文章目录
- 前言
- 一、张量操作
- 二、csv文件数据操作
- 数据预处理(读入csv文件作为pytorch能处理的)
- 来源
前言
张量的一些处理和操作
csv文件数据操作
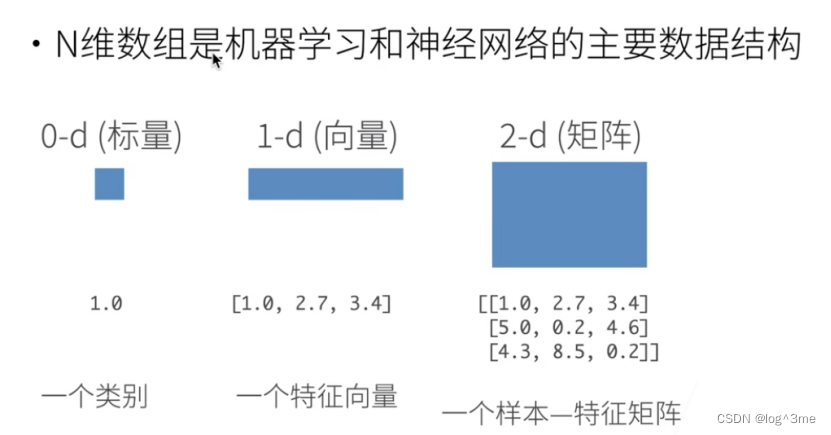
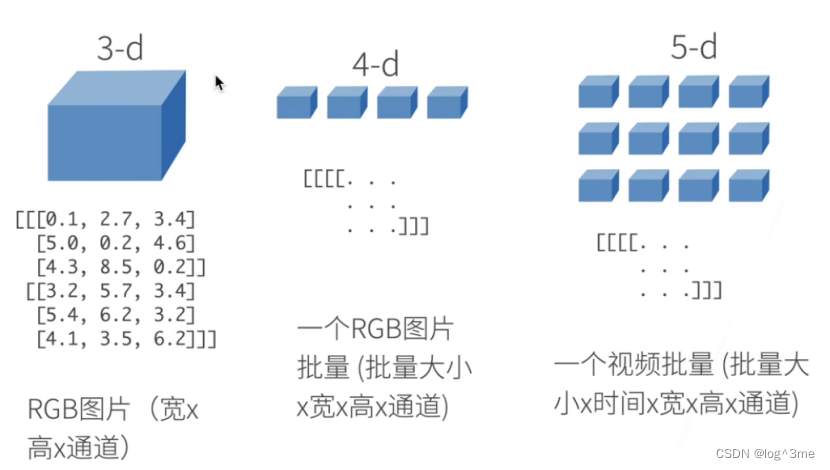
一、张量操作
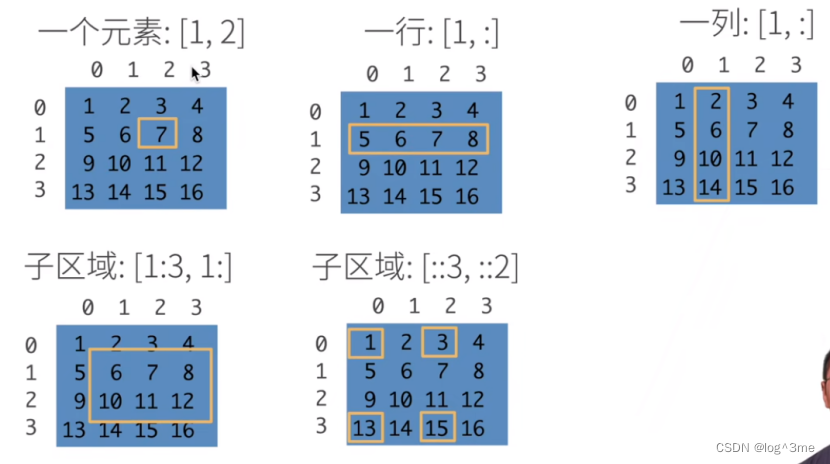
[:,1]表示全部行 第二列
[:]是全取
[1:3,1:]:1:3表示1~3的左闭右开区间,1:表示从第一列开始的全部
[::3,::2]:表示每隔3行取一行,每隔2列取一列
import torch
# 张量表示
x = torch.arange(12)
print(x)
print(x.shape) # shape属性访问张量的形状 ([12])表示向量(就一个维度) 长度12
print(x.numel()) # 张量中元素总数
# 改变张量形状而不改变元素数量和元素值 reshape函数
x = x.reshape((3, 4)) # 注意reshape后地址不变,所以如果x = torch.arange(12);y=x.reshape((3,4));y[:]=2;更改y后x也会改变
print(x)
# 使用全0/全1
print(torch.zeros(2, 3, 4)) # 3行4列 的三维数组
print(torch.ones(1, 3, 4)) # 3行4列 的三维数组(二维数组(3,4))
# torch.tensor([3.5]) # 创建一个一维的
print(torch.tensor([[2, 1, 4, 3], [1, 2, 3, 4], [4, 3, 2, 1]])) # 手动创建一个二维数组
print(torch.tensor([[2, 1, 4, 3], [1, 2, 3, 4], [4, 3, 2, 1]]).shape)
print(torch.tensor([[[2, 1, 4, 3], [1, 2, 3, 4], [4, 3, 2, 1]]])) # 手动创建一个三维数组
print(torch.tensor([[[2, 1, 4, 3], [1, 2, 3, 4], [4, 3, 2, 1]]]).shape)
# 常见加减运算
x = torch.tensor([1.0, 2, 4, 8]) # 创建浮点向量
y = torch.tensor([2, 2, 2, 3])
print(x + y, x - y, x * y, x / y, x ** y) # x**y表示对x求幂(二次方)
# 指数运算e的x次方
print(torch.exp(x))
x = torch.arange(12, dtype=torch.float32).reshape(3, 4) # (1,3,4)三维
y = torch.tensor([[2.0, 1, 4, 3], [1, 2, 3, 4], [4, 3, 2, 1]])
print(torch.cat((x, y), dim=0)) # 表示在行上堆起来
print(torch.cat((x, y), dim=1)) # 表示在列上堆起来
print(x == y) # 按元素判断是否等于 构建二元张量
print(x.sum()) # 对x全部求和
# 广播机制(可能会造成代码可以运行,但是结果不对) 3*1矩阵+1*2矩阵可以相加 会让3*1复制一下变成3*2 1*2复制一下边城3*2 两个3*2相加
a = torch.arange(3).reshape((3, 1))
b = torch.arange(2).reshape((1 * 2))
print(a + b)
print(x[-1]) # 最后一行
print(x[1:3]) # 1和2行(第2和第3行)
# 将元素写入矩阵
x[1, 2] = 9 # 修改第2行第三列
# 为多个元素赋相同值
x[0:2, :] = 12
# 遇到大矩阵时不要频繁赋值,可以采用id的方法
# id类似指针,表明y的唯一标识号,赋值后之前的内存已经被析构掉
before = id(y)
y = y + x
print(id(y) == before)
# 执行原地操作
z = torch.zeros_like(y) # 创建和y的shape和数据类型一样的 不过数都是0
print('id(z):', id(z))
z[:] = x + y # z中所有元素=x+y,对z的元素改写
print('id(z):', id(z))
# 如果没有重复使用x,也可以用x[:]=x+y或x+=y减少内存开销
before = id(x)
x += y
print(id(x) == before)
# x转换为numpy张量
A = x.numpy()
B = torch.tensor(A)
print(A)
print(B)
# 大小为1的张量转化为python标量
a = torch.tensor([3.5])
print(a, a.item(), float(a), int(a))
二、csv文件数据操作
数据预处理(读入csv文件作为pytorch能处理的)
代码如下(示例):
import os
import pandas as pd
# 创建人工数据集,并存入csv(逗号分隔的文件)
os.makedirs(os.path.join('..', 'data'), exist_ok=True) # 创建名为data的文件夹
data_file = os.path.join('..', 'data', 'house_tiny.csv') # 创建csv文件
with open(data_file, 'w') as f:
f.write('NumRooms,Alley,Price\n') # 列名
f.write('NA,Pave,127500\n') # 每行表示一个数据样本
f.write('2,NA,106000\n')
f.write('4,NA,178100\n')
f.write('NA,NA,140000\n')
# 读取csv
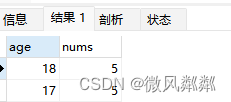
data = pd.read_csv(data_file)
print(data)
# 处理缺失数据 通常是删除和插入,最简单的方法是将这一行丢掉。
inputs, outputs = data.iloc[:, 0:2], data.iloc[:, 2] # 把data中第1-2列读入inputs ,第3列读入outputs
inputs = inputs.fillna(inputs.mean(numeric_only=1)) # 将所有nan的填入这一列的均值(只有数值的可以平均,string的没法平均)
print(inputs)
# 对于input中的nan视为一个类别(0/1)
inputs = pd.get_dummies(inputs, dummy_na=True, dtype=int) # 不把dtype改为int的话会显示true false
print(inputs)
# 现在inputs和outputs中的所有条目都是数值类型,它们可以转换为张量格式
X, Y = torch.tensor(inputs.values), torch.tensor(outputs.values)
print(X, Y)
来源
b站 跟李沐学AI 动手学深度学习v2 04