SpringBoot实用开发篇
第三方属性bean绑定
@ConfigurationProperties
使用@ConfigurationProperties为第三方bean绑定属性
配置文件
datasource:
driverClassName: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
servers:
ipAddress: 192.168.0.1
port: 80
timeout: -1
ServerConfig类:
@Data
//@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "servers")
public class ServerConfig {
private String ipAddress;
private int port;
private long timeout;
}
SpringBoot启动类文件中
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableConfigurationProperties(ServerConfig.class)
public class DemoApplication {
@Bean
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "datasource")
public DruidDataSource dataSource() {
DruidDataSource ds = new DruidDataSource();
return ds;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ConfigurableApplicationContext ctx = SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication.class);
ServerConfig bean = ctx.getBean(ServerConfig.class);
System.out.println(bean);
DruidDataSource bean1 = ctx.getBean(DruidDataSource.class);
System.out.println(bean1.getDriverClassName());
}
}
注意:@EnableConfigurationProperties与@Component不能同时使用
解除使用@ConfigurationProperties注释警告
在pom.xml中添加
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId>
</dependency>
宽松绑定
@ConfigurationProperties绑定属性支持属性名宽松绑定
注意:宽松绑定不支持注解@Value引用单个属性的方式
常用计量单位应用
SpringBoot支持JDK8提供的时间与空间计量单位
ServerConfig类:
@Data
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "servers")
public class ServerConfig {
private String ipAddress;
private int port;
private long timeout;
@DurationUnit(ChronoUnit.MINUTES)
private Duration serverTimeOut;
@DataSizeUnit(DataUnit.MEGABYTES)
private DataSize dataSize;
}
application.yml
datasource:
driverClassName: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
servers:
timeout: -1
ipAddress: 192.168.0.1
port: 80
serverTimeOut: 3
dataSize: 10
bean属性校验
使用@Validated注解启用校验功能
首先在pom文件中添加依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.validation</groupId>
<artifactId>validation-api</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.hibernate</groupId>
<artifactId>hibernate-validator</artifactId>
<version>5.2.4.Final</version>
</dependency>
ServerConfig类文件
@Data
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "servers")
@Validated
public class ServerConfig {
private String ipAddress;
@Max(value = 8888, message = "最大值不能超过8888")
@Min(value = 202, message = "最小值不能低于202")
private int port;
private long timeout;
@DurationUnit(ChronoUnit.MINUTES)
private Duration serverTimeOut;
@DataSizeUnit(DataUnit.MEGABYTES)
private DataSize dataSize;
}
进制数据转换规则
yml文件中:
datasource:
driverClassName: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
password1: 0123
password: "0123"
测试类:
@SpringBootTest
public class TestYml {
@Value("${datasource.password1}")
private String password1;
@Value("${datasource.password}")
private String password;
@Test
void contextLoads() {
System.out.println(password1);
System.out.println(password);
}
}
测试
加载测试专用属性
在启动测试环境时可以通过properties和args参数设置测试环境专用的属性
// properties属性可以为当前测试用例添加临时的属性配置
//@SpringBootTest(properties = {"test.prop=testValue1"})
// args属性可以为当前测试用例添加临时的命令行参数
//@SpringBootTest(args = {"--test.prop=testValue2"})
// properties属性的优先级比args的优先级高
@SpringBootTest( args = {"--test.prop=testValue2"}, properties = "test.prop=testValue1")
public class TestYml {
@Value("${test.prop}")
private String msg;
@Test
void testProperties() {
System.out.println(msg);
}
}
优势:比多环境开发中的测试环境影响范围更小,仅对当前测试类有效
加载测试专用配置
使用@Import注解加载当前测试类专用的配置
MsgConfig类
@Configuration
public class MsgConfig {
@Bean
public String msg() {
return "bean msg";
}
}
TestCon测试类
@SpringBootTest
@Import(MsgConfig.class)
public class TestCon {
@Autowired
private String msg;
@Test
void testConfig() {
System.out.println(msg);
}
}
在测试类启动web环境
模拟端口
@SpringBootTest(webEnvironment = SpringBootTest.WebEnvironment.DEFINED_PORT)
public class TestWeb {
@Test
void test() {
}
}
虚拟请求测试
BookController类:
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/book")
public class BookController {
@GetMapping
public String getById() {
System.out.println("getById is running .....");
return "springboot";
}
}
测试类:
@SpringBootTest(webEnvironment = SpringBootTest.WebEnvironment.DEFINED_PORT)
// 开启虚拟MVC调用
@AutoConfigureMockMvc
public class TestWeb {
@Test
// 注入虚拟MVC调用对象
void testWeb(@Autowired MockMvc mvc) throws Exception {
// 创建虚拟请求,当前访问路径为/book
MockHttpServletRequestBuilder builder = MockMvcRequestBuilders.get("/book");
// 执行相应的请求
mvc.perform(builder);
}
}
虚拟请求状态匹配
void testWeb(@Autowired MockMvc mvc) throws Exception {
MockHttpServletRequestBuilder builder = MockMvcRequestBuilders.get("/booka");
// 执行相应的请求
ResultActions action = mvc.perform(builder);
// 设定预期值 与真实值进行比较, 成功测试通过 失败测试失败
// 定义本次调用的预期值
StatusResultMatchers status = MockMvcResultMatchers.status();
// 创建虚拟请求,当前访问路径为/book
// 预期本次调用是成功的,返回的字节码为200
ResultMatcher ok = status.isOk();
// 添加预期值到本次调用过程中进行匹配
action.andExpect(ok);
}
虚拟请求体匹配
@Test
void testBody(@Autowired MockMvc mvc) throws Exception {
MockHttpServletRequestBuilder builder = MockMvcRequestBuilders.get("/book");
// 执行相应的请求
ResultActions action = mvc.perform(builder);
// 设定预期值 与真实值进行比较, 成功测试通过 失败测试失败
// 定义本次调用的预期值
ContentResultMatchers content = MockMvcResultMatchers.content();
ResultMatcher result = content.string("springboot");
// 添加预期值到本次调用过程中进行匹配
action.andExpect(result);
}
虚拟匹配请求体(json)
虚拟请求体(json)匹配
BookController
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/book")
public class BookController {
@GetMapping
public String getById() {
System.out.println("getById is running .....");
return "{\"id\":1,\"name\":\"zhanshan\",\"age\":21}";
}
}
测试类:
@Test
void testJson(@Autowired MockMvc mvc) throws Exception {
MockHttpServletRequestBuilder builder = MockMvcRequestBuilders.get("/book");
// 执行相应的请求
ResultActions action = mvc.perform(builder);
// 设定预期值 与真实值进行比较, 成功测试通过 失败测试失败
// 定义本次调用的预期值
ContentResultMatchers content = MockMvcResultMatchers.content();
ResultMatcher result = content.json("{\"id\":1,\"name\":\"zhanshan\",\"age\":21}");
// 添加预期值到本次调用过程中进行匹配
action.andExpect(result);
}
匹配json值是否相等,如果相等,正常输出,如果不匹配,则失败
匹配响应头
虚拟请求头匹配
测试类:
@Test
void testWeb(@Autowired MockMvc mvc) throws Exception {
MockHttpServletRequestBuilder builder = MockMvcRequestBuilders.get("/book");
// 执行相应的请求
ResultActions action = mvc.perform(builder);
// 设定预期值 与真实值进行比较, 成功测试通过 失败测试失败
// 定义本次调用的预期值
HeaderResultMatchers content = MockMvcResultMatchers.header();
ResultMatcher contentType = content.string("Content-Type", "text/plain;charset=UTF-8");
// 添加预期值到本次调用过程中进行匹配
action.andExpect(contentType);
}
数据层测试事务回滚
测试类:
@SpringBootTest
@Transactional
//@Rollback(value = false)
public class TestTran {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@Test
void testSave() {
User user = new User();
user.setName("小小");
user.setAge(20);
userService.save(user);
}
}
当加上@Transaction运行时,结果:
当加上@Transaction和@Rollback(false)运行,结果:

为了测试用例添加事务,加上@Transactional,SpringBoot会对测试用例对应的事务提交操作进行回滚们也就是说springBoot会意识到这是个测试,不会进行提交事务但是会占用id,数据库中不会真的插入。
但是如果想要在测试用例中提交事务,可以通过@Rollback(false),这样事务不会回滚。@Rallback注解默认值是true,如果是false就不会回滚,测试数据就可以在数据库中显示
测试用例数据通常采用随机值进行测试,使用SpringBoot提供的随机数为其赋值
配置文件:
testcase:
book:
id: ${random.int} #随机整数
id2: ${random.int(10)} #10以内随机数
type: ${random.int(5,10)} #5到10随机数
name: ${random.value} #随机字符串,MD5字符串,32位
uuid: ${random.uuid} #随机uuid
publishTime: ${random.long} #随机整数(long范围)
说明:
- ${random.int}表示随机整数
- ${random.int(10)}表示10以内的随机数
- ${random.int(10,20)}表示10到20的随机数
- 其中()可以是任意字符,例如[],!!均可
定义一个类:
@Component
@Data
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "testcase.book")
public class BookCase {
private int id;
private int id2;
private int type;
private String uuid;
private String name;
private long publishTime;
}
测试类输出:
@SpringBootTest( args = {"--test.prop=testValue2"}, properties = "test.prop=testValue1")
public class TestYml {
@Value("${test.prop}")
private String msg;
@Autowired
private BookCase bookCase;
@Test
void testProperties() {
System.out.println(msg);
System.out.println(bookCase);
}
}
数据层解决方案
现有数据层解决方案技术选型
Druid + MyBatis-Plus + MySQL
- 数据源:DruidDataSource
- 持久化技术:MyBatis-Plus / MyBatis
- 数据库:MySQL
数据源配置格式:
格式一:
spring:
datasource:
druid:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test
username: root
password: root
格式二:
spring:
datasource:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test
username: root
password: root
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
SpringBoot提供了3种内嵌的数据源对象供开发者选择
- HikariCP:默认内置数据源对象
- Tomcat提供DataSource:HikariCP不可用的情况下,且在Web环境中,将使用tomcat服务器配置的数据源对象
- Commons DBCP:HikariCP不可用,tomcat数据源也不可用,将使用dbcp数据源
解决方案:JdbcTemplate
跳转:JdbcTemplate_没办法,我就是这么菜的博客-CSDN博客
SpringBoot配置:
依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jdbc</artifactId>
</dependency>
配置:
spring:
jdbc:
template:
query-timeout: -1 #查询超过时间
max-rows: 500 #最大行数
fetch-size: -1 # 批处理量
NOSQL
Redis
Redis是一款key-value存储结构的内存级NoSQL数据库
- 支持多种数据存储格式
- 支持持久化
- 支持集群
Redis安装与启动(window版)
-
windows解压安装或一键式安装
-
服务端启动命令
redis-server.exe redis.windows.conf -
客户端启动命令
redis-cli.exe
安装过程:Redis安装_没办法,我就是这么菜的博客-CSDN博客
SpringBoot整合Redis(默认是lettuce)
填入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
application.yml
spring:
redis:
host: 127.0.0.1
port: 6379
客户端测试类:
@SpringBootTest
class RedisApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
@Test
void set() {
ValueOperations ops = redisTemplate.opsForValue();
ops.set("age", 41);
}
@Test
void get() {
ValueOperations ops = redisTemplate.opsForValue();
Object age = ops.get("age");
System.out.println(age);
}
@Test
void hset() {
HashOperations hops = redisTemplate.opsForHash();
hops.put("info", "a", "aa");
}
@Test
void hget() {
HashOperations hops = redisTemplate.opsForHash();
Object o = hops.get("info", "a");
System.out.println(o);
}
}
客户端:StringRedisTemplate以字符串作为key和value,与redis客户端操作等效
@SpringBootTest
public class StringRedisTemplateTest {
@Autowired
private StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate;
@Test
void get() {
ValueOperations<String, String> ops = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue();
String name = ops.get("name");
System.out.println(name);
}
}
客户端选择:jedis
<dependency>
<groupId>redis.clients</groupId>
<artifactId>jedis</artifactId>
</dependency>
配置客户端
spring:
redis:
host: localhost #127.0.0.1
port: 6379
client-type: jedis
jedis:
pool:
max-active: 10
配置客户端专用属性
spring:
redis:
host: localhost
port: 6379
client-type: lettuce:
jedis:
pool:
max-active: 10
lettuce:
pool:
max-active: 16
注意:
lettuce与jedis区别
- jedis连接Redis服务器是直连模式,当多线程模式下使用jedis会存在线程安全问题,解决方案可以通过配置连接池使每个连接专用,这样整体性能就大受影响
- lettuce基于Netty框架进行与Redis服务器连接,底层设计中采用StatefulRedisConnection。StatefulRedisConnection自身是线程安全的,可以保障并发访问安全问题,所以一个连接可以被多个线程复用,当然lettuce也支持多连接实例一起工作
MongoDB
MongDB是一个开源、高性能、无模式的文档型数据库。NoSQL数据库产品中的一种,是最像关系型数据库的非关系型数据库
示例:
-
淘宝用户数据
-
存储位置:数据库
-
特征:永久性存储,修改频度极低
-
-
游戏装备数据、游戏道具数据
- 存储位置:数据库、MongoDB
- 特征:永久性存储与临时存储相结合、修改频度较高
-
直播数据、打赏数据、粉丝数据
- 存储位置:数据库、MongoDB
- 特征:永久性存储与临时存储相结合,修改频度极高
-
物联网数据
- 存储数据:MongoDB
- 特征:临时存储、修改频度飞速
window版Mongo启动
-
服务端启动
mongod --dbpath=..\data\db -
客户端启动
mongo --host=127.0.0.1 --port=27017
安装地址:
MongoDB安装_没办法,我就是这么菜的博客-CSDN博客
SpringBoot整合MongoDB
添加依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-mongodb</artifactId>
</dependency>
配置文件
spring:
data:
mongodb:
uri: mongodb://localhost/test
测试类:
@SpringBootTest
class DemoApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private MongoTemplate mongoTemplate;
@Test
void contextLoads() {
Book book = new Book();
book.setId(1);
book.setName("springboot");
book.setType("springboot");
book.setDescription("springboot");
mongoTemplate.save(book);
}
@Test
void find(){
List<Book> all = mongoTemplate.findAll(Book.class);
System.out.println(all);
}
}
Elasticsearch(ES)
Elasticsearch是一个分布式全文搜索引擎
相关概念:
- 倒排索引:根据关键字查找id,在由id查找部分信息
- 创建文档:用于存储一条数据,每一条数据就是一个文档
- 使用文档:根据关键字找到相关信息
下载与安装:
ES(Elasticsearch)和Kibana(Windows)安装_没办法,我就是这么菜的博客-CSDN博客
安装分词器IK
可以傻瓜式安装:
打开es文件夹中的bin,然后打开命令行,输入如下代码(我安装的es是7.6.2版本的):
./elasticsearch-plugin install https://github.com/medcl/elasticsearch-analysis-ik/releases/download/v7.6.2/elasticsearch-analysis-ik-7.6.2.zip
注意:要保持上诉代码中两个版本号要一致
最后重新启动es,不报错就说明安装成功了。
使用
创建索引并指定规则
{
"mappings":{
"properties":{
"id":{
"type":"keyword"
},
"name":{
"type":"text",
"analyzer":"ik_max_word",
"copy_to":"all"
},
"type":{
"type":"keyword"
},
"description":{
"type":"text",
"analyzer":"ik_max_word",
"copy_to":"all"
},
"all":{
"type":"text",
"analyzer":"ik_max_word"
}
}
}
}
创建/查询/删除索引
PUT http://localhost:9200/books
GET http://localhost:9200/books
DELETE http://localhost:9200/books
结果:
创建:
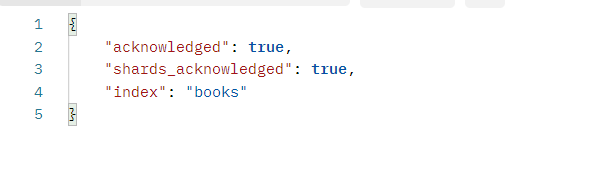
删除:

创建文档
POST http://localhost:9200/books/_doc #使用系统生成id
POST http://localhost:9200/books/_create/1 #使用指定id
POST http://localhost:9200/books/_doc/1 #使用指定id
{
"name": "springboot",
"type": "springboot",
"description": "springboot"
}
查询文档:
GET http://localhost:9200/books/_doc/1 #查询单个文档
GET http://localhost:9200/books/_search #查询全部文档
条件查询:
GET http://localhost:9200/books/_search?q=name:springboot
删除文档:
DELETE http://localhost:9200/books/_doc/1
修改文档(全量修改)
PUT http://localhost:9200/books/_doc/1
{
"name": "springboot",
"type": "springboot",
"description": "springboot"
}
部分修改:
POST http://localhost:9200/books/_update/1
{
"doc":{
"name":"springboot"
}
}
SpringBoot整合ES
导入坐标
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-elasticsearch</artifactId>
</dependency>
配置:
spring:
datasource:
druid:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url: mysql:jdbc://localhost:3306/dctest
username: root
password: root
elasticsearch:
rest:
uris: http://localhost:9200
mybatis:
configuration:
log-impl: org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImpl
客户端:
@Autowired
private ElasticsearchRestTemplate template;
void fn(){
Book books = template.get("books", Book.class);
System.out.println(books);
}
SpringBoot平台并没有跟随ES的更新速度进行同步更新,ES提供了High Level Client操作ES
导入坐标:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.elasticsearch.client</groupId>
<artifactId>elasticsearch-rest-high-level-client</artifactId>
</dependency>
客户端:
private RestHighLevelClient client;
// 修饰在方法上,在每一个测试方法(所有@Test、@RepeatedTest、@ParameterizedTest或者@TestFactory注解的方法)之前执行一次
@BeforeEach
void setUp() {
HttpHost host = HttpHost.create("http://localhost:9200");
RestClientBuilder builder = RestClient.builder(host);
client = new RestHighLevelClient(builder);
}
// 修饰在方法上,在每一个测试方法(所有@Test、@RepeatedTest、@ParameterizedTest或者@TestFactory注解的方法)都执行完毕后执行,每个测试类运行时只会执行一次
@AfterEach
void tearDown() throws IOException {
client.close();
}
@Test
void testCreateIndex() throws IOException {
CreateIndexRequest request = new CreateIndexRequest("books");
client.indices().create(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
}
批量添加文档
/批量添加文档
@Test
void testCreateDocAll() throws IOException {
List<Book> bookList = bookDao.selectList(nul1);BulkRequest bulk = new BulkRequest();
for (Book book : bookList) {
IndexRequest request = new IndexRequest("books").id(book.getId().tostring());
String json = JSON.toJSONString(book);
request.source(json,XContentType.JSON);
bulk.add(request);
}
client.bulk(bulk,RequestOptions .DEFAULT);
}
整合第三方技术
缓存
-
缓存是一种介于数据永久存储介质与数据之间的数据临时存储介质
-
使用缓存可以有效的减少低速数据读取过程的次数(例如磁盘io),提高系统性能
-
缓存不仅可以用于提高永久性存储介质的数据读取效率,还可以提供临时的数据存储空间
SpringBoot提供了缓存技术,方便缓存使用
启用缓存
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boat-starter-cache</artifactId>
</dependency>
设置缓存的方式;
- @EnableCaching
- @Cacheable
生成验证码
SpringBoot提供的缓存技术除了默认的缓存方案,还可以对其他缓存技术进行整合,统一接口,方便缓存技术的开发与管理
案例:手机验证码
需求:
-
输入手机号获取验证码,组织文档以短信形式发送给用户(页面模拟)
-
输入手机号和验证码验证结果
需求分析:
-
提供controller,传入手机号,业务层通过手机号计算出独有的6位验证码数据,存入缓存后返回此数据
-
提供controller,传入手机号与验证码,业务层通过手机号从缓存中读取验证码与输入验证码进行比对,返回比对结果
代码展示:
SMSCode实体类:
@Data
public class SMScode {
// 手机号
private String tele;
// 验证码
private String code;
}
CodeUtils工具类(生成验证码):
@Component
public class CodeUtils {
// 用于补全验证码
private String[] patch = {"000000", "00000", "0000", "000", "00", "0", ""};
// 生成验证码
public String generator(String tele){
int hash = tele.hashCode();
int encryption = 20206666;
long result = hash * encryption;
long nowTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
result = result ^ nowTime;
long code = result % 1000000;
code = code < 0 ? -code : code;
String codeStr = code + "";
int len = codeStr.length();
return patch[len] + codeStr;
}
// 从缓存中获取smsCode对象
@Cacheable(value = "smsCode", key = "#tele")
public String get(String tele) {
return null;
}
}
业务层:
public interface SMSCodeService {
String sendCodeToSMS(String tele);
boolean checkCode(SMScode smScode);
}
@Service
public class SMSCodeServiceImpl implements SMSCodeService{
@Autowired
private CodeUtils codeUtils;
// 将验证码存入缓存中
@Override
@CachePut(value = "smsCode", key = "#tele")
public String sendCodeToSMS(String tele) {
String generator = codeUtils.generator(tele);
return generator;
}
@Override
public boolean checkCode(SMScode smsCode) {
// 取出内存中的验证码与传递过来的验证码比对,如果相同返回true
String code = smsCode.getCode();
String cacheCode = codeUtils.get(smsCode.getTele());
return code.equals(cacheCode);
}
}
控制层:
@RestController
@EnableCaching
@RequestMapping("/sms")
public class SMSController {
@Autowired
private SMSCodeService service;
/**
* 获取验证码
* @param
* @return
*/
@GetMapping
public String getCode(String tele){
String code = service.sendCodeToSMS(tele);
return code;
}
/**
* 检验验证码是否和缓存中的相同
* @param
* @return
*/
@PostMapping
public boolean checkCode(SMScode smScode){
return service.checkCode(smScode);
}
}
缓存供应商变更:Ehcache
缓存设定为使用Ehcache
spring:
datasource:
druid:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url: mysql:jdbc://localhost:3306/dctest
username: root
password: root
cache:
type: ehcache
ehcache:
config: classpath:ehcache.xml
mybatis:
configuration:
log-impl: org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImpl
server:
port: 80
配置文件ehcache.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<ehcache xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:noNamespaceSchemaLocation="http://ehcache.org/ehcache.xsd"
updateCheck="false">
<!-- 默认缓存策略
eternal:是否永久存在,设置为true则不会被清除,此时与timeout冲突,通常设置为false
disPersistrnt:是否启用磁盘持久化
maxElementsInMemory:最大缓存数量
overflowToDisk:超过最大缓存数量是否持久化到磁盘
timeToIdleSesconds:最大不活动间隔,设置过长缓存容易溢出,设置过短无效果,可用于记录时效性数据,录验证码
timeToLiverSeconds:最大存活时间
memoryStoreEvictionPolicy:缓存清除策略
-->
<defaultCache
eternal="false"
diskPersistent="false"
maxElementsInMemory="1000"
overflowToDisk="false"
timeToIdleSeconds="60"
timeToLiveSeconds="60"
memoryStoreEvictionPolicy="LRU"/>
<cache
name="smsCode"
eternal="false"
diskPersistent="false"
maxElementsInMemory="1000"
overflowToDisk="false"
timeToIdleSeconds="60"
timeToLiveSeconds="60"
memoryStoreEvictionPolicy="LRU"/>
</ehcache>
数据淘汰策略(补充):
影响数据淘汰的相关配置
检测易失数据(可能会过期的数据集server.db[i].expires)
- volatile-lru:挑选最近最少使用的数据淘汰
- volatile-lfu:挑选最近使用次数最少的数据淘汰
- volatile-ttl:挑选将要过期的数据淘汰
- volatile-random:任意选择数据淘汰
缓存供应商变更:Redis
加入Redis坐标(缓存供应商实现)
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-redis</artifactId>
<version>1.4.7.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
配置Redis服务器,缓存设定为使用Redis
spring:
cache:
type: redis
redis:
use-key-prefix: false # 是否使用前缀名(系统定义前缀名)
key-prefix: sms #追加自定义前缀名
cache-null-values: false # 是否允许存储空值
time-to-live: 10s #有效时长
redis:
host: 127.0.0.1
port: 6379
mecached
下载与安装mecached
mecached是一个高性能的分布式,基于内存的key-value存储的对象缓存系统(但他并不是一个数据库),用于动态Web应用以减轻数据库负载
下载
首先,windows无官方版本,下载地址:http://static.runoob.com/download/memcached-win64-1.4.4-14.zip
安装
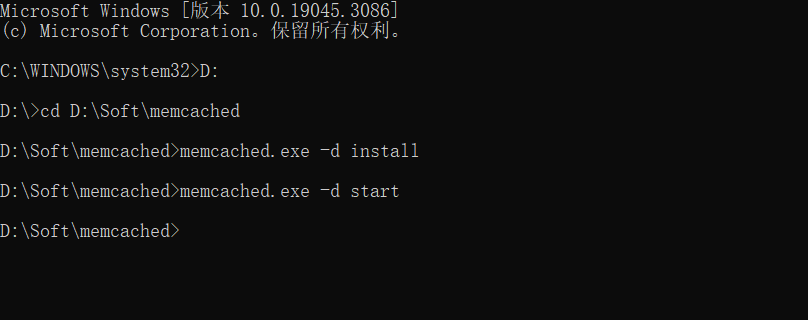
解压下载的安装包,我的安装包路径是:D:\Soft\memcached
以管理员身份进入命令行界面,进入当前包目录下
依次输入如下命令
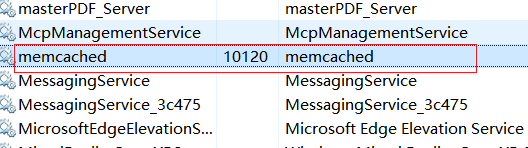
memcached.exe -d install #安装命令
memcached.exe -d start #启动服务
memcached.exe -d stop #停止服务
缓存供应商变更:memcached
memcached客户端选择
- Memcached Client for java:最早期客户端,稳定可靠,用户群广
- SpyMemcached:效率更高
- Xmemcached:并发处理更好
SpringBoot未提供对memcached的整合,需要使用硬编码地方式实现客户端初始化管理
加入Xmemcache坐标(缓存供应商实现)
<dependency>
<groupId>com.googlecode.xmemcached</groupId>
<artifactId>xmemcached</artifactId>
<version>2.4.7</version>
</dependency>
配置memcached服务器必要属性
memcached:
# memcached服务器地址
servers: localhost:11211
# 连接池的数量
poolSize: 10
# 设置默认操作超时
opTimeout: 3000
创建读取属性配置信息类,加载配置
@Component
@Data
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "memcached")
public class XMemcachedProperties {
private String servers;
private int poolSize;
private long opTimeout;
}
创建客户端配置类
@Configuration
public class XMemcachedConfig {
@Autowired
private XMemcachedProperties xMemcachedProperties;
@Bean
public MemcachedClient memcachedClient() throws IOException {
MemcachedClientBuilder memcachedClientBuilder = new XMemcachedClientBuilder(xMemcachedProperties.getServers());
memcachedClientBuilder.setConnectionPoolSize(xMemcachedProperties.getPoolSize());
memcachedClientBuilder.setOpTimeout(xMemcachedProperties.getOpTimeout());
MemcachedClient memcachedClient = memcachedClientBuilder.build();
return memcachedClient;
}
}
配置memcached属性
@Service
public class SMSCodeServiceImpl implements SMSCodeService{
@Autowired
private CodeUtils codeUtils;
@Autowired
private MemcachedClient memcachedClient;
@Override
public String sendCodeToSMS(String tele) {
String code = codeUtils.generator(tele);
try {
memcachedClient.set(tele, 10, code);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return code;
}
@Override
public boolean checkCode(SMScode smScode) {
String code = null;
try {
code = memcachedClient.get(smScode.getTele()).toString();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return smScode.getCode().equals(code);
}
}
jetcache缓存方案
jetCacje对SpringCache进行了封装,在原有功能基础上实现了多级缓存、缓存统计、自动刷新、异步调用、数据报表等功能
jetCache设定了本地缓存与远程缓存的多级缓存解决方案
- 本地缓存(local)
- LinkedHashMap
- Caffeine
- 远程缓存(remote)
- Redis
- Tair
远程缓存方案
导入依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alicp.jetcache</groupId>
<artifactId>jetcache-starter-redis</artifactId>
<version>2.6.2</version>
</dependency>
配置文件application.yml:
spring:
main:
allow-circular-references: true # 配置允许循环依赖
datasource:
druid:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url: mysql:jdbc://localhost:3306/dctest
username: root
password: root
jetcache:
remote:
default:
type: redis
host: localhost
port: 6379
poolConfig:
maxTotal: 50
mybatis:
configuration:
log-impl: org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImpl
server:
port: 80
工具类CodeUtils:
@Component
public class CodeUtils {
// 用于补全验证码
private String[] patch = {"000000", "00000", "0000", "000", "00", "0", ""};
// 生成验证码
public String generator(String tele){
int hash = tele.hashCode();
int encryption = 20206666;
long result = hash * encryption;
long nowTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
result = result ^ nowTime;
long code = result % 1000000;
code = code < 0 ? -code : code;
String codeStr = code + "";
int len = codeStr.length();
return patch[len] + codeStr;
}
// 从缓存中获取smsCode对象
@Cacheable(value = "smsCode", key = "#tele")
public String get(String tele) {
return null;
}
}
SMSCodeServiceImpl:
@Service
public class SMSCodeServiceImpl implements SMSCodeService{
@Autowired
private CodeUtils codeUtils;
@CreateCache(name = "jetCache", expire = 3600, timeUnit = TimeUnit.SECONDS)
private Cache<String, String> jetCache;
@Override
public String sendCodeToSMS(String tele) {
String code = codeUtils.generator(tele);
jetCache.put(tele, code);
return code;
}
@Override
public boolean checkCode(SMScode smScode) {
String code = jetCache.get(smScode.getTele());
return smScode.getCode().equals(code);
}
}
SpringEsApplication:
@SpringBootApplication
// jetcache启用的主开关
@EnableCreateCacheAnnotation
public class SpringEsApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringEsApplication.class, args);
}
}
本地缓存方案
配置文件application.yml:
spring:
main:
allow-circular-references: true # 配置允许循环依赖
datasource:
druid:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url: mysql:jdbc://localhost:3306/dctest
username: root
password: root
jetcache:
local:
default:
type: linkedhashmap
keyConvertor: fastjson
remote:
default:
type: redis
host: localhost
port: 6379
poolConfig:
maxTotal: 50
mybatis:
configuration:
log-impl: org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImpl
server:
port: 80
SMSCodeServiceImpl:
@Service
public class SMSCodeServiceImpl implements SMSCodeService{
@Autowired
private CodeUtils codeUtils;
@CreateCache(name = "jetCache_", expire = 1000, timeUnit = TimeUnit.SECONDS)
private Cache<String, String> jetCache;
@Override
public String sendCodeToSMS(String tele) {
String code = codeUtils.generator(tele);
jetCache.put(tele, code);
return code;
}
@Override
public boolean checkCode(SMScode smScode) {
String code = jetCache.get(smScode.getTele());
return smScode.getCode().equals(code);
}
}
j2cache
j2cache是一个缓存整合框架,可以提供缓存的整合方案,使各种缓存搭配使用,自身不提供缓存功能
基于ehcache + redis进行整合
任务
定时任务是企业级应用中的常见操作
- 年度报表
- 缓存统计报告
- 等等
Quartz
Quartz技术是一个比较成熟的定时任务框架
- 工作(Job):用于定义具体执行的工作
- 工作明细(JobDetail):用于描述定时工作相关的信息
- 触发器(Trigger):描述了工作明细与调度器的对应关系
- 调度器(Scheduler):描述了触发工作的执行规则,通常使用cron表达式定义规则
导入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-quartz</artifactId>
</dependency>
定义任务Bean,按照Quartz的开发规范制作,继承QuartzJobBean
public class MyQuartz extends QuartzJobBean {
@Override
protected void executeInternal(JobExecutionContext context) throws JobExecutionException {
System.out.println("quartz task run...");
}
}
创建Quartz配置类,定义工作明细(JobDetail)与触发器的(Trigger)bean
@Configuration
public class QuartzConfig {
@Bean
public JobDetail printJobDetail(){
//绑定具体的工作
return JobBuilder.newJob(MyQuartz.class).storeDurably().build();
}
@Bean
public Trigger printJobTrigger(){
ScheduleBuilder schedBuilder = CronScheduleBuilder.cronSchedule("0/5 * * * * ?");
//绑定对应的工作明细
return TriggerBuilder.newTrigger().forJob(printJobDetail()).withSchedule(schedBuilder).build();
}
}
工作明细中要设置对应的具体工作,使用newJob()操作传入对应的工作任务类型即可
触发器需要绑定任务,使用forJob()操作传入绑定的工作明细对象。这里可以为工作明细设置名称然后使用名称绑定,也可以直接调用对应方法绑定。触发器中核心的规则是执行时间,这里使用的是调度器定义执行时间,执行时间描述方式使用的是cron表达式。
注意:cron表达式的格式不能乱设置
总结
- SpringBoot整合Quartz就是将Quartz对应的核心对象交给spring容器管理,包含两个对象,JobDetail和Trigger对象
- JobDetail对象描述的是工作的执行信息,需要绑定一个QuartzJobBean类型的对象
- Trigger对象定义了一个触发器,需要为其指定绑定的JobDetail是哪个,同时设置执行周期调度器
Task
spring对Quartz进行了简化,开发了自己的任务管理组件——Task
开启定时任务功能,在引导类上开启定时任务功能的开关,使用注解@EnableScheduling
@SpringBootApplication
/*// 开启定时任务功能
@EnableScheduling*/
public class SpringtaskApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringtaskApplication.class, args);
}
}
定义Bean,在对应要定时执行的操作上方,使用注解@Scheduled定义执行时间,执行时间的描述方式还是cron表达式
@Component
public class MyBean {
@Scheduled(cron = "0/1 * * * * ?")
public void print(){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" :spring task run...");
}
}
配置文件:
spring:
task:
scheduling:
pool:
size: 1 # 任务调度线程池大小 默认 1
thread-name-prefix: ssm_ # 调度线程名称前缀 默认 scheduling-
shutdown:
await-termination: false # 线程池关闭时等待所有任务完成
await-termination-period: 10s # 调度线程关闭前最大等待时间,确保最后一定关闭
总结:
- spring task需要使用注解@EnableScheduling开启定时任务功能
- 为定时执行的任务设置执行周期,描述方式cron表达式
邮件
相关标准
- SMTP(SImple Mail Transfer Protocol):简单邮件传输邮件,用于发送电子邮件的传输协议
- POP3(Post Office Protocol - Version 3):用于接收电子邮件的标准协议
- IMAP(Internet Mail Access Protocol):互联网消息协议,是POP3的替代协议
发送简单邮件
导入SpringBoot整合javamail的starter
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-mail</artifactId>
</dependency>
配置文件
spring:
mail:
host: smtp.QQ.com
username: @QQ.com
password:
注意
password获取需要开启设置中账号服务
开启之后会返回密码。
实现类
package com.dc.service.impl;
import com.dc.service.SendMailService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.mail.SimpleMailMessage;
import org.springframework.mail.javamail.JavaMailSender;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
/**
* -----在希望中绽放,在苦难中坚持------
*
* @author 暮辰
*/
@Service
public class SendMailServiceImpl implements SendMailService {
@Autowired
private JavaMailSender javaMailSender;
// 发送人
private String from = "@QQ.com(韩信)";
// 标题
private String subject = "测试邮件";
//接收人
private String to = "@QQ.com";
// 正文
private String context = "测试邮件正文内容";
@Override
public void sendMail() {
SimpleMailMessage message = new SimpleMailMessage();
message.setFrom(from);
message.setTo(to);
message.setSubject(subject);
message.setText(context);
javaMailSender.send(message);
}
}
结果:

发送多个邮件(附件、复杂正文)
发送简单邮件仅需要提供对应的4个基本信息即可。如果想发送复杂邮件,需要更换邮件对象。使用MimeMessage可以发送特殊邮件
发送网页正文邮件
@Service
public class SendMailServiceImpl2 implements SendMailService {
@Autowired
private JavaMailSender javaMailSender;
// 发送人
private String from = "2629177225@QQ.com(韩信)";
// 接收人
private String to = "2629177225@QQ.com";
// 标题
private String subject = "测试邮件";
// 正文
private String context = "<img src='ABC.JPG'/><a href='https://www.itcast.cn'>点开有惊喜</a>";
@Override
public void sendMail() {
try {
MimeMessage message = javaMailSender.createMimeMessage();
MimeMessageHelper helper = new MimeMessageHelper(message);
helper.setFrom(from + "小甜甜");
helper.setTo(to);
helper.setSubject(subject);
// 设置正文支持html解析
helper.setText(context, true);
javaMailSender.send(message);
} catch (MessagingException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}

发送带有附件的邮件
@Service
public class SendMailServiceImpl3 implements SendMailService {
@Autowired
private JavaMailSender javaMailSender;
// 发送人
private String from = "2629177225@QQ.com(韩信)";
// 接收人
private String to = "2629177225@QQ.com";
// 标题
private String subject = "测试邮件";
// 正文
private String context = "测试邮件正文";
@Override
public void sendMail() {
try {
MimeMessage message = javaMailSender.createMimeMessage();
// 设置支持附件
MimeMessageHelper helper = new MimeMessageHelper(message, true);
helper.setFrom(from);
helper.setTo(to);
helper.setSubject(subject);
// 设置正文支持html解析
helper.setText(context);
// 添加附件
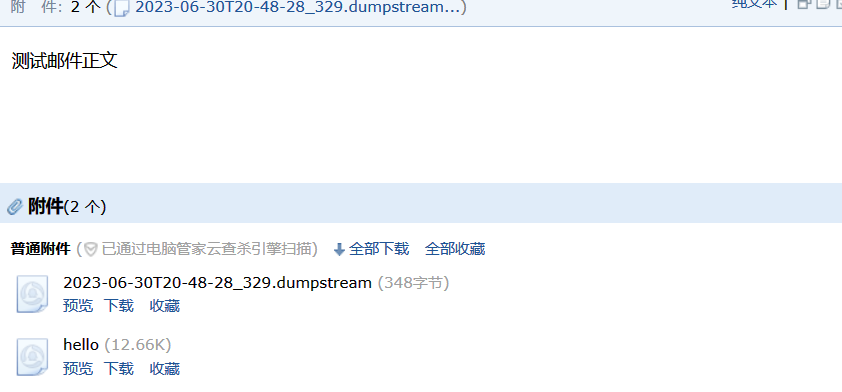
File f1 = new File("D:\\Soft\\IntelliJ IDEA 2022.1.4\\Workspace\\SpringBoot\\springbootemail\\target\\surefire-reports\\2023-06-30T20-48-28_329.dumpstream");
File f2 = new File("D:\\Soft\\IntelliJ IDEA 2022.1.4\\Workspace\\SpringBoot\\springbootemail\\target\\img\\q.jpeg");
helper.addAttachment(f1.getName(), f1);
helper.addAttachment("hello", f2);
javaMailSender.send(message);
} catch (MessagingException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
总结
SpringBoot整合javamail其实就是简化了发送邮件的客户端对象,JavaMailSender的初始化过程,通过配置的形式加载信息简化开发过程
消息
消息的概念
从广义角度来说,消息就是消息,但是和消息又有所不同。信息通常被定义为一组数据,而消息除了具有数据的特征之外,还有消息的来源与接收的概念。通常发哦是那个消息的一方称为消息的生产者,接收消息的一方称为消息的消费者。
为什么要设置生产者和消费者?消息通常就是一组数据,但是消息由于有了生产者和消费者,就出现了消息中所包含的信息可以被二次解读,生产者发送消息,可以理解为生产者发送了一个信息,也可以理解为生产者发送了一个命令;消费者接收消息,可以理解为消费者得到一个信息,也可以理解为消费者得到了一个命令。对比以下,可以发现信息是一个基本数据,而命令则可以关联下一个命令,这样就可以理解为基于接收的消息相当于得到了一个行为动作,使用这些行为动作就可以组织成一个业务逻辑,进行进一步的操作。总的来说,消息其实也是一组信息,只是为其赋予了全新的含义,因为有了消息的流动,并且是有方向性的流动,带来了基于流动的行为产生的全新解读。开发者就可以基于消息的这种特殊解,将其换成代码中的指令。
还可以将消息分为同步消息和异步消息
所谓同步消息就是生产者发送完消息,等待消费者处理,消费者处理完将结果告知生产者,然后生产者继续向上执行业务。这种模式过于卡生产者的业务执行连续性,在现在的企业级开发中,上述这种业务场景通常不会采用消息的形式进行处理
所谓异步消息就是生产者发送完消息,无需等待消费者处完毕,生产者继续向下执行其他动作。比如生产者发送了一个日志消息给日志系统,发送过去以后生产者就向下做其他事情了,无需关注日志系统的执行结果。日志系统根据接收到的日志信息继续进行业务执行,是单纯的记录日志,还是记录日志并报警,这些和生产者无关,这样生产者的业务执行效率就会大幅度提升。并且可以通过添加多个消费者来处理同一个生产者发送的消息类提高系统的高并发性,改善系统工作效率,提高用户体验。一旦某个消费者由于各种问题宕机了,也不会对业务产生影响,提高了系统的高可用性。
Java处理消息的标准规范
目前企业级开发中广泛使用的信息处理技术共三大类,具体如下:
- JMS
- AMQP
- MQTT
JMS
JMS(Java Message Service),这是一个规范,作用等同于JDBC规范,提供了与消息服务相关的API接口
JMS消息模型
JMS规范中规范了消息有两种模型。分别是点对点模型和发布订阅模型
点对点模型:peer-2-peer,生产者会将消息发送到一个保存消息的容器中,通常使用队列模型,使用队列保存消息。一个队列的消息只能被一个消费者消费,会未被及时消费导致超时。这种模型下,生产者和消费者是一对一绑定的。
发布订阅模型:publish-subscribe,生产者将消息发送到一个保存消息的容器中,也是使用队列模型保存。但是消息可以被多个消费者消费,生产者和消费者完全独立,相互不需要感知对方的存在。
JMS消息种类
根据消息中包含的数据种类划分,可以将消息换分成6种消息
- TextMessage
- MapMessage
- BytesMessage
- StreamMessage
- ObjectMessage
- Message(只有消息头和属性)
AMQP
AMQP(Advanced Message Queuing Protocol):一种协议(高级消息队列协议,也是消息代理规范),规范了网络交换的数据格式,兼容JMS操作
优点
具有跨平台性,服务器供应商,生产者,消费者可以使用不同的语言来实现
JMS消息种类
AMQP消息种类:byte[]
AMQP在JMS的消息模型基础上又进行了进一步的扩展,除了点对点和发布订阅的模型,开发了几种全新的消息模型,适应各种各样的消息发送
AMQP消息模型
- direct exchange
- fanout exchanage
- topic exchange
- headers exchange
- system exchange
目前实现了AMQP协议的消息中间件技术也很多,而且都是较为流行的技术,例如:RabbitMQ、StormMQ、RocketMQ
MQTT
MQTT(Message Queueing Telemetry Transport)消息队列遥测传输,专为小设备设计,是物联网(IOT)生态系统中主要成分之一。
KafKa
KafKa,一种高吞吐量的分布式发布订阅消息系统,提供实时消息功能。KafKa技术并不是作为消息中间件为主要功能的产品,但是其拥有发布订阅的工作模式,也可以充当消息中间件来使用,而且目前企业级开发中其身影也不少见。
购物订单发送手机短信案例
手机验证码案例需求如下:
- 执行下单业务时(模拟此过程),调用消息服务,将要发送短信的订单id传递给消息中间件
- 消息处理服务接收到要发送的订单id后输出订单id(模拟发短信)
订单业务
业务层接口
public interface OrderService {
void order(String id);
}
模拟传入订单id,执行下订单业务,参数为虚拟设定,实际应为订单对应的实体类
业务层实现
@Service
public class OrderServiceImpl implements OrderService {
@Autowired
private MessageService messageService;
@Override
public void order(String id) {
// 一系列操作,包含各种服务调用,处理各种业务
System.out.println("订单处理开始");
// 短信消息处理
messageService.sendMessage(id);
System.out.println("订单处理结束");
System.out.println();
}
}
业务层转调短信处理的服务MessageService
表现层服务
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/orders")
public class OrderController {
@Autowired
private OrderService orderService;
@PostMapping("{id}")
public void order(@PathVariable String id){
orderService.order(id);
}
}
表现层对外开发接口传入订单id即可(模拟)
短信处理业务
业务层接口
public interface MessageService {
void sendMessage(String id);
String doMessage();
}
短信处理业务层接口提供两个操作,发送要处理的订单id到消息中间件,另一个操作目前暂且设计成处理消息,实际消息的处理过程不应该是手动执行,应该是自动执行,到具体实现时在进行设计
业务层实现
@Service
public class MessageServiceImpl implements MessageService {
private ArrayList<String> msgList = new ArrayList<String>();
@Override
public void sendMessage(String id) {
System.out.println("待发送的短信的订单已纳入处理队列" + id);
msgList.add(id);
}
@Override
public String doMessage() {
String id = msgList.remove(0);
System.out.println("已完成短信发送业务,id:"+ id);
return id;
}
}
短信处理业务层实现中使用集合先模拟消息队列,观察效果
表现层服务
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/msgs")
public class MessageController {
@Autowired
private MessageService messageService;
@GetMapping
public String doMessage(){
String id = messageService.doMessage();
return id;
}
}
短信处理表现层接口暂且开发出一个处理消息的入口,但是此业务是对应业务层中设计的模拟接口,实际业务不需要设计此接口
SpringBoot整合ActiveMQ
ActiveMQ是MQ产品中的元老级产品,早期标准产品之一,在AMQP协议没有出现之前,占据了消息中间件市场的绝大部分份额,后期因为AMQP系列产品的出现,迅速走弱。目前仅在一些线上运行的产品中出现,新产品开发较少采用
安装
下载地址:ActiveMQ (apache.org)
推荐下载5.16.2版本的
解压后的文件如下
启动服务器
运行bin目录下的win32或win64目录下的(根据自己的操作系统),activemq.bat命令即可,默认对外服务端口为61616
这时可以访问http://127.0.0.1:8161/这个端口打开ActiveMQ的管理界面,如下:
首先输入访问用户名和密码,初始化用户名和密码相同,均为admin,成功登录后进入管理后台界面。
这样视为启动ActiveMQ服务成功
整合
导入整合ActiveMQ的starter
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-activemq</artifactId>
</dependency>
配置ActiveMQ的服务器地址
spring:
activemq:
broker-url: tcp://localhost:61616
使用JmsMessagingTemplate操作ActiveMQ
@Service
public class MessageServiceImpl implements MessageService {
@Autowired
private JmsMessagingTemplate messagingTemplate;
@Override
public void sendMessage(String id) {
System.out.println("待发送短信的订单已纳入处理队列, id:" + id);
messagingTemplate.convertAndSend("order.queue.id" ,id);
}
@Override
public String doMessage() {
String id = messagingTemplate.receiveAndConvert("order.queue.id", String.class);
System.out.println("已完成短信发送业务, id:" + id);
return id;
}
}
发送消息需要先将消息的类型转换成字符串,然后再发送,所以是convertAndSend,定义消息发送的位置,和具体的消息内容,此处使用id作为消息内容
接收消息需要先将消息接收到,然后再转换成指定的数据类型,所以是receiveAndConvert,接收消息除了读取的位置,还要给出转换后的数据的具体类型
使用消息监听器在服务器启动后,监听指定位置,当消息出现后,立即消费消息
@Component
public class MessageListener {
@JmsListener(destination = "order.queue.id")
@SendTo("order.other.queue.id")
public String receive(String id){
System.out.println("已完成短信发送业务,id:"+ id);
return "new" + id;
}
}
使用注解@JmsListener定义当前方法监听ActiveMQ中指定名称的消息队列
如果当前消息队列处理完还需要继续向下传递当前消息到另一个队列中,这时需要使用注解@SendTo即可,这样可以构造连续执行的顺序消息队列
切换消息模型由点对点模型到发布订阅模型,修改jms配置即可
spring:
activemq:
broker-url: tcp://localhost:61616
jms:
pub-sub-domain: true
pub-sub-domain默认值为false,即点对点模型,修改为true后就是发布订阅模型
总结
- SpringBoot整合ActiveMQ提供了JmsMessagingTemplate对象作为客户端操作消息队列
- 操作ActiveMQ需要配置ActiveMQ服务器地址,默认端口61616
- 企业开发时通常使用监听器来处理消息队列中的消息,设置监听器使用注解@JmsListener
- 配置jms的pub-sub-domain属性可以在点对点模型和发布订阅模型间切换消息模型
SpringBoot整合RabbitMQ
RabbitMQ是MQ产品中的目前较为流行的产品之一,它遵从AMQP协议。RabbitMQ的底层实现语言使用的是Erlang,所以安装RabbitMQ需要先安装ErLang
Erlang安装
下载地址:Downloads - Erlang/OTP
一键傻瓜式安装,安装完毕需要重启!!!
安装过程中可能会出现依赖windows组件的提示,根据提示下载安装即可
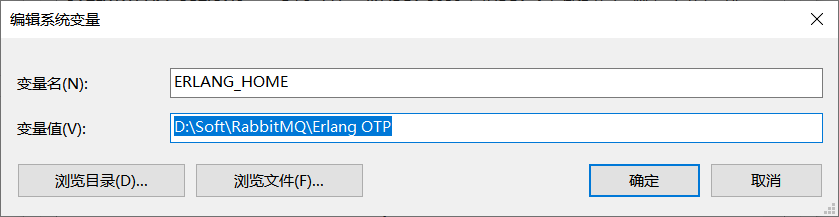
配置:
安装
安装包下载地址:Installing on Windows — RabbitMQ
下载完成后一键傻瓜式安装,安装完毕后会得到如下文件
启动服务器
rabbitmq-service.bat start # 启动服务
rabbitmq-service.bat stop # 停止服务
rabbitmqctl status # 查看服务状态
运行bin目录下的rabbitmq-service.bat命令即可,start参数表示启动,stop参数表示退出,默认对外服务端口5672
注意:启动rabbitmq的过程实际上是开启rabbitmq对应的系统服务,需要管理员权限方可执行
说明:activemq与rabbitmq有端口冲突问题,要确保另一个处于关闭状态
访问web管理服务
RabbitMQ也提供有web控制台服务,但是此功能是一个插件,需要先启用才可以使用
rabbitmq-plugins.bat list # 查看当前所有插件的运行状态
rabbitmq-plugins.bat enable rabbitmq_management # 启动rabbitmq_management插件
启动插件后可以在插件运行状态中查看是否运行,运行后通过浏览器即可打开服务后台管理界面
http://localhost:15672
web管理服务默认端口15672,访问后可以打开RabbitMQ的管理界面,如下:
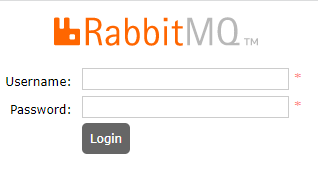
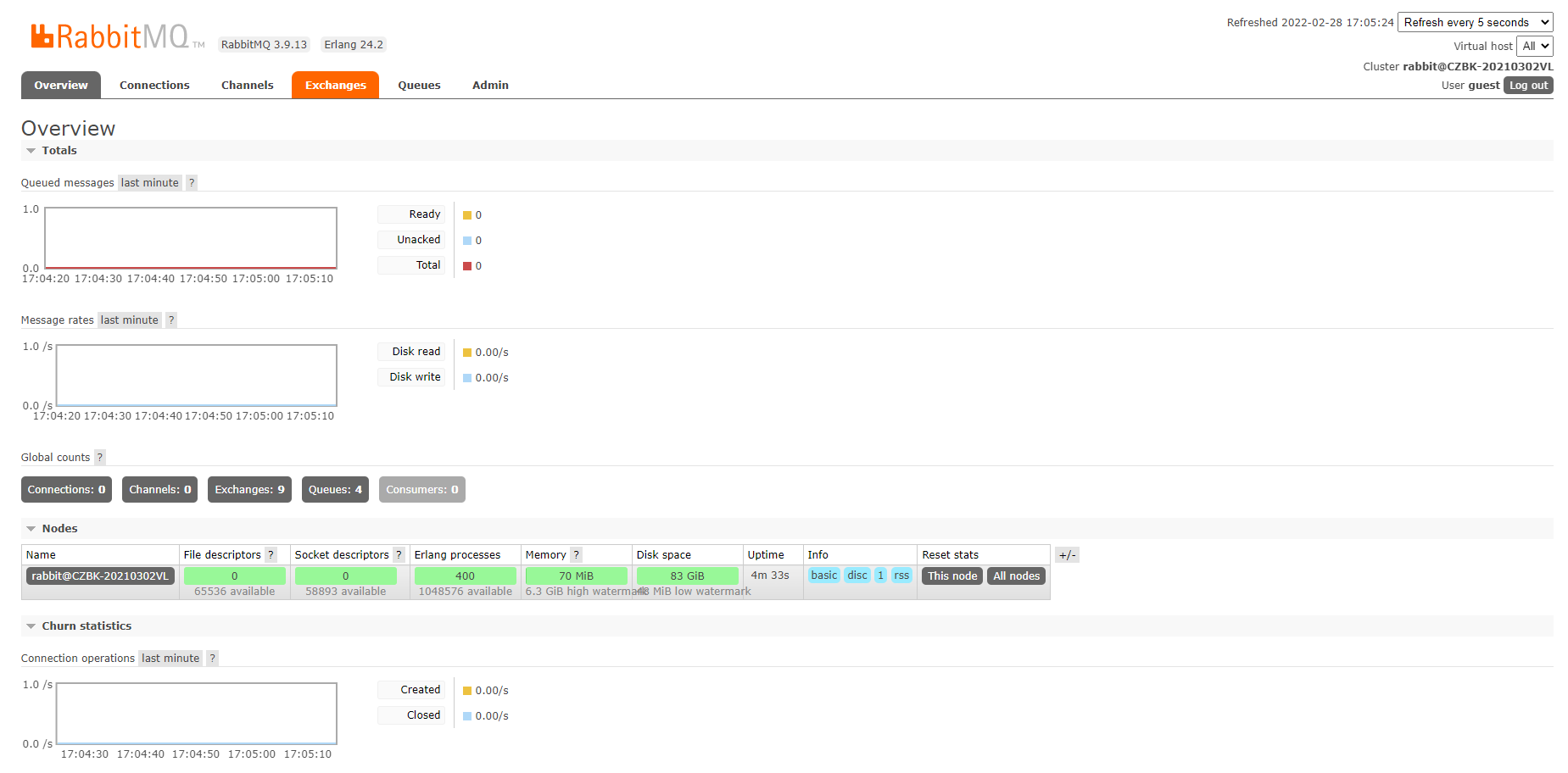
首先输入访问用户名和密码,初始化用户名和密码相同,均为:guest,成功登录后进入管理后台界面,如下:
注意:如果这里在启动的时候出现如下问题
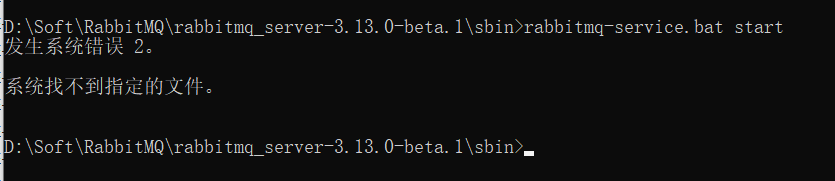
解决:
通过cmd命令行进入rabbit的sbin目录
# 启动rabbitmq_managemen是管理后台的插件、我们要开启这个插件才能通过浏览器访问登录页面
rabbitmq-plugins enable rabbitmq_management
# 启动rabbitmq
rabbitmq-server start
#访问登录页面 用户名和密码都是guest
http://localhost:15672
这样配置之后,就可以成功了
整合(direct模型)
RabbitMQ满足AMQP协议,因此不同的消息模型对应的制作不同,先使用最简单的direct模型开发
导入SpringBoot整合AMQP的starter,AMQP协议默认实现为rabbitMQ方案
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-amqp</artifactId>
</dependency>
配置文件
spring:
activemq:
broker-url: tcp://localhost:61616
jms:
pub-sub-domain: true
template:
default-destination: demo
rabbitmq:
host: localhost
port: 5672
server:
port: 80
初始化直连模式系统设置
由于RabbitMQ不同模型要使用不同的交换机,因此需要先初始化RabbitMQ相关的对象,例如队列,交换机
@Configuration
public class RabbitConfigDirect {
@Bean
public Queue directQueue(){
return new Queue("direct_queue");
}
@Bean
public Queue directQueue2() {
return new Queue("direct_queue2");
}
@Bean
public DirectExchange directExchange() {
return new DirectExchange("directExchange");
}
@Bean
public Binding bindingDirect(){
return BindingBuilder.bind(directQueue()).to(directExchange()).with("direct");
}
@Bean
public Binding bindingDirect2(){
return BindingBuilder.bind(directQueue2()).to(directExchange()).with("direct2");
}
}
队列Queue与直连交换机DirectExchange创建后,还需要绑定他们之间的Bingding,这样就可以通过交换机操作对应队列
使用AmpqTemplate操作RabbitMQ
@Service
public class MessageServiceRabbitmqDirectlImpl implements MessageService {
@Autowired
private AmqpTemplate amqpTemplate;
@Override
public void sendMessage(String id) {
System.out.println("待发送短信的订单已纳入处理队列(rabbitmq direct),id:"+id);
amqpTemplate.convertAndSend("directExchange","direct2",id);
}
}
amqp协议中的操作API接口名称看上去和jms规范的操作API接口很相似,但是传递参数差异很大
使用消息监听器在服务器启动后,监听指定位置,当消息出现后,立即消费消息
@Component
public class MessageAMQListener {
@RabbitListener(queues = "direct_queue")
public void receive(String id){
System.out.println("已完成短信发送业务(rabbitmq direct),id:"+id);
}
}
使用注解@RabbitListener定义当前方法监听RabbitMQ中指定名称的消息队列
整合(topic模型)
前面两个步骤一致
初始化主题模式系统设置
@Configuration
public class RabbitConfigDirect {
@Bean
public Queue topicQueue(){
return new Queue("topic_queue");
}
@Bean
public Queue topicQueue2(){
return new Queue("topic_queue2");
}
@Bean
public TopicExchange topicExchange(){
return new TopicExchange("topicExchange");
}
@Bean
public Binding bindingTopic(){
return BindingBuilder.bind(topicQueue()).to(topicExchange()).with("topic.*.id");
}
@Bean
public Binding bindingTopic2(){
return BindingBuilder.bind(topicQueue2()).to(topicExchange()).with("topic.orders.*");
}
}
主题模式支持routingKey匹配模式,*表示匹配一个单词,#表示匹配任意内容,这样就可以通过主题交换机将消息分发到不同的队列中
使用AmqpTemplate操作RabbitMQ
@Service
public class MessageServiceRabbitmqDirectlImpl implements MessageService {
@Autowired
private AmqpTemplate amqpTemplate;
@Override
public void sendMessage(String id) {
System.out.println("待发送短信的订单已纳入处理队列(rabbitmq topic),id:"+id);
amqpTemplate.convertAndSend("topicExchange","topic.orders.id",id);
}
}
发送消息后,根据当前提供的routingKey与绑定交换机时设定的routingKey进行匹配,规则匹配成功,消息才会进入到对应的队列中
使用消息监听器在服务器启动后,监听指定队列
@Component
public class MessageAMQListener {
@RabbitListener(queues = "topic_queue")
public void receive(String id){
System.out.println("已完成短信发送业务(rabbitmq topic 1),id:"+id);
}
@RabbitListener(queues = "topic_queue2")
public void receive2(String id){
System.out.println("已完成短信发送业务(rabbitmq topic 22222222),id:"+id);
}
}
使用注解@RabbitListener定义当前方法监听RabbitMQ中指定名称的消息队列
总结:
- SpringBoot整合RabbitMQ提供了AmqpTemplate对象作为客户端操作消息队列
- 操作ActiveMQ需要配置ActiveMQ服务器地址,默认端口为5672
- 企业开发时通常使用监听器来处理消息队列中的消息,设置监听器使用注解@RabbitListener
- RabbitMQ有5种消息模型,使用的队列相同,但是交换机不同。交换机不同,对应的消息进入的策略也不同
SprintBoot整合RocketMQ
安装
官网地址:下载 | RocketMQ (apache.org)
解压后文件的格式
-
bin:启动脚本,包括shell脚本和CMD脚本
-
conf:实例配置文件,包括broker配置文件、logback配置文件等
-
lib:依赖jar包。包括Netty、commons-lang、FastJson等
配置
注意:RocketMQ不支持jdk11,推荐使用jdk8
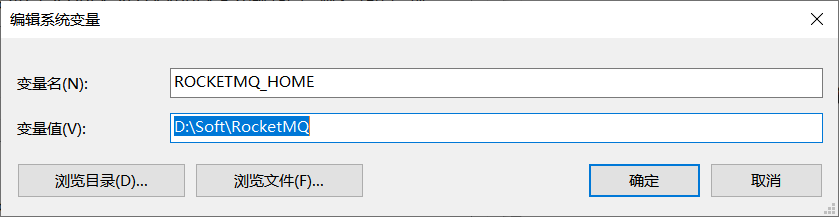
右键此电脑,选择电脑属性,进入系统环境变量点击新建
修改broker的配置文件
打开broker.conf文件
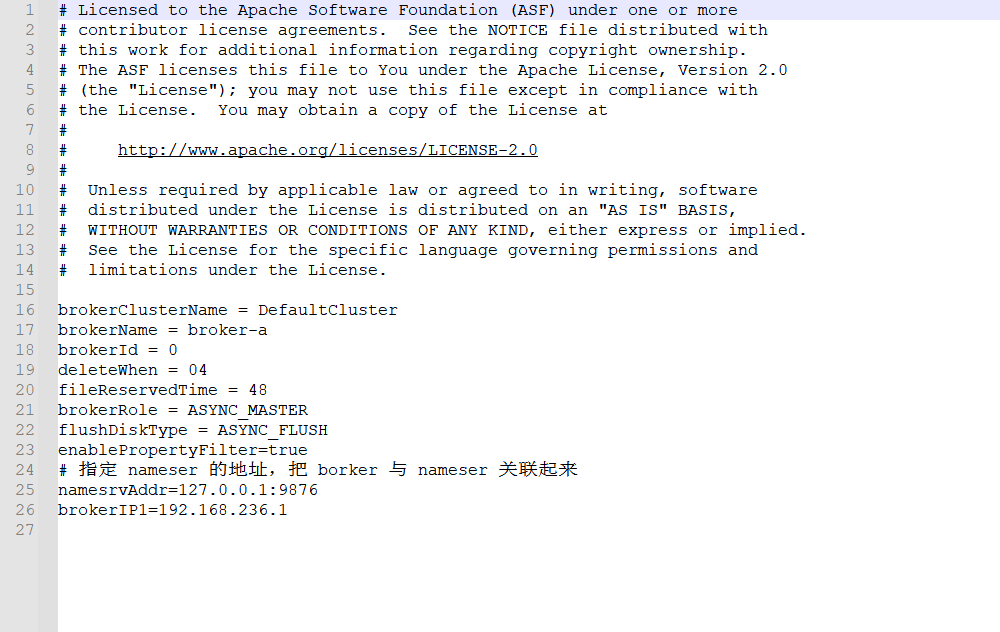
添加配置
enablePropertyFilter=true
# 指定 nameser 的地址,把 borker 与 nameser 关联起来
namesrvAddr=127.0.0.1:9876
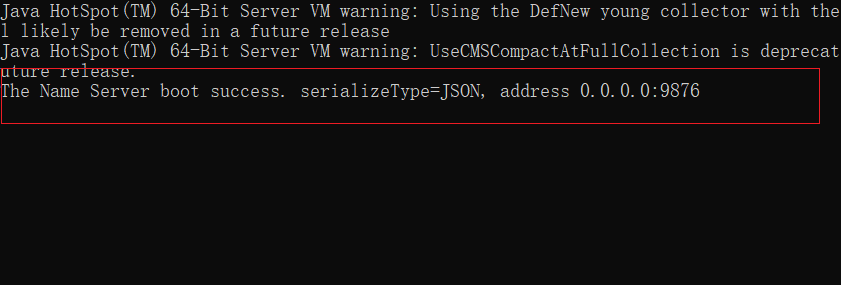
先启动在bin文件下双击mqnamesrv
这样表示成功
启动broker
在bin文件夹启动cmd(或者双击mqbroker.cmd)
启动命令:
mqbroker.cmd -c ../conf/broker.conf
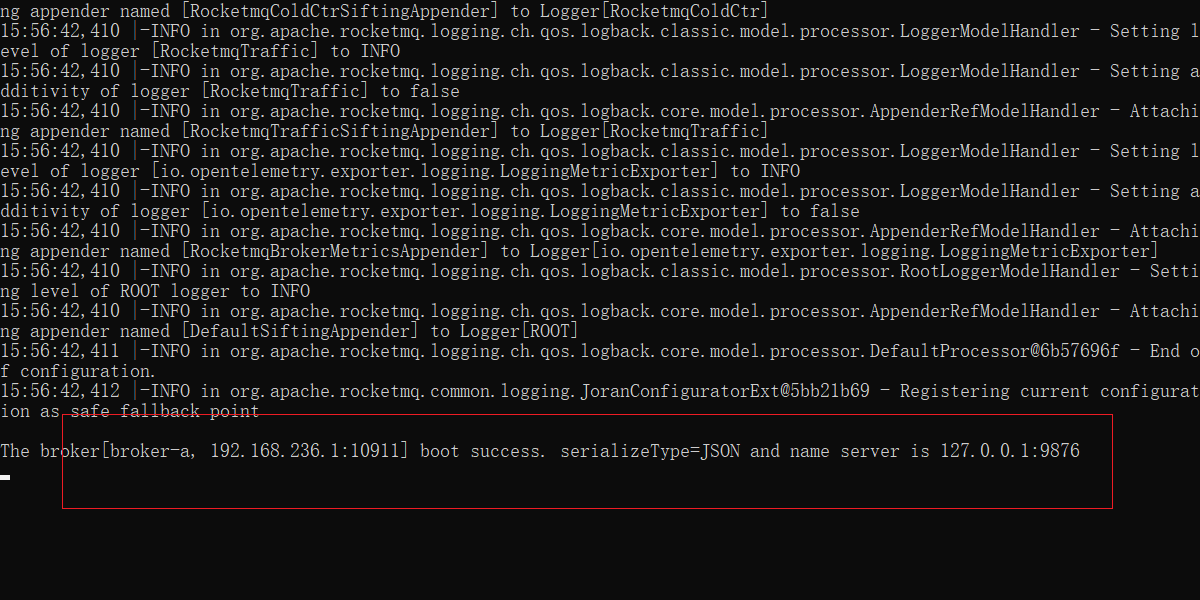
注意
如果出现以下问题
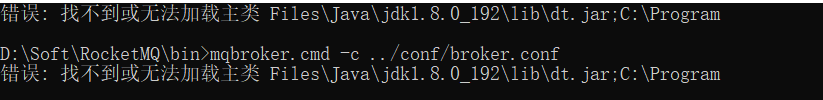
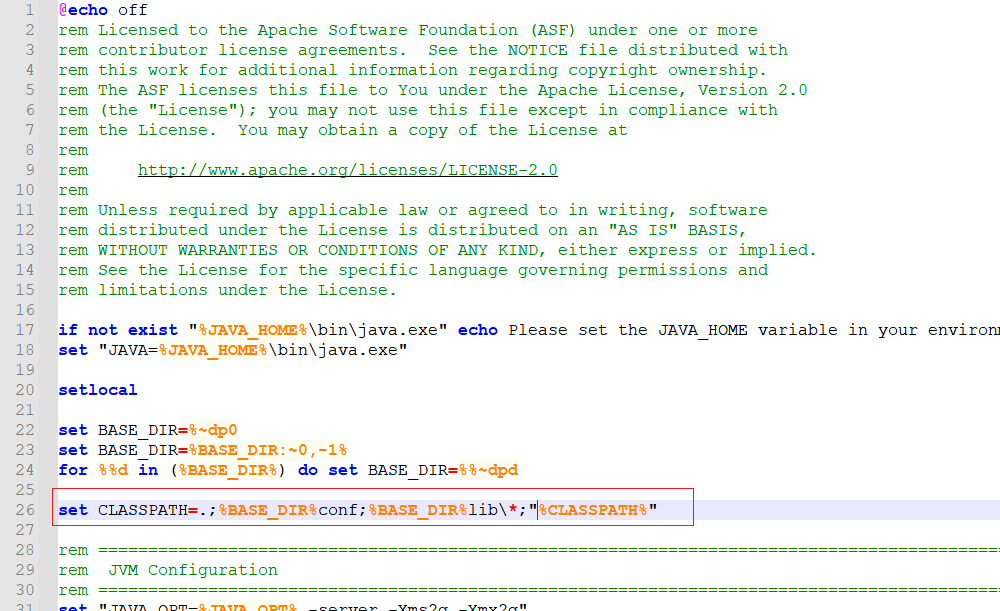
解决:
用notepad++打开runbroker.cmd文件,将CLASSPATH加上引号
整合(异步消息)
导入SpringBoot整合RocketMQ的starter,此坐标不由SpringBoot维护版本
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.rocketmq</groupId>
<artifactId>rocketmq-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>2.2.1</version>
</dependency>
配置文件
rocketmq:
name-server: localhost:9876
producer:
group: group_rocketmq
server:
port: 80
设置默认的生产者消费者所属组group
使用RocketMQTemplate操作RocketMQ
@Service
public class MessageServiceRocketmqImpl implements MessageService {
@Autowired
private RocketMQTemplate rocketMQTemplate;
@Override
public void sendMessage(String id) {
System.out.println("待发送短信的订单已纳入队列(rocketmq), id:"+ id);
SendCallback callback = new SendCallback() {
@Override
public void onSuccess(SendResult sendResult) {
System.out.println("消息发送成功");
}
@Override
public void onException(Throwable throwable) {
System.out.println("消息发送失败");
}
};
rocketMQTemplate.asyncSend("o_id", id, callback);
}
}
使用asyncSend方法发送异步消息
使用消息监听器在服务器启动后,监听指定位置,当消息出现后立即消费消息
@Component
@RocketMQMessageListener(topic = "o_id",consumerGroup = "group_rocketmq")
public class MessageListener implements RocketMQListener<String> {
@Override
public void onMessage(String id) {
System.out.println("已完成短信发送业务(rocketmq),id:"+id);
}
}
RocketMQ的监听器必须按照标准格式开发,实现RocketMQListener接口,泛型为消息类型
使用注解@RocketMQMessageListener定义当前类监听RabbitMQ中指定组、指定名称的消息队列
总结
- SpringBoot整合RocketMQ使用RocketMQTemplate对象作为客户端操作消息队列
- 操作RocketMQ需要配置RocketMQ服务器地址,默认端口9876
- 企业开发时通常使用监听器来处理消息队列中的消息,设置监听器使用注解@RocketMQMessageListener
SpringBoot整合Kafka
安装
下载地址:Apache Kafka
注意:不要现在源码

解压后文件格式如下:
安装Kafka之前要先安装zookeeper
windows环境下安装zookeeper_没办法,我就是这么菜的博客-CSDN博客
在windows目录中进入cmd命令行中,执行如下命令
zookeeper-server-start.bat ..\..\config\zookeeper.properties # 启动zookeeper
kafka-server-start.bat ..\..\config\server.properties # 启动kafka
zookeeper-server-start命令即可启动注册中心,默认对外服务器端口2181
kafka-server-start命令即可启动kafka服务器,默认对外服务端口9092
创建主题
kafka是基于主题操作的,操作之前需要先初始化topic
# 创建topic
kafka-topics.bat --create --zookeeper localhost:2181 --replication-factor 1 --partitions 1 --topic itheima
# 查询topic
kafka-topics.bat --zookeeper 127.0.0.1:2181 --list
# 删除topic
kafka-topics.bat --delete --zookeeper localhost:2181 --topic itheima
测试服务器启动状态
kafka提供有一套测试服务器功能的测试程序,运行bin目录下的windows目录下的命令即可使用
kafka-console-producer.bat --broker-list localhost:9092 --topic itheima # 测试生产消息
kafka-console-consumer.bat --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 --topic itheima --from-beginning # 测试消息消费
整合
导入SpringBoot整合Kafka的starter,此坐标由SpringBoot维护版本
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.kafka</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-kafka</artifactId>
</dependency>
配置文件
spring:
kafka:
bootstrap-servers: localhost:9092
consumer:
group-id: order
server:
port: 80
设置默认的生产者消费者所属组id
使用KafkaTemplatcae操作Kafka
@Service
public class MessageServiceImpl implements MessageService {
@Autowired
private KafkaTemplate<String, String> kafkaTemplate;
@Override
public void sendMessage(String id) {
System.out.println("待发送短信的订单已纳入处理队列(kafka), id:" + id);
kafkaTemplate.send("demo2022", id);
}
}
使用send方法发送消息,需要传入topic名称
使用消息监听器在服务器启动后,监听指定位置,当消息出现后,立即消费消息
@Component
public class MessageListener {
@KafkaListener(topics = "demo2022")
public void onMessage(ConsumerRecord<String, String> record) {
System.out.println("已完成短信发送业务(kafka), id:"+ record.value());
}
}
使用注解@KafkaListener定义当前方法监听Kafka中指定topic的消息,接收到的消息封装在对象ConsumerRecord中,获取数据从ConsumerRecord对象中获取即可
总结
- SpringBoot整合Kafka使用KafkaTemplate对象作为客户端操作消息队列
- 操作Kafka需要配置Kafka服务器地址,默认端口9092
- 企业开发时通常使用监听器来处理消息队列中的消息,设置监听器使用注解@KafkaListener。接收消息保存在形参ConsumerRecord对象中
监控
监控:就是通过软件的方式展示另一个软件的运行情况,运行的情况则通过各种各样的指标数据反馈给监控人员。如网络是否顺畅、服务器是否在运行、程序的功能是否能够百分百运行成功,内存是否够用,等等
监控的意义
对于现代的互联网程序来说,规模越来越大,功能越来越复杂,还要追求更好的客户体验,因此要监控的信息量也就比较大了。由于现在的互联网程序大部分都是基于微服务的程序,一个程序的运行需要若干个服务来保障,因此第一个要监控的指标就是服务是否正常运行,也就是监控服务状态是否处理宕机状态。一旦发现某个服务宕机了,必须马上给出对应的解决方案,避免整体应用功能受影响。其次,由于互联网程序服务的客户量是巨大的,当客户的请求在短时间内集中达到服务器后,就会出现各种程序运行指标的波动。比如内存占用严重,请求无法及时响应处理等,这就是第二个要监控的重要指标,监控服务运行指标。虽然软件是对外提供用户的访问要求,完成对应功能的,但是后台的运行是否平稳,是否出现了不影响客户使用的功能隐患,这些也是要密切监控的,此时就需要在不停机的情况下,监控系统运行情况下,日志是一个不错的手段。如果众多日志中找到开发者或运维人员所关注的日志信息,简单快速有效的过滤出要看的日志也是监控系统需要考虑的问题,这就是第三个要监控的指标,监控程序运行日志。如果快速控制服务器的启停也是程序运行过程中不可避免地问题,这就是第四个监控项,管理服务状态
总结
- 监控是一个非常重要地工作,是保障程序正常运行的基础手段
- 监控的过程通过一个监控程序运行,他汇总所有被监控的程序的信息集中统一展示
- 被监控程序需要主动上报自己被监控,同时设置哪些指标被监控
可视化监控平台
SpringBoot Admin,这是一个开源社区项目,用于管理和监控SpringBoot应用程序。这个项目中包含由客户端和服务端两部分,而监控平台指的就是服务端。
服务端开发
导入SpringBoot admin对应的starter,版本与当前使用的SpringBoot版本保持一致,并将其配置成web工程
<dependency>
<groupId>de.codecentric</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-admin-starter-server</artifactId>
<version>2.5.4</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
上述过程可以通过创建项目时勾选的形式实现
在引导类上添加注解@EnableAdminServer,声明当前应用启动后作为SpringBootAdmin的服务器使用
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableAdminServer
public class DemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication.class, args);
}
}
配置端口号
server.port=80
这里服务器就开发好了,启动后就可以访问当前程序了,界面如下:
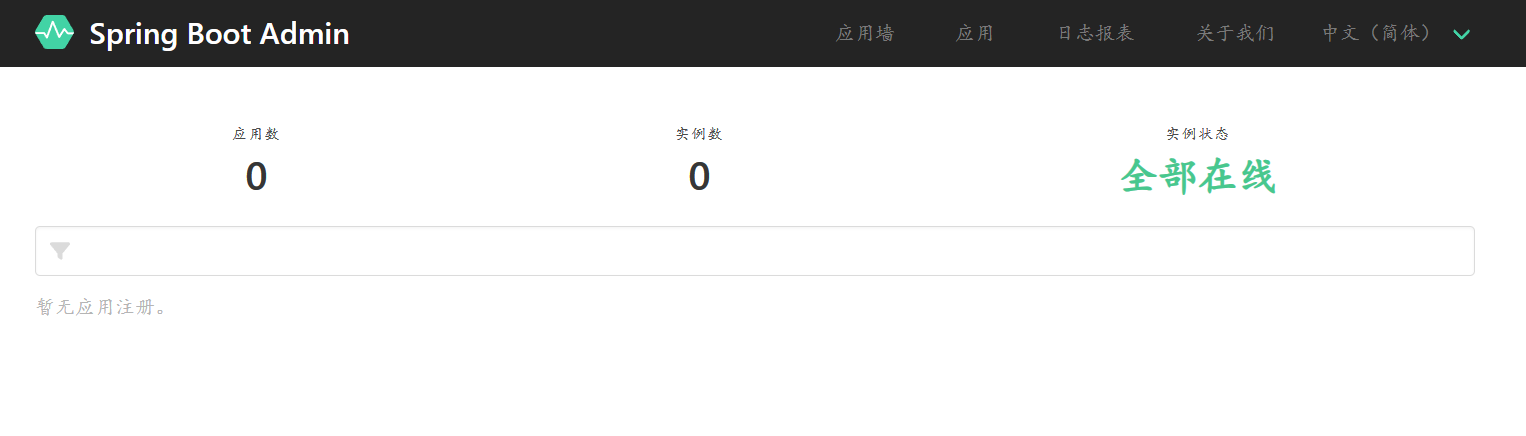
由于目前没有启动任何被监视的程序,所以里面什么信息也没有。
客户端开发
客户端程序开发其实和服务端开发思路基本相似,多了一些配置而已
导入SpringBoot Admin对应的starter,版本与当前使用的SpringBoot版本保持一致,并将其配置成web工程
<dependency>
<groupId>de.codecentric</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-admin-starter-client</artifactId>
<version>2.5.4</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
上述过程也可以通过创建项目时使用勾选的形式完成,端口配置要一致,否则会冲突
设置当前客户端将信息上传到哪个服务器上,通过yml文件配置
spring:
boot:
admin:
client:
url: http://localhost:80
这里客户端就可以启动了。启动后再次访问服务端程序,界面如下:
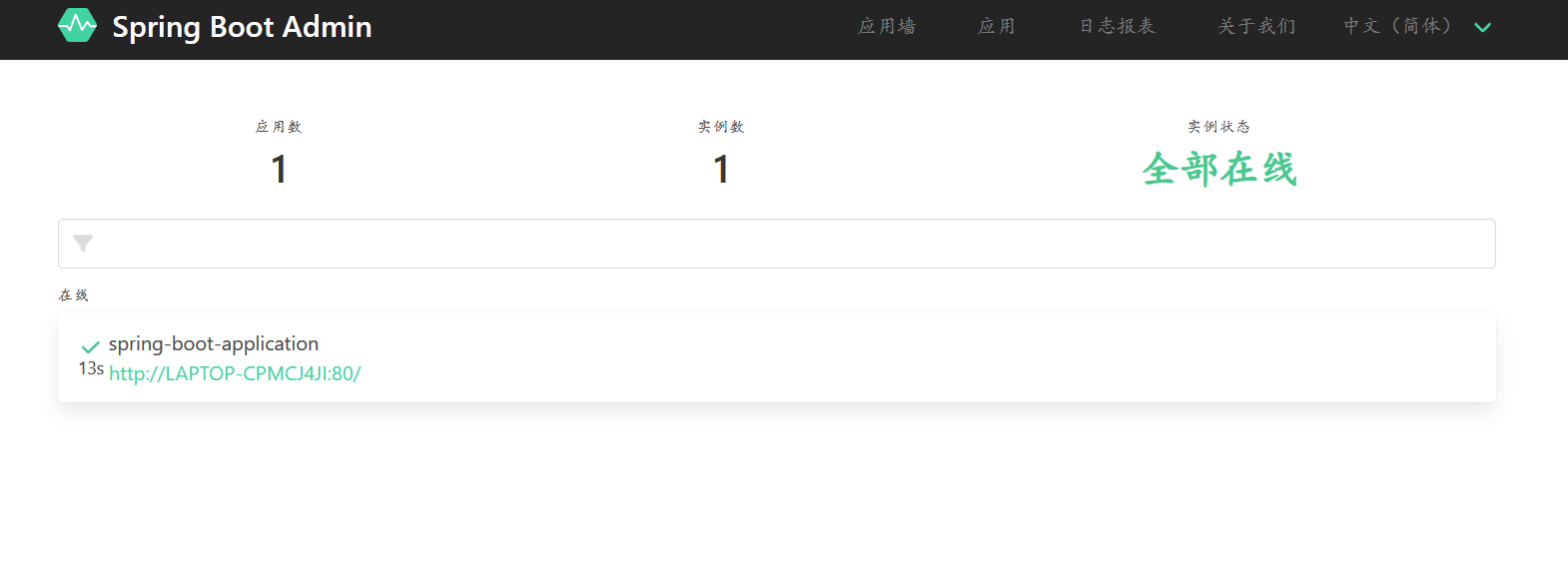
可以看到当前监控了一个程序,点击进去查看详情信息

由于当前没有设置开放哪些信息给监控服务器,所以看不到有效信息。
可以通过以下配置看到信息
- 开发指定信息给服务器
- 允许服务器以HTTP请求的方式获取对应的信息
配置如下:
客户端配置
server:
port: 8080 #不要跟服务端的端口一致
spring:
boot:
admin:
client:
url: http://localhost:80 #服务端的访问路径
management:
endpoint:
health:
show-details: always
endpoints:
web:
exposure:
include: "*"
结果:
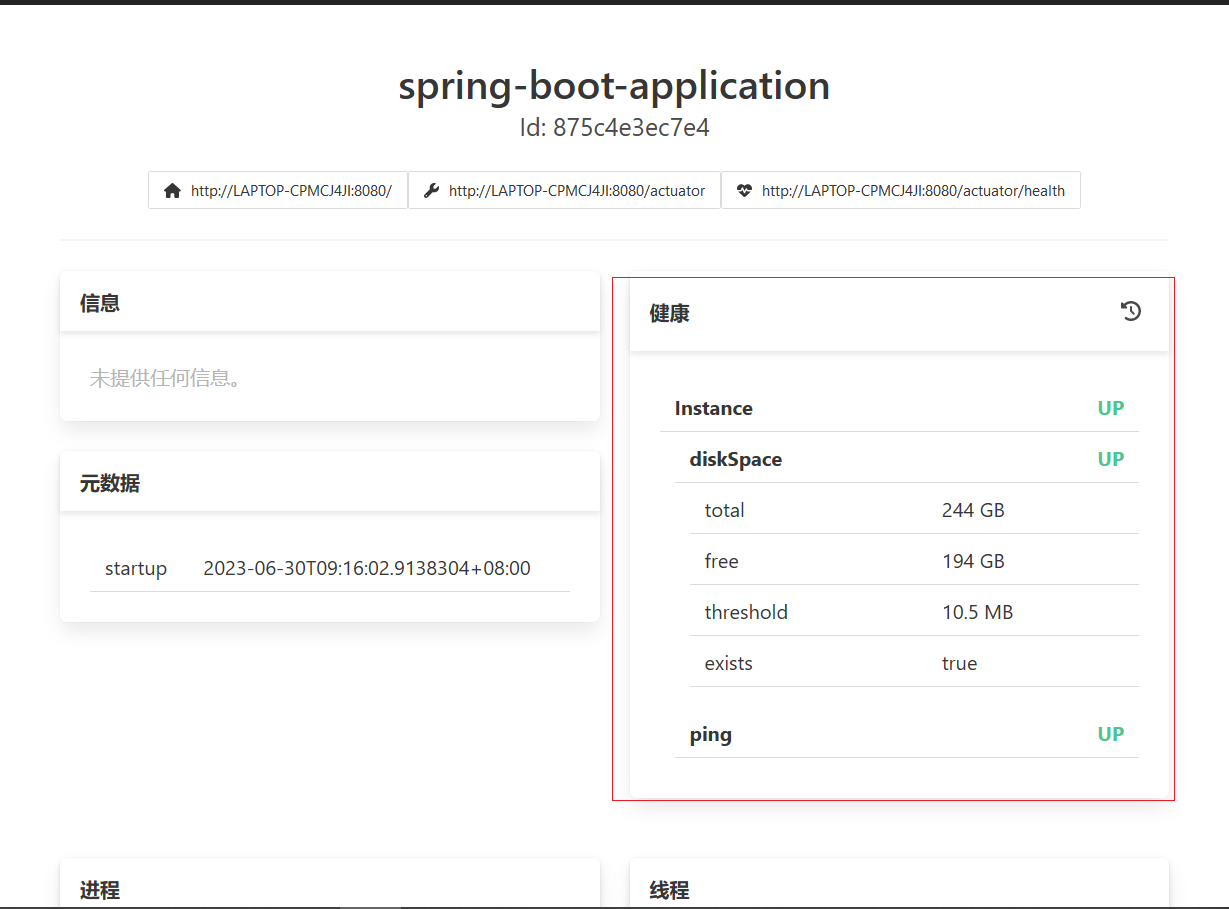
通过配置可以开放所有的健康信息明细
management:
endpoint:
health:
show-details: always
SpringBootadmin的客户端默认开放了13组信息给服务器,但是这些信息除了健康信息之外,其他的信息都不让通过HTTP请求查看,所以需要查阅的内容项,使用*表示查阅全部,要带引号
endpoints:
web:
exposure:
include: "*"
配置后在刷新服务器页面,就可以看到所有的信息
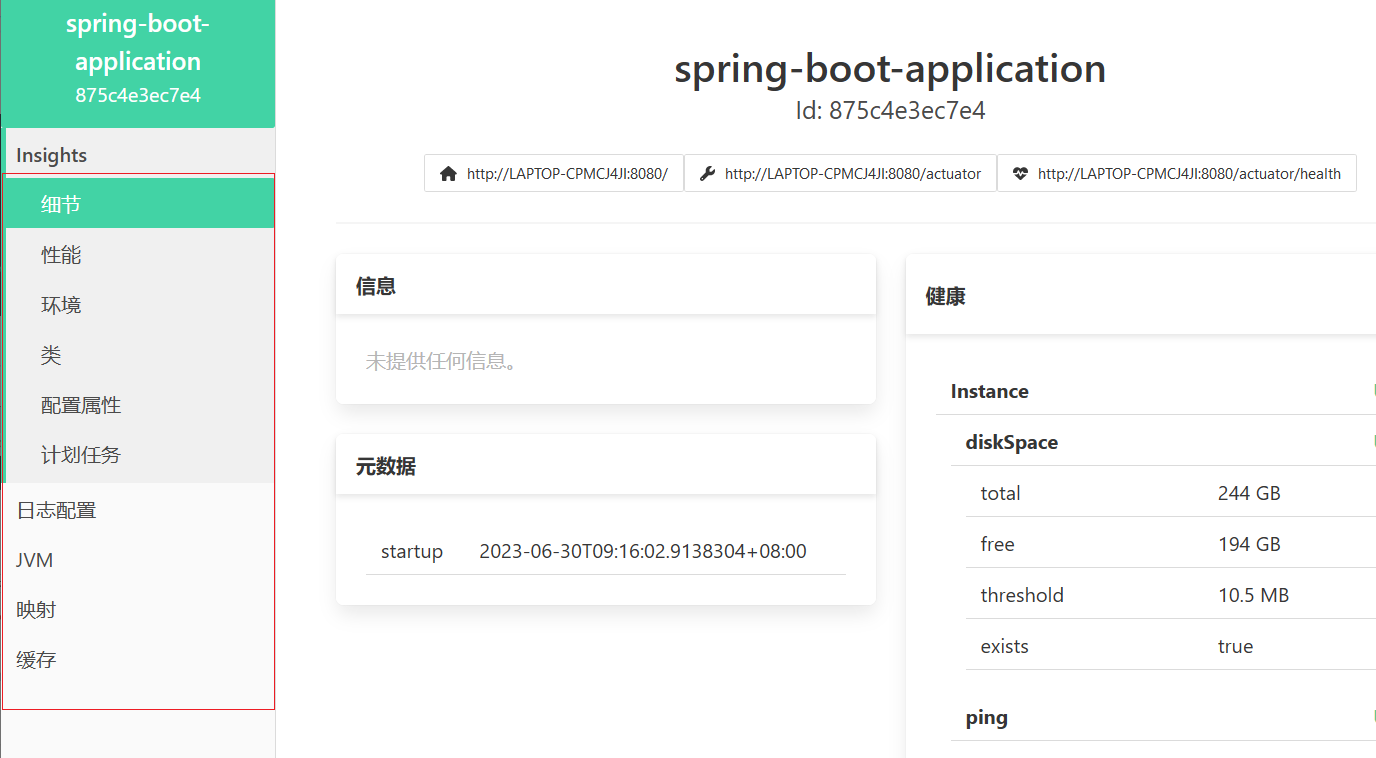
以上界面中展示的信息包含了13组信息,有性能指标监控,加载的bean列表,加载的系统属性,日志的显示控制等等
配置多个客户端
可以通过配置客户端的方式在其他的SpringBoot程序中添加客户端坐标,这样当前服务器姐可以监控多个客户端程序。每个客户端展示不同的监控信息。
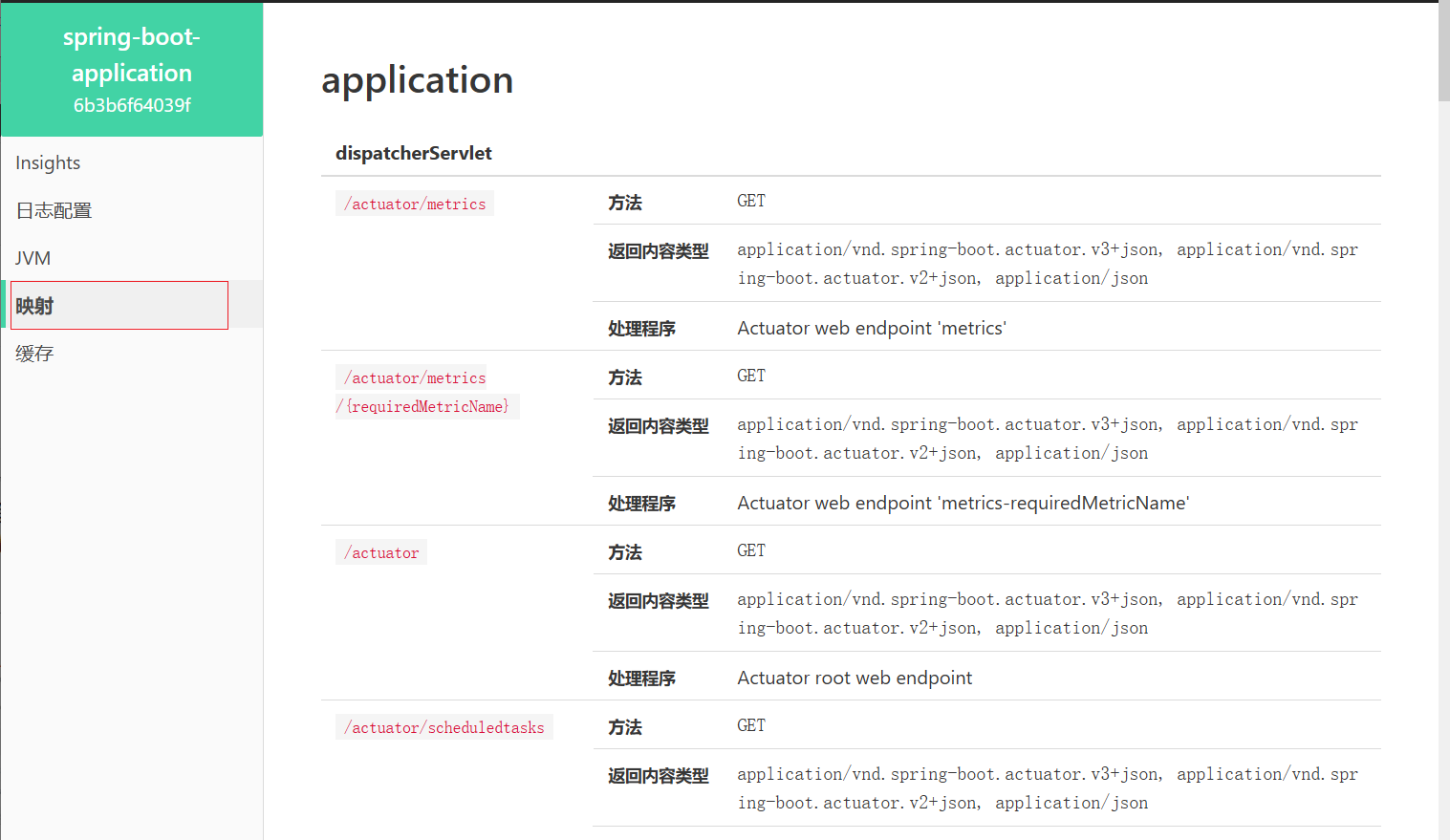
监控原理
通过查阅监控中的映射指标可知,当前系统中可以运行的所有请求路径,其中大部分路径以/actuator开头
这些路径可以访问,通过发送这些请求可知,返回的信息与监控面板中的数据存在着对应关系
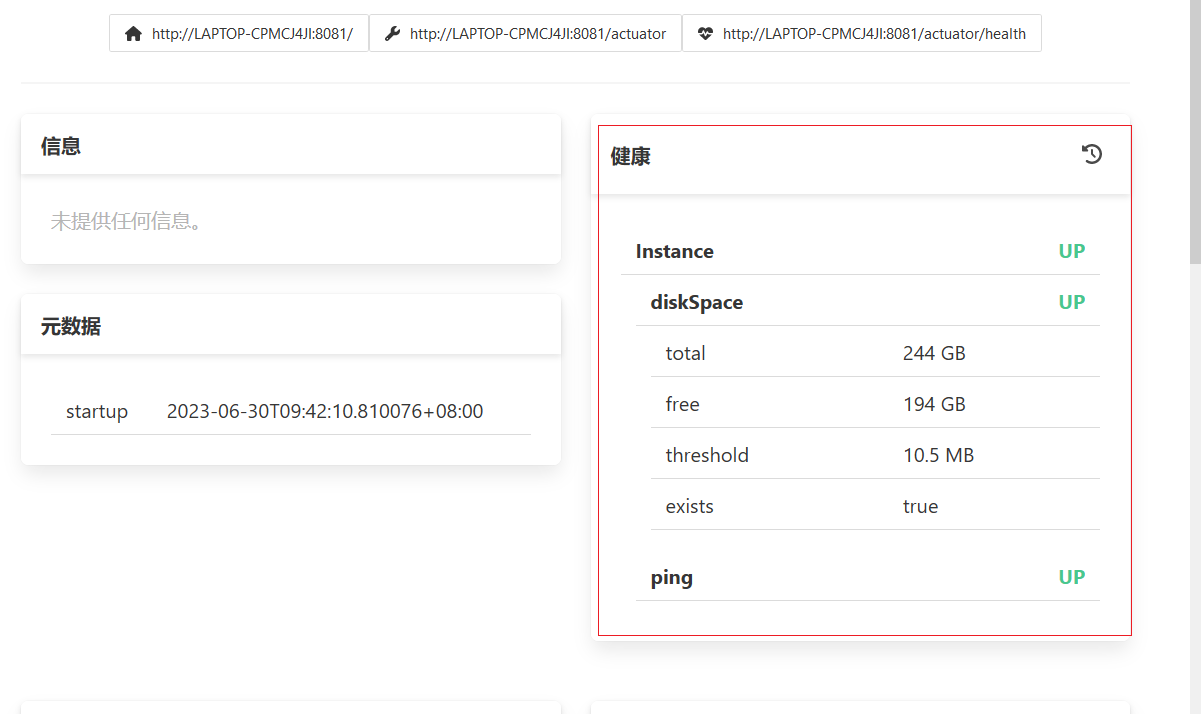
监控中显示的信息实际上是通过发送请求后得到json数据,然后展示出来。按照上述操作,可以发送更多的以/actuator开头的链接地址,获取更多的数据,这些数据汇总到一起组成了监控平台显示的所有数据。
这是因为导入SpringBootAdmin的对应的client,在这个资源中导入了一个名称叫actuator的包。

Actuator可以称为端点,描述了一组监控信息,SpringBootAdmin提供了多个内置端点,通过访问端点就可以获取对应的监控信息,也可以根据需要自定义端点信息。通过发送请求路径**/actutor可以访问应用所有端点信息,如果端点中还有明细信息可以发送请求/actuator/端点名称**来获取详细信息。以下列出了所有端点信息说明:
| ID | 描述 | 默认启用 |
|---|---|---|
| auditevents | 暴露当前应用程序的审计事件信息 | 是 |
| beans | 显示应用程序中所有Spring Bean的完整列表 | 是 |
| caches | 暴露可用的缓存 | 是 |
| conditions | 显示在配置和自动配置类上评估的条件以及它们匹配或不匹配的原因 | 是 |
| configprops | 显示所有@ConfigurationProperties的校对清单 | 是 |
| env | 暴露Spring ConfigurableEnvironment中的属性 | 是 |
| flyway | 显示已应用的Flyway数据库迁移 | 是 |
| health | 显示应用程序健康信息 | 是 |
| httptrace | 显示HTTP追踪信息(默认情况下,最后100个HTTP请求/响应交换) | 是 |
| info | 显示应用程序信息 | 是 |
| integerationgraph | 显示Spring Integration图 | 是 |
| loggers | 显示和修改应用程序中日志记录器的配置 | 是 |
| liquibase | 显示已应用的Liquibase数据库迁移 | 是 |
| metrics | 显示当前应用程序的指标度量信息 | 是 |
| mappings | 显示所有@RequestMapping路径的整理清单 | 是 |
| schedule dtasks | 显示应用程序中的调度任务 | 是 |
| sessions | 允许从Spring Session支持的会话存储中检索和删除用户会话。当使用Spring Session的响应式Web应用程序支持时不可用 | 是 |
| shutdown | 正常关闭应用程序 | 否 |
| threaddump | 执行线程dump | 是 |
| heapdump | 返回一个hprof堆dump文件 | 是 |
| jolokia | 通过HTTP暴露JMXbean(当Jolokia在classpath上时,不适用于WebFlux) | 是 |
| logfile | 返回日志文件的内容(如果已设置logging.file或logging.path属性)。支持使用HTTP Range头来检索部分日志文件的内容 | 是 |
| prometheus | 以可以由Prometheus服务器抓取的格式暴露指标 | 是 |
通过配置可以设置端点是否对外开放功能。使用enable属性控制端点是否对外开放。其中health端点为默认端点,不能关闭
management:
endpoint:
health: # 端点名称
show-details: always
info: # 端点名称
enabled: true # 是否开放
为了方便开发者快速配置端点,SpringBoot Admin设置了13个较为常用的端点作为默认开放的端点,如果需要控制默认开放的端点的开放状态,可以通过配置设置,如下:
management:
endpoints:
enabled-by-default: true # 是否开启默认端点,默认值true
上述端点开启后,就可以通过端点对应的路径查看对应的信息了。但是此时还不能通过HTTP请求查询此信息,还需要开启通过HTTP请求查询的端点名称,使用"*",可以简化配置成开放所有端点的WEB端HTTP请求权限
management:
endpoints:
web:
exposure:
include: "*"
对于端点的配置有两组信息,一组是endpoints开头的,对所有端点进行配置,一组是endpoint开头的,对具体端点进行配置
management:
endpoint: # 具体端点的配置
health:
show-details: always
info:
enabled: true
endpoints: # 全部端点的配置
web:
exposure:
include: "*"
enabled-by-default: true
总结
- 被监控客户端通过添加actuator的坐标可以对外提供被访问的端点功能
- 端点功能的开放与关闭可以通过配置进行控制
- web端默认无法获取所有端点信息,通过配置开放端点功能
自定义监控指标
端点描述了被监控的信息,除了系统默认的指标,还可以自行添加显示的指标。
INFO端点
info端点描述了当前应用的基本信息,可以通过两种形式快速配置info端点的信息
-
配置形式
在yml文件中通过设置info节点的信息就可以快速配置端点信息
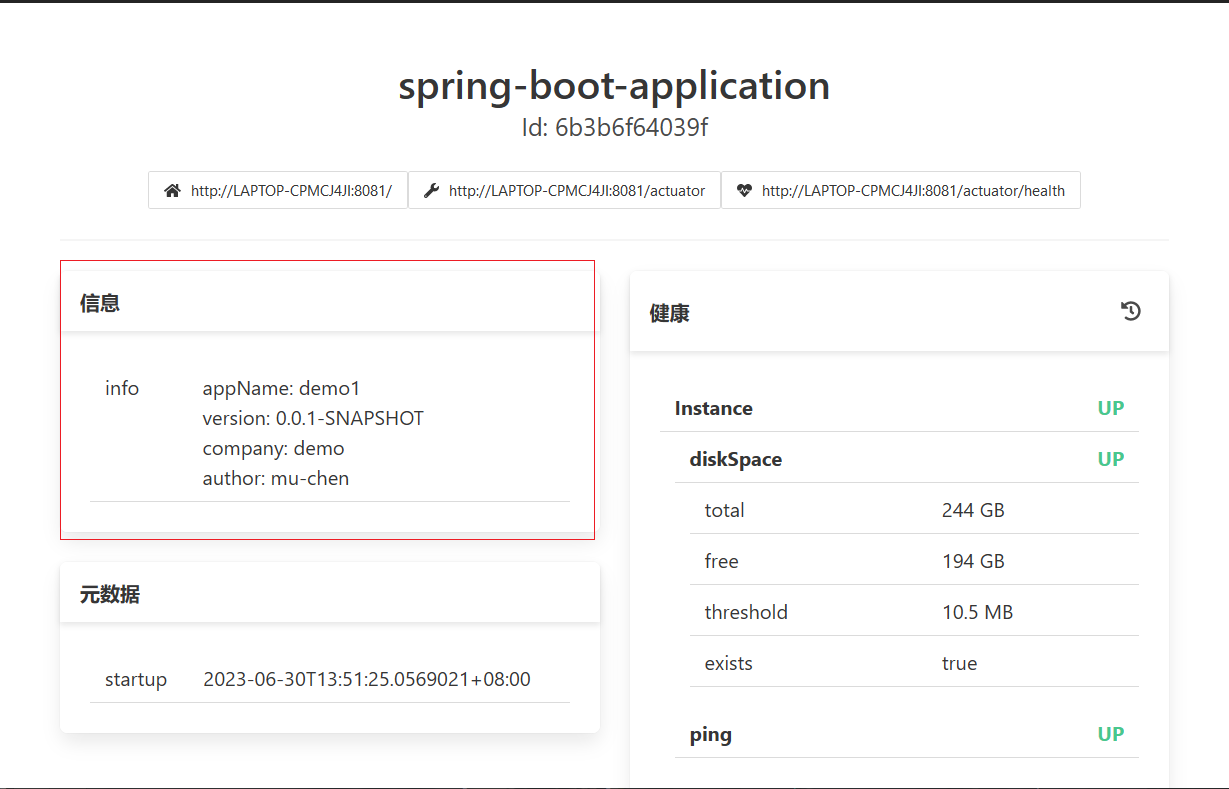
server: port: 8081 spring: boot: admin: client: url: http://localhost:80 # 服务端口号 management: endpoint: health: show-details: always info: enabled: true endpoints: web: exposure: include: "*" info: info: appName: @project.artifactId@ version: @project.version@ company: demo author: mu-chen配置完毕后,对应信息显示在监控平台上
-
编程形式
通过配置的形式只能添加固定的数据,如果需要动态数据还可以通过配置bean的方式为info端点添加消息,此消息与配置信息共存
@Component public class InfoConfig implements InfoContributor { @Override public void contribute(Info.Builder builder) { builder.withDetail("runTime", System.currentTimeMillis()); // 添加单个信息 Map infoMap = new HashMap(); infoMap.put("buildTime", "2006"); // 添加一组信息 builder.withDetails(infoMap); } }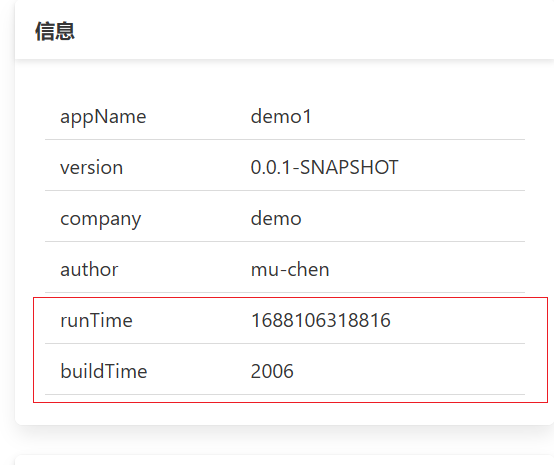
Health端点
health端点描述当前应用的运行健康指标,即应用的运行是否成功,通过编程的形式可以扩展指标信息
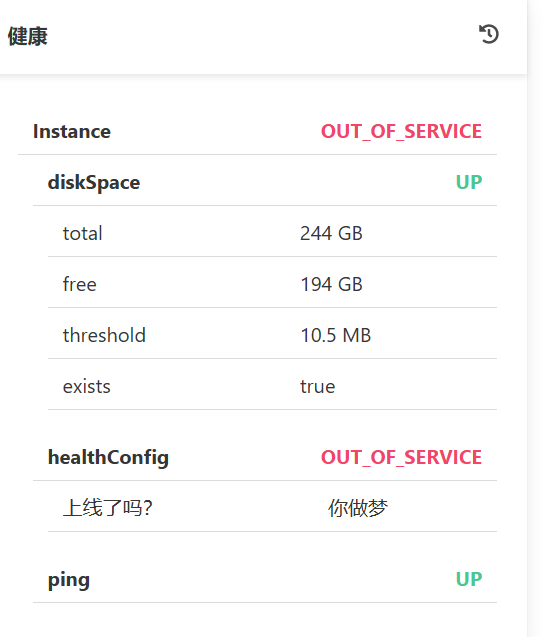
@Component
public class HealthConfig extends AbstractHealthIndicator {
@Override
protected void doHealthCheck(Health.Builder builder) throws Exception {
boolean condition = false;
if (condition) {
// 设置运行状态为启动状态
builder.status(Status.UP);
builder.withDetail("runTime", System.currentTimeMillis());
Map infoMap = new HashMap();
infoMap.put("bulidTime", "2006");
builder.withDetails(infoMap);
} else {
builder.status(Status.OUT_OF_SERVICE);
// 设置运行状态为不在服务状态
builder.withDetail("上线了吗?", "你做梦");
}
}
}
当任意一个组件状态不为up时,整体应用对外服务状态为非UP状态
Metrics端点
metrics端点描述了性能指标,除了系统自带的监控性能指标,还可以自定义性能指标
自定义端点
可以根据业务需要自定义端点,方便业务监控
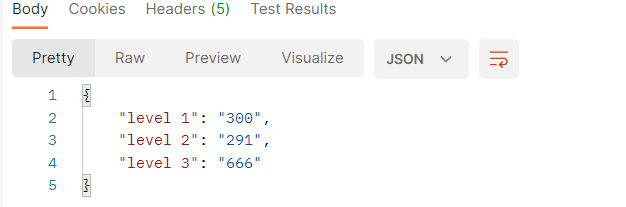
@Component
@Endpoint(id = "pay", enableByDefault = true)
public class PayEndpoint {
@ReadOperation
public Object getPay() {
Map payMap = new HashMap();
payMap.put("level 1", "300");
payMap.put("level 2", "291");
payMap.put("level 3", "666");
return payMap;
}
}
由于此端点数据SpringBoot Admin无法预知该如何展示,所以通过界面无法看到此数据,通过HTTP请求路径可以获取到当前端点的信息,但是需要先开启当前端点对外功能,或者设置当前端点为默认开发的端点
总结
- 端点的指标可以自定义,但是每种不同的指标根据其功能不同,自定义方法不同
- info端点通过配置和编程的方式都可以添加端点指标
- health端点通过编程的方式添加端点指标,需要注意要为对应指标添加启动状态的逻辑设定
- metrics指标通过在业务中添加监控操作设置指标
- 可以自定义端点添加更多的指标