"message":"new999哈哈哈",
"oth":"??999??"
}
},
"upsert":{
"id":3,
"message":"3333333"
}
}
我们甚至可以使用 _update 接口使用 ctx[‘_op’] 来达到删除一个文档的目的,比如:
当检测文档的 字段id 是否为 888,如果为 888 的话,那么该文档将被删除,否则将不做任何事情。
POST test/_update/1
{
"script": {
"source":"""
if(ctx._source.id == 888){
ctx.op = 'delete'
}else {
ctx.op = 'none'
}
"""
}
}
#------返回---------
{
"_index": "test",
"_id": "1",
"_version": 7,
"result": "deleted",
"_shards": {
"total": 2,
"successful": 1,
"failed": 0
},
"_seq_no": 11,
"_primary_term": 1
}
使用 script 的一些高级操作,比如我们可以通过如下的方法来添加一个崭新的字段,新增加了一个叫做 newfield 的字段:
POST test/_update/2
{
"script" : {
"source": "ctx._source.newfield=4",
"lang": "painless"
}
}
#----------------------
{
"_index": "test",
"_id": "2",
"_score": 1,
"_source": {
"id": 888,
"message": "new哈哈哈",
"age": 22222,
"newfield": 4
}
}
# --------------也可以删除字段-------------
POST test/_update/2
{
"script" : {
"source": "ctx._source.remove(\"newfield\")",
"lang": "painless"
}
}
在这里请注意的是:一旦一个字段被创建,那么它就会存在于更新的 mapping 中。即便针对 id 为 1 的文档删除了 newfield,但是 newfield 还将继续存在于 twitter 的 mapping 中。我们可以使用如下的命令来查看 twitter 的 mapping:
GET test/_mapping
#---------返回结果-----------
{
"test": {
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"age": {
"type": "long"
},
"id": {
"type": "keyword"
},
"message": {
"type": "text"
},
"newfield": {
"type": "long"
}
}
}
}
}
UPSERT 一个文档
术语 “upsert” 宽松地表示更新或插入,即更新文档(如果存在),否则,插入新文档。
doc_as_upsert 参数检查具有给定ID的文档是否已经存在,并将提供的 doc 与现有文档合并。 如果不存在具有给定 id 的文档,则会插入具有给定文档内容的新文档。
下面的示例使用 doc_as_upsert 合并到 id 为 10 的文档中,或者如果不存在则插入一个新文档:
POST test/_update/10
{
"doc":{
"age":"10",
"id":"10",
"newfield":"55",
"message":"messssss"
},
"doc_as_upsert":true
}
检查一个文档是否存在
HEAD test/_doc/10
# ---成功返回---
200 - OK
#------不存在-----
404 - Not Found
删除一个文档
DELETE test/_doc/11
#成功返回
{
"_index": "test",
"_id": "11",
"_version": 2,
"result": "deleted",
"_shards": {
"total": 2,
"successful": 1,
"failed": 0
},
"_seq_no": 17,
"_primary_term": 1
}
在不在id的情况下,先查询后删除,以下是把message等于14的都删除
HEAD test/_doc/14
#--
200 - OK
POST test/_delete_by_query
{
"query":{
"match":{
"message":"14"
}
}
}
HEAD test/_doc/14
#---
404 - Not Found
检查一个索引是否存在
HEAD tt
200 - OK
删除一个索引
删除一个索引 是非常直接的。我们可以直接使用如下的命令来进行删除:
DELETE tt
#删除成功返回
{
"acknowledged": true
}
批处理命令
上面我们已经了解了如何使用 REST 接口来创建一个 index,并为之创建(Create),读取(Read),修改(Update),删除文档(Delete)(CRUD)。因为每一次操作都是一个 REST 请求,对于大量的数据进行操作的话,这个显得比较慢。ES 创建一个批量处理的命令给我们使用。这样我们在一次的 REST 请求中,我们就可以完成很多的操作。这无疑是一个非常大的好处。下面,我们来介绍一下这个 _bulk 命令。
我们使用如下的命令来进行 bulk 操作:
POST _bulk
{ "index" : { "_index" : "twitter", "_id": 1} }
{"user":"双榆树-张三","message":"今儿天气不错啊,出去转转去","uid":2,"age":20,"city":"北京","province":"北京","country":"中国","address":"中国北京市海淀区","location":{"lat":"39.970718","lon":"116.325747"}}
{ "index" : { "_index" : "twitter", "_id": 2 }}
{"user":"东城区-老刘","message":"出发,下一站云南!","uid":3,"age":30,"city":"北京","province":"北京","country":"中国","address":"中国北京市东城区台基厂三条3号","location":{"lat":"39.904313","lon":"116.412754"}}
{ "index" : { "_index" : "twitter", "_id": 3} }
{"user":"东城区-李四","message":"happy birthday!","uid":4,"age":30,"city":"北京","province":"北京","country":"中国","address":"中国北京市东城区","location":{"lat":"39.893801","lon":"116.408986"}}
{ "index" : { "_index" : "twitter", "_id": 4} }
{"user":"朝阳区-老贾","message":"123,gogogo","uid":5,"age":35,"city":"北京","province":"北京","country":"中国","address":"中国北京市朝阳区建国门","location":{"lat":"39.718256","lon":"116.367910"}}
{ "index" : { "_index" : "twitter", "_id": 5} }
{"user":"朝阳区-老王","message":"Happy BirthDay My Friend!","uid":6,"age":50,"city":"北京","province":"北京","country":"中国","address":"中国北京市朝阳区国贸","location":{"lat":"39.918256","lon":"116.467910"}}
{ "index" : { "_index" : "twitter", "_id": 6} }
{"user":"虹桥-老吴","message":"好友来了都今天我生日,好友来了,什么 birthday happy 就成!","uid":7,"age":90,"city":"上海","province":"上海","country":"中国","address":"中国上海市闵行区","location":{"lat":"31.175927","lon":"121.383328"}}
在上面的命令中,我们使用了 bulk 指令来完成我们的操作。在输入命令时,我们需要特别的注意:千万不要添加除了换行以外的空格,否则会导致错误。在上面我们使用的 index 用来创建一个文档。为了说明问题的方便,我们在每一个文档里,特别指定了每个文档的 id。当执行完我们的批处理 bulk 命令后,我们可以看到:
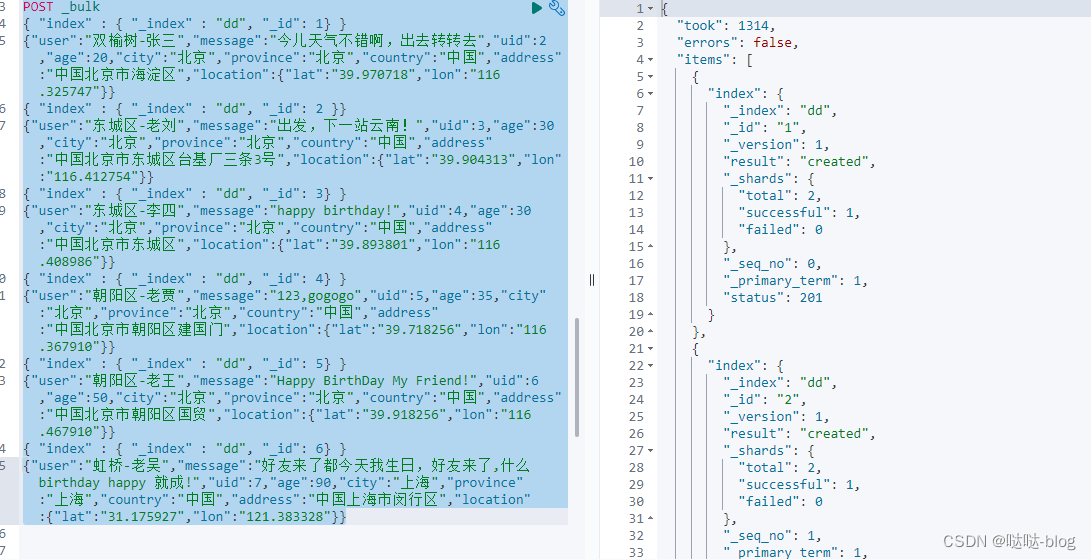
在实际的使用中,我们必须注意的是:一个好的起点是批量处理 1,000 到 5,000 个文档,总有效负载在 5MB 到 15MB 之间。如果我们的 payload 过大,那么可能会造成请求的失败。
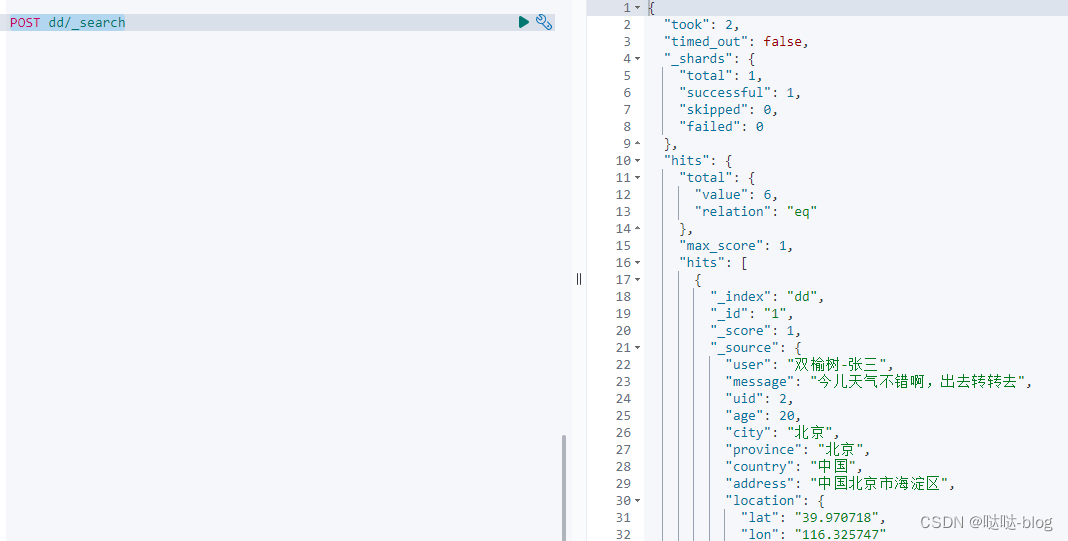
通过 POST dd/_search 查询
统计 GET dd/_count
上面我们已经使用了 index 来创建6条文档记录。我也可以尝试其它的命令,比如 create:
POST _bulk
{ "create" : { "_index" : "dd", "_id": 1} }
{"user":"双榆树-张三","message":"今儿天气不错啊,出去转转去","uid":2,"age":20,"city":"北京","province":"北京","country":"中国","address":"中国北京市海淀区","location":{"lat":"39.970718","lon":"116.325747"}}
{ "index" : { "_index" : "dd", "_id": 2 }}
{"user":"东城区-老刘","message":"出发,下一站云南!","uid":3,"age":30,"city":"北京","province":"北京","country":"中国","address":"中国北京市东城区台基厂三条3号","location":{"lat":"39.904313","lon":"116.412754"}}
{ "index" : { "_index" : "dd", "_id": 3} }
{"user":"东城区-李四","message":"happy birthday!","uid":4,"age":30,"city":"北京","province":"北京","country":"中国","address":"中国北京市东城区","location":{"lat":"39.893801","lon":"116.408986"}}
{ "index" : { "_index" : "dd", "_id": 4} }
{"user":"朝阳区-老贾","message":"123,gogogo","uid":5,"age":35,"city":"北京","province":"北京","country":"中国","address":"中国北京市朝阳区建国门","location":{"lat":"39.718256","lon":"116.367910"}}
{ "index" : { "_index" : "dd", "_id": 5} }
{"user":"朝阳区-老王","message":"Happy BirthDay My Friend!","uid":6,"age":50,"city":"北京","province":"北京","country":"中国","address":"中国北京市朝阳区国贸","location":{"lat":"39.918256","lon":"116.467910"}}
{ "index" : { "_index" : "dd", "_id": 6} }
{"user":"虹桥-老吴","message":"好友来了都今天我生日,好友来了,什么 birthday happy 就成!","uid":7,"age":90,"city":"上海","province":"上海","country":"中国","address":"中国上海市闵行区","location":{"lat":"31.175927","lon":"121.383328"}}
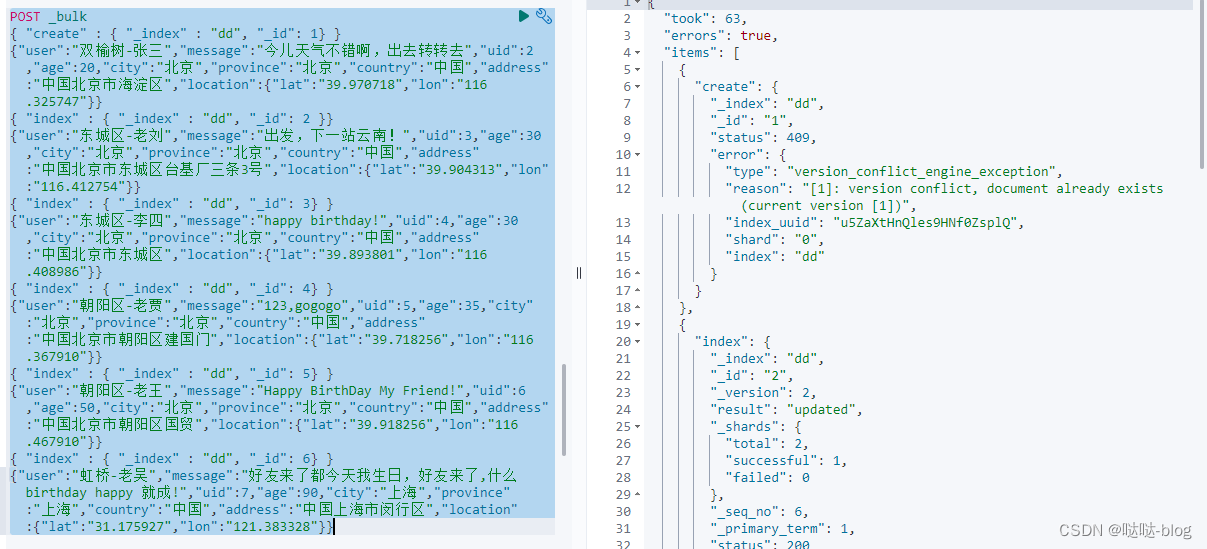
从上面的信息,我们可以看出来 index 和 create 的区别。index 总是可以成功,它可以覆盖之前的已经创建的文档,但是 create 则不行,如果已经有以那个 id 为名义的文档,就不会成功。
我们可以使用 delete 来删除一个已经创建好的文档:
POST _bulk
{ "delete" : { "_index" : "dd", "_id": 1 }}
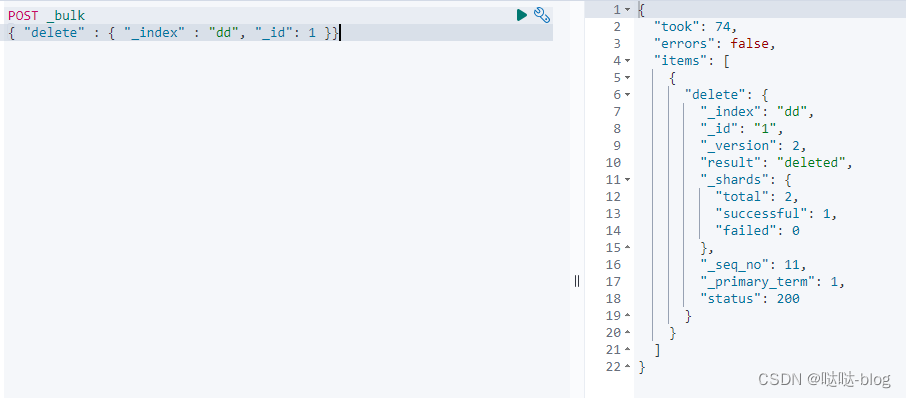
可以看到 id 为1的文档已经被删除了。我可以通过如下的命令来查看一下:
批量修改
POST _bulk
{ "update" : { "_index" : "dd", "_id": 2 }}
{"doc": { "city": "长沙"}}
索引统计
GET dd/_stats
同时获得多个索引统计值
GET dd,test/_stats
通配符
GET dd*/_stats