文章目录
- 一、Stream结果收集
- 1.1 结果收集到集合中
- 1.2 结果集收集到数组中
- 1.3 对流中数据做聚合运算
- 1.4 对流中数据做分组操作
- 1.5 对流中的数据做分区操作
- 1.6 对流中的数据做拼接
- 二、并行的Stream流
- 2.1 串行的Stream流
- 2.2 并行流
- 2.2.1获取并行流
- 2.2.2 并行流操作
- 2.3 串行流与并行流对比
- 2.4 线程安全问题
🌕博客x主页:己不由心王道长🌕!
🌎文章说明:JDK8新特性🌎
✅系列专栏:Java基础
🌴本篇内容:对JDK8的新特性进行学习和讲解🌴
☕️每日一语:这个世界本来就不完美,如果我们再不接受不完美的自己,那我们要怎么活。☕️
🚩 交流社区:己不由心王道长(优质编程社区)
一、Stream结果收集
1.1 结果收集到集合中
/**
* @Author Administrator
* @Date 2023/6/30 15:23
* @description Stream结果集收集测试
* @Version 1.0
*/
public class test01 {
@Test
public void test01(){
//收集到list集合中
List<String> list = Stream.of("王也", "诸葛青", "冯宝宝", "张楚岚")
.collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(list);
//收集到set集合中
Set<String> collect = Stream.of("王也", "王也", "诸葛青", "冯宝宝", "张楚岚")
.collect(Collectors.toSet());
System.out.println(collect);
}
}
[王也, 诸葛青, 冯宝宝, 张楚岚]
[诸葛青, 冯宝宝, 张楚岚, 王也]
这里有一个关于单元测试的常见错误,踩坑一下:
如果在test目录和main目录有同级且方法名相同的方法,执行单元测试的时候执行的是main目录下的方法,但是main目录下的方法并非@Test测试方法,所以会报以下错误:
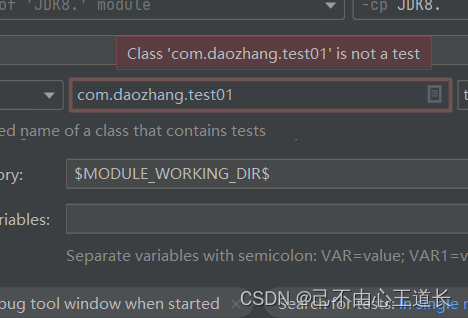
解决办法就是改变main目录同名类或者放入不同的层次中。
1.2 结果集收集到数组中
Stream中提供了toArray方法来将结果放到一个数组中,返回值类型是Object[],如果我们要指定返回的类型,那么可以使用另一个重载的toArray(IntFunction f)方法:
/**
* @Author Administrator
* @Date 2023/6/30 15:54
* @description
* @Version 1.0
*/
public class test02 {
@Test
public void test01(){
Object[] objects = Stream.of("王也", "诸葛青", "冯宝宝", "张楚岚")
.toArray();
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(objects));
}
}
结果:
[王也, 诸葛青, 冯宝宝, 张楚岚]
1.3 对流中数据做聚合运算
当我们使用Stream流处理数据后,可以像数据库的聚合函数一样对某个字段进行操作,比如获得最大值,最小值,求和,平均值,统计数量。
/**
* @Author Administrator
* @Date 2023/6/30 15:54
* @description
* @Version 1.0
*/
public class test03 {
@Test
public void test01() {
/**
* 找出最大年龄
*/
Optional<Person> MaxAge = Stream.of(
new Person("王也", 18),
new Person("张楚岚", 13),
new Person("冯宝宝", 108),
new Person("诸葛青", 15)
).collect(Collectors.maxBy((x, y) -> x.getAge() - y.getAge()));
System.out.println(MaxAge);
/**
* 找出最小年龄
*/
Optional<Person> MinAge = Stream.of(
new Person("王也", 18),
new Person("张楚岚", 13),
new Person("冯宝宝", 108),
new Person("诸葛青", 15)
).collect(Collectors.minBy((x, y) -> x.getAge() - y.getAge()));
System.out.println(MinAge);
/**
* 计算年龄综合
*/
Integer sumAge = Stream.of(
new Person("王也", 18),
new Person("张楚岚", 13),
new Person("冯宝宝", 108),
new Person("诸葛青", 15)
).collect(Collectors.summingInt(Person::getAge));
System.out.println(sumAge);
/**
* 计算年龄平均值
*/
Double ava = Stream.of(
new Person("王也", 18),
new Person("张楚岚", 13),
new Person("冯宝宝", 108),
new Person("诸葛青", 15)
).collect(Collectors.averagingInt(Person::getAge));
System.out.println(ava);
}
1.4 对流中数据做分组操作
当我们使用Stream流处理数据后,可以根据某个属性将数据分组:
/**
* @Author Administrator
* @Date 2023/6/30 15:54
* @description
* @Version 1.0
*/
public class test04 {
@Test
public void test01() {
/**
* 单级分组
*/
Map<Integer, List<Person>> collect = Stream.of(
new Person("王也", 18),
new Person("张楚岚", 13),
new Person("冯宝宝", 108),
new Person("诸葛青", 15)
).collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Person::getAge));
collect.forEach((k,v)-> System.out.println(k+"\t"+v));
/**
* 多级分组,先根据名字分组,随后根据年龄分组
*/
Map<Integer, Map<String, List<Person>>> collect1 = Stream.of(
new Person("王也", 18),
new Person("张楚岚", 13),
new Person("冯宝宝", 108),
new Person("王也", 22),
new Person("诸葛青", 13),
new Person("诸葛青", 14),
new Person("诸葛青", 19)
).collect(Collectors.groupingBy(
Person::getAge,
Collectors.groupingBy(p -> p.getAge() > 18 ? "成年" : "未成年")
));
collect1.forEach((k,v)->{
System.out.println(k);
v.forEach((k1,v1)->{
System.out.println("\t"+k1+"\t"+v1);
});
});
}
}
结果:
18 [Person{name='王也', age=18, high=null}]
108 [Person{name='冯宝宝', age=108, high=null}]
13 [Person{name='张楚岚', age=13, high=null}]
15 [Person{name='诸葛青', age=15, high=null}]
18
未成年 [Person{name='王也', age=18, high=null}]
19
成年 [Person{name='诸葛青', age=19, high=null}]
22
成年 [Person{name='王也', age=22, high=null}]
108
成年 [Person{name='冯宝宝', age=108, high=null}]
13
未成年 [Person{name='张楚岚', age=13, high=null}, Person{name='诸葛青', age=13, high=null}]
14
未成年 [Person{name='诸葛青', age=14, high=null}]
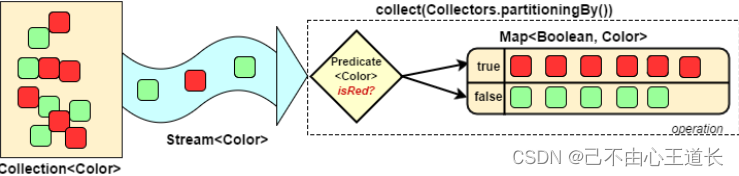
1.5 对流中的数据做分区操作
Collectors.partitioningBy会根据值是否为true,把集合中的数据分割为两个列表,一个true列表,一个false列表:
/**
* @Author Administrator
* @Date 2023/6/30 15:54
* @description
* @Version 1.0
*/
public class test05 {
@Test
public void test01(){
Map<Boolean, List<Person>> collect = Stream.of(
new Person("王也", 18),
new Person("张楚岚", 13),
new Person("冯宝宝", 108),
new Person("王也", 22),
new Person("诸葛青", 13),
new Person("诸葛青", 14),
new Person("诸葛青", 19)
).collect(Collectors.partitioningBy(p -> p.getAge() > 18));
collect.forEach((k,v)->{
System.out.println(k);
System.out.println(v);
});
}
}
结果:
false
[Person{name='王也', age=18, high=null}, Person{name='张楚岚', age=13, high=null}, Person{name='诸葛青', age=13, high=null}, Person{name='诸葛青', age=14, high=null}]
true
[Person{name='冯宝宝', age=108, high=null}, Person{name='王也', age=22, high=null}, Person{name='诸葛青', age=19, high=null}]
1.6 对流中的数据做拼接
Collectors.joining会根据指定的连接符,将所有的元素连接成一个字符串:
/**
* @Author Administrator
* @Date 2023/6/30 15:54
* @description
* @Version 1.0
*/
public class test06 {
@Test
public void test01(){
String collect = Stream.of(
new Person("王也", 18),
new Person("张楚岚", 13),
new Person("冯宝宝", 108),
new Person("王也", 22),
new Person("诸葛青", 13),
new Person("诸葛青", 14),
new Person("诸葛青", 19)
).map(Person::getName)
.collect(Collectors.joining());
System.out.println(collect);
String collect1 = Stream.of(
new Person("王也", 18),
new Person("张楚岚", 13),
new Person("冯宝宝", 108),
new Person("王也", 22),
new Person("诸葛青", 13),
new Person("诸葛青", 14),
new Person("诸葛青", 19)
).map(Person::getName)
.collect(Collectors.joining("_"));
System.out.println(collect1);
String collect2 = Stream.of(
new Person("王也", 18),
new Person("张楚岚", 13),
new Person("冯宝宝", 108),
new Person("王也", 22),
new Person("诸葛青", 13),
new Person("诸葛青", 14),
new Person("诸葛青", 19)
).map(Person::getName)
.collect(Collectors.joining("_","aaa","zzz"));
System.out.println(collect2);
}
结果:
王也张楚岚冯宝宝王也诸葛青诸葛青诸葛青
王也_张楚岚_冯宝宝_王也_诸葛青_诸葛青_诸葛青
aaa王也_张楚岚_冯宝宝_王也_诸葛青_诸葛青_诸葛青zzz
二、并行的Stream流
2.1 串行的Stream流
我们前面使用的Stream流都是串行,也就是在一个线程上面执行。
/**
* @Author Administrator
* @Date 2023/6/30 15:23
* @description Stream结果集收集测试
* @Version 1.0
*/
public class test07 {
@Test
public void test01(){
long count = Stream.of(1, 2, 3, 8, 9, 7, 5, 6, 2, 8, 4, 10)
.filter(s -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + "" + s);
return s > 3;
}).count();
System.out.println(count);
}
}
输出:
Thread[main,5,main]1
Thread[main,5,main]2
Thread[main,5,main]3
Thread[main,5,main]8
Thread[main,5,main]9
Thread[main,5,main]7
Thread[main,5,main]5
Thread[main,5,main]6
Thread[main,5,main]2
Thread[main,5,main]8
Thread[main,5,main]4
Thread[main,5,main]10
2.2 并行流
parallelStream其实就是一个并行执行的流,它通过默认的ForkJoinPool,可以提高多线程任务的速
度。
2.2.1获取并行流
我们可以通过两种方式来获取并行流。
- 通过List接口中的parallelStream方法来获取
- 通过已有的串行流转换为并行流(parallel)
实现:
/**
* 测试获取两种并行流的方法
*/
@Test
public void test02(){
//方式一、通过List集合获取
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
//获取并行流
Stream<String> stream = list.parallelStream();
//方式二、通过已有的串行流转换为并行流
Stream<Integer> parallel = Stream.of(1, 2, 3, 4).parallel();
}
2.2.2 并行流操作
/**
* 并行流操作
*/
@Test
public void test03(){
long count = Stream.of(1, 5, 6, 8, 9, 7, 10)
.parallel()
.filter(s -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + "" + s);
return s > 3;
}).count();
}
效果:
Thread[main,5,main]9
Thread[main,5,main]8
Thread[main,5,main]10
Thread[main,5,main]7
Thread[ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-1,5,main]5
Thread[ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-1,5,main]6
Thread[ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-2,5,main]1
2.3 串行流与并行流对比
我们通过for循环,串行Stream流,并行Stream流来对10亿个数字求和。看看消耗时间对比:
package com.daozhang;
import org.junit.After;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.util.stream.LongStream;
import java.util.stream.Stream;
/**
* @Author Administrator
* @Date 2023/6/30 19:05
* @description
* @Version 1.0
*/
public class test08 {
private static long times = 1000000000;
private long startTimes;
private long endTimes;
@Before
public void before(){
startTimes = System.currentTimeMillis();
}
@After
public void after(){
endTimes =System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(endTimes-startTimes);
}
/**
* 普通for循环
*/
@Test
public void forTest(){
long res = 0;
for(int i=0;i<times;i++){
res+=i;
}
}
//消耗时间:380
/**
* 串行流
*/
@Test
public void test02(){
System.out.println("串行流");
LongStream.rangeClosed(0,times)
.reduce(0,Long::sum);
}
//消耗时间:429
/**
* 并行流
*/
@Test
public void test03(){
System.out.println("并行流");
LongStream.rangeClosed(0,times)
.parallel()
.reduce(0,Long::sum);
}
//消耗时间:198
}
通过案例我们可以看到parallelStream的效率是最高的。
Stream并行处理的过程会分而治之,也就是将一个大的任务切分成了多个小任务,这表示每个任务都是
一个线程操作。
2.4 线程安全问题
在多线程的处理下,肯定会出现数据安全问题。如下:
package com.daozhang;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @Author Administrator
* @Date 2023/6/30 19:18
* @description
* @Version 1.0
*/
public class test09 {
@Test
public void test01(){
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i=0;i<1000;i++){
list.add(i);
}
System.out.println(list.size());
List<Integer> listnew = new ArrayList<>();
list.parallelStream()
.forEach(listnew::add);
System.out.println(listnew.size());
}
}
报错异常:
java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException: 366
at java.util.ArrayList.add(ArrayList.java:459)
at java.util.stream.ForEachOps$ForEachOp$OfRef.accept(ForEachOps.java:184)
at java.util.ArrayList$ArrayListSpliterator.forEachRemaining(ArrayList.java:1374)
at java.util.stream.AbstractPipeline.copyInto(AbstractPipeline.java:481)
at java.util.stream.ForEachOps$ForEachTask.compute(ForEachOps.java:291)
at java.util.concurrent.CountedCompleter.exec(CountedCompleter.java:731)
at java.util.concurrent.ForkJoinTask.doExec(ForkJoinTask.java:289)
at java.util.concurrent.ForkJoinPool.helpComplete(ForkJoinPool.java:1870)
at java.util.concurrent.ForkJoinPool.externalHelpComplete(ForkJoinPool.java:2467)
at java.util.concurrent.ForkJoinTask.externalAwaitDone(ForkJoinTask.java:324)
at java.util.concurrent.ForkJoinTask.doInvoke(ForkJoinTask.java:405)
at java.util.concurrent.ForkJoinTask.invoke(ForkJoinTask.java:734)
at java.util.stream.ForEachOps$ForEachOp.evaluateParallel(ForEachOps.java:160)
at java.util.stream.ForEachOps$ForEachOp$OfRef.evaluateParallel(ForEachOps.java:174)
at java.util.stream.AbstractPipeline.evaluate(AbstractPipeline.java:233)
at java.util.stream.ReferencePipeline.forEach(ReferencePipeline.java:418)
at java.util.stream.ReferencePipeline$Head.forEach(ReferencePipeline.java:583)
at com.daozhang.test09.test01(test09.java:24)
at sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke0(Native Method)
at sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(NativeMethodAccessorImpl.java:62)
at sun.reflect.DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.java:43)
at java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke(Method.java:498)
at org.junit.runners.model.FrameworkMethod$1.runReflectiveCall(FrameworkMethod.java:50)
at org.junit.internal.runners.model.ReflectiveCallable.run(ReflectiveCallable.java:12)
at org.junit.runners.model.FrameworkMethod.invokeExplosively(FrameworkMethod.java:47)
at org.junit.internal.runners.statements.InvokeMethod.evaluate(InvokeMethod.java:17)
at org.junit.runners.ParentRunner.runLeaf(ParentRunner.java:325)
at org.junit.runners.BlockJUnit4ClassRunner.runChild(BlockJUnit4ClassRunner.java:78)
at org.junit.runners.BlockJUnit4ClassRunner.runChild(BlockJUnit4ClassRunner.java:57)
at org.junit.runners.ParentRunner$3.run(ParentRunner.java:290)
at org.junit.runners.ParentRunner$1.schedule(ParentRunner.java:71)
at org.junit.runners.ParentRunner.runChildren(ParentRunner.java:288)
at org.junit.runners.ParentRunner.access$000(ParentRunner.java:58)
at org.junit.runners.ParentRunner$2.evaluate(ParentRunner.java:268)
at org.junit.runners.ParentRunner.run(ParentRunner.java:363)
at org.junit.runner.JUnitCore.run(JUnitCore.java:137)
at com.intellij.junit4.JUnit4IdeaTestRunner.startRunnerWithArgs(JUnit4IdeaTestRunner.java:69)
at com.intellij.rt.junit.IdeaTestRunner$Repeater$1.execute(IdeaTestRunner.java:38)
at com.intellij.rt.execution.junit.TestsRepeater.repeat(TestsRepeater.java:11)
at com.intellij.rt.junit.IdeaTestRunner$Repeater.startRunnerWithArgs(IdeaTestRunner.java:35)
at com.intellij.rt.junit.JUnitStarter.prepareStreamsAndStart(JUnitStarter.java:235)
at com.intellij.rt.junit.JUnitStarter.main(JUnitStarter.java:54)
针对这个问题,我们的解决方案有哪些呢?
- 加同步锁
- 使用线程安全的容器
- 通过Stream中的toArray/collect操作
package com.daozhang;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Vector;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
import java.util.stream.IntStream;
/**
* @Author Administrator
* @Date 2023/6/30 19:25
* @description 解决并行流安全问题
* @Version 1.0
*/
public class test10 {
/**
* 加线程同步锁
*/
@Test
public void test01(){
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
Object obj = new Object();
IntStream.rangeClosed(0,1000)
.parallel()
.forEach(s->{
synchronized (obj){
list.add(s);
}
});
System.out.println(list.size());
}
/**
* 使用线程安全的容器
*/
@Test
public void test02(){
Vector v = new Vector();
Object obj = new Object();
IntStream.rangeClosed(0,1000)
.forEach(s->{
synchronized (obj){
v.add(s);
}
});
System.out.println(v.size());
}
/**
* 将线程不安全的容器转换为线程安全的容器
*/
@Test
public void test03(){
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
//转换
List<Integer> list1 = Collections.synchronizedList(list);
IntStream.rangeClosed(0,1000)
.parallel()
.forEach(s->{
list1.add(s);
});
System.out.println(list1.size());
}
}